更好的阅读体验
二分图匹配
考虑如何将二分图匹配问题,转化为流网络。设置 1 1 1 个汇点和源点,从源点向二分图一侧的每一个点连边,从另一侧向汇点连边,边权均为 1 1 1,二分图中的边也全部加入,权值设为 1 1 1。这样,二分图的最大匹配等于流网络的最大流。
P2756 飞行员配对方案问题
题意:给定 1 1 1 个二分图,求最大匹配。
匈牙利算法是可以求二分图最大匹配的,不过太慢了。不妨,使用上述的方式建立出流网络,并使用 Dinic 求解出该网络的最大流即可。
举个例子:左图为样例的二分图,而右图为建立的流网络。

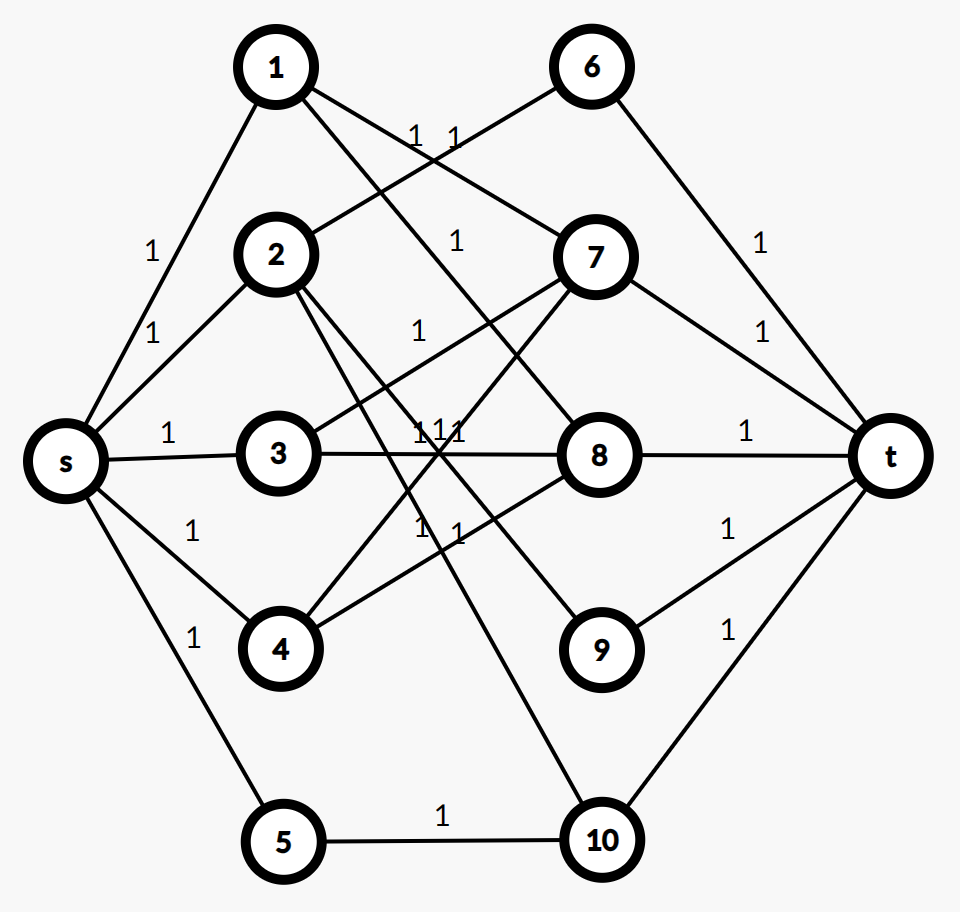
浅析流网络最大流与二分图最大匹配的相等性:
对于网络流的题目,只需要考虑对于任意的一个最大匹配,都能对应到一个可行流;而对于任意一个可行流都能对应到一个最大匹配。
对于任意的一个最大匹配,都能对应到一个可行流:若选择边 E 1 , E 2 , … , E k E_1,E_2, \dots ,E_k E1,E2,…,Ek,则可行流中的这些边均为 1 1 1,且令这些边左端的顶点分别为 V 1 , V 2 , … , V t V_1,V_2,\dots,V_t V1,V2,…,Vt,右端的为 V 1 ′ , V 2 ′ , … , V t ′ V'_1,V'_2,\dots, V'_t V1′,V2′,…,Vt′,则可行流的 s → V i s\rightarrow V_i s→Vi 这些边均为 1 1 1; V i ′ → t V'_i\rightarrow t Vi′→t 这些边也均为 1 1 1。由于匹配不存在 2 2 2 条边有公共顶点,所以一定满足容量限制与流量守恒。
对于任意的一个可行流,都能对应到一个最大匹配:可行流中流量为 1 1 1 的没有 s s s 和 t t t 的边即为最大匹配,由于流量守恒,最多有 1 1 1 条边流向一个点,所以满足对于任意 2 2 2 条边,都不存在公共点。
故,只需要用 Dinic 跑一遍最大流即可,输出方案就是找出所有反向边流量为 1 1 1(或正向边流量为 0 0 0)的边即可。
注意:二分图下的 Dinic 算法极为特殊,时间复杂度为 O ( n 2 n ) O(n^2\sqrt n) O(n2n)
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define fi first
#define se second
#define int long long
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 1e2 + 10, M = 1e5 + 10;
int n, m, s, t;
int h[N], e[M], ne[M], f[M], idx;
int d[N], cur[N];
void add(int a, int b, int c) {
e[idx] = b, ne[idx] = h[a], f[idx] = c, h[a] = idx ++;
e[idx] = a, ne[idx] = h[b], f[idx] = 0, h[b] = idx ++;
}
bool bfs() {
memset(d, -1, sizeof d);
queue<int> q;
q.emplace(s), cur[s] = h[s], d[s] = 0;
while (q.size()) {
auto u = q.front();
q.pop();
for (int i = h[u]; ~i; i = ne[i]) {
int j = e[i];
if (d[j] == -1 && f[i]) {
d[j] = d[u] + 1, cur[j] = h[j];
if (j == t) return 1;
q.emplace(j);
}
}
}
return 0;
}
int find(int u, int lim) {
if (u == t) return lim;
int flow = 0;
for (int i = cur[u]; ~i && flow < lim; i = ne[i]) {
int j = e[i];
if (d[j] == d[u] + 1 && f[i]) {
int tmp = find(j, min(lim - flow, f[i]));
if (!tmp) d[j] = -1;
f[i] -= tmp, f[i ^ 1] += tmp, flow += tmp;
}
}
return flow;
}
int dinic() {
int res = 0, flow;
while (bfs()) while (flow = find(s, 1e18)) res += flow;
return res;
}
signed main() {
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
memset(h, -1, sizeof h);
cin >> m >> n;
s = 0, t = n + 1;
int u, v;
while (cin >> u >> v && u != -1) {
add(u, v, 1);
}
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i ++)
add(s, i, 1);
for (int i = m + 1; i <= n; i ++)
add(i, t, 1);
