#学习自用#
union
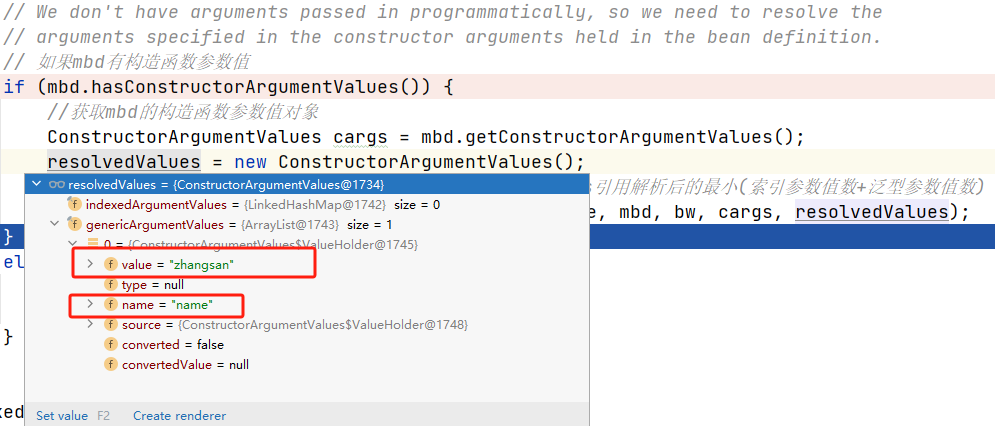
共用体和结构体相似,但是共用体一次只能占用一个成员的内存,所有成员共用同一地址。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
union A
{
int int_val;
float float_val;
}a;
int main()
{
a.float_val = 2.0f;
cout << a.float_val << endl;
cout << a.int_val << endl;
cin.get();
}这里a.int_val并不等于2,因为int_val与float_val地址相同,int_val的值其实是float_val在内存中的值。我们可以通过下面这串代码来理解。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
float b = 2.0;
int a=*(int*) & b;
cout << a << endl;
a = b;
cout << a << endl;
cin.get();
}第一个部分,int a=*(int*) & b ,是取b的地址然后强转为整型指针,再解引用赋值给a,和int_val与float_val的情况类似;而第二个部分,存在隐式转换,实际上是 a=(int )b ;这个部分的结果a=2 。
虚析构函数
虚析构函数并不是在子类中复写基类的析构函数,更像是在基类析构函数的基础上加一个析构函数。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Base
{
public:
Base() { cout << "Base construct\n"; }
~Base() { cout << "Base distroy\n"; }
};
class Derive:public Base
{
public:
Derive() { cout << "Derive construct\n"; }
~Derive() { cout << "Derive distroy\n"; }
};
int main()
{
Base* base = new Base();
delete base;
cout << "------------\n";
Derive* derive = new Derive();
delete derive;
cout << "------------\n";
Base* poly = new Derive();
delete poly;
cin.get();
}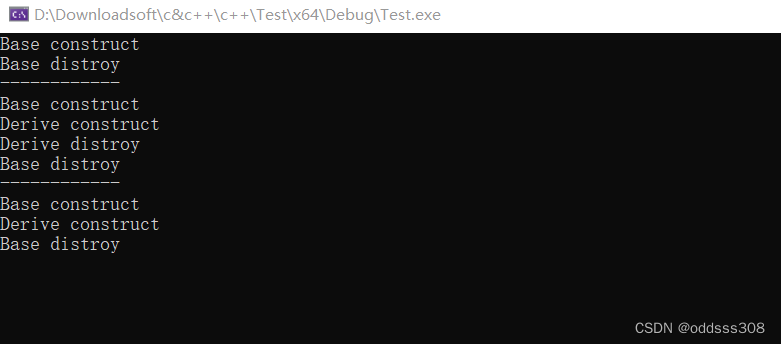
在删除poly时并没有调用Derive的析构函数,这里可能会导致内存泄漏,改进方法就是使用虚析构函数。 在基类的虚构函数名前加上virtual即可。只要一个类拥有子类,那么它的析构函数就必须是虚函数否则无法保证安全的扩展这个类。
类型转换
C++中用于类型转换的有static_cast ,reinterpret_cast,dynamic_cast,以及 const_cast,相比于C风格的类型转换,这些语句增加了一些检查功能,各自的使用也有一些限制,下面进行一些简单的介绍。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
double a = 5.25;
double b = (int)a + 5.3;
cout << b << endl;
b = static_cast<int>(a) + 5.3;
cout << b << endl;
cout << "------------------\n";
int c = 1;
b = *(double*) &c;
cout << b << endl;
b = *reinterpret_cast<double*>(&c);
cout << b << endl;
cout << "------------------\n";
cin.get();
}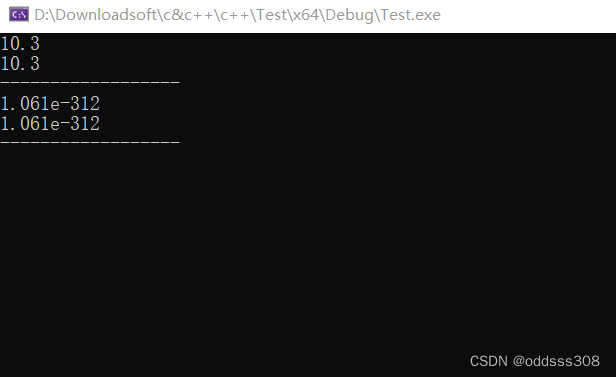
static_cast只能实现一些基本类型的转换比如float,int之类的,无法实现整型地址向double类型指针的转换,可以看到C风格的转换也可以实现这些功能,如果对性能有要求用C风格是最好的。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Base
{
public:
virtual void prt() { cout << "Base type\n"; }
virtual ~Base() { cout << "Base distroy\n"; }
};
class Derive:public Base
{
public:
void prt()override { cout << "Derive type\n"; }
~Derive() { cout << "Derive distroy\n"; }
};
int main()
{
Base* b1 = new Base();//指向父类的父类指针
Base* b2 = new Derive();//指向子类的父类指针
Derive* derive = dynamic_cast<Derive*>(b1);
if (!derive)
cout << "transmition fail\n";
else
derive->prt();
derive = dynamic_cast<Derive*>(b2);
if (!derive)
cout << "transmition fail\n";
else
derive->prt();
delete (b1,b2);//错误的,只删除了b2
cin.get();
}dynamic_cast用于有继承关系的转换,转换不成功会返回null,转换不成功的情况:1)两个没有继承关系的类指针之间的转换。2)下行转换(父转子)的情况中,指向父类的父类指针转换为子类指针会失败,而指向子类的父类指针可以转换为子类指针。3)上行转换不会失败。4)delete (b1,b2)涉及逗号表达式,逗号表达式的值是右值,所以只删除了b2。如果是delete b1,b2 那么就只删除b1因为逗号的优先级很低,相当于(delete b1),b2 这里b2不起作用。