目录
1.后缀表达式
2.表达式括号匹配
3.表达式求值
4.表达式的转换
5.机器翻译
1.后缀表达式
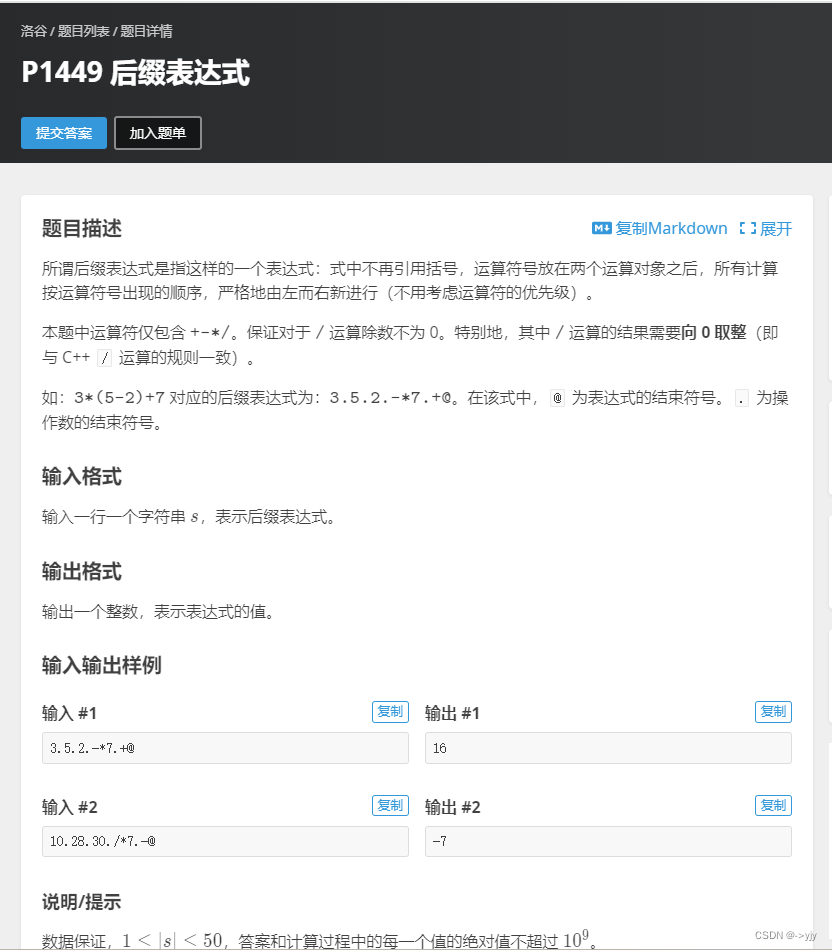
后缀表达式 - 洛谷
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
using namespace std;
int stk[100]; // 用于存储操作数的栈
int index = 0; // 栈顶索引
int main() {
char op; // 当前读取的字符
int now = 0; // 当前构建的数字
bool readingNumber = false; // 是否正在读取一个数字
while ((op = getchar()) != '@') { // 读取字符直到结束符 '@'
if (op >= '0' && op <= '9') {
// 构建当前数字
now *= 10;
now += op - '0';
readingNumber = true;
}
else if (op == '.') {
// 数字结束,压入栈中
if (readingNumber) {
stk[++index] = now;
now = 0;
readingNumber = false;
}
}
else if (op == '+') {
// 加法操作
stk[index - 1] = stk[index - 1] + stk[index];
index--;
}
else if (op == '-') {
// 减法操作
stk[index - 1] = stk[index - 1] - stk[index];
index--;
}
else if (op == '*') {
// 乘法操作
stk[index - 1] = stk[index - 1] * stk[index];
index--;
}
else if (op == '/') {
// 除法操作,结果向零取整
stk[index - 1] = stk[index - 1] / stk[index];
index--;
}
}
// 输出最终结果