cout << dinic() << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < idx; i += 2)
if (e[i] != t && e[i ^ 1] != s && !f[i])
cout << e[i ^ 1] << " " << e[i] << endl;
return 0;
}
习题
P3254 圆桌问题,与原建图方式有略微差异。
参考代码#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define fi first
#define se second
#define int long long
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 5e2 + 10, M = 1e5 + 10;
int m, n, s, t;
int a[N], b[N];
int h[N], e[M], f[M], ne[M], idx;
int d[N], cur[N];
void add(int a, int b, int c) {
e[idx] = b, ne[idx] = h[a], f[idx] = c, h[a] = idx ++;
e[idx] = a, ne[idx] = h[b], f[idx] = 0, h[b] = idx ++;
}
bool bfs() {
memset(d, -1, sizeof d);
queue<int> q;
q.emplace(s), d[s] = 0, cur[s] = h[s];
while (q.size()) {
int u = q.front();
q.pop();
for (int i = h[u]; ~i; i = ne[i]) {
int j = e[i];
if (d[j] == -1 && f[i]) {
d[j] = d[u] + 1;
cur[j] = h[j];
if (j == t) return 1;
q.emplace(j);
}
}
}
return 0;
}
int find(int u, int lim) {
if (u == t) return lim;
int flow = 0;
for (int i = cur[u]; ~i && flow < lim; i = ne[i]) {
cur[u] = i;
int j = e[i];
if (d[j] == d[u] + 1 && f[i]) {
int tmp = find(j, min(lim - flow, f[i]));
if (!tmp) d[j] = -1;
f[i] -= tmp, f[i ^ 1] += tmp, flow += tmp;
}
}
return flow;
}
int dinic() {
int res = 0, flow;
while (bfs()) while (flow = find(s, 1e18)) res += flow;
return res;
}
signed main() {
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
memset(h, -1, sizeof h);
cin >> m >> n;
s = 0, t = n + m + 1;
int tot = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i ++)
cin >> a[i], add(s, i, a[i]), tot += a[i];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++)
cin >> b[i], add(i + m, t, b[i]);
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i ++)
for (int j = m + 1; j <= n + m; j ++)
add(i, j, 1);
if (dinic() == tot) {
cout << 1 << endl;
std::vector<vector<int>> way(m + 1);
for (int i = 0; i < idx; i += 2)
if (e[i] != t && e[i ^ 1] != s && !f[i])
way[e[i ^ 1]].emplace_back(e[i] - m);
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i ++) {
for (auto v : way[i])
cout << v << " ";
cout << endl;
}
} else {
cout << 0 << endl;
}
return 0;
}
多源汇最大流
本质上只不过是源点不是 1 1 1 个,汇点也不是 1 1 1 个了,那么其实只需要再设一个超级源点连向所有源点,边权为 + ∞ +\infty +∞,表示向这些源点可以流任意多流量,也就是说从这些源点可以流出任意多流量;同样的,从每一个汇点向超级汇点连一条 + ∞ +\infty +∞ 的边,表示这些汇点可以流向超级汇点任意多流量,也就是说这些汇点都可以接纳任意多的流量。
这样的新流网络的最大流就是源网络的最大流,所以只需要对于新网络跑一遍 Dinic 即可。
习题
AcWing 2234. 多源汇最大流,模版题
参考代码#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <queue>
#define int long long
