文章目录
- 一.报告概要
- 二.测试环境
- 三.手工测试用例
- 四.编写测试用例
- 五.自动化测试Selenium
- 测试项目主要特点
一.报告概要
-
项目概要
本项目是一个全功能的个人博客系统,旨在提供一个用户友好、功能全面的平台,允许用户注册、登录、浏览博客、查看详细内容、发表评论以及发布和管理个人博文。项目的核心功能包括博客列表、博客详情页、用户登录注册、个人中心和发布博客功能。 -
技术栈
SpringBoot, SpringMVC ,MyBatis, MySQL, HTML, CSS, JavaScript -
测试报告目的
测试报告的主要目的是验证博客系统的功能完整性、性能和安全性。通过对每个核心功能的综合测试,确保系统能够在真实环境中稳定运行,并满足用户的预期需求。此外,报告还旨在识别潜在的问题和缺陷,为后续的开发和改进提供指导。 -
测试报告范围和日期
测试范围:涵盖所有核心功能的单元测试、集成测试和系统测试。特别关注用户交互、数据完整性、接口可靠性以及性能和安全性。 -
测试日期:测试活动预计从2023年10月1日开始,至2023年10月31日结束。
-
测试总体执行情况
主要针对常见功能进行测试例如:博客登录页面,博客列表页面,博客详情页,博客编辑页…
二.测试环境
硬件:D0573AC9-C173-436A-B8B2-2549602DAD4C
软件:Google Chrome
开发工具:IDEA
测试工具:自动化测试工具Selenium
操作系统:Windows 11家庭中文版
浏览器版本:Google Chrome 版本 124.0.6367.119(正式版本) (64 位)
三.手工测试用例
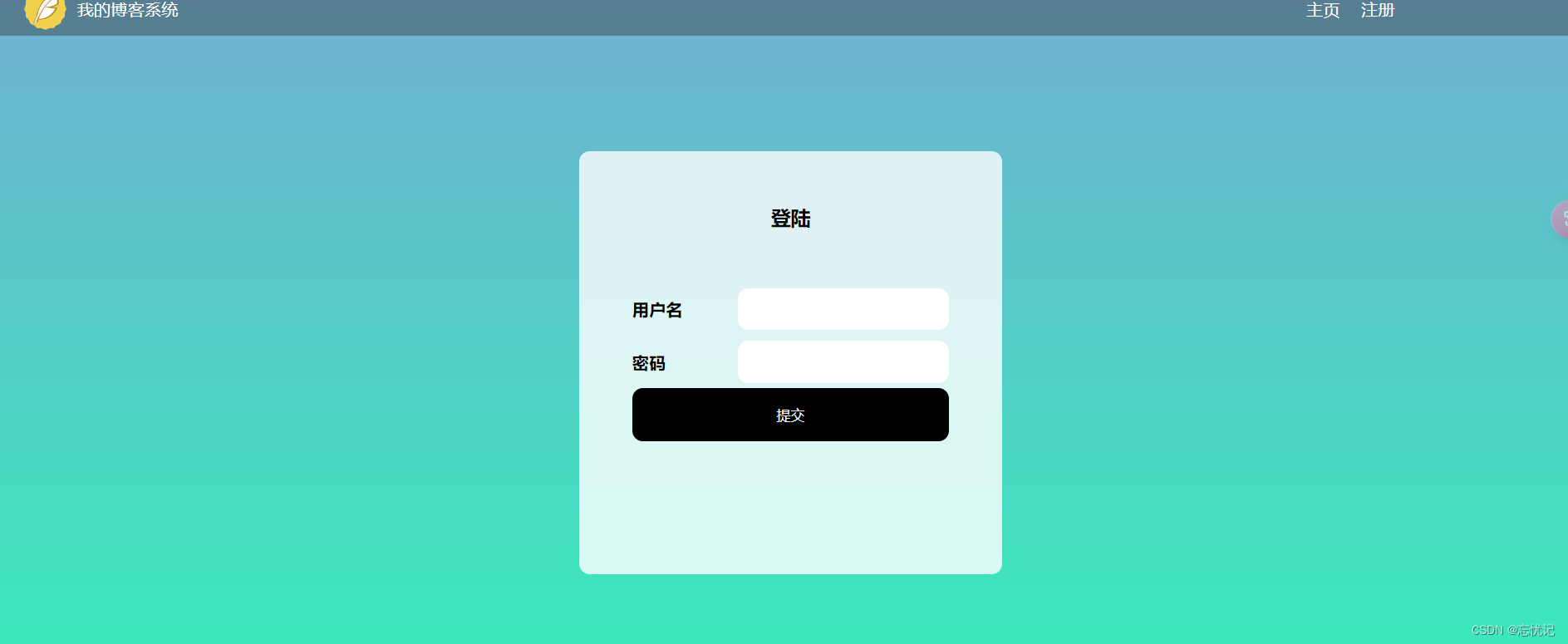
博客登录页
博客注册页:
个人博客列表页
博客详情页:
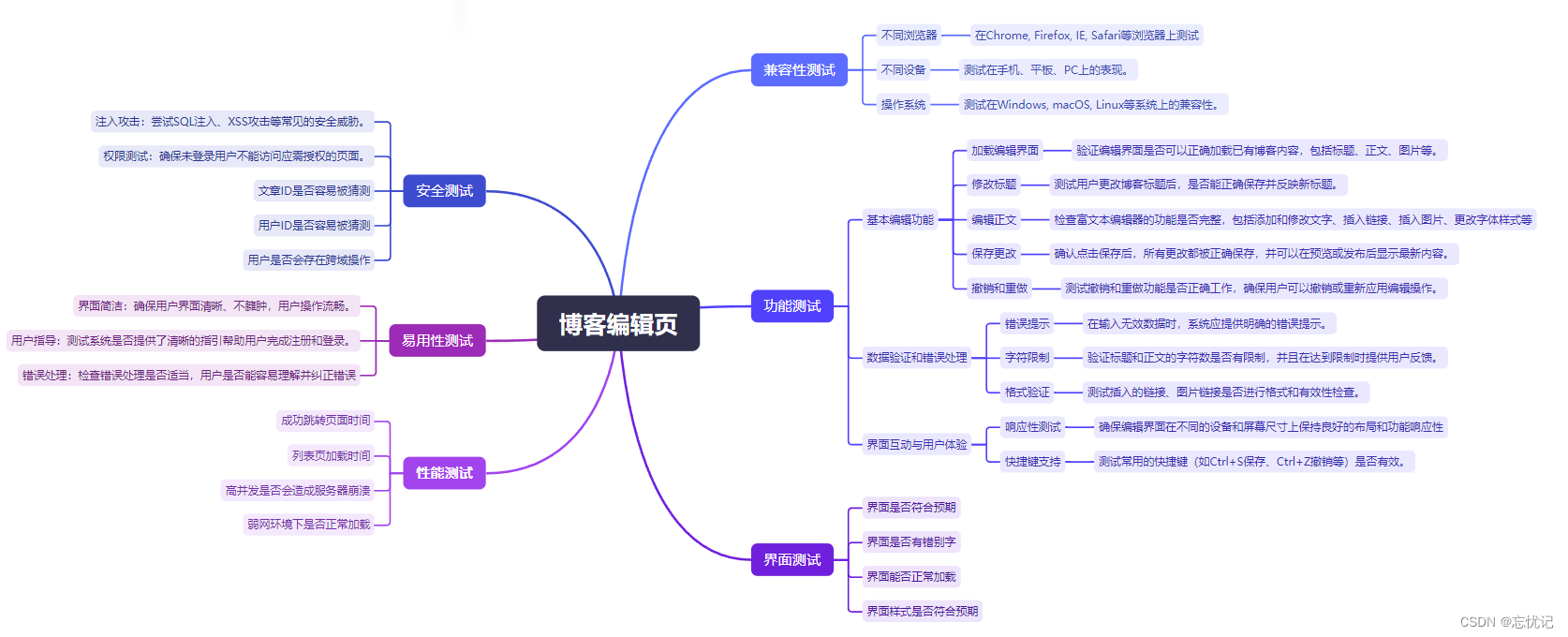
博客编辑页:
四.编写测试用例
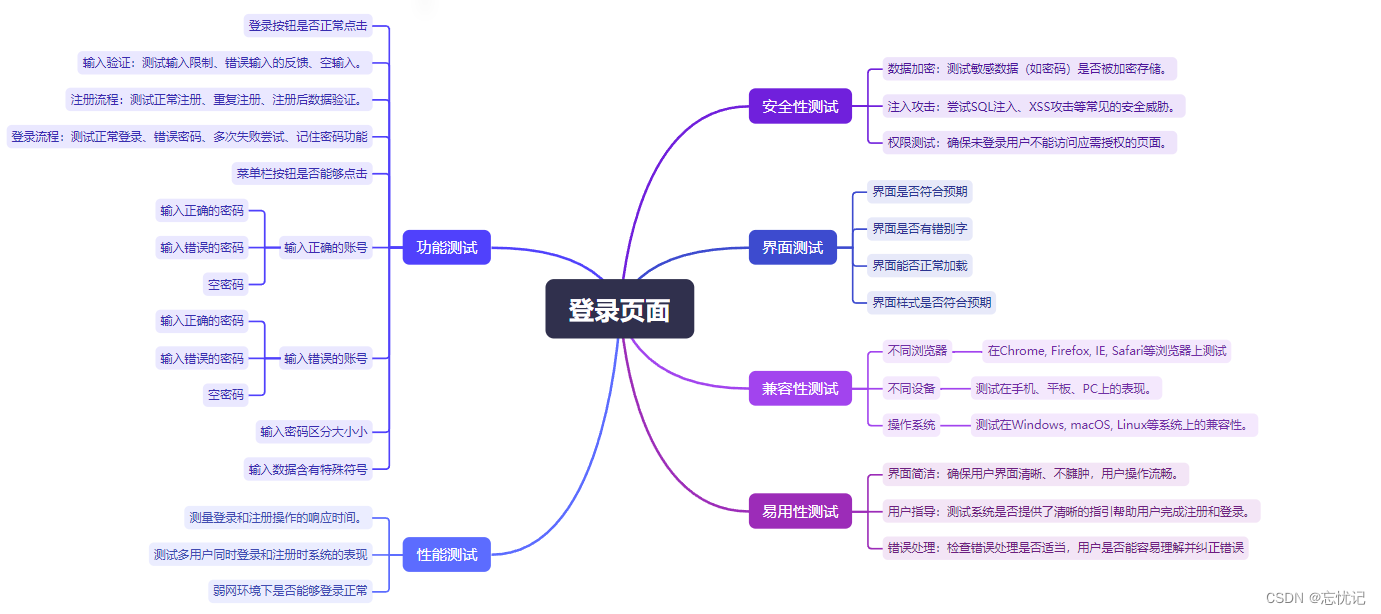
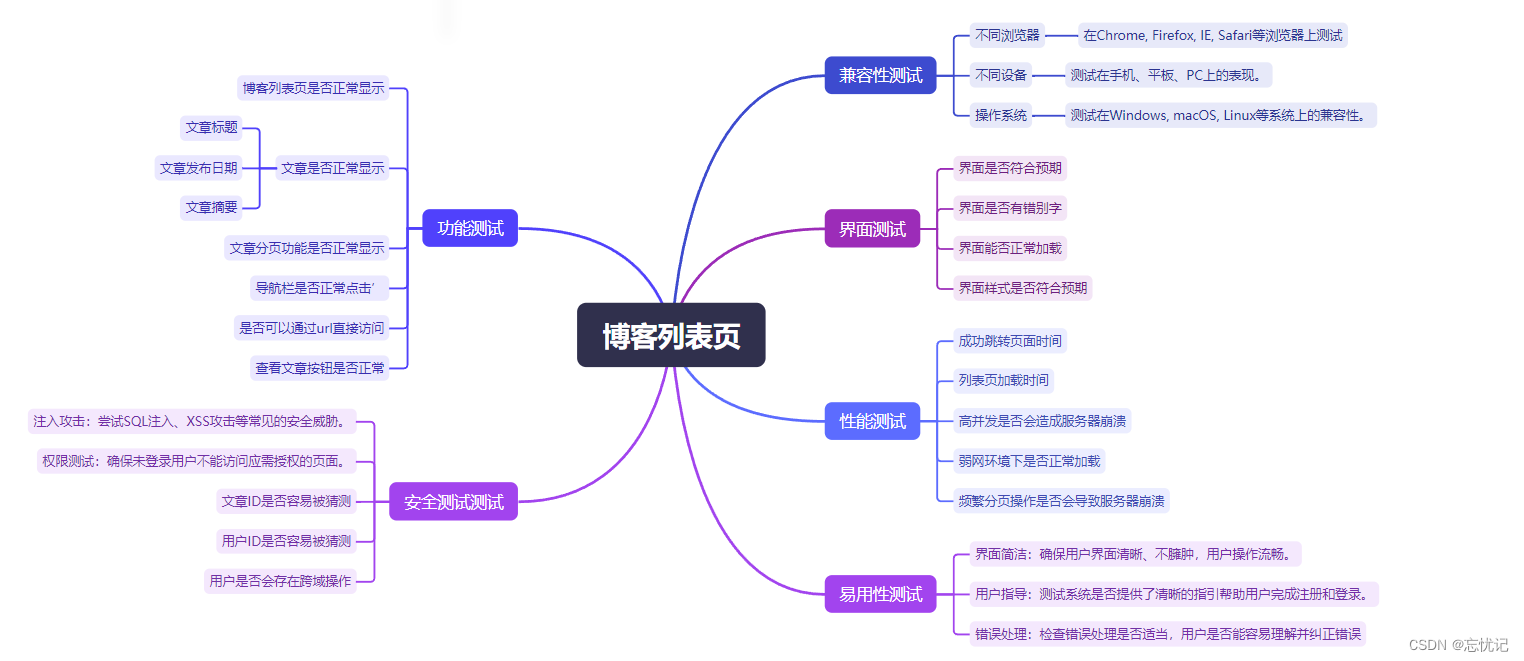
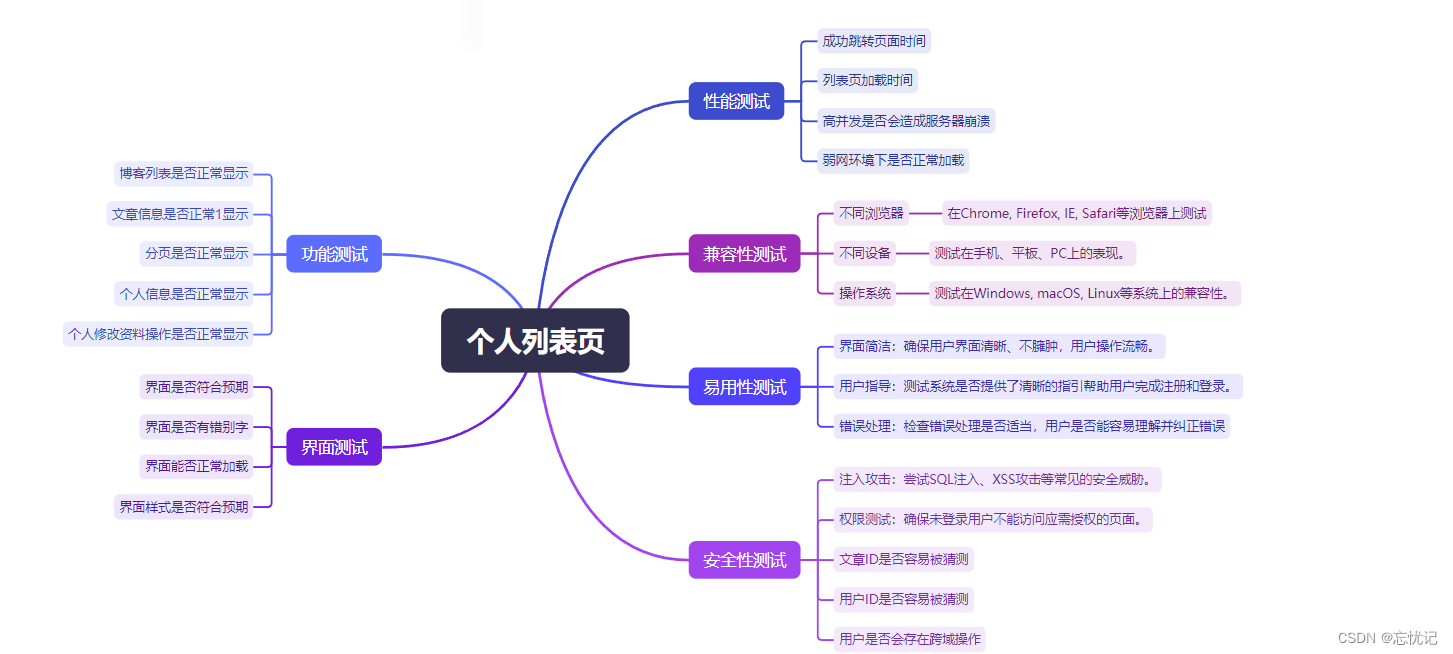
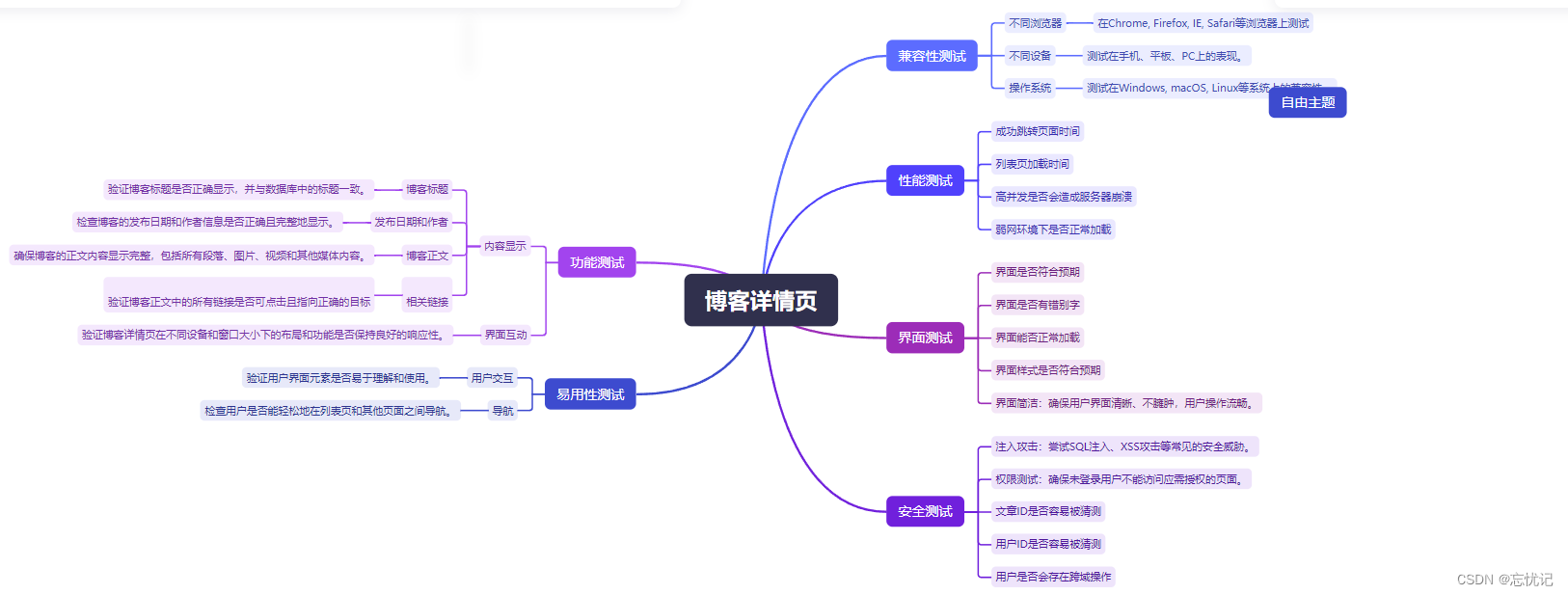
五.自动化测试Selenium
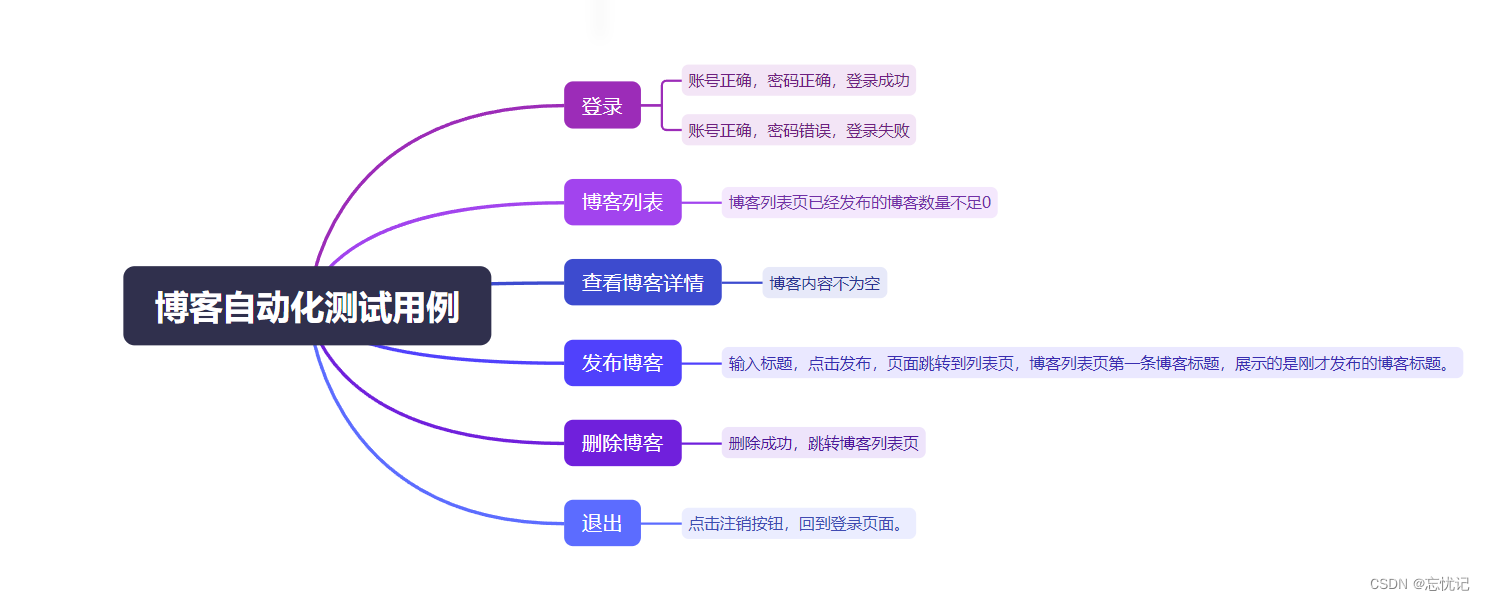
代码展示
package Blog;
import com.sun.org.apache.xpath.internal.operations.Or;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.*;
import org.junit.jupiter.params.ParameterizedTest;
