BERT
Bert (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers)预训练模型是 Google 2018开源的自然语言模型,主要有以下特点。
- 像它名字一样,BERT最显著的特点是其能够为文本中的每个标记考虑双向上下文。与传统的基于先前标记预测标记的语言模型(从左到右或单向模型)不同,它查看前后标记(一次查看整个序列),以理解和预测单词的上下文。
- 采用了 Transformer 架构,通过自注意力机制关注自身与句子中其他单词的关系。
- 通过 MLM 和 NSP 两个任务进行预训练,MLM 在预训练期间,随机遮蔽句子的词,模型的目标是仅基于其上下文预测掩蔽字的原始值。在NSP中,模型给出句子对,并必须预测第二句是否是原始文档中的后续句子。
- BERT 可以添加一个额外的输出层进行微调,而无需进行大量的任务特定修改。这包括问答、情感分析和语言推理等任务。微调步骤略微调整预训练参数,以专门为手头的特定任务定制模型,利用在预训练期间学习到的丰富表示。
本文通过微调 BERT 实现情感分析。
Transformer 模型中的QKV
开始代码之前,再回顾一下 Q、K、V,这是三个 Tansformer 中最重要的公式,
查询(Q) Q 在自注意力层中代表当前词,Q 帮助模型理解在特定上下文中哪些信息是重要的,可以理解为:问那一个词在句子中是需要关注的。
键(K) 用于与Q(查询)进行匹配,键的作用是作为一种标识,最终生成相关性得分。
值(V) 表示与每个Token关联的实际内容,当 Q 对应的Token被认为是重要的,相应的值就会在输出中获得更多的关注,V决定了自注意力的输出。
公式如下:
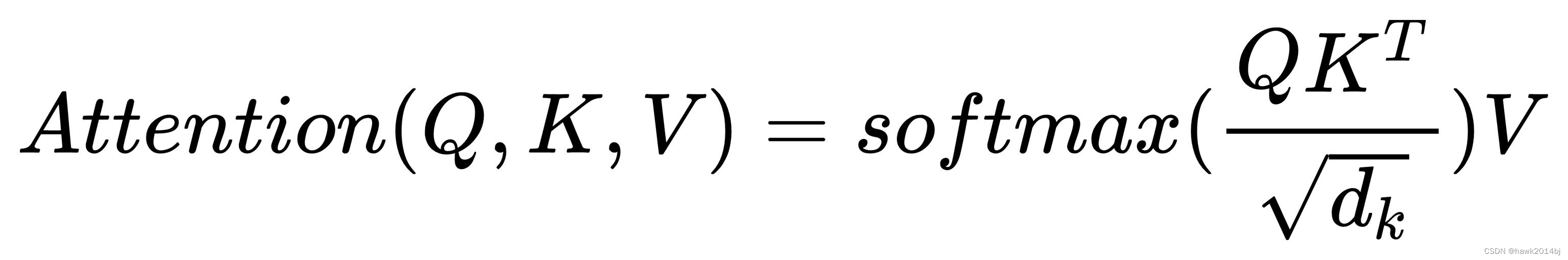
- 首先计算注意力得分:Q和 K 之间的点积,得到注意力得分。这里可以简单理解一下,两个向量的乘法,也是两个向量的内积,内积越大,说明其2个向量相似度越高。
- Softmax函数:将这些得分通过softmax函数进行标准化,这样得分就转换为概率形式,表明每个值(V)的相对重要性(权重)。
- 最后,模型将这些标准化的得分与对应的值(V)相乘,加权输出。
Pytorch 实现情感分析
安装依赖
pip install addict
数据准备
import random
import time
import numpy as np
from tqdm import tqdm
import torch
from torch import nn
import torch.optim as optim
import torchtext
# 设定随机数的种子,
torch.manual_seed(1234)
np.random.seed(1234)
random.seed(1234)
#生成预处理和单词分割的函数
import re
import string
from utils.bert import BertTokenizer
#来自文件夹“utils”的bert.py
def preprocessing_text(text):
'''IMDb预处理'''
# 删除换行代码
text = re.sub('<br />', '', text)
#将逗号和句号以外的标点符号全部替换成空格
for p in string.punctuation:
if (p == ".") or (p == ","):
continue
else:
text = text.replace(p, " ")
#在句号和逗号前后插入空格
text = text.replace(".", " . ")
text = text.replace(",", " , ")
return text
#将逗号和句号以外的标点符号全部替换成空格
tokenizer_bert = BertTokenizer(
vocab_file="./vocab/bert-base-uncased-vocab.txt", do_lower_case=True)
#定义同时负责预处理和分词处理的函数
#指定分词处理的函数,注意不要使用tokenizer_bert,而应指定使tokenizer_bert.tokenize
def tokenizer_with_preprocessing(text, tokenizer=tokenizer_bert.tokenize):
text = preprocessing_text(text)
ret = tokenizer(text) # tokenizer_bert
return ret
#定义在读入数据时,对读到的内容应做的处理
max_length = 256
TEXT = torchtext.data.Field(sequential=True, tokenize=tokenizer_with_preprocessing, use_vocab=True,
lower=True, include_lengths=True, batch_first=True, fix_length=max_length, init_token="[CLS]", eos_token="[SEP]", pad_token='[PAD]', unk_token='[UNK]')
LABEL = torchtext.data.Field(sequential=False, use_vocab=False)
