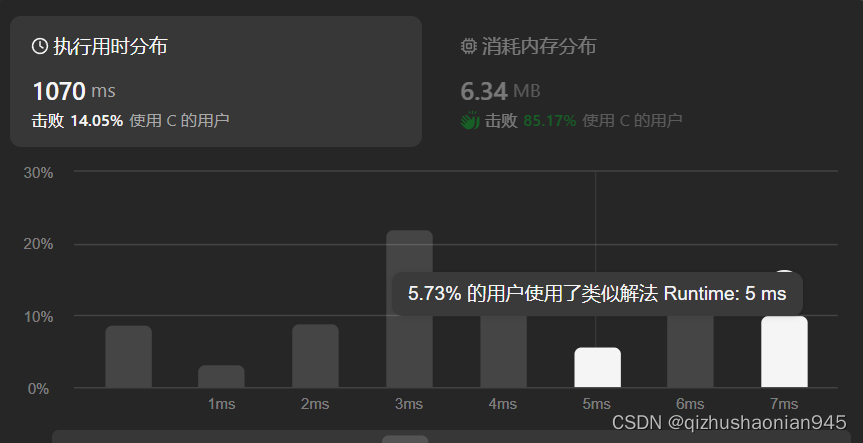
在下图中的0,3,1,2位置如何变换成0,1,2,3
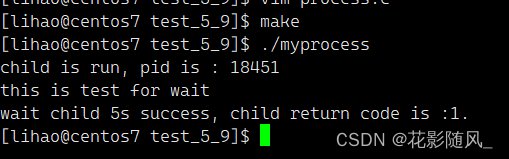
先显示结果:

变换之后图:

这边提供两种解决方案:
第一种:将坐标值相加求和,采用冒泡排序实现从小到大排序,此时能确定两点位置,一是0二是3位置,对于副对角线上12两点,需要进一步判断,这边图片明显点2位置的x值距离0点相对1点来说更近,因此可以判断出1,2点。从而实现。
代码实现:
for (int j = 0; j < sumPoints.size(); j++) {
for (int i = 1; i < sumPoints.size(); i++) {
if (sumPoints[j] > sumPoints[i]) {
newPoints = points[i];
points[i] = points[j];
points[j] = newPoints;
}
}
}
if (points[1].x - points[0].x < points[2].x - points[0].x) {
Point p;
p = points[1];
points[1] = points[2];
points[2] = p;
}第二种:采用min_elemen(),和max_element()两个函数,首先两个函数的理解进行解释:
min_elemen(数组开始位置,数组结束位置)函数返回的最小值的指针,这个要注意。
int a[] = { 42, 13, 12, 68, 25, 6, 5, 32 };
int len = sizeof(a) / sizeof(int);
auto s1 = max_element(a, a + len);
auto s2 = min_element(a, a + len);
cout << s1 << endl; //指向值最大的元素的地址
cout << s2 << endl; //指向值最小的元素的地址
cout << *s1 << endl; //值最大的元素
cout << *s2 << endl; //值最小的元素
cout << s1 - a << endl; //值最大的元素的索引
cout << s2 - a << endl; //值最小的元素的索引因此就有一种思想:对于0,3点,xy相加的值的值分别最小最大,而对于1,2两点,xy相减值分别最小最大。只需把角标提取,放入新的点集,继而读出即可。
代码实现:
for (int i = 0; i < points.size(); i++) {
cout << points[i].x << ", " << points[i].y << endl;
sumPoints.push_back(points[i].x + points[i].y);
cout << sumPoints[i] << endl;
}
for (int i = 0; i < points.size(); i++) {
subPoints.push_back(points[i].x - points[i].y);
cout << subPoints[i] << endl;
} newPoints.push_back(points[min_element(sumPoints.begin(),sumPoints.end()) - sumPoints.begin()]);
newPoints.push_back(points[max_element(subPoints.begin(), subPoints.end()) - subPoints.begin()]);
newPoints.push_back(points[min_element(subPoints.begin(), subPoints.end()) - subPoints.begin()]);
newPoints.push_back(points[max_element(sumPoints.begin(), sumPoints.end()) - sumPoints.begin()]);



![[C++核心编程-05]----C++类和对象之对象的初始化和清理](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/8c950650f9cf4766998c55b1c4c52e3a.png)


![【Linux】-Linux用户和权限[3]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/7c50269125da44a2a0a53ce32467b50f.png)