import org.junit.jupiter.params.provider.Arguments;
import org.junit.jupiter.params.provider.CsvFileSource;
import org.junit.jupiter.params.provider.MethodSource;
import org.openqa.selenium.By;
import org.openqa.selenium.JavascriptExecutor;
import org.openqa.selenium.WebElement;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import java.util.stream.Stream;
import static java.lang.Thread.sleep;
@TestMethodOrder(MethodOrderer.OrderAnnotation.class)
public class BlogCases extends InitAndEnd{
public static Stream<Arguments> Generator() {
return Stream.of(Arguments.arguments("http://42.192.83.143:8563/blog_system/blog_detail.html", "博客详情页",
"自动化测试"));
}
/**
*
* 输入正确的账号,密码登录成功
*/
@Order(1)
@ParameterizedTest
@CsvFileSource(resources = "LoginSuccess.csv")
void LoginSuccess(String username, String password, String blog_list_url) {
System.out.println(username + password + blog_list_url);
// 打开博客登录页面
webDriver.get("http://42.192.83.143:8563/blog_system/blog_login.html");
webDriver.manage().timeouts().implicitlyWait(3, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
// 输入账号admin
webDriver.findElement(By.cssSelector("#username")).sendKeys(username);
webDriver.manage().timeouts().implicitlyWait(3, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
