1. 用队列实现栈。
225. 用队列实现栈 - 力扣(LeetCode)
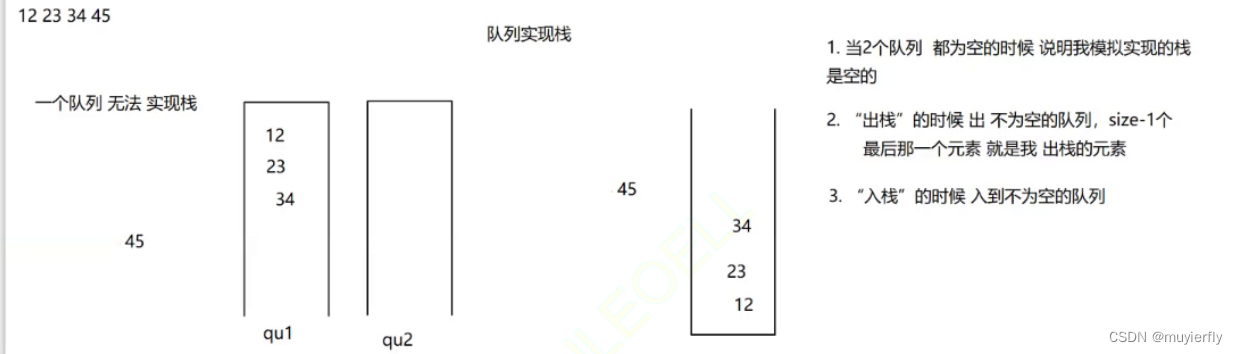
一个队列无法实现栈
尝试使用两个队列
1)push元素的时候应当放在那里?哪个队列不为空就放在哪里
2)出栈的时候,出不为空的队列size-1元素,剩余元素是要出栈的元素
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
class MyStack {
private Queue<Integer> qu1;
private Queue<Integer> qu2;
public MyStack() {
qu1 = new LinkedList<>();
qu2 = new LinkedList<>();
}
public void push(int x) {
//放到不为空的队列
if(!qu1.isEmpty()) {
qu1.offer(x);
}else if(!qu2.isEmpty()) {
qu2.offer(x);
}else {
//如果都是空的 放到第一个
qu1.offer(x);
}
}
public int pop() {
//两个队列都是空的: 栈为空
if(empty()) {
return -1;
}
if(!qu1.isEmpty()) {
int currentSize = qu1.size();
for (int i = 0; i < currentSize-1; i++) {
int x = qu1.poll();
qu2.offer(x);
}
return qu1.poll();//最后一个数据返回
}
if(!qu2.isEmpty()) {
int currentSize = qu2.size();
for (int i = 0; i < currentSize-1; i++) {
int x = qu2.poll();
qu1.offer(x);
}
return qu2.poll();//最后一个数据返回
}
return -1;
}
//peek方法
public int top() {
if(empty()) {
return -1;
}
if(!qu1.isEmpty()) {
int currentSize = qu1.size();
int x = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < currentSize; i++) {
x = qu1.poll();
qu2.offer(x);
}
return x;//最后一个数据返回
}
if(!qu2.isEmpty()) {
int currentSize = qu2.size();
int x = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < currentSize; i++) {
x = qu2.poll();
qu1.offer(x);
}
return x;//最后一个数据返回
}
return -1;
}
public boolean empty() {
return qu1.isEmpty() && qu2.isEmpty();
}
}2.用栈实现队列。
. - 力扣(LeetCode)

class MyQueue {
//定义两个栈
private Stack<Integer> s1;
private Stack<Integer> s2;
//入的时候统一入到s1中
//出的时候统一出到s2中
//实例化两个栈
public MyQueue() {
s1=new Stack<>();
s2=new Stack<>();
}
public void push(int x) {
s1.push(x);
}
public int pop() {
if(empty()){
return -1;
}
if(s2.empty()){
while(!s1.empty()){
s2.push(s1.pop());
}
}
return s2.pop();
}
public int peek() {
if(s1.empty()){
return -1;
}
if(s2.empty()){
while(!s1.empty()){
s2.push(s1.pop());
}
}
return s2.peek();
}
public boolean empty() {
return s1.empty()&&s2.empty();
}
}