在一个进程中,创建一个子线程。
主线程负责:向文件中写入数据
子线程负责:从文件中读取数据
要求使用线程的同步逻辑,保证一定在主线程向文件中写入数据成功之后,子线程才开始运行,去读取文件中的数据
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <semaphore.h>
#include <wait.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/sem.h>
#include <semaphore.h>
#include <sys/msg.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
#include <sys/un.h>
char* Getline(char* buf,int size);//写入终端函数
void* read_date(void* arg);//读取函数
int flag=1;
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
int wfd = open("./data.txt",O_WRONLY);
pthread_t id;
if(pthread_create(&id,0,read_date,0)!=0){
perror("pthread_create");
return 1;
}
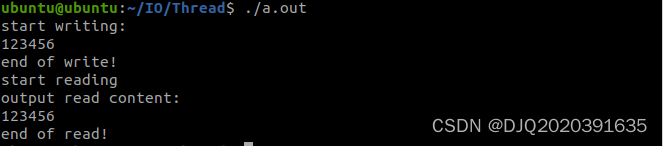
puts("start writing:");
char wr[128]={0};
Getline(wr,128);
while(1){
while(1){
if(flag==1){break;}
}
ssize_t wrtval=write(wfd,wr,128);
if(wrtval==sizeof(wr)){break;}
}
puts("end of write!");
close(wfd);
flag=0;
sleep(1);//给予全局变量flag一定缓冲时间
return 0;
}
void* read_date(void *arg){
while(1){
if(flag==0){break;}
}
puts("start reading");
char str[128]={0};
ssize_t rfd = open("./data.txt",O_RDONLY);
int rrtval=read(rfd,str,128);
puts("output read content:");
printf("%s\n",str);
close(rfd);
puts("end of read!");
//flag=1;
}
char* Getline(char* buf,int size){
fgets(buf,size,stdin);
int len=strlen(buf);
if(buf[len-1]=='\n'){
buf[len-1]=0;
}
}
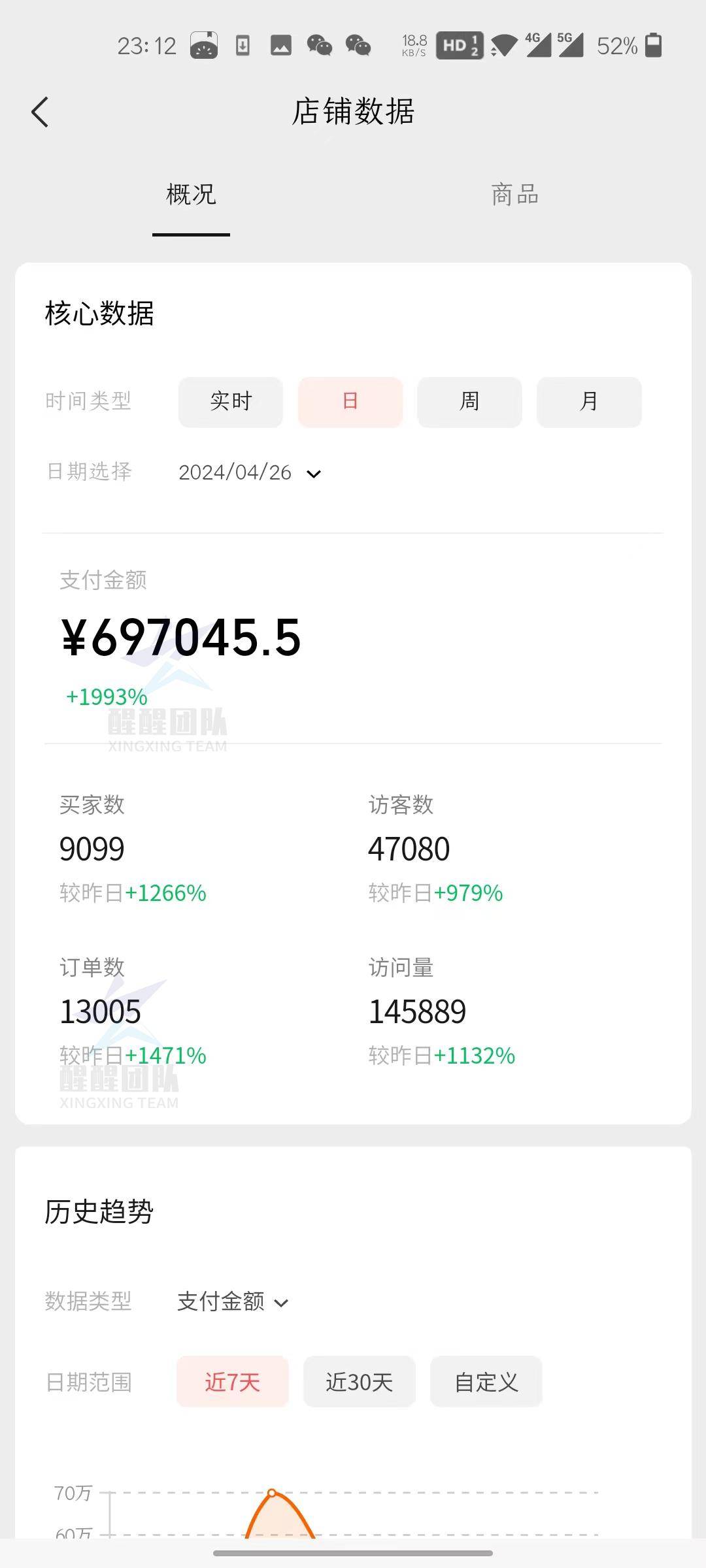
运行结果: