目录
1. 注释
1.1 单行注释
1.2 多行注释
1.3 文档注释
2. 函数
2.1 定义
2.2 可选参数
2.3 可选参数 默认值
2.4 命名参数 默认值
2.5 函数内定义
2.6 Funcation 返回函数对象
2.7 匿名函数
2.8 作用域
3. 操作符
3.1 操作符表
3.2 算术操作符
3.3 相等相关的操作符
3.4 类型判定操作符
3.5 条件表达式
3.6 位和移位操作符
3.7 级联操作符
3.8 其他操作符
4. 流程控制
5. 异常
错误的两种类型
5.1 Exception 类
5.2 Error 类
5.3 抛出错误
5.4 捕获错误
5.5 重新抛出错误以及finally
5.6 自定义异常
1. 注释
1.1 单行注释
// Symbol libraryName = new Symbol('dart.core');
1.2 多行注释
/*
* Symbol
*
Symbol libraryName = new Symbol('dart.core'); MirrorSystem mirrorSystem = currentMirrorSystem(); LibraryMirror libMirror = mirrorSystem.findLibrary(libraryName); libMirror.declarations.forEach((s, d) => print('$s - $d'));
*/
一般用在需要说明 类 函数 功能 输入 输出
1.3 文档注释
/// `main` 函数
///
/// 符号
/// 枚举
///
void main() {
...
}
类、函数 请用 /// 方式定义,后期导出文档有帮助
2. 函数
2.1 定义
int add(int x) {
return x + 1;
}
调用
add(1);2.2 可选参数
int add(int x, [int? y, int? z]) {
if (y == null) {
y = 1;
}
if (z == null) {
z = 1;
}
return x + y + z;
}
调用
add(1, 2);可选参数:
使用方括号 [] 来定义可选参数 y 和 z。调用函数时可以选择传入或者不传入这两个参数。
可空类型:
int? 表示 int 类型的值可以是 null。如果没有使用 int?,那么 Dart 不允许把 null 赋值给该参数。
默认值逻辑:
在函数内部,通过 if (y == null) 和 if (z == null) 检查 y 和 z 是否为 null,如果是则赋值为默认的 1。