cout << stk[1] << endl;
return 0;
}

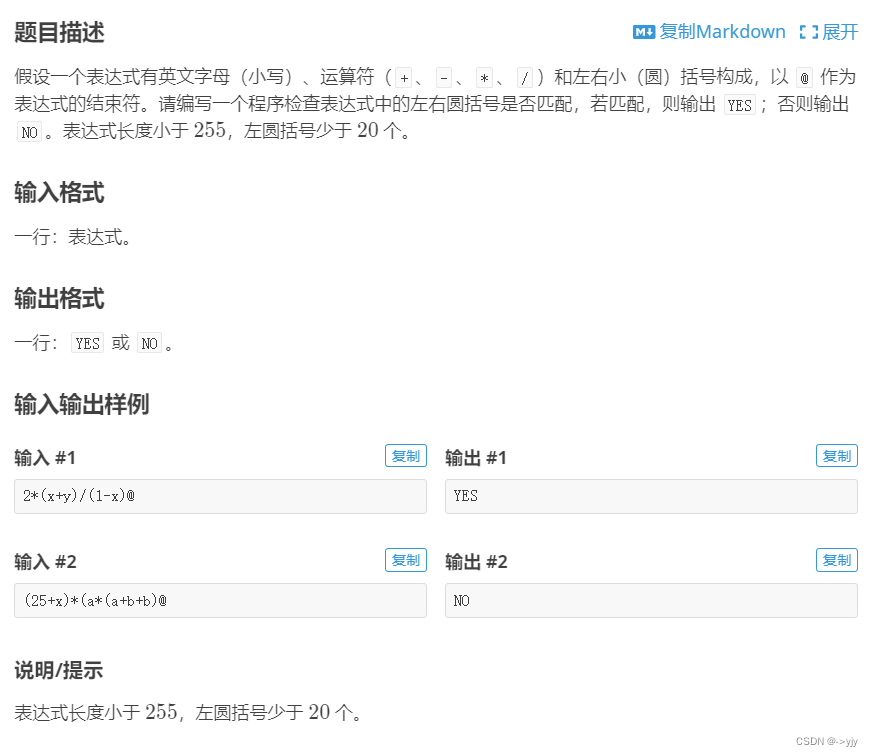
2.表达式括号匹配
表达式括号匹配 - 洛谷
#include<iostream>
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s;
cin >> s;
int isMatch = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
if (s[i] == '(') {
isMatch++;
}
else if (s[i] == ')') {
isMatch--;
if (isMatch < 0) {
cout << "NO";
return 0;
}
}
}
if (!isMatch) {
cout << "YES";
}
else {
cout << "NO";
}
return 0;
}

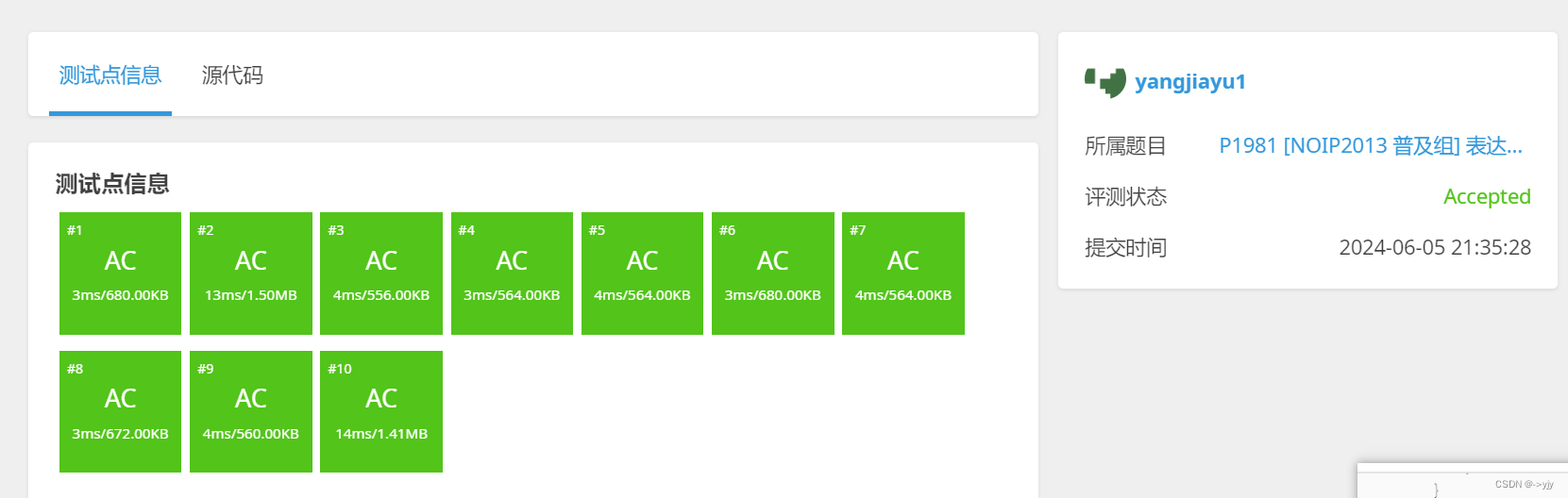
3.表达式求值
[NOIP2013 普及组] 表达式求值 - 洛谷


如果用Python
print(intput()%10000)
首先是思路:
-
可以用一个栈储存运算符
-
并用另一个栈储存需要运算的数字
#include <iostream>
#include <stack>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
stack<int> num; // 定义一个栈存储数字
stack<char> op; // 定义一个栈存储运算符
string input;
int sum = 0, ans, t, t1, t2; // t, t1, t2均为临时变量
int applyOp(int a, int b, char oper) {
if (oper == '*') return (a * b) % 10000;
if (oper == '+') return (a + b) % 10000;
return 0;
}
int main() {
cin >> input;