# (注释):再次确认各个参数
# sequential: 数据长度是否可变?由于文章长度是不固定的,因此指定True,标签则指定False
# tokenize: 用于指定读入文章时所需执行的预处理和分词处理函数
# use_vocab:指定是否将单词添加到词汇表中
# lower:指定是否将英文字母转换为小写字母
# include_length: 指定是否返回文章的单词数量
# batch_first:指定是否在开头处生成批次的维度信息
# fix_length::指定是否确保所有文章都为相同长度,长度不足的填充处理
# init_token, eos_token, pad_token, unk_token:指定使用什么单词来表示、文章开头、文章结尾、填充和未知单词
#从data文件夹中读取各个tsv文件
#使用BERT进行处理,执行时间大约为10分钟
train_val_ds, test_ds = torchtext.data.TabularDataset.splits(
path='./data/', train='IMDb_train.tsv',
test='IMDb_test.tsv', format='tsv',
fields=[('Text', TEXT), ('Label', LABEL)])
#使用torchtext.data.Dataset的split函数将数据划分为训练数据和验证数据
train_ds, val_ds = train_val_ds.split(
split_ratio=0.8, random_state=random.seed(1234))
#BERT是使用BERT掌握的所有单词来创建BertEmbedding模块的,因此将使用全部单词作为词汇表
# 为此不会使用训练数据来生成词汇表
# #首先为BERT准备字典型变量
from utils.bert import BertTokenizer, load_vocab
vocab_bert, ids_to_tokens_bert = load_vocab(
vocab_file="./vocab/bert-base-uncased-vocab.txt")
#虽然很想写成TEXT.vocab.stoi= vocab_bert (stoi意为string_to_ID,将单词转换为 ID 的字典的形式
#但是如果不执行一次bulild_vocab,TEXT对象就不会初始化vocab的成员变量
#程序会产生“'Field' object has no attribute 'vocab'”这一错误信息
#首先调用build_vocab创建词汇表,然后替换BERT的词汇表
TEXT.build_vocab(train_ds, min_freq=1)
TEXT.vocab.stoi = vocab_bert
#创建DataLoader(在torchtext中被称为iterater)
batch_size = 32 #BERT中经常使用16和32
train_dl = torchtext.data.Iterator(
train_ds, batch_size=batch_size, train=True)
val_dl = torchtext.data.Iterator(
val_ds, batch_size=batch_size, train=False, sort=False)
test_dl = torchtext.data.Iterator(
test_ds, batch_size=batch_size, train=False, sort=False)
#集中保存到字典对象中
dataloaders_dict = {"train": train_dl, "val": val_dl}
#确认执行结果,使用验证数据的数据集进行确认
batch = next(iter(val_dl))
print(batch.Text)
print(batch.Label)
#确认小批次中第一句话的内容
text_minibatch_1 = (batch.Text[0][1]).numpy()
#将ID还原成单词
text = tokenizer_bert.convert_ids_to_tokens(text_minibatch_1)
print(text)
准备模型
class BertForIMDb(nn.Module):
'''在BERT模型中增加了IMDb的正面/负面分析功能的模型'''
def __init__(self, net_bert):
super(BertForIMDb, self).__init__()
#BERT模块
self.bert = net_bert # BERTモデル
#在head中添加正面 / 负面预测
#输入是BERT输出的特征量的维度,输出是正面和负面这两种
self.cls = nn.Linear(in_features=768, out_features=2)
#权重初始化处理
nn.init.normal_(self.cls.weight, std=0.02)
nn.init.normal_(self.cls.bias, 0)
def forward(self, input_ids, token_type_ids=None, attention_mask=None, output_all_encoded_layers=False, attention_show_flg=False):
'''
input_ids: 形状为[batch_size, sequence_length]的文章的单词ID序列
token_type_ids:形状为[batch_size, sequence_length],表示每个单词是属于第一句还是第二句的id
attention_mask:与Transformer的掩码作用相同的掩码