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
const int SIZE = 5e5 + 10;
int N, M, Sc, Tc, S, T;
int h[SIZE], e[SIZE], ne[SIZE], f[SIZE], idx;
int D[SIZE], Current[SIZE];
void add(int a, int b, int c) {
e[idx] = b, ne[idx] = h[a], f[idx] = c, h[a] = idx ++;
e[idx] = a, ne[idx] = h[b], f[idx] = 0, h[b] = idx ++;
}
bool BFS() {
memset(D, -1, sizeof D);
queue<int> Q;
Q.push(S), D[S] = 0, Current[S] = h[S];
while (Q.size()) {
int u = Q.front();
Q.pop();
for (int i = h[u]; ~i; i = ne[i]) {
int j = e[i];
if (D[j] == -1 && f[i]) {
D[j] = D[u] + 1;
Current[j] = h[j];
if (j == T) return true;
Q.push(j);
}
}
}
return false;
}
int Find(int u, int limit) {
if (u == T) return limit;
int flow = 0;
for (int i = Current[u]; ~i && flow < limit; i = ne[i]) {
Current[u] = i;
int j = e[i];
if (D[j] == D[u] + 1 && f[i]) {
int T = Find(j, min(f[i], limit - flow));
if (!T) D[j] = -1;
f[i] -= T, f[i ^ 1] += T, flow += T;
}
}
return flow;
}
int Dinic() {
int Result = 0, flow;
while (BFS()) while (flow = Find(S, 1e18)) Result += flow;
return Result;
}
signed main() {
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
memset(h, -1, sizeof h);
cin >> N >> M >> Sc >> Tc;
S = 0, T = N + 1;
while (Sc --) {
int u;
cin >> u;
add(S, u, 1e18);
}
while (Tc --) {
int u;
cin >> u;
add(u, T, 1e18);
}
while (M --) {
int a, b, c;
cin >> a >> b >> c;
add(a, b, c);
}
cout << Dinic() << endl;
return 0;
}
关键边
POJ3204 Ikki’s Story I - Road Reconstruction
题意:给定 1 1 1 个流网络,求有多少条边,满足增加该边边权后能使最大流增加。
考虑一条边满足什么条件使得增加容量后会使得最大流增加,回顾求最大流的过程:每一次在残留网络中找增广路径,并加到最大流中。
那么,如果容量增加后,最大流增加,那么必然是增加流量后产生 1 1 1 条增广路径。所以,对于每一条边 ( u , v ) (u,v) (u,v),只需要判断是否存在 1 1 1 条增广路径 s → u s\rightarrow u s→u 以及 1 1 1 增广路径 v → t v\rightarrow t v→t。判断的方法就是在最大流的残留网络中 DFS,记录每次走 > 0 >0 >0 的边能到达那些点即可。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define fi first
#define se second
#define int long long
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 5e2 + 10, M = 2e4 + 10;
int n, m, s, t;
int h[N], e[M], ne[M], f[M], idx;
int d[N], cur[N], vis[2][N];
void add(int a, int b, int c) {
e[idx] = b, ne[idx] = h[a], f[idx] = c, h[a] = idx ++;
e[idx] = a, ne[idx] = h[b], f[idx] = 0, h[b] = idx ++;
}
bool bfs() {
memset(d, -1, sizeof d);
queue<int> q;
q.emplace(s), d[s] = 0, cur[s] = h[s];
while (q.size()) {
int u = q.front();
q.pop();
for (int i = h[u]; ~i; i = ne[i]) {
int j = e[i];
if (d[j] == -1 && f[i]) {
d[j] = d[u] + 1, cur[j] = h[j];
if (j == t) return 1;