2.3 可选参数 默认值
int add(int x, [int y = 1, int z = 2]) {
return x + y;
}
调用
int(1, 2);就是cpp的缺省值
2.4 命名参数 默认值
int add({int x = 1, int y = 1, int z = 1}) {
return x + y + z;
}
调用
int(x: 1, y: 2);这个会比可选参数更灵活,可以调用的时候再指定传参
2.5 函数内定义
void main(){
int add(int x){
return x + x;
}
print(add(1));
}cpp的就是lambda
2.6 Funcation 返回函数对象
Function makeAdd(int x) {
return (int y) => x + y;
}
调用
var add = makeAdd(1);
print(add(5));这里是add接收了一个函数对象,然后在print里面调用了返回的函数对象
2.7 匿名函数
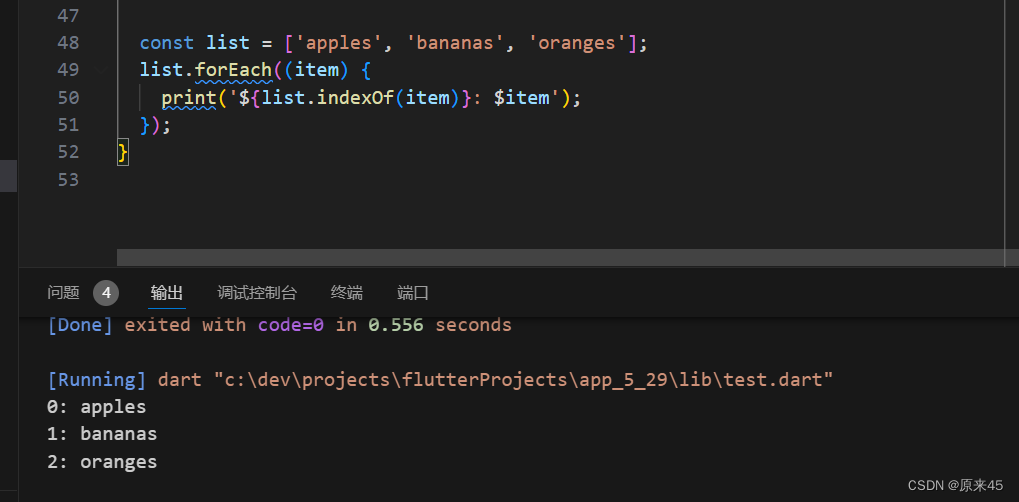
下面代码定义了只有一个参数 item 且没有参数类型的匿名方法。 List 中的每个元素都会调用这个函数,打印元素位置和值的字符串:
const list = ['apples', 'bananas', 'oranges'];
list.forEach((item) {
print('${list.indexOf(item)}: $item');
});
箭头函数 如果只有一个表达式
list.forEach((item) => print('${list.indexOf(item)}: $item'));2.8 作用域
下面是一个嵌套函数中变量在多个作用域中的示例:
bool topLevel = true;
void main() {
var insideMain = true;
void myFunction() {
var insideFunction = true;
void nestedFunction() {
var insideNestedFunction = true;
assert(topLevel);
assert(insideMain);
assert(insideFunction);
assert(insideNestedFunction);
}
}
}注意 nestedFunction() 函数可以访问包括顶层变量在内的所有的变量。简单说就是被包含的作用域内可以访问包含其的外部变量