output_all_encoded_layers:用于指定是返回全部12个Transformer的列表还是只返回最后一项的标识
attention_show_flg:指定是否返回Self−Attention的权重的标识
'''
#BERT的基础模型部分的正向传播
#进行正向传播处理る
if attention_show_flg == True:
'''指定attention_show时,也同时返回attention_probs'''
encoded_layers, pooled_output, attention_probs = self.bert(
input_ids, token_type_ids, attention_mask, output_all_encoded_layers, attention_show_flg)
elif attention_show_flg == False:
encoded_layers, pooled_output = self.bert(
input_ids, token_type_ids, attention_mask, output_all_encoded_layers, attention_show_flg)
#使用输入文章的第一个单词[CLS]的特征量进行正面/负面分类处理
vec_0 = encoded_layers[:, 0, :]
vec_0 = vec_0.view(-1, 768) # 将size转换为batch size、hidden size
out = self.cls(vec_0)
#指定attention_show时,也同时返回attention_probs(位于最后一位的)
if attention_show_flg == True:
return out, attention_probs
elif attention_show_flg == False:
return out
#网络设置完毕
net = BertForIMDb(net_bert)
#设置为训练模式
net.train()
print('网络设置完毕')
#只处理位于最后的BertLayer模块的梯度计算和添加的分类适配器
#1.首先,将所有的梯度计算设置为False
for name, param in net.named_parameters():
param.requires_grad = False
#2.设置对位于最后的BertLayer模块进行梯度计算
for name, param in net.bert.encoder.layer[-1].named_parameters():
param.requires_grad = True
#3.设置打开识别器的梯度计算
for name, param in net.cls.named_parameters():
param.requires_grad = True
#设置最优化算法
#BERT的原有部分作为精调
optimizer = optim.Adam([
{'params': net.bert.encoder.layer[-1].parameters(), 'lr': 5e-5},
{'params': net.cls.parameters(), 'lr': 5e-5}
], betas=(0.9, 0.999))
#设置损失函数
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
# nn.LogSoftmax()を計算してからnn.NLLLoss(negative log likelihood loss)を計算
#创建用于训练模型的函数
def train_model(net, dataloaders_dict, criterion, optimizer, num_epochs):
#确认GPU是否可用
device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
print("使用的设备:", device)
print('-----start-------')
#将网络载入GPU中
net.to(device)
#如果网络结构比较固定,则开启硬件加速
torch.backends.cudnn.benchmark = True
#小批次的尺寸
batch_size = dataloaders_dict["train"].batch_size
#epoch的循环
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
#每轮epoch的训练和验证循环
for phase in ['train', 'val']:
if phase == 'train':
net.train() #将模型设置为训练模式
else:
net.eval() #将模型设置为验证模式
epoch_loss = 0.0 #epoch的损失总和
epoch_corrects = 0 #epoch的正确答案数量
iteration = 1
#保存开始时间
t_epoch_start = time.time()
t_iter_start = time.time()
#以minibatch为单位从数据加载器中读取数据的循环
for batch in (dataloaders_dict[phase]):
#batch是Text和Lable的字典型变量
#如果能使用GPU,则将数据送入GPU中
inputs = batch.Text[0].to(device) # 文章
labels = batch.Label.to(device) # 标签
#初始化optimizer
