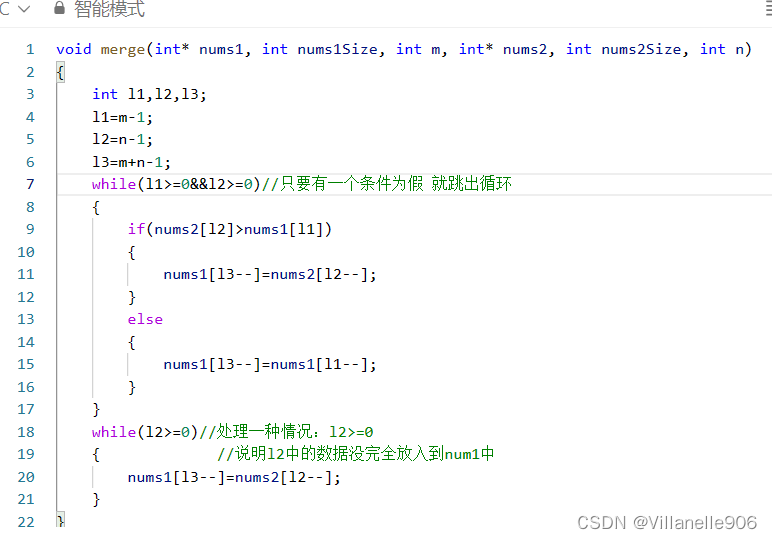
考研笔记整理,本篇作为树与二叉树的基本概念习题,供小伙伴们参考~🥝🥝
之前的博文链接在此:数据结构05:树与二叉树[C++]-CSDN博客~🥝🥝
- 第1版:王道书的课后习题~🧩🧩
编辑:梅头脑🌸
参考用书:王道考研《2025年 数据结构考研复习指导》
目录
🧵01 三叉树最小高度
🧵02 节点与度(一)
🧵03 节点与度(二)
🧵04 二叉树节点与度
🧵05 满二叉树节点数
🧵06 完全二叉树节点数
🧵07 满二叉树节点与编号
🧵08 顺序存储二叉树的公共祖先
🧵09 k二叉树节点
🔚结语
🧵01 三叉树最小高度
🧩题目
含有n个结点的三叉树的最小高度是多少?
📇解题思路
高度为1的三叉树有1个结点,等比数列求和公式为:1 = 1x(3^1-1)/(3-1) = 1
高度为2的三叉树有4个结点,等比数列求和公式为:1+3 = 1x(3^2-1)/(3-1) = 4
高度为3的三叉树有13个结点,等比数列求和公式为:1+3+9 = 1x(3^3-1)/(3-1) = 13
...
高度为n的三叉树有1+3+9+...+3^(n-1)个结点,等比数列求和公式为:n = 1+3+9+...+3^(h-1) = 1x(3^h-1)/(3-1) = (3^h-1)/2
移项:3^h = 2*n + 1,取对数:h = log3(2*n + 1),向上取整,即为最小高度。
🧵02 节点与度(一)
🧩题目
已知一棵度为4的树中,度为0,1,2,3 的结点数分别为14,4,3,2个,求该树的节点总数n和度为4的结点个数,并给出推导过程。
📇解题思路
节点数 = 分支数 + 1,因为没有指向根节点的分支;
节点数 = 14 + 4 + 3 + 2 = 23;
度为1、2、3的分支数 = 14*0 + 4*1 + 3*2 + 2*3 = 4 + 6 + 6 = 16;
度为4的分支数 = 总分支数 - 度为1、2、3的分支数 = 23 - 16 = 7;
度为4的结点数 = (度为4的分支数 + 1) / 4 = (7 + 1) / 4 = 2;
节点总数 = 度为1、2、3的结点数 + 度为4的结点数 = 14 + 4 + 3 + 2 + 2 = 25;
🧵03 节点与度(二)
🧩题目
已知一棵度为m的树中,有n1个度为1的节点,有n2个度为2的节点……有nm个度为m的节点,问该树有多少叶节点?
