A题 签到题
代码如下
//A
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#define int long long
#define endl '\n'
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(0),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0);
using namespace std;
signed main()
{
IOS
int a,b,c,d;
cin>>a>>b>>c>>d;
cout<<a+b+2*c+3*d<<endl;
return 0;
} 
B题 签到题
代码如下
//B
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cmath>
#define int long long
#define endl '\n'
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(0),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0);
#define q 3.1415926535
using namespace std;
signed main()
{
IOS
int x,y;
cin>>x>>y;
double r,s,a,b,c,d;
cin>>a>>b;
r=sqrt(x*x+y*y);
c=a*b-(int)(a*b);
printf("%.10f",2*r*sin((c*2*q)/2));
return 0;
} 

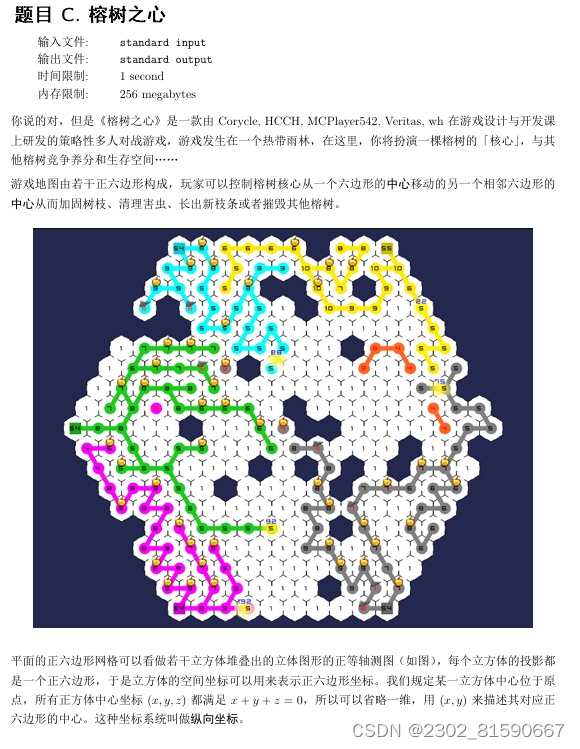
C题 签到题
代码如下
//C
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cmath>
#define int long long
#define endl '\n'
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(0),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0);
using namespace std;
double x,y,a,b;
signed main()
{
IOS
cin>>a>>b;
x=a/2+b/2;
y=(sqrt(3)*a)/2-(sqrt(3)*b)/2;
printf("%.6f %.6f",x,y);
return 0;
} 

D题


思路:这个题题意虽说到了树但其实就考了一个贪心,可以把他给的支配关系用数组存起来,然后找到最多的数,就把这个数当成父节点就行了
代码如下
//D
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cmath>
#define int long long
#define endl '\n'
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(0),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0);
using namespace std;
int m[200010];
signed main()
{
IOS
int a,b,c,d,ma=-1e9,t;
cin>>a>>b;
for(int i=1;i<=b;i++)
{
cin>>c>>d;
m[c]++;
}
for(int i=1;i<=a;i++)
{
if(m[i]>ma)
{
ma=m[i];
t=i;
}
}
for(int i=1;i<=a;i++)
{
if(i==t)
cout<<0<<" ";
else
cout<<t<<" ";
}
return 0;
} E题
思路:这个也是一个贪心题,就是让给的数从后往前遍历,如果是0就直接输出,不是就把这个数存到下标为这个数的后面
代码如下
//E
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cmath>
#include<vector>
#define int long long
#define endl '\n'
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(0),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0);
using namespace std;
int ma[200010];
vector<int>m[200010];
int n,a,b;
signed main()
{
IOS
cin>>n;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
cin>>ma[i];
}
for(int i=n;i>0;i--)
{
if(ma[i]==0)
{
cout<<i<<" ";
for(int j=0;j<m[i].size();j++)
{
cout<<m[i][j]<<" ";
}
}
else
{
m[ma[i]].push_back(i);
for(int j=0;j<m[i].size();j++)
{
m[ma[i]].push_back(m[i][j]);
}
}
}
return 0;
}