optimizer.zero_grad()
#计算正向传播
with torch.set_grad_enabled(phase == 'train'):
#输入BertForIMDb中
outputs = net(inputs, token_type_ids=None, attention_mask=None,
output_all_encoded_layers=False, attention_show_flg=False)
loss = criterion(outputs, labels) #计算损失
_, preds = torch.max(outputs, 1) #对标签进行预测
#训练时执行反向传播
if phase == 'train':
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
if (iteration % 10 == 0): #每10个iter显示一次loss
t_iter_finish = time.time()
duration = t_iter_finish - t_iter_start
acc = (torch.sum(preds == labels.data)
).double()/batch_size
print('迭代 {} || Loss: {:.4f} || 10iter: {:.4f} sec. ||本次迭代的准确率:{}'.format(
iteration, loss.item(), duration, acc))
t_iter_start = time.time()
iteration += 1
#更新损失和正确答案数量的合计值
epoch_loss += loss.item() * batch_size
epoch_corrects += torch.sum(preds == labels.data)
#每轮epoch的loss和准确率
t_epoch_finish = time.time()
epoch_loss = epoch_loss / len(dataloaders_dict[phase].dataset)
epoch_acc = epoch_corrects.double(
) / len(dataloaders_dict[phase].dataset)
print('Epoch {}/{} | {:^5} | Loss: {:.4f} Acc: {:.4f}'.format(epoch+1, num_epochs,
phase, epoch_loss, epoch_acc))
t_epoch_start = time.time()
return net
开始训练
#执行学习和验证处理
num_epochs = 2
net_trained = train_model(net, dataloaders_dict,
criterion, optimizer, num_epochs=num_epochs)
#对完成学习的网络参数进行保存
save_path = './weights/bert_fine_tuning_IMDb.pth'
torch.save(net_trained.state_dict(), save_path)
测试
#对使用测试数据时模型的准确率进行求解
device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
net_trained.eval() #将模型设置为验证模式
net_trained.to(device) #如果GPU可用,则将数据送入GPU中
#记录epoch的正确答案数量的变量
epoch_corrects = 0
for batch in tqdm(test_dl): #test数据的DataLoader
#test数据的DataLoader
#如果GPU可用,则将数据送入GPU中
device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
inputs = batch.Text[0].to(device) # 文章
labels = batch.Label.to(device) #标签
#计算正向传播
with torch.set_grad_enabled(False):
#输入BertForIMDb中
outputs = net_trained(inputs, token_type_ids=None, attention_mask=None,
output_all_encoded_layers=False, attention_show_flg=False)
loss = criterion(outputs, labels) #计算损失
_, preds = torch.max(outputs, 1) #进行标签预测
epoch_corrects += torch.sum(preds == labels.data) #更新正确答案数量的合计
#准确率
epoch_acc = epoch_corrects.double() / len(test_dl.dataset)
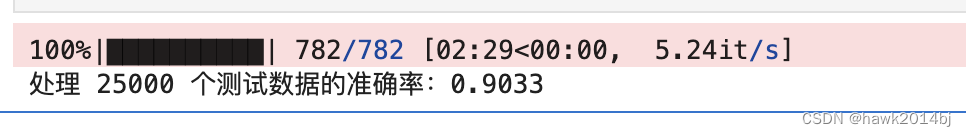
print('处理 {} 个测试数据的准确率:{:.4f}'.format(len(test_dl.dataset), epoch_acc))
正确率达到 90%
Bert 模型比之前的 Transformer 模型实现的情感分析效果要好,但是BERT 只是实现了 Encoder Layer,如果需要做更复杂的任务还需要 Decoder Layer,例如翻译,对话等等。