// 输入密码123
webDriver.findElement(By.cssSelector("#password")).sendKeys(password);
webDriver.manage().timeouts().implicitlyWait(3, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
// 点击提交按钮
webDriver.findElement(By.cssSelector("#submit")).click();
webDriver.manage().timeouts().implicitlyWait(3, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
// 跳转到列表页
// 获取到当前页面url
String cur_url = webDriver.getCurrentUrl();
webDriver.manage().timeouts().implicitlyWait(3, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
// 如果url=http://42.192.83.143:8563/blog_system/blog_list.html,测试通过,否则测试不通过
Assertions.assertEquals(blog_list_url, cur_url);
// 列表页展示用户信息是admin
// 用户名是admin测试通过,否则测试不通过
webDriver.manage().timeouts().implicitlyWait(3, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
webDriver.manage().timeouts().implicitlyWait(3, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
String cur_admin = webDriver.findElement(By.cssSelector("body > div.container > div.left > div > h3")).getText();
Assertions.assertEquals(username, cur_admin);
}
/**
* 博客列表页博客数量不为0
*/
@Order(2)
@Test
void BlogList() {
// 打开博客列表页
webDriver.get("http://42.192.83.143:8563/blog_system/blog_list.html");
// 获取页面上所有博客标题对应的元素