📇解题思路
节点数 = 分支数 + 1,因为没有指向根节点的分支;
节点数 = n0 + n1 + n2 + n3 + …… + nm;
分支数 = n0*0 + n1*1 + n2*2 + n3*3 + …… + nm*m;
代入等式,n0 + n1 + n2 + n3 + …… + nm = n0*0 + n1*1 + n2*2 + n3*3 + …… + nm*m + 1;
n0节点总数 = n1*(1-0) + n2*(2-1) + n3*(3-1) + …… + nm*(m-1) + 1 ;
🧵04 二叉树节点与度
🧩题目
在一棵完全二叉树中, 含有n0个叶结点, 当度为1的结点数为1时, 该树的高度是多少 ? 当度为1的结点数为0时,该树的高度是多少 ?
📇解题思路
二叉树的节点数n = n0 + n1 + n2,其中n0为叶子节点数,n1为度为1的节点数,n2为度为2的节点数;
二叉树的节点数n = 分支数 + 1 = n1 + 2 * n2 + 1;
联立以上两个等式,得到n0 = n2 + 1;
又因为完全二叉树的高度h = log2(n + 1),向上取整;
当度为1的结点数为1时,n = n0 + 1 + n0 - 1 = 2 * n0,所以 h = log2[2 * n0 + 1],向上取整;
当度为1的结点数为0时,n = n0 + n0 - 1 = 2 * n0 - 1,所以 h = log2[2 * n0],向上取整;
🧵05 满二叉树节点数
🧩题目
一棵有n个结点的满二叉树有多少个分支结点和多少个叶结点?该满二叉树的高度是多少?
📇解题思路
二叉树的节点数n = n0 + n1 + n2,其中n0为叶子节点数,n1为度为1的节点数,n2为度为2的节点数;
满二叉树不存在n1。又因为二叉树满足 n0 = n2 + 1;
所以,满二叉树的节点数n = 2 * n0 - 1 = 2 * n2 + 1; 节点 n0 = (n + 1) / 2, 节点 n2 = (n - 1) / 2;
满二叉树的节点n = 2^h - 1,高度h = log2(n + 1)。
🧵06 完全二叉树节点数
🧩题目
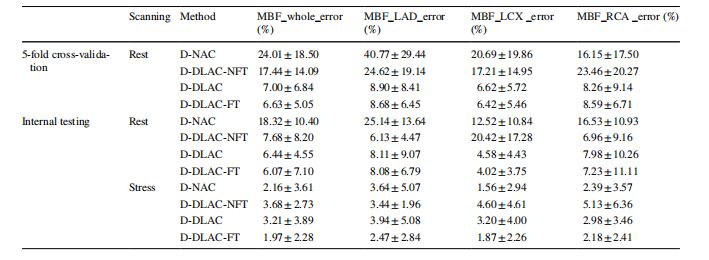
已知完全二叉树的第9层有 240个结点,则整个完全二叉树有多少个结点 ? 有多少个叶结点 ?
📇解题思路
完全二叉树的第n层最多有 2^(n-1) 个结点,第9层最多有 2^8 = 256 个结点;因此,考虑到完全二叉树的性质,240个节点均为叶结点;
但叶结点并非仅有第9层才有,第8层也有叶结点,第8层最多有 2^7 = 128 个结点,被第9层用掉 240 / 2 = 120个叶结点,还剩 8 个叶结点;整棵树共计248个叶结点,没有 n1 节点;
完全二叉树的结点数 n = n0 + n1 + n2 = n0 + (n0 - 1) = 2 * (240 + 8) - 1 = 495 个结点;
🧵07 满二叉树节点与编号
🧩题目
一棵高度为h的满 m又树有如下性质 : 根结点所在层次为第1层,第h层上的结点都是叶结点,其余各层上每个结点都有m棵非空子树,若按层次自顶向下,同一层自左向右
顺序从1开始对全部结点进行编号,试问 :
1)各层的结点个数是多少 ?
2)编号为i的结点的双亲结点(若存在)的编号是多少 ?
3)编号为i的结点的第k个孩子结点(若存在)的编号是多少 ?