3. 操作符
3.1 操作符表

优先级顺序 上面左边 优先级高于 右边下面
3.2 算术操作符
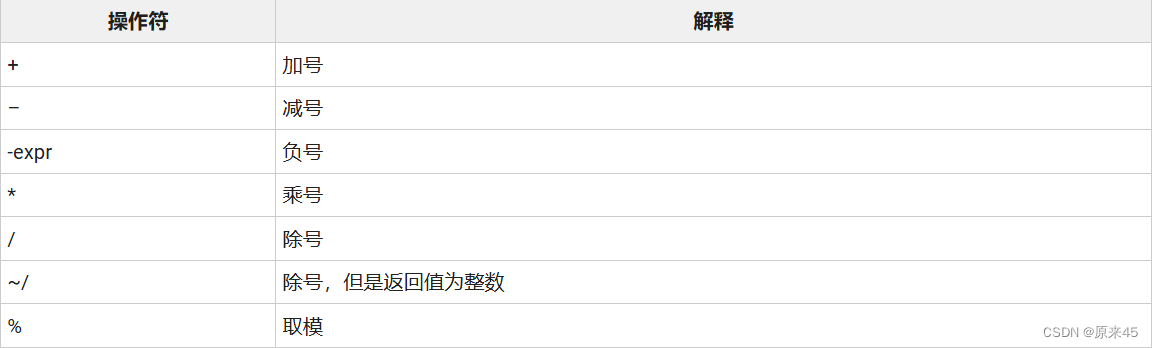
3.3 相等相关的操作符
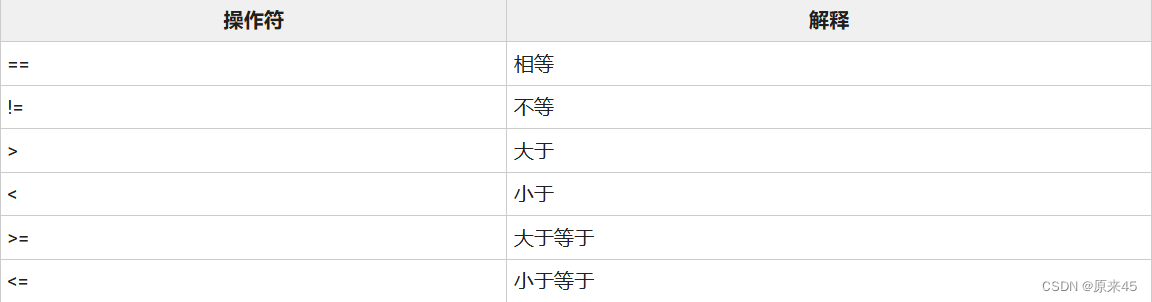
3.4 类型判定操作符
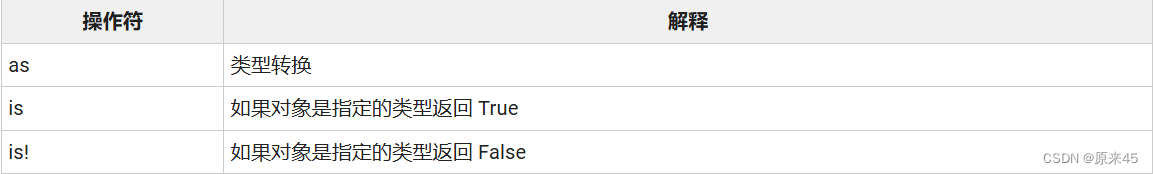
int a = 123;
String b = 'ducafecat';
String c = 'abc';
print(a as Object);
print(b is String);
print(c is! String);3.5 条件表达式

bool isFinish = true;
String txtVal = isFinish ? 'yes' : 'no';
bool isFinish;
isFinish = isFinish ?? false;
or
isFinish ??= false;
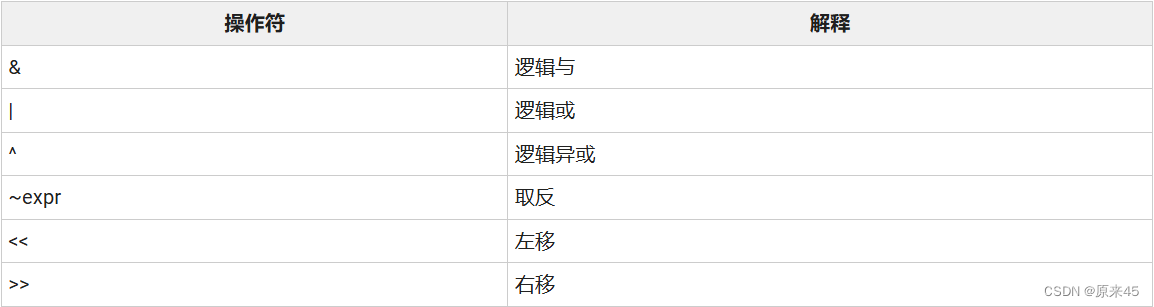
3.6 位和移位操作符
3.7 级联操作符

StringBuffer sb = StringBuffer();
sb
..write('hello')
..write('word')
..write('\n')
..writeln('doucafecat');如果没有级联操作符,就需要 sb.write(...);sb.write(...);....
3.8 其他操作符

String a;
print(a?.length);4. 流程控制
if else;for;while;do while;switch case;break;continue;相信这些就不用博主多说了哈
值得一提的是 continue 有一点不一样
continue 跳转指定位置(就像cpp的go to,新增了这个功能)
String command = "close";
switch (command) {
case "open":
print("open");
break;
case "close":
print("close");
continue doClear;
case "close2":
print("close2");
continue doClear;
doClear:
case "doClose":
print("doClose");
break;
default:
print("other");
}5. 异常