webDriver.manage().timeouts().implicitlyWait(3, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
int title_num = webDriver.findElements(By.cssSelector(".title")).size();
// 如果元素数量不为0,测试通过
Assertions.assertNotEquals(0 ,title_num);
}
/**
* 博客详情页校验
* url
* 博客标题
* 页面title是“博客详情页”
*/
@Order(4)
@ParameterizedTest
@MethodSource("Generator")
void BlogDetail(String expected_url, String expected_title, String expected_blog_title) {
// 找到第一篇博客对应的产看全文按钮
webDriver.manage().timeouts().implicitlyWait(3, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
webDriver.findElement(By.xpath("/html/body/div[2]/div[2]/div[1]/a")).click();
// 获取当前页面url
webDriver.manage().timeouts().implicitlyWait(3, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
String cur_url = webDriver.getCurrentUrl();
webDriver.manage().timeouts().implicitlyWait(3, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
// 获取当前页面title
String cur_title = webDriver.getTitle();
webDriver.manage().timeouts().implicitlyWait(3, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
// 获取博客标题
String cur_blog_title = webDriver.findElement(By.cssSelector("body > div.container > div.right > div > h3")).getText();
webDriver.manage().timeouts().implicitlyWait(3, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
Assertions.assertEquals(expected_title ,cur_title);
Assertions.assertEquals(expected_blog_title, cur_blog_title);
if(cur_url.contains(expected_url)) {
System.out.println("测试通过");
} else {
System.out.println(cur_url);
System.out.println("测试不通过");
}
}
/**
*
* 写博客
*/
@Order(3)
@Test
void EditBlog() throws InterruptedException {
// 找到写博客按钮,点击
webDriver.findElement(By.cssSelector("body > div.nav > a:nth-child(5)")).click();
webDriver.manage().timeouts().implicitlyWait(3, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
// 通过Js讲鼻涕进行输入
((JavascriptExecutor)webDriver).executeScript("document.getElementById(\"title\").value=\"自动化测试\"");
sleep(3000);
// 点击发布
webDriver.findElement(By.cssSelector("#submit")).click();
sleep(3000);
// 获取当前页面url
String cur_url = webDriver.getCurrentUrl();
Assertions.assertEquals("http://42.192.83.143:8563/blog_system/blog_list.html", cur_url);
}
/**
* 校验已发布博客标题
* 校验已发布博客时间
*/
@Order(5)
@Test
void BlogInfoChecked() {
webDriver.get("http://42.192.83.143:8563/blog_system/blog_list.html");
// 获取第一篇博客标题
String first_blog_title = webDriver.findElement(By.cssSelector("body > div.container > div.right > div:nth-child(1) > div.title")).getText();
// 获取第一篇博客发布时间
