一.线程
1.线程的概念
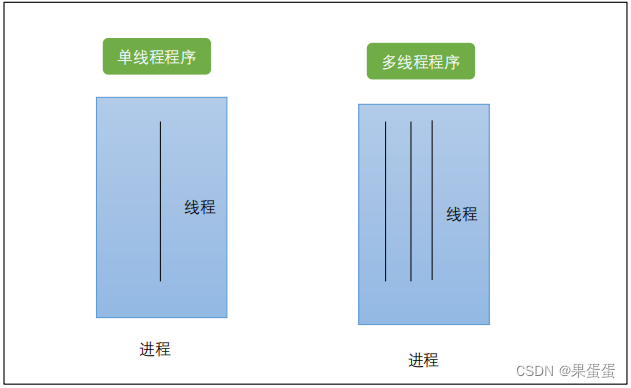
线程是进程内部的一条执行序列或执行路径,一个进程可以包含多条线程。
2.线程的三种实现方式
◼ 内核级线程:由内核创建,创建开销大,内核能感知到线程的存在
◼ 用户级线程:线程的创建有用户空间的线程库完成;内核不知道线程的存在
◼
组合级线程:兼顾以上两者的优点,
区别:两个处理器,用户级线程在内核上无法并行处理,只能交替执行;内核级可以同时执行;组合技在不同的空间采用不同的处理方式
线程同步的方法:信号量,互斥锁,条件变量,读写锁
Ps -elf 查看线程ID

Linux 中线程的实现:
Linux 实现线程的机制非常独特。从内核的角度来说,它并没有线程这个概念。Linux 把
所有的线程都当做进程来实现。内核并没有准备特别的调度算法或是定义特别的数据结构来
表征线程。相反,线程仅仅被视为一个与其他进程共享某些资源的进程。每个线程都拥有唯
一隶属于自己的 task_struct,所以在内核中,它看起来就像是一个普通的进程(只是线程和
其他一些进程共享某些资源,如地址空间)。
3.进程与线程的区别
◼ 进程是资源分配的最小单位,线程是 CPU 调度的最小单位
◼ 进程有自己的独立地址空间,线程共享进程中的地址空间
◼ 进程的创建消耗资源大,线程的创建相对较小
◼ 进程的切换开销大,线程的切换开销相对较小
二.线程使用
1.线程库
#include <pthread.h>
/*
pthread_create()用于创建线程
thread: 接收创建的线程的 ID
attr: 指定线程的属性
start_routine: 指定线程函数
arg: 给线程函数传递的参数
成功返回 0, 失败返回错误码
*/
int pthread_create(pthread_t *thread, const pthread_attr_t *attr,
void *(*start_routine) (void *), void *arg);13.
/*
pthread_exit()退出线程
retval:指定退出信息
*/
int pthread_exit(void *retval);
/*
pthread_join()等待 thread 指定的线程退出,线程未退出时,该方法阻塞
retval:接收 thread 线程退出时,指定的退出信息
*/
int pthread_join(pthread_t thread, void **retval);多线程代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <pthread.h>
void * pthread_fun(void *arg)
{
int i = 0;
for(; i < 5; ++i)
{
sleep(1);
printf("fun thread running\n");
}
pthread_exit("fun over");
}
int main()
{
pthread_t tid;
int res = pthread_create(&tid, NULL, pthread_fun, NULL);
assert(res == 0);
int i = 0;
for(; i < 5; ++i)
{
sleep(1);
printf("main thread running\n");
}
char *s = NULL;
pthread_join(tid, (void **)&s);
printf("s = %s\n", s);
exit(0);
}三.线程同步
线程同步指的是当一个线程在对某个临界资源进行操作时,其他线程都不可以对这个资
源进行操作,直到该线程完成操作,其他线程才能操作,也就是协同步调,让线程按预定的
先后次序进行运行。
线程同步的方法有四种:互斥锁、信号量、条件变量、读写锁。
1.互斥锁
#include <pthread.h>
int pthread_mutex_init(pthread_mutex_t *mutex, pthread_mutexattr_t *attr);//初始化锁
int pthread_mutex_lock(pthread_mutex_t *mutex);//上锁,其他线程无法使用
int pthread_mutex_unlock(pthread_mutex_t *mutex);//开锁
int pthread_mutex_destroy(pthread_mutex_t *mutex);//销毁锁
为什么线程需要同步和互斥的操作?