q.emplace(j);
}
}
}
return 0;
}
int find(int u, int lim) {
if (u == t) return lim;
int flow = 0;
for (int i = cur[u]; ~i && flow < lim; i = ne[i]) {
cur[u] = i;
int j = e[i];
if (d[j] == d[u] + 1 && f[i]) {
int tmp = find(j, min(lim - flow, f[i]));
if (!tmp) d[j] = -1;
f[i] -= tmp, f[i ^ 1] += tmp, flow += tmp;
}
}
return flow;
}
int dinic() {
int res = 0, flow;
while (bfs()) while (flow = find(s, 1e18)) res += flow;
return res;
}
void dfs(int u, int k) {
vis[k][u] = 1;
for (int i = h[u]; ~i; i = ne[i]) {
int j = e[i];
if (!vis[k][j] && f[i ^ k])
dfs(j, k);
}
}
signed main() {
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
memset(h, -1, sizeof h);
cin >> n >> m;
s = 0, t = n - 1;
while (m --) {
int u, v, w;
cin >> u >> v >> w;
add(u, v, w);
}
dinic();
dfs(s, 0), dfs(t, 1);
int res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < idx; i += 2)
if (vis[0][e[i ^ 1]] && vis[1][e[i]])
res ++;
cout << res << endl;
return 0;
}
拆点
POJ3281 Dining
题意:有
n
n
n 头奶牛,
F
F
F 个食物和
D
D
D 个饮料,每头奶牛可以吃某些食物和饮料,但都只能吃食物和饮料各一个。求最多能满足多少头奶牛。(三分图匹配)
考虑继续使用类似二分图的建网络流的方式,举个例子:


不过,这样真的能够求出最终的答案吗?答案是否定的。

考虑局部的这样一个位置,最大流得到话会流出 2 2 2 的,也就是这个奶牛会贡献 2 2 2,而应该是 1 1 1。
所以,就要拆点了!
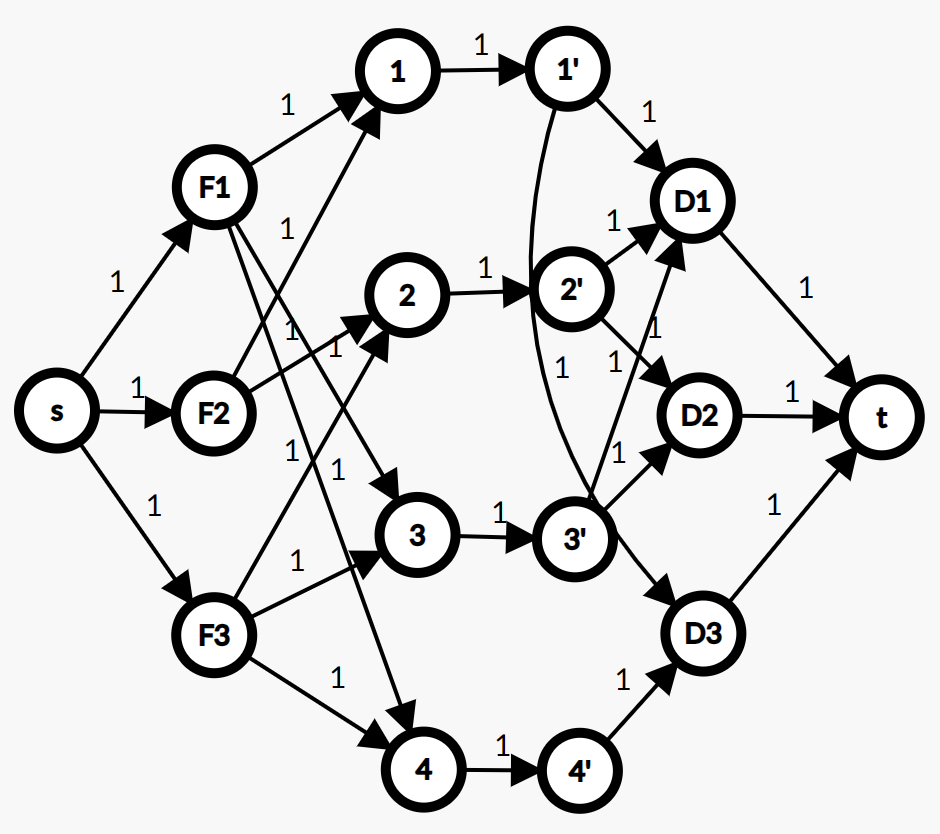 通过,流量守恒,就可以使得通过每一个点的流量最多为 $1$,也就满足了题意。
通过,流量守恒,就可以使得通过每一个点的流量最多为 $1$,也就满足了题意。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define fi first
#define se second
#define int long long
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 4e2 + 10, M = 1e5 + 10;
int n, m, k, s, t;
int h[N], e[M], ne[M], f[M], idx;
int d[N], cur[N];
void add(int a, int b, int c) {
e[idx] = b, ne[idx] = h[a], f[idx] = c, h[a] = idx ++;
e[idx] = a, ne[idx] = h[b], f[idx] = 0, h[b] = idx ++;
}
bool bfs() {
memset(d, -1, sizeof d);
queue<int> q;
q.emplace(s), d[s] = 0, cur[s] = h[s];
while (q.size()) {
int u = q.front();
q.pop();
for (int i = h[u]; ~i; i = ne[i]) {
int j = e[i];
if (d[j] == -1 && f[i]) {
d[j] = d[u] + 1, cur[j] = h[j];
if (j == t) return 1;
q.emplace(j);
}
}
}
return 0;
}
int find(int u, int lim) {
if (u == t) return lim;
int flow = 0;
for (int i = cur[u]; ~i && flow < lim; i = ne[i]) {
cur[u] = i;
int j = e[i];
if (d[j] == d[u] + 1 && f[i]) {
int tmp = find(j, min(lim - flow, f[i]));
if (!tmp) d[j] = -1;
f[i] -= tmp, f[i ^ 1] += tmp, flow += tmp;
}
}
return flow;
}
int dinic() {
int res = 0, flow;
while (bfs()) while (flow = find(s, 1e18)) res += flow;
return res;
}
signed main() {