4)编号为i的结点有右兄弟的条件是什么 ? 其右兄弟结点的编号是多少 ?
📇解题思路
1)等比数列,第i层的结点个数是 m^(i-1);
3)在三叉树中,节点2、3、4的双亲节点为1,节点5、6、7的双亲节点为2,即孩子节点 = (双亲节点i - 1) * 3 + 1 + k;同理,在m叉树中,第2、3、...m + 1的双亲节点为1,节点m + 2、m + 3、...2m + 1的双亲节点为2,即孩子节点 = (双亲节点i - 1) * m + 1 + k;
2)根据3)题,第1个孩子节点 = (双亲节点i - 1) * m + 2;因此,编号为i的结点的双亲结点的编号是 ((i - 2) / m) + 1,向下取整;
4)根据3)题,最后1个孩子节点i = (双亲节点 - 1) * m + 1;因此,编号为i的结点有右兄弟的条件是 (i - 1) % m != 0,其右兄弟结点的编号是 i + 1;
🧵08 顺序存储二叉树的公共祖先
🧩题目
已知一棵二叉树按顺序存储结构进行存储,设计一个算法,求编号分别为i和j的两个结点的最近的公共祖先结点的值。
📇友情配图
我们以下的代码以这棵树为例,为了方便求祖先,这里将数组编号与内容对应一致~
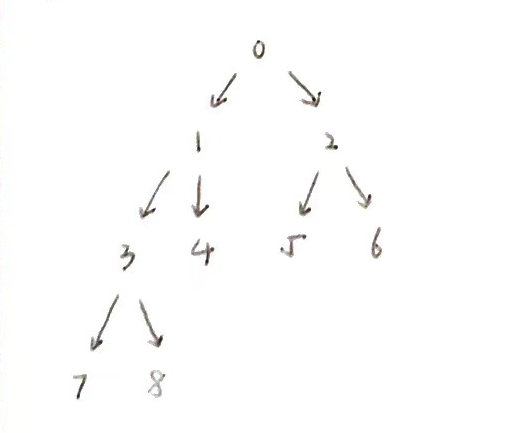
以下解法的核心思路都是建立在:
- 父节点序号 = (子节点序号 - 1)/ 2 的基础上,注意计算机运算会自动向下取整;
- 假设树中节点没有负值,返回-1表示该节点不存在。
📇解题思路1:使用2个栈完成遍历
使用两个栈,分别存储节点 1 和 2 的祖先。
然后从两个栈的起点开始同时遍历,如果节点相同,表明该节点是二者公共祖先;否则,该节点不满足题目要求,停止循环。
这个解题代码的空间复杂度和时间复杂度都很高,完全不推荐!
⌨️解题代码
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
// 二叉树的顺序存储结构
typedef struct {
vector<int> tree;
} SqBiTree;
int find_common_ancestor(SqBiTree T, int i, int j) {
if (i < 0 || i >= T.tree.size() || j == -1 || j >= T.tree.size()) {
return -1;
}
// 根据节点下标,确认祖先节点的位置,并将祖先全部入栈
int index1 = i;
int index2 = j;
stack<int> ancestor1;
stack<int> ancestor2;
do {
ancestor1.push(T.tree[index1]);
if (index1 > 1) { index1 = (index1 - 1) / 2; }
else { index1 = index1 - 1; }
} while (index1 >= 0);
do {
ancestor2.push(T.tree[index2]);
if (index2 > 1) index2 = (index2 - 1) / 2;
else { index2 = index2 - 1; }
} while (index2 >= 0);
// 从栈顶开始遍历,如果节点相同,继续往下遍历;如果节点不同,退出循环
int common_ancestor = -1;
while (!ancestor1.empty() && !ancestor2.empty()) {
if (ancestor1.top() != ancestor2.top()) { break; }
common_ancestor = ancestor1.top();
ancestor1.pop();
ancestor2.pop();
}
return common_ancestor;
}
int main() {
SqBiTree T = { {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8} };
int node1 = -1, node2 = -1, result = -1;
node1 = 7, node2 = 8;
result = find_common_ancestor(T, node1, node2);
cout << "节点 " << node1 << " 与 " << node2 << " 的公共祖先是节点 " << result << endl;
node1 = 5, node2 = 2;
result = find_common_ancestor(T, node1, node2);
cout << "节点 " << node1 << " 与 " << node2 << " 的公共祖先是节点 " << result << endl;
node1 = 3, node2 = 6;
result = find_common_ancestor(T, node1, node2);
cout << "节点 " << node1 << " 与 " << node2 << " 的公共祖先是节点 " << result << endl;
node1 = 9, node2 = 3;
result = find_common_ancestor(T, node1, node2);
cout << "节点 " << node1 << " 与 " << node2 << " 的公共祖先是节点 " << result << endl;
return 0;
}⌨️跑题代码
以下这个代码跑题了,传入的参数是节点值,而非节点编号,😣——
