目录
DAY27
39. 组合总和
解题思路&代码
40.组合总和II
解题思路&代码
131.分割回文串
解题思路&代码
DAY27
39. 组合总和
力扣题目链接(opens new window)
给定一个无重复元素的数组 candidates 和一个目标数 target ,找出 candidates 中所有可以使数字和为 target 的组合。
candidates 中的数字可以无限制重复被选取。
说明:
- 所有数字(包括 target)都是正整数。
- 解集不能包含重复的组合。
示例 1:
- 输入:candidates = [2,3,6,7], target = 7,
- 所求解集为: [ [7], [2,2,3] ]
本题是 集合里元素可以用无数次,那么和组合问题的差别 其实仅在于 startIndex上的控制
题目链接/文章讲解:代码随想录
视频讲解:带你学透回溯算法-组合总和(对应「leetcode」力扣题目:39.组合总和)| 回溯法精讲!_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
解题思路&代码
思路:
题目中的无限制重复被选取,吓得我赶紧想想 出现0 可咋办,然后看到下面提示:1 <= candidates[i] <= 200,我就放心了。
本题和77.组合 (opens new window),216.组合总和III (opens new window)的区别是:本题没有数量要求,可以无限重复,但是有总和的限制,所以间接的也是有个数的限制。
注意图中叶子节点的返回条件,因为本题没有组合数量要求,仅仅是总和的限制,所以递归没有层数的限制,只要选取的元素总和超过target,就返回!
而在77.组合 (opens new window)和216.组合总和III (opens new window)中都可以知道要递归K层,因为要取k个元素的组合
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum(int[] candidates, int target) {
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
Arrays.sort(candidates);// 先进行排序
backtracking(res, new ArrayList<>(), candidates, target, 0, 0);
return res;
}
public void backtracking (List<List<Integer>> res, List<Integer> path, int[] candidates, int target, int sum, int idx) {
// 找到了数字和为 target 的组合
if (sum == target) {
res.add(new ArrayList<> (path));
return;
}
for (int i = idx; i < candidates.length; i++) {
// 如果 sum + candidates[i] > target 就终止遍历
if (sum + candidates[i] > target) break;
path.add(candidates[i]);
sum += candidates[i];
backtracking(res, path, candidates, target, sum, i);
sum -= candidates[i];
path.remove(path.size() -1); // 回溯,移除路径 path 最后一个元素
}
}
}40.组合总和II
力扣题目链接(opens new window)
给定一个数组 candidates 和一个目标数 target ,找出 candidates 中所有可以使数字和为 target 的组合。
candidates 中的每个数字在每个组合中只能使用一次。
说明: 所有数字(包括目标数)都是正整数。解集不能包含重复的组合。
- 示例 1:
- 输入: candidates = [10,1,2,7,6,1,5], target = 8,
- 所求解集为:
[
[1, 7],
[1, 2, 5],
[2, 6],
[1, 1, 6]
]本题开始涉及到一个问题了:去重。
注意题目中给我们 集合是有重复元素的,那么求出来的 组合有可能重复,但题目要求不能有重复组合。
题目链接/文章讲解:代码随想录
视频讲解:回溯算法中的去重,树层去重树枝去重,你弄清楚了没?| LeetCode:40.组合总和II_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
解题思路&代码
思路:
本题的难点在于区别2中:集合(数组candidates)有重复元素,但还不能有重复的组合
我们是要同一树层上使用过,还是同一树枝上使用过呢?
回看一下题目,元素在同一个组合内是可以重复的,怎么重复都没事,但两个组合不能相同。
所以我们要去重的是同一树层上的“使用过”,同一树枝上的都是一个组合里的元素,不用去重。
树层去重的话,需要对数组排序!
此题还需要加一个bool型数组used,用来记录同一树枝上的元素是否使用过。
class Solution {
LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>();
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