String first_blog_time = webDriver.findElement(By.xpath("/html/body/div[2]/div[2]/div[1]/div[2]")).getText();
// 校验博客标题是不是自动化测试
Assertions.assertEquals("自动化测试", first_blog_title);
// 如果时间是2023-5-23年发布的,测试通过
if(first_blog_title.contains("2023-05-23")) {
System.out.println("测试通过");
} else {
System.out.println("当前时间是:" + first_blog_time);
System.out.println("测试不通过");
}
}
/**
*
* 删除和刚才发布的博客
*/
@Order(6)
@Test
void DeleteBlog() throws InterruptedException {
// 打开博客列表页面
webDriver.get("http://42.192.83.143:8563/blog_system/blog_list.html");
// 点击全文按钮
webDriver.manage().timeouts().implicitlyWait(3, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
webDriver.findElement(By.cssSelector("body > div.container > div.right > div:nth-child(1) > a")).click();
// 点击删除按钮
webDriver.manage().timeouts().implicitlyWait(3, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
webDriver.findElement(By.cssSelector("body > div.nav > a:nth-child(7)")).click();
sleep(3000);
// 博客列表页第一篇博客标题不是“自动化测试”
String first_blog_title = webDriver.findElement(By.xpath("/html/body/div[2]/div[2]/div[1]/div[1]")).getText();
// 校验当前博客标题不等于“自动化测试”
webDriver.manage().timeouts().implicitlyWait(3, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
Assertions.assertNotEquals(first_blog_title, "自动测试");