因为线程引入共享了进程的地址空间,导致了一个线程操作数据时候,极其容易影响到其他线程的情况;对其他线程造成不可控因素,或引起异常,逻辑结果不正确的情况;这也是线程不安全的原因!
因为线程引入共享了进程的地址空间,导致了一个线程操作数据时候,极其容易影响到其他线程的情况;对其他线程造成不可控因素,或引起异常,逻辑结果不正确的情况;这也是线程不安全的原因!
重点概念:

示例代码如下,主线程和函数线程模拟访问打印机,主线程输出第一个字符‘a’表示开
始使用打印机,输出第二个字符‘a’表示结束使用,函数线程操作与主线程相同。(由于打
印机同一时刻只能被一个线程使用,所以输出结果不应该出现 abab)
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<pthread.h>
#include<semaphore.h>
//sem_t sem;
pthread_mutex_t mutex;
void* fun1(void* arg)
{
for(int i=0;i<5;i++)
{
//sem_wait(&sem);
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
printf("A");
fflush(stdout);
int n=rand()%3;
sleep(n);
printf("A");
fflush(stdout);
//sem_post(&sem);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
n=rand()%3;
sleep(n);
}
}
void* fun2(void* arg)
{
for(int i=0;i<5;i++)
{
//sem_wait(&sem);
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
printf("B");
fflush(stdout);
int n=rand()%3;
sleep(n);
printf("B");
fflush(stdout);
//sem_post(&sem);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
n=rand()%3;
sleep(n);
}
}
int main()
{
//sem_init(&sem,0,1);
pthread_mutex_init(&mutex,NULL);
pthread_t id1,id2;
pthread_create(&id1,NULL,fun1,NULL);
pthread_create(&id2,NULL,fun2,NULL);
pthread_join(id1,NULL);
pthread_join(id2,NULL);
//sem_destroy(&sem);
pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex);
exit(0);
}
2.信号量
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <semaphore.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
char buff[128] = {0};
sem_t sem1;
sem_t sem2;
void* PthreadFun(void *arg)
{
int fd = open("a.txt", O_RDWR | O_CREAT, 0664);
assert(fd != -1);
//函数线程完成将用户输入的数据存储到文件中
while(1)
{
sem_wait(&sem2);
if(strncmp(buff, "end", 3) == 0)
{
break;
}
write(fd, buff, strlen(buff));
memset(buff, 0, 128);
sem_post(&sem1);
}
sem_destroy(&sem1);
sem_destroy(&sem2);
}
int main()
{
sem_init(&sem1, 0, 1);
sem_init(&sem2, 0, 0);
pthread_t id;
int res = pthread_create(&id, NULL, PthreadFun, NULL);
assert(res == 0);
//主线程完成获取用户数据的数据,并存储在全局数组 buff 中
while(1)
{
sem_wait(&sem1);
printf("please input data: ");
fflush(stdout);
fgets(buff, 128, stdin);
buff[strlen(buff) - 1] = 0;
sem_post(&sem2);
if(strncmp(buff, "end", 3) == 0)
{
break;
}
}
pthread_exit(NULL);
}3.条件变量
条件变量是利用线程间共享的全局变量进行同步的一种机制。
主要包括两个动作:一个线程等待”条件变量的条件成立”而挂起;另一个线程使”条件成立”(给出条件成立信号)。
为了防止竞争,条件变量的使用总是和一个互斥锁结合在一起。
条件变量类型为 pthread_cond_t。
条件变量接口
pthread_cond_init() //初始化
pthread_cond_wait() //等待将信息存入并等待达到唤醒条件
pthread_cond_signal() //只唤醒一个
pthread_cond_broadcast() //唤醒所以有的线程条件变量有什么用
使用条件变量可以以原子方式阻塞线程,直到某个特定条件为真为止。条件变量始终与互斥锁一起使用,对条件的测试是在互斥锁(互斥)的保护下进行的。
如果条件为假,线程通常会基于条件变量阻塞,并以原子方式释放等待条件变化的互斥锁。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <pthread.h>
pthread_cond_t cond;
pthread_mutex_t mutex;
void* funa(void* arg)
{
char* s =(char*)arg;
while(1)
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