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
// 二叉树的顺序存储结构
typedef struct {
vector<int> tree;
} SqBiTree;
int find_common_ancestor(SqBiTree T, int node1, int node2) {
// 从数组中找到 node1, node2的下标
int locate1 = -1;
int locate2 = -1;
for(int i = 0; i < T.tree.size(); i++){
if (T.tree[i] == node1) { locate1 = i; }
if (T.tree[i] == node2) { locate2 = i; }
}
if (locate1 == -1 || locate2 == -1) { return -1; }
// 根据节点下标,确认祖先节点的位置,并将祖先全部入栈
int index1 = locate1;
int index2 = locate2;
stack<int> ancestor1;
stack<int> ancestor2;
do {
ancestor1.push(T.tree[index1]);
if (index1 > 1) { index1 = (index1 - 1) / 2; }
else {index1 = index1 - 1;}
} while (index1 >= 0);
do {
ancestor2.push(T.tree[index2]);
if (index2 > 1) index2 = (index2 - 1) / 2;
else { index2 = index2 - 1; }
} while (index2 >= 0);
// 从栈顶开始遍历,如果节点相同,继续往下遍历;如果节点不同,退出循环
int common_ancestor = -1;
while (!ancestor1.empty() && !ancestor2.empty()) {
if (ancestor1.top() != ancestor2.top()) { break; }
common_ancestor = ancestor1.top();
ancestor1.pop();
ancestor2.pop();
}
return common_ancestor;
}
int main() {
SqBiTree T = { {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8} };
int node1 = -1, node2 = -1, result = -1;
node1 = 7, node2 = 8;
result = find_common_ancestor(T, node1, node2);
cout << "节点 " << node1 << " 与 " << node2 << " 的公共祖先是节点 " << result << endl;
node1 = 5, node2 = 2;
result = find_common_ancestor(T, node1, node2);
cout << "节点 " << node1 << " 与 " << node2 << " 的公共祖先是节点 " << result << endl;
node1 = 3, node2 = 6;
result = find_common_ancestor(T, node1, node2);
cout << "节点 " << node1 << " 与 " << node2 << " 的公共祖先是节点 " << result << endl;
node1 = 9, node2 = 3;
result = find_common_ancestor(T, node1, node2);
cout << "节点 " << node1 << " 与 " << node2 << " 的公共祖先是节点 " << result << endl;
return 0;
}
📇解题思路2:使用2个循环完成遍历
从2个节点的位置开始向祖先遍历,每次循环时,较远的节点找到其祖先,然后判断2个节点的祖先此时是否相等~
相比上一个代码,代码的数量、遍历的次数和使用的空间都减少了很多~
⌨️解题代码
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
// 二叉树的顺序存储结构
typedef struct {
vector<int> tree;
} SqBiTree;
int find_common_ancestor(SqBiTree T, int i, int j) {
if (i < 0 || i >= T.tree.size() || j == -1 || j >= T.tree.size()) {
return -1;
}
// 根据节点下标,确认祖先节点的位置
while (i != j) {
if (i > j)
i = (i - 1) / 2;
else
j = (j - 1) / 2;
}
return T.tree[i];
}
int main() {
SqBiTree T = { {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8} };
int node1 = -1, node2 = -1, result = -1;
node1 = 7, node2 = 8;