}
/**
* 注销
*/
@Order(7)
@Test
void Logout() {
webDriver.manage().timeouts().implicitlyWait(3, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
webDriver.findElement(By.cssSelector("body > div.nav > a:nth-child(6)")).click();
webDriver.manage().timeouts().implicitlyWait(3, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
// 校验url(登录url)
String cur_url = webDriver.getCurrentUrl();
Assertions.assertEquals("http://42.192.83.143:8563/blog_system/blog_login.html", cur_url);
// 校验提交按钮
WebElement webElement = webDriver.findElement(By.cssSelector("#submit"));
Assertions.assertNotNull(webElement);
}
}
1. 初始化测试环境:
继承InitAndEnd类,该类可能负责初始化WebDriver和关闭浏览器。
2. 生成测试数据:
使用Stream Generator()方法生成测试数据,这里只生成了一个测试案例,即博客详情页的URL、页面标题和博客标题。
3. 登录成功测试 (LoginSuccess):
使用@CsvFileSource读取CSV文件中的用户名、密码和预期的博客列表URL。
打开博客登录页面并输入账号密码。
点击提交按钮,验证是否成功跳转到博客列表页。
检查页面上是否显示了正确的用户名。
4. 博客列表页测试 (BlogList):
打开博客列表页面,验证博客标题的数量是否不为0。
博客详情页校验 (BlogDetail):
使用@MethodSource引入测试数据生成器。
点击博客列表中的“查看全文”按钮,验证当前URL、页面标题和博客标题是否符合预期。
5. 写博客测试 (EditBlog):
点击“写博客”按钮,使用JavaScript设置博客标题为“自动化测试”。
点击发布按钮,验证是否成功跳转到博客列表页面。
校验已发布博客信息 (BlogInfoChecked):
访问博客列表页面,检查最新博客的标题是否为“自动化测试”。
检查博客的发布时间是否为特定日期。
6. 删除博客测试 (DeleteBlog):
打开博客列表页面,点击“查看全文”按钮。