pthread_cond_wait(&cond,&mutex);//添加到条件变量的等待队列,阻塞
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
if(strncmp(s,"end",3)==0)
{
break;
}
printf("funa:%s\n",s);
}
}
void* funb(void* arg)
{
char* s =(char*)arg;
while(1)
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
pthread_cond_wait(&cond,&mutex);//添加到条件变量的等待队列,阻塞
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
if(strncmp(s,"end",3)==0)
{
break;
}
printf("funb:%s\n",s);
}
}
int main()
{
pthread_mutex_init(&mutex,NULL);
pthread_cond_init(&cond,NULL);
pthread_t id1,id2;
char buff[128]={0};
pthread_create(&id1,NULL,funa,buff);
pthread_create(&id2,NULL,funb,buff);
while(1)
{
char tmp[128]={0};
fgets(tmp,128,stdin);
strcpy(buff,tmp);
if(strncmp(tmp,"end",3)==0)
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
pthread_cond_broadcast(&cond);//唤醒所有线程
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
break;
}
else
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
pthread_cond_signal(&cond);//唤醒一个
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
}
}
pthread_join(id1,NULL);
pthread_join(id2,NULL);
pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex);
pthread_cond_destroy(&cond);
exit(0);
}
4.读写锁
读写锁:是一对锁,分为读锁和写锁,允许多个线程同时获取读写锁,但再通过一时间,只允许一个线程获得写锁,或者可以由多个线程获得读锁
接口:
#include <pthread.h>
int pthread_rwlock_init(pthread_rwlock_t *rwlock, pthread_rwlockattr_t *attr);
int pthread_rwlock_rdlock(pthread_rwlock_t *rwlock);
int pthread_rwlock_wrlock(pthread_rwlock_t *rwlock);
int pthread_rwlock_unlock(pthread_rwlock_t *rwlock);
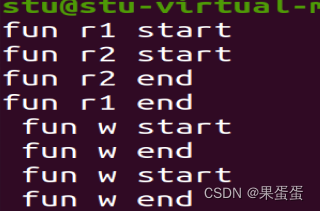
int pthread_rwlock_destroy(pthread_rwlock_t *rwlock);代码示例
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<pthread.h>
pthread_rwlock_t lock;
void* fun_r1(void* arg)
{
for(int i=0;i<10;i++)
{
pthread_rwlock_rdlock(&lock);
printf("fun r1 start\n");
int n=rand()%3;
sleep(n);
printf("fun r1 end\n");
pthread_rwlock_unlock(&lock);
n=rand()%3;
sleep(n);
}
}
void* fun_r2(void* arg)
{
for(int i=0;i<10;i++)
{
pthread_rwlock_rdlock(&lock);
printf("fun r2 start\n");
int n=rand()%3;
sleep(n);
printf("fun r2 end\n");
pthread_rwlock_unlock(&lock);
n=rand()%3;
sleep(n);
}
}
void* fun_w(void* arg)
{
for(int i=0;i<10;i++)
{
pthread_rwlock_wrlock(&lock);
printf(" fun w start\n");
int n=rand()%3;
sleep(n);
printf(" fun w end\n");
pthread_rwlock_wrlock(&lock);
n = rand()%3;
sleep(n);
}
}
int main()
{
pthread_rwlock_init(&lock,NULL);
pthread_t id1,id2,id3;
pthread_create(&id1,NULL,fun_r1,NULL);
pthread_create(&id2,NULL,fun_r2,NULL);
pthread_create(&id3,NULL,fun_w,NULL);
pthread_join(id1,NULL);
pthread_join(id2,NULL);
pthread_join(id3,NULL);
pthread_rwlock_destroy(&lock);
exit(0);
}

![每日一题 第九十七期 洛谷 [NOIP2000 提高组] 方格取数](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/e0eec6693b9f4c9889c2b0ebf9f85a99.png#pic_center)