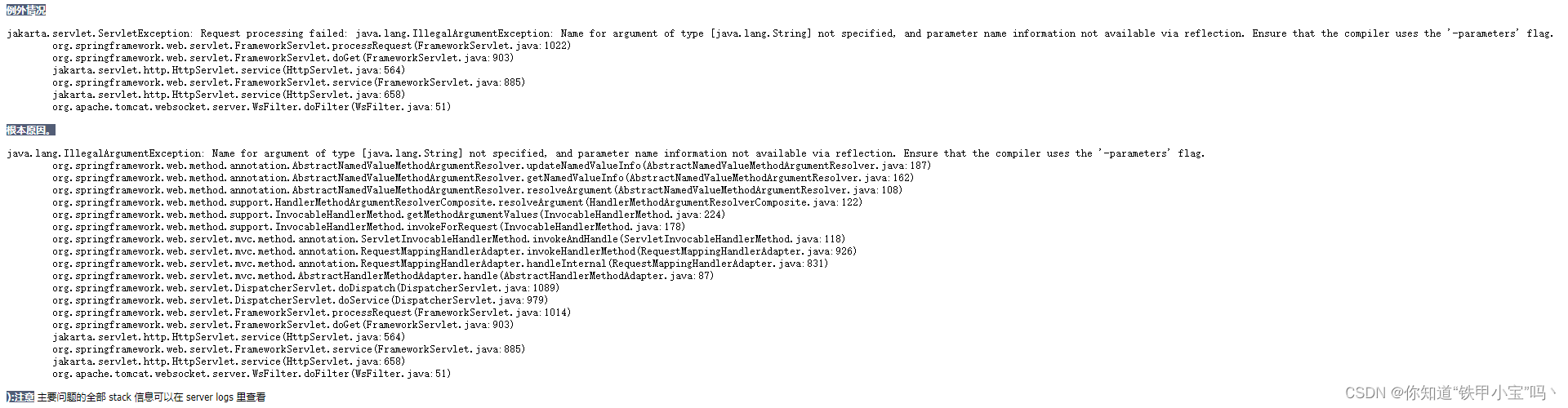
三、请说明如何在一棵 B 树中找出最小关键字,以及如何找出某一给定关键字的前驱。如果要写代码,请用go语言。
文心一言:
在B树(也称为B-tree)中,最小的关键字总是位于最左边的叶子节点的最左边的元素。要找到最小关键字,你需要从根节点开始,并沿着最左边的孩子节点一直向下搜索,直到达到一个叶子节点。
要找到给定关键字的前驱(即小于给定关键字且最接近给定关键字的元素),你需要首先定位到包含给定关键字的叶子节点或该节点之前的节点。如果给定关键字不存在于树中,你需要找到最接近但小于给定关键字的叶子节点。这通常涉及从根节点开始,沿着树向下搜索,在每次比较时选择小于或等于给定关键字的子树。
以下是使用Go语言实现的B树查找最小关键字和给定关键字前驱的基本逻辑(注意:完整的B树实现将包含许多其他函数和细节,这里仅给出关键部分的伪代码/框架):
package main
import (
"fmt"
)
// 假设这是B树的节点结构,这里为了简化,只包含了一些关键字段
type BTreeNode struct {
keys []int // 关键字数组
children []*BTreeNode // 子节点数组
// 其他字段如度数、是否叶子节点等在此省略
}
// 查找最小关键字
func (node *BTreeNode) findMinKey() (int, bool) {
if node == nil {
return 0, false // 返回默认值或错误表示
}
for node.children != nil && len(node.children) > 0 { // 向下遍历直到叶子节点
node = node.children[0] // 选择最左边的子节点
}
if len(node.keys) == 0 {
return 0, false // 如果没有关键字,返回错误或默认值
}
return node.keys[0], true // 返回最小关键字
}
// 查找给定关键字的前驱
func (node *BTreeNode) findPredecessor(key int) (int, bool) {
if node == nil {
return 0, false // 返回默认值或错误表示
}
var predKey int
var predFound bool
// 搜索树直到叶子节点
for node.children != nil {
idx := node.findInsertIndex(key) // 找到应该插入key的位置
if idx > 0 { // 如果key大于当前节点的某个关键字,则前驱可能在此节点中
predKey = node.keys[idx-1]
predFound = true
}
node = node.children[idx] // 继续向下搜索
}
// 如果在叶子节点中没有找到key,则predKey可能是正确的前驱
// 如果在叶子节点中找到了key,那么我们需要向上回溯到前驱节点
// 这里省略了回溯逻辑,因为完整的实现会更复杂
// 返回前驱关键字(如果存在)
return predKey, predFound
}
// findInsertIndex 在节点中查找插入key的位置(仅用于说明,不是完整实现)
func (node *BTreeNode) findInsertIndex(key int) int {
// ... 这里应该实现一个搜索算法来找到key应该插入的位置
// 作为示例,这里仅返回0(总是插入到最左边)
return 0
}
func main() {
// 假设你有一个B树root