for (int i = 0; i < input.length(); i++) {
if (isdigit(input[i])) { // 字符转数字
sum = sum * 10 + (input[i] - '0');
if (i == input.length() - 1 || !isdigit(input[i + 1])) {
sum = sum % 10000; // 取模,后四位
num.push(sum);
sum = 0;
}
}
else if (input[i] == '+' || input[i] == '*') { // 运算符
while (!op.empty() && (op.top() == '*' || (op.top() == '+' && input[i] == '+'))) {
t1 = num.top(); num.pop();
t2 = num.top(); num.pop();
t = applyOp(t2, t1, op.top());
op.pop();
num.push(t);
}
op.push(input[i]);
}
}
while (!op.empty()) {
t1 = num.top(); num.pop();
t2 = num.top(); num.pop();
t = applyOp(t2, t1, op.top());
op.pop();
num.push(t);
}
ans = num.top(); // 可直接输出栈顶元素
cout << ans << endl;
return 0;
}
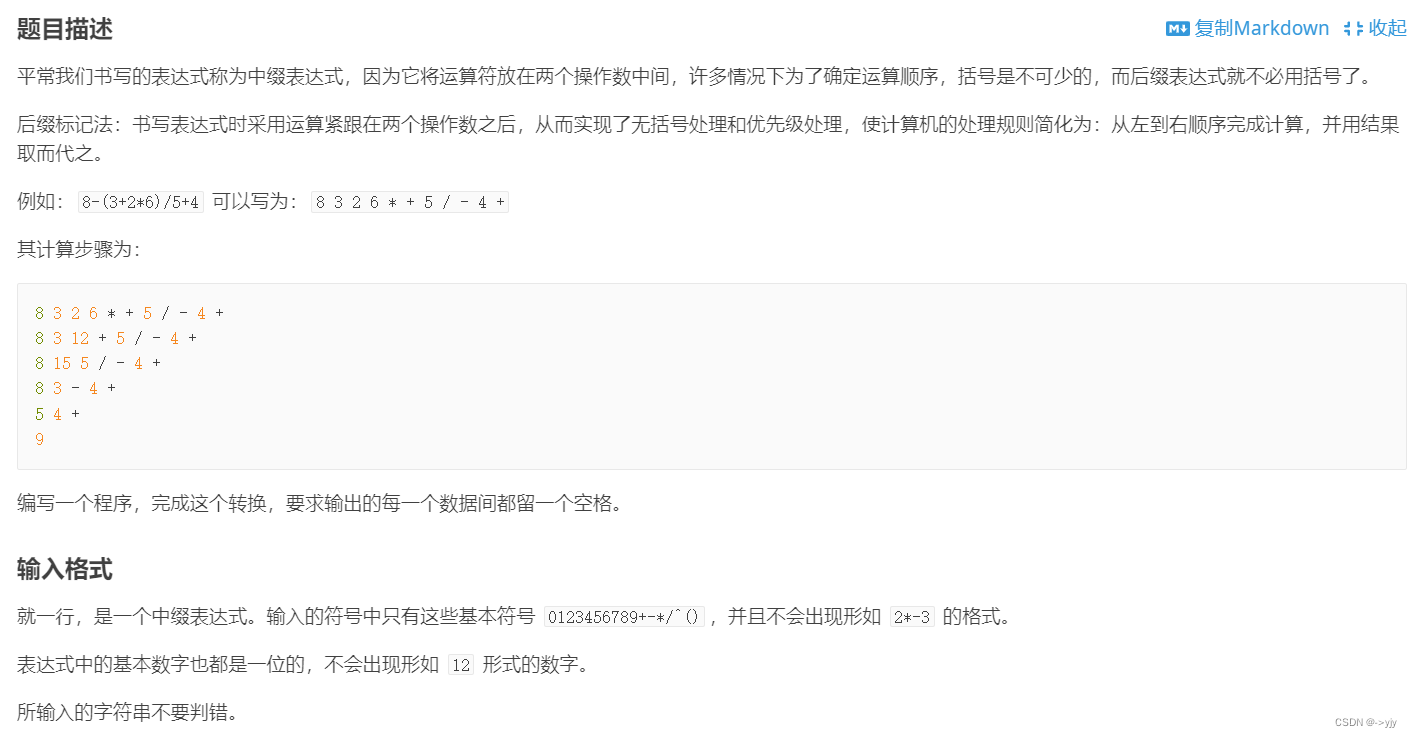
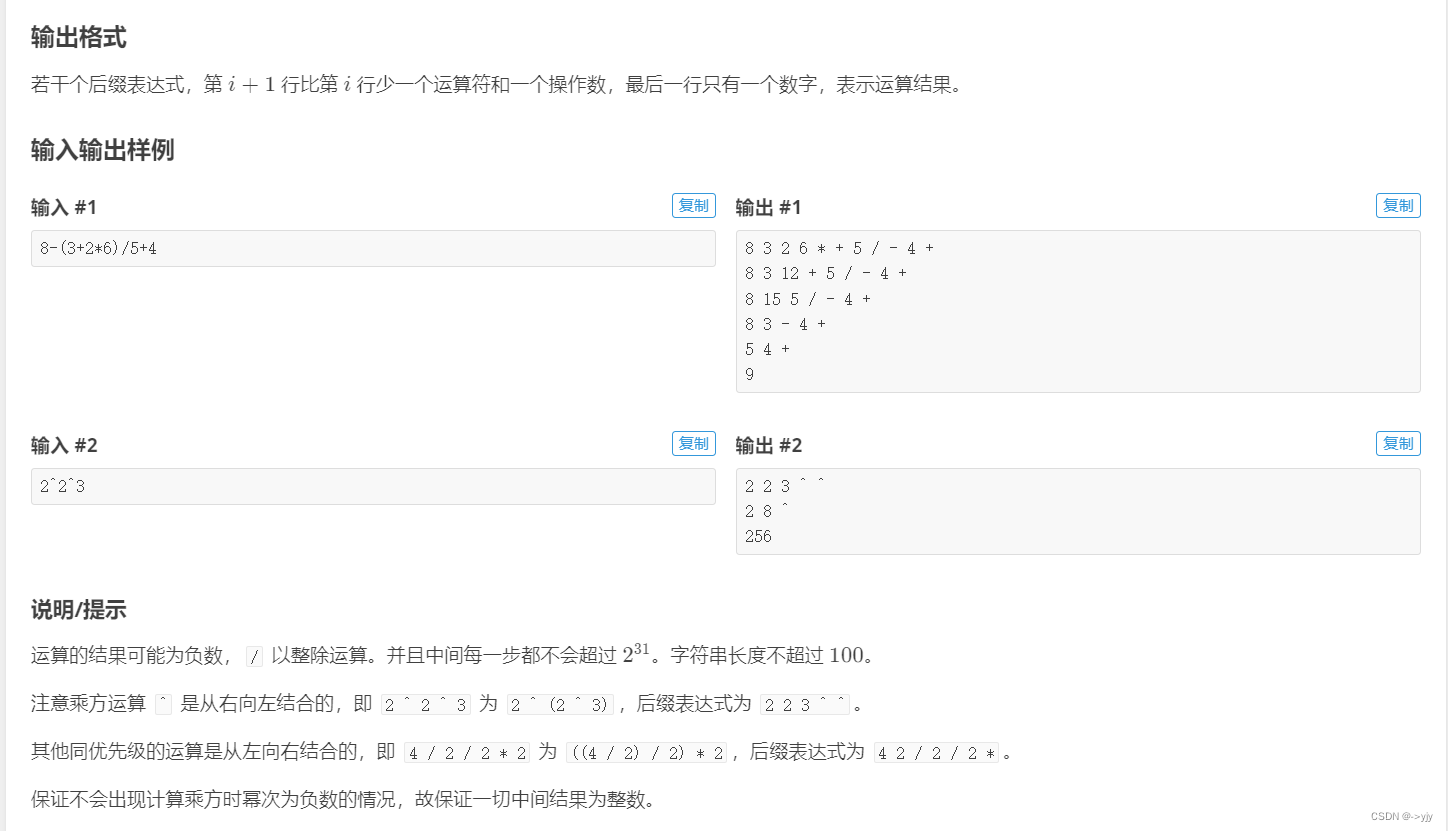
4.表达式的转换
表达式的转换 - 洛谷
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
stack<char> dat, op;
stack<int> num, dat2;
int check(char c)
{
switch (c)
{
case '+':return 1;
