什么是代理
假设有一个核心方法叫转账,为了安全性考虑,不能让用户直接访问接口。此时涉及到了代理,这使得用户只能访问代理类,增加了访问限制。
代理的定义:给目标对象提供一个代理对象,并且由代理对象控制着对目标对象的引用。
代理如何实现
基于JDK的代理
① 静态代理
由代理类代理目标类:
目标类生成一个目标对象,代理类首先会生成代理对象,代理对象代理目标对象,普通用户只能访问代理对象。

一个类中可能有很多方法,代理类怎么知道代理目标类的哪个方法呢?除了直接写过去,我们还可以在接口当中定义目标类当中需要被代理的方法。让目标类实现一个接口,同时代理类也去实现这个接口。
注意:实现接口的是类,而用户访问的是对象。
为什么有接口:接口定义的方法其子类必须实现,让目标类实现在接口当中定义的核心方法(目标类实现了接口),为了通知代理类代理目标类当中的哪个核心方法,我们也让代理类实现接口。
在具体实现的过程中,为了保证职能的单一性,功能增强部分的代码最好不写在目标类里。
如何实现静态代理
public interface ByClothes { //代理类和目标类都要继承该接口
//在接口当中定义需要代理的方法
public void clothes(String size) ;
}public class ClothesFactory implements ByClothes{ //目标类 :制作衣服
public void clothes(String size) { //目标类的核心
System.out.println("已经为您定制好了一件大小为" + size + "的衣服");
}
}public class StaticProxy implements ByClothes{ //代理类
private ClothesFactory clothesFactory = new ClothesFactory();
//这个地方就是核心方法
@Override
public void clothes(String size) {
front(); //功能增强
clothesFactory.clothes(size); //核心方法
end(); //功能增强
}
public void front() {
System.out.println("市场调研");
}
public void end() {
System.out.println("售后服务");
}
}public class Test { //用户
public static void main(String[] args) {
StaticProxy proxy = new StaticProxy();
proxy.clothes("XXXL");
}
}
② 动态代理
动态代理指的是一个代理类代理多个目标类。
如何实现?类是创建对象的模板
一个代理类生成多个代理对象即可。
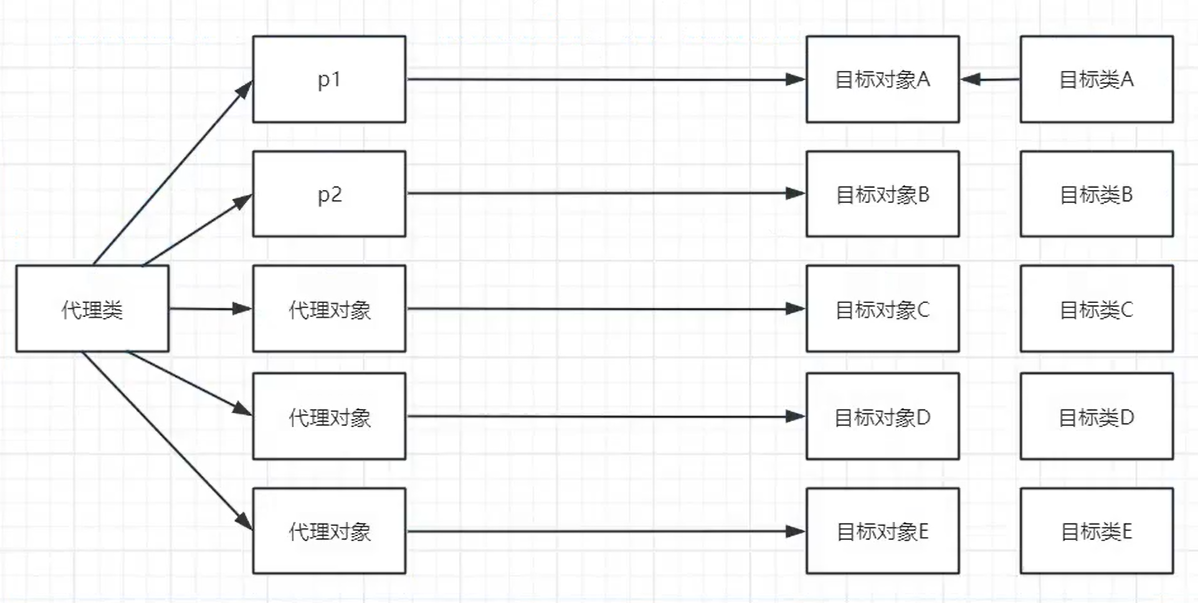
为了实现动态化,我们要想办法告诉代码想要代理的是什么。
如何实现动态代理
public interface ByClothes { //代理类和目标类都要继承该接口
//在接口当中定义需要代理的方法
public void clothes(String size) ;
}public interface ByShoes {
public void shoes(Integer size); //接口当中不需要具体实现
}public class ClothesFactory implements ByClothes{ //目标类 :制作衣服
public void clothes(String size) { //目标类的核心
System.out.println("已经为您定制好了一件大小为" + size + "的衣服");
}
}public class ShoesFactory implements ByShoes{
@Override
public void shoes(Integer size) {
System.out.println("已经为您定制了大小为" + size + "码的鞋子");
}
}import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
public class DTProxy implements InvocationHandler {
//被代理的对象
private Object factory;
public DTProxy(Object factory) {
this.factory = factory;
}
//为了能够动态的去实现新增的接口
//factory.getClass() ---------> 对象名.getClass() == class.forName("全类名") //生成代理对象
public Object getProxyInstance() {
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(factory.getClass().getClassLoader(), factory.getClass().getInterfaces(), this);
}
//我们会根据getProxyInstance()方法中所得到的接口信息,得到核心方法
//我们只需要用反射的方式执行这些方法
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
method.invoke(factory, args);
return null;
}
}public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ClothesFactory clothesFactory = new ClothesFactory();
DTProxy p1 = new DTProxy(clothesFactory);
ByClothes c1 = (ByClothes) p1.getProxyInstance();
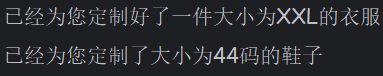
c1.clothes("XXL");
ShoesFactory shoesFactory = new ShoesFactory();
DTProxy p2 = new DTProxy(shoesFactory);
ByShoes c2 = (ByShoes) p2.getProxyInstance();
c2.shoes(44);
}
}
![[XYCTF]-PWN:Intermittent解析(pop栈内数据构造shellcode,自己编写shellcode)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/c68635b39b944ed6809fc731c39cf7ce.png)