错误的两种类型
5.1 Exception 类
Exception class
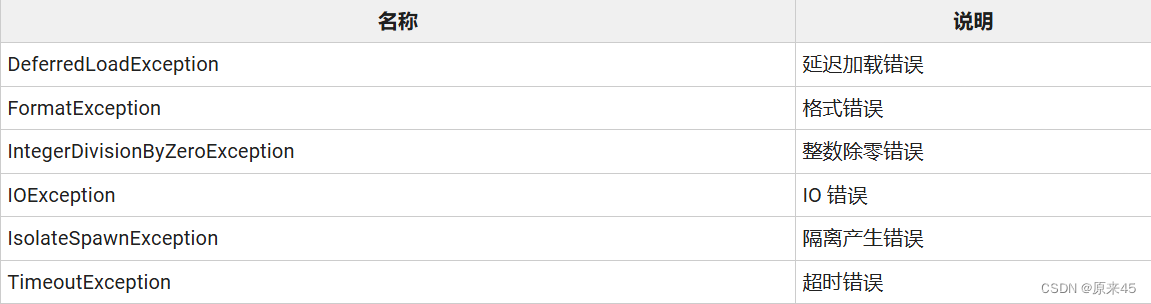
可以捕获,可以安全处理
5.2 Error 类
Error class
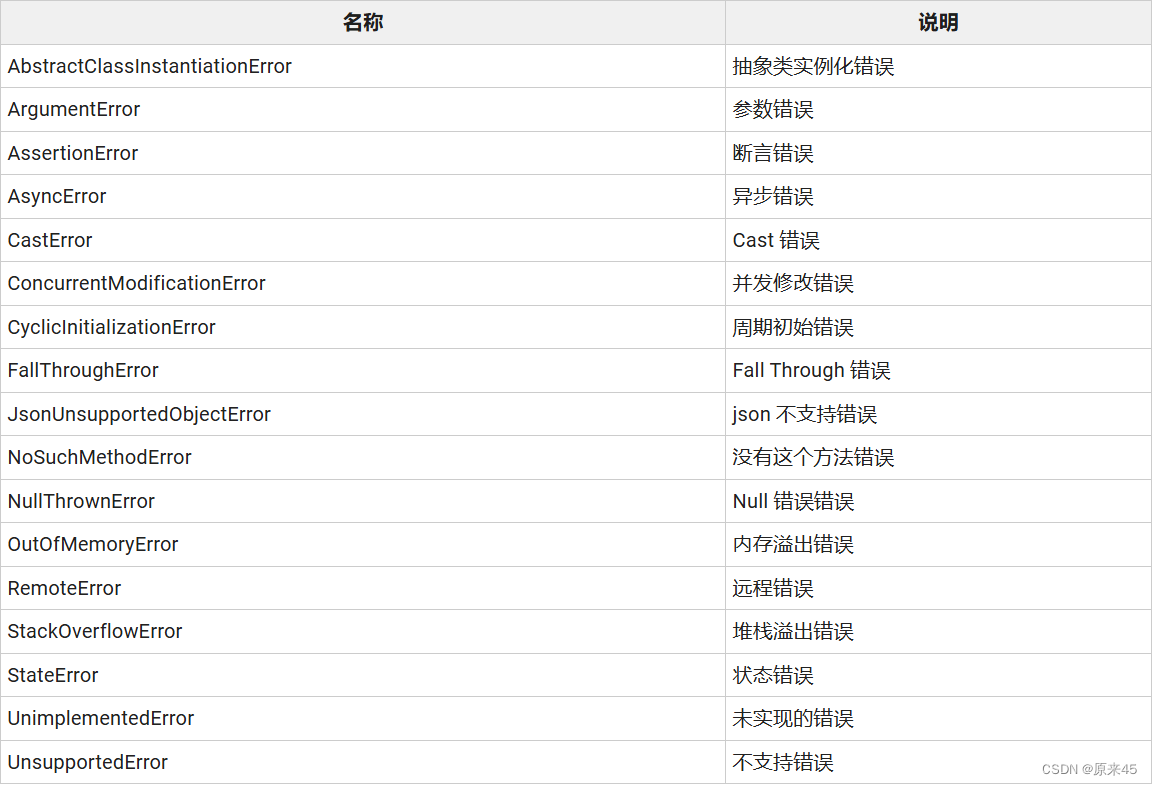
一般用在不可恢复,容易崩溃的情况
5.3 抛出错误
// Exception 对象
throw new FormatException('这是一个格式错误提示');
// Error 对象
throw new OutOfMemoryError();
// 任意对象
throw '这是一个异常';5.4 捕获错误
try {
// throw new FormatException('这是一个格式错误提示');
throw new OutOfMemoryError();
} on OutOfMemoryError {
print('没有内存了');
} catch (e) {
print(e);
}5.5 重新抛出错误以及finally
try {
throw new OutOfMemoryError();
} on OutOfMemoryError {
print('没有内存了');
rethrow;
} catch (e) {
print(e);
} finally {
print('end');
}try里面是抛出错误,on是捕获特定错误,catch是捕获所有错误,retgrow是重新抛出异常,finally是不管有没有错都会走的!
5.6 自定义异常
implements关键字可以自定义异常
class DioError implements Exception {
DioError(this.message, this.type);
final String message;
final String type;
@override
String toString() {
return 'DioError{message: $message, type: $type}';
}
}
void main(List<String> args) {
throw DioError("error", "type");
}创作不易,希望读者三连支持 💖
赠人玫瑰,手有余香 💖
![[PyQt5] 窗口接收WM_COPY消息](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/2bd655b074d0466983d24b773ecf81c0.png)