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
memset(h, -1, sizeof h);
cin >> n >> m >> k;
s = 0, t = n * 2 + m + k + 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) {
int cf, cd, x;
cin >> cf >> cd;
for (int j = 1; j <= cf; j ++)
cin >> x, add(x, i + m, 1);
for (int j = 1; j <= cd; j ++)
cin >> x, add(i + m + n, x + m + n + n, 1);
}
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i ++)
add(s, i, 1);
for (int i = m + n * 2 + 1; i < t; i ++)
add(i, t, 1);
for (int i = m + 1; i <= m + n; i ++)
add(i, i + n, 1);
cout << dinic() << endl;
return 0;
}
习题
P2766 最长不下降子序列问题
参考代码#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define fi first
#define se second
#define int long long
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 1e3 + 10, M = 4e5 + 10;
int n, s, t;
int a[N], dp[N];
int h[N], e[M], ne[M], f[M], idx;
int d[N], cur[N];
void add(int a, int b, int c) {
e[idx] = b, ne[idx] = h[a], f[idx] = c, h[a] = idx ++;
e[idx] = a, ne[idx] = h[b], f[idx] = 0, h[b] = idx ++;
}
bool bfs() {
memset(d, -1, sizeof d);
queue<int> q;
q.emplace(s), d[s] = 0, cur[s] = h[s];
while (q.size()) {
int u = q.front();
q.pop();
for (int i = h[u]; ~i; i = ne[i]) {
int j = e[i];
if (d[j] == -1 && f[i]) {
d[j] = d[u] + 1, cur[j] = h[j];
if (j == t) return 1;
q.emplace(j);
}
}
}
return 0;
}
int find(int u, int lim) {
if (u == t) return lim;
int flow = 0;
for (int i = cur[u]; ~i && flow < lim; i = ne[i]) {
cur[u] = i;
int j = e[i];
if (d[j] == d[u] + 1 && f[i]) {
int tmp = find(j, min(lim - flow, f[i]));
if (!tmp) d[j] = -1;
f[i] -= tmp, f[i ^ 1] += tmp, flow += tmp;
}
}
return flow;
}
int dinic() {
int res = 0, flow;
while (bfs()) while (flow = find(s, 1e18)) res += flow;
return res;
}
signed main() {
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
memset(h, -1, sizeof h);
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++)
cin >> a[i];
s = 0, t = 2 * n + 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) {
dp[i] = 1, add(i, i + n, 1);
std::vector<int> opt;
for (int j = 1; j < i; j ++)
if (a[j] <= a[i] && dp[j] + 1 > dp[i])
opt.clear(), opt.emplace_back(j), dp[i] = dp[j] + 1;
else if (a[j] <= a[i] && dp[j] + 1 == dp[i])
opt.emplace_back(j);
for (auto v : opt)
add(n + v, i, 1);
}
int res = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++)
res = max(res, dp[i]);
cout << res << endl;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) {
if (dp[i] == res)
add(i + n, t, 1);
if (dp[i] == 1)
add(s, i, 1);