case '-':return 1;
case '*':return 2;
case '/':return 2;
case '^':return 3;
case '(':return 0;
case ')':return 0;
default:return -1;
}
}
int js(int x, int y, char t)
{
switch (t)
{
case '+':return x + y;
case '-':return x - y;
case '*':return x * y;
case '/':return x / y;
case '^':return pow(x, y);
default:return -0x3f3f3f3f;
}
}
void change(string s)
{
int len = s.size();
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
if (isdigit(s[i]))dat.push(s[i]);
else if (s[i] == '(')op.push(s[i]);
else if (s[i] == ')')
{
char t = op.top();
while (t != '(')
{
op.pop();
dat.push(t);
t = op.top();
}
op.pop();//要弹出左括号
}
else if (check(s[i]) >= 1 && check(s[i]) <= 3)//为运算符
{
if (!op.empty())
{
char t = op.top();
while (!op.empty() && check(s[i]) <= check(t))
{
if (check(s[i]) == check(t) && s[i] == '^')break;//在s[i]与栈顶都是^号时也能进栈
op.pop();
dat.push(t);
if (!op.empty())t = op.top();
}
}
op.push(s[i]);
}
}
while (!op.empty())
{
char t = op.top();
op.pop();
dat.push(t);
}
while (!dat.empty())
{
char t = dat.top();
dat.pop();
op.push(t);
}
while (!op.empty())
{
char t = op.top();
cout << t << ' ';
op.pop();
dat.push(t);
}
cout << endl;
}
void calc()
{
while (!dat.empty())
{
char t = dat.top();
dat.pop();
op.push(t);
}
while (!op.empty())
{
char t = op.top();
op.pop();
if (isdigit(t))num.push(t - '0');
else
{
int x = num.top();
num.pop();
int y = num.top();
num.pop();
num.push(js(y, x, t));//传参数时要把x和y反过来
while (!num.empty())
{
int t = num.top();
num.pop();
dat2.push(t);
}
while (!dat2.empty())
{
int t = dat2.top();
cout << t << ' ';
dat2.pop();
num.push(t);
}
while (!op.empty())
{
char t = op.top();
cout << t << ' ';
op.pop();
dat.push(t);
}
while (!dat.empty())
{
char t = dat.top();
dat.pop();
op.push(t);
}
cout << endl;
}
}
}
int main()
{
string s;
cin >> s;
change(s);
calc();
return 0;
}5.机器翻译
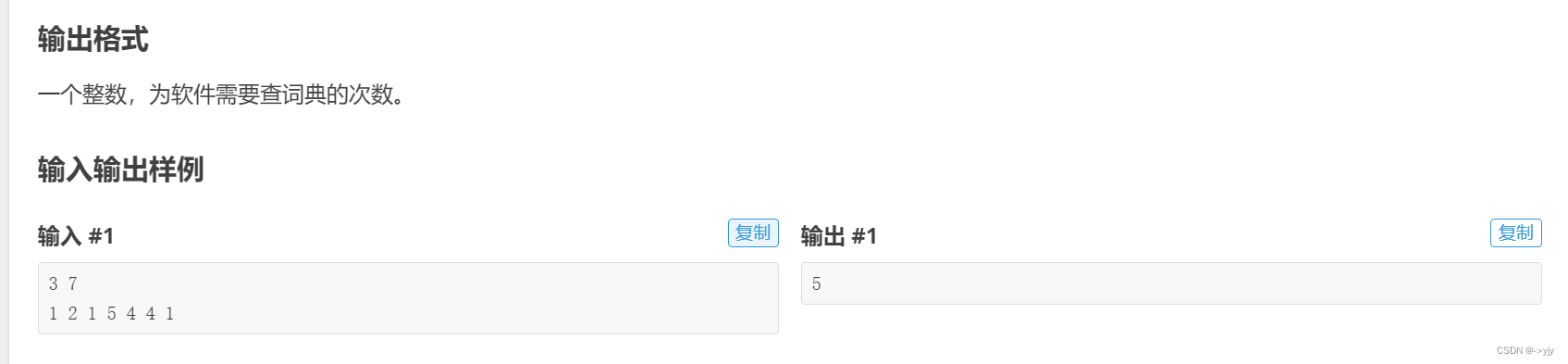
https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P1540

import java.util.*;
/**
* Author : yjy
* Desc
*/
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int N = sc.nextInt();
int M = sc.nextInt();
int[] arr = new int[M];
for(int i=0;i<M;i++){
arr[i] = sc.nextInt();
}
int res = 0;
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
if(queue.contains(arr[i])){
continue;
}
else{
if(queue.size()==N){
queue.poll();
}
queue.offer(arr[i]);
res++;
}
}
System.out.println(res);
}
}
#include<iostream>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int n, m, x, ans, l, r, a[1005], b[1005];
int main()
{
cin >> m >> n;
l = 0, r = 0;//初始化两个指针
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
scanf("%d", &x);//边读边做
if (a[x] == 0) {//没有被访问过
ans++;
r++;
b[r] = x; a[x] = 1;
if (r > m) {
l++; a[b[l]] = 0;
}
}
}
cout << ans;
return 0;
}

![主流数据库的大数据插入对比(mssql[sql server]、oracle、postgresql、mysql、sqlite)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/ae2942b4056745efb7575d4baee4c8d6.png)