boolean[] used;
int sum = 0;
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum2(int[] candidates, int target) {
used = new boolean[candidates.length];
// 加标志数组,用来辅助判断同层节点是否已经遍历,这样没有遍历的数组元素默认为false
Arrays.fill(used, false);
// 为了将重复的数字都放到一起,所以先进行排序
Arrays.sort(candidates);
backTracking(candidates, target, 0);
return res;
}
private void backTracking(int[] candidates, int target, int startIndex) {
if (sum == target) {
res.add(new ArrayList(path));
}
for (int i = startIndex; i < candidates.length; i++) {
if (sum + candidates[i] > target) {//剪枝操作
break;
}
/** 出现重复节点,同层的第一个节点已经被访问过,所以直接跳过,主要是判断前一个元素是否相同,
相同情况下是属于同层所以不能使用(判断是否同层是通过是否发生了回溯判断的),需要跳过,只要树层去重,树枝不用去重*/
if (i > 0 && candidates[i] == candidates[i - 1] && !used[i - 1]) {
continue;
}
used[i] = true;//每次访问了就标记一下与false形成区别
sum += candidates[i];
path.add(candidates[i]);
// 每个节点仅能选择一次,所以从下一位开始
backTracking(candidates, target, i + 1);
used[i] = false;//回溯一下标记
sum -= candidates[i];
path.removeLast();
}
}
}131.分割回文串
力扣题目链接(opens new window)
给定一个字符串 s,将 s 分割成一些子串,使每个子串都是回文串。
返回 s 所有可能的分割方案。
示例: 输入: "aab" 输出: [ ["aa","b"], ["a","a","b"] ]
本题较难,大家先看视频来理解 分割问题,明天还会有一道分割问题,先打打基础。
代码随想录
视频讲解:带你学透回溯算法-分割回文串(对应力扣题目:131.分割回文串)| 回溯法精讲!_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
解题思路&代码
思路:
切割问题类似组合问题。
例如对于字符串abcdef:
- 组合问题:选取一个a之后,在bcdef中再去选取第二个,选取b之后在cdef中再选取第三个.....。
- 切割问题:切割一个a之后,在bcdef中再去切割第二段,切割b之后在cdef中再切割第三段.....。
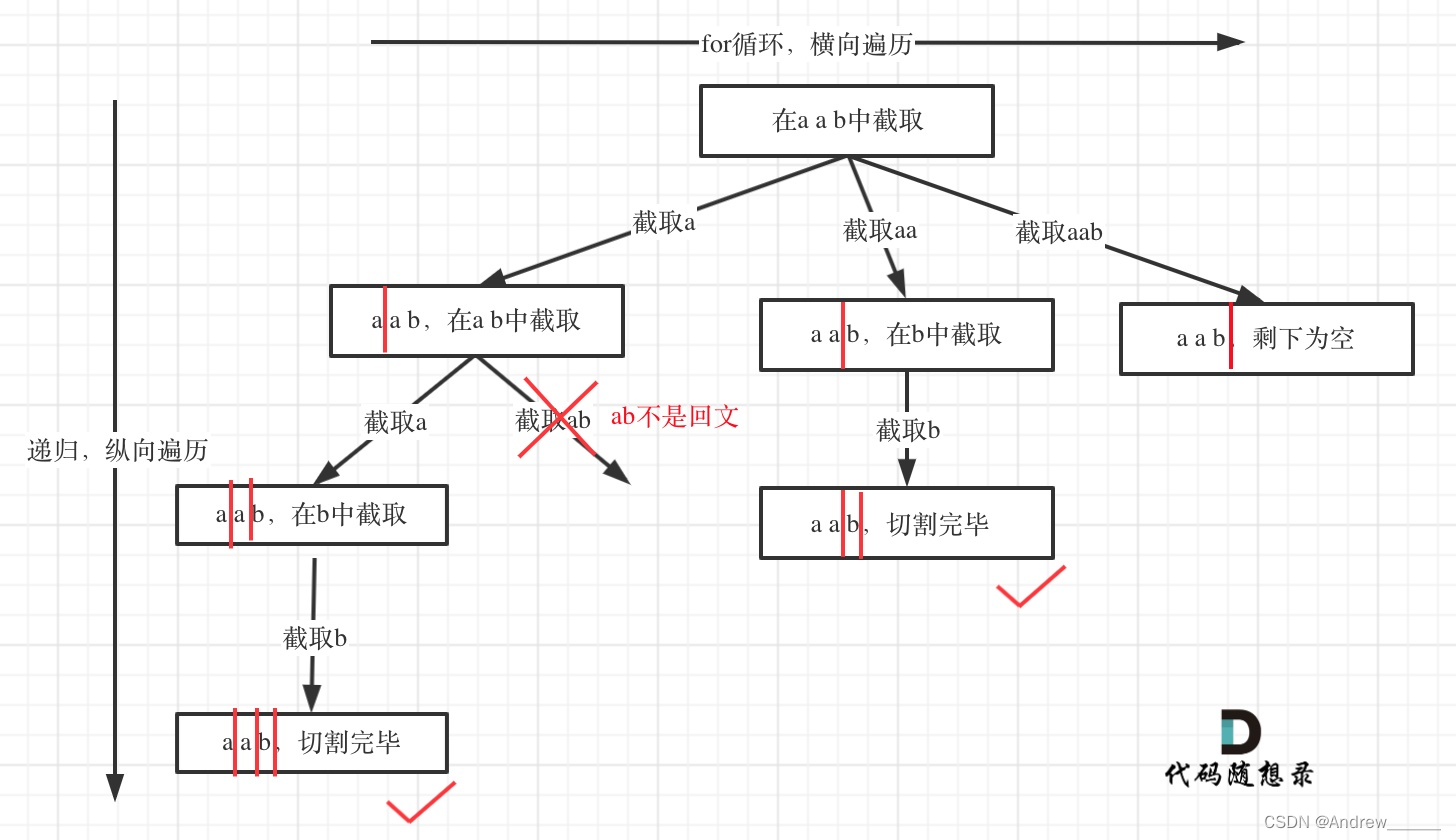
这道题目在leetcode上是中等,但可以说是hard的题目了
那么难究竟难在什么地方呢?
如下几个难点:
- 切割问题可以抽象为组合问题
- 如何模拟那些切割线
- 切割问题中递归如何终止
- 在递归循环中如何截取子串
- 如何判断回文
class Solution {
List<List<String>> lists = new ArrayList<>();
Deque<String> deque = new LinkedList<>();
public List<List<String>> partition(String s) {
backTracking(s, 0);
return lists;
}
private void backTracking(String s, int startIndex) {
//如果起始位置大于s的大小,说明找到了一组分割方案
if (startIndex >= s.length()) {
lists.add(new ArrayList(deque));
return;
}
for (int i = startIndex; i < s.length(); i++) {
//如果是回文子串,则记录
if (isPalindrome(s, startIndex, i)) {
String str = s.substring(startIndex, i + 1);// 截取符合要求的子串
deque.addLast(str);
} else {
continue;
}
//起始位置后移,保证不重复
backTracking(s, i + 1);
deque.removeLast();
}
}
//判断是否是回文串
private boolean isPalindrome(String s, int startIndex, int end) {
for (int i = startIndex, j = end; i < j; i++, j--) {
if (s.charAt(i) != s.charAt(j)) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}