}
res = dinic();
cout << res << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < idx; i += 2) {
if (e[i ^ 1] == 1 && e[i] == 1 + n || e[i ^ 1] == 1 + n && e[i] == t || e[i ^ 1] == s && e[i] == 1)
f[i] = 1e18;
else if (e[i ^ 1] == n && e[i] == n + n || e[i ^ 1] == n + n && e[i] == t || e[i ^ 1] == s && e[i] == n)
f[i] = 1e18;
}
res += dinic();
cout << min(res, n) << endl;
return 0;
}
POJ3498 March of the Penguins
参考代码#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define fi first
#define se second
#define int long long
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 2e2 + 10, M = 2e4 + 10;
int n, s, t;
double ld;
int h[N], e[M], ne[M], f[M], idx;
int d[N], cur[N];
struct Node {
int x, y;
int tot, cnt;
double operator- (const Node &tmp)const {
int a = x - tmp.x, b = y - tmp.y;
return sqrt(a * a * 1.0 + b * b * 1.0);
}
}pg[N];
void add(int a, int b, int c) {
e[idx] = b, ne[idx] = h[a], f[idx] = c, h[a] = idx ++;
e[idx] = a, ne[idx] = h[b], f[idx] = 0, h[b] = idx ++;
}
bool bfs() {
memset(d, -1, sizeof d);
queue<int> q;
q.emplace(s), d[s] = 0, cur[s] = h[s];
while (q.size()) {
int u = q.front();
q.pop();
for (int i = h[u]; ~i; i = ne[i]) {
int j = e[i];
if (d[j] == -1 && f[i]) {
d[j] = d[u] + 1, cur[j] = h[j];
if (j == t) return 1;
q.emplace(j);
}
}
}
return 0;
}
int find(int u, int lim) {
if (u == t) return lim;
int flow = 0;
for (int i = cur[u]; ~i && flow < lim; i = ne[i]) {
cur[u] = i;
int j = e[i];
if (d[j] == d[u] + 1 && f[i]) {
int tmp = find(j, min(lim - flow, f[i]));
if (!tmp) d[j] = -1;
f[i] -= tmp, f[i ^ 1] += tmp, flow += tmp;
}
}
return flow;
}
int dinic() {
int res = 0, flow;
while (bfs()) while (flow = find(s, 1e18)) res += flow;
return res;
}
void solve() {
cin >> n >> ld;
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++)
cin >> pg[i].x >> pg[i].y >> pg[i].tot >> pg[i].cnt, sum += pg[i].tot;
s = 0;
std::vector<int> res;
for (t = 1; t <= n; t ++) {
memset(h, -1, sizeof h);
idx = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) {
add(s, i, pg[i].tot), add(i, i + n, pg[i].cnt);
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j ++)
if (i != j && pg[j] - pg[i] <= ld)
add(i + n, j, 1e18);
}
if (dinic() == sum)
res.emplace_back(t);
}
if (res.empty())
cout << -1 << endl;
else {
for (auto v : res)
cout << v - 1 << " ";
cout << endl;
}
}
signed main() {
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
int dt;
cin >> dt;
while (dt --)
solve();
return 0;
}