result = find_common_ancestor(T, node1, node2);
cout << "节点 " << node1 << " 与 " << node2 << " 的公共祖先是节点 " << result << endl;
node1 = 5, node2 = 2;
result = find_common_ancestor(T, node1, node2);
cout << "节点 " << node1 << " 与 " << node2 << " 的公共祖先是节点 " << result << endl;
node1 = 3, node2 = 6;
result = find_common_ancestor(T, node1, node2);
cout << "节点 " << node1 << " 与 " << node2 << " 的公共祖先是节点 " << result << endl;
node1 = 9, node2 = 3;
result = find_common_ancestor(T, node1, node2);
cout << "节点 " << node1 << " 与 " << node2 << " 的公共祖先是节点 " << result << endl;
return 0;
}⌨️跑题代码
和上面的理由一样,以下这个代码跑题了,传入的参数是节点值,而非节点编号,😣——
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
// 二叉树的顺序存储结构
typedef struct {
vector<int> tree;
} SqBiTree;
int find_common_ancestor(SqBiTree T, int node1, int node2) {
// 从数组中找到 node1, node2的下标
int locate1 = -1;
int locate2 = -1;
for(int i = 0; i < T.tree.size(); i++){
if (T.tree[i] == node1) { locate1 = i; }
if (T.tree[i] == node2) { locate2 = i; }
}
if (locate1 == -1 || locate2 == -1) { return -1; }
// 根据节点下标,确认祖先节点的位置
while (locate1 != locate2) {
if (locate1 > locate2)
locate1 = (locate1 - 1) / 2;
else
locate2 = (locate2 - 1) / 2;
}
return T.tree[locate1];
}
int main() {
SqBiTree T = { {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8} };
int node1 = -1, node2 = -1, result = -1;
node1 = 7, node2 = 8;
result = find_common_ancestor(T, node1, node2);
cout << "节点 " << node1 << " 与 " << node2 << " 的公共祖先是节点 " << result << endl;
node1 = 5, node2 = 2;
result = find_common_ancestor(T, node1, node2);
cout << "节点 " << node1 << " 与 " << node2 << " 的公共祖先是节点 " << result << endl;
node1 = 3, node2 = 6;
result = find_common_ancestor(T, node1, node2);
cout << "节点 " << node1 << " 与 " << node2 << " 的公共祖先是节点 " << result << endl;
node1 = 9, node2 = 3;
result = find_common_ancestor(T, node1, node2);
cout << "节点 " << node1 << " 与 " << node2 << " 的公共祖先是节点 " << result << endl;
return 0;
}
🧵09 k二叉树节点
🧩题目
【2016统考真题】若一棵非空k(k >= 2)又树T中的每个非叶结点都有k个孩子,则称I为正则k叉树。请回答下列问题并给出推导过程。
1)若T有m个非叶结点,则T中的叶结点有多少个 ?
2)若T的高度为h(单结点的树h = 1),则T的结点数最多为多少个 ? 最少为多少个 ?
📇解题思路
1) 最少是除了根节点层与底层外,每层有1个节点有k个孩子,其它 k-1 个节点是叶结点:n = m + n0 = 1 + k * m, n0 = (k - 1)*m + 1;
2) 最多是满二叉树:1 + k + k^2 + ... = (k^(h - 1) - 1)(k - 1); 最少是1 + k + k + ... = k * (h - 1) + 1;
🔚结语
博文到此结束,写得模糊或者有误之处,欢迎小伙伴留言讨论与批评,督促博主优化内容{例如有错误、难理解、不简洁、缺功能}等,博主会顶锅前来修改~😶🌫️
我是梅头脑,本片博文若有帮助,欢迎小伙伴动动可爱的小手默默给个赞支持一下,收到点赞的话,博主肝文的动力++~🌟🌟
同系列的博文:🌸数据结构_梅头脑_的博客-CSDN博客
同博主的博文:🌸随笔03 笔记整理-CSDN博客