点击删除按钮,验证列表中是否不再显示“自动化测试”标题的博客。
7. 注销测试 (Logout):
点击注销按钮,验证是否成功跳转到登录页面,并检查登录按钮是否存在。
测试用例排序:
使用@TestMethodOrder和OrderAnnotation确保测试用例按指定顺序执行。
6. 等待机制:
代码中多次使用ThreadUtil.sleep和webDriver.manage().timeouts().implicitlyWait来等待页面元素加载。
7. 异常处理:
测试用例EditBlog中使用throws InterruptedException声明可能抛出的中断异常。
8. 断言验证:
使用Assertions类来验证测试结果是否符合预期。
这个测试流程涵盖了博客系统的主要功能,包括登录、列表展示、详情查看、写博客、信息校验、删除博客和注销。每个测试用例都设计有明确的预期结果,并通过断言来验证这些预期是否得到满足。
测试项目主要特点
-
自动化测试工具和框架的应用:
通过采用自动化测试工具如Selenium和JUnit 5,您的项目实现了自动化测试脚本的编写,这有助于提高测试效率和系统运行的稳定性。 -
UI测试的自动化:
自动化测试涵盖了用户界面(UI)测试,这有助于减少人力投入,因为UI测试通常比较耗时且容易出错。 -
持续集成和持续交付(CI/CD):
自动化测试与CI/CD流程相结合,可以在软件开发周期的早期发现问题,从而加快软件发布的速度。 -
参数化测试:
使用参数化测试方法,您可以用不同的输入值多次运行相同的测试,这使得测试用例更加整洁,同时提高了代码的可读性和可维护性。 -
隐式等待的使用:
通过使用隐式等待(implicitlyWait),您的测试脚本能够自动等待页面元素加载完成,这提高了自动化测试运行的效率和稳定性。 -
屏幕截图功能:
当测试失败时,自动捕获屏幕截图,这为问题的溯源和解决提供了方便,因为截图可以直观地展示出错时的页面状态。 -
测试用例的顺序执行:
使用@TestMethodOrder注解确保测试用例按照预定的顺序执行,这对于依赖于特定执行顺序的场景至关重要。 -
异常处理:
测试脚本中包含了异常处理机制,如throws InterruptedException,这有助于确保测试在遇到异常时能够优雅地处理。 -
断言验证:
测试脚本中使用了断言(Assertions)来验证测试结果是否符合预期,这是自动化测试中验证测试是否通过的关键部分。 -
详细的测试报告:
测试结束后,可以生成包含所有测试结果的详细报告,这对于团队成员和项目利益相关者了解测试进度和结果非常有用。 -
测试数据的动态生成:
通过自定义方法如Generator()动态生成测试数据,提高了测试的灵活性和可维护性。 -
跨浏览器兼容性测试:
虽然您的描述中没有明确提到,但Selenium支持跨浏览器测试,这可以确保您的应用在不同的浏览器上都能正常工作。