// root := &BTreeNode{...} // 初始化B树和填充数据
// 查找最小关键字
minKey, found := root.findMinKey()
if found {
fmt.Printf("最小关键字是: %d\n", minKey)
} else {
fmt.Println("树为空或没有关键字")
}
// 查找给定关键字的前驱(假设key是要查找的前驱的关键字)
key := ... // 设置要查找的前驱的关键字
predKey, predFound := root.findPredecessor(key)
if predFound {
fmt.Printf("关键字 %d 的前驱是: %d\n", key, predKey)
} else {
fmt.Printf("没有找到关键字 %d 的前驱\n", key)
}
}
请注意,上面的代码是一个简化的框架,并没有包含B树的所有复杂性和完整的findInsertIndex实现。在完整的B树实现中,findInsertIndex函数将需要实现一个完整的搜索算法来找到插入给定关键字的位置,这通常涉及比较关键字并确定应该进入哪个子节点。此外,findPredecessor函数也需要处理回溯到前驱节点的情况,这在上面的代码中被省略了
讯飞星火:
在B树中,最小关键字总是位于最左侧的叶节点。因此,我们可以通过从根节点开始,沿着左子节点一直向下遍历,直到找到一个没有左子节点的节点,该节点存储的就是最小关键字。
对于给定关键字的前驱,如果该关键字存在于B树中,那么它的前驱就是它左兄弟节点中的最后一个关键字(如果存在的话)。否则,我们需要向上回溯到父节点,然后转向右兄弟节点,继续这个过程,直到找到前驱或者到达根节点。
以下是Go语言的实现:
type BTreeNode struct {
leaf bool
keys []int
ch []*BTreeNode
}
func (t *BTreeNode) minimum() int {
if t.leaf {
return t.keys[0]
}
return t.ch[0].minimum()
}
func (t *BTreeNode) predecessor(key int) int {
i := sort.SearchInts(t.keys, key)
if i > 0 {
return t.keys[i-1]
}
if t.leaf {
return -1
}
return t.ch[i].maximum()
}
func (t *BTreeNode) maximum() int {
if t.leaf {
return t.keys[len(t.keys)-1]
}
return t.ch[len(t.ch)-1].maximum()
}
在这个代码中,我们首先定义了一个B树节点的结构体,包含了一个布尔值表示是否是叶子节点,一个整数切片存储关键字,以及一个B树节点切片存储子节点。然后我们定义了三个方法:minimum()用于找出最小关键字,predecessor()用于找出给定关键字的前驱,maximum()用于找出最大关键字。
360智脑:
B树中最小关键字可以通过遍历树的最左边的分支一直到底层得到,而某个给定关键字的前驱则是在删除该关键字之前位于其左边的最近的一个关键字。在B树中,每个节点都包含一个指向左子树的最大关键字和指向右子树的最小关键字的指针,因此找到最小关键字和前驱都是相对直接的过程。
以下是Go语言中查找B树最小关键字和前驱的伪代码示例:
type BTreeNode struct {
left *BTreeNode
right *BTreeNode
parent *BTreeNode
keys []KeyType
values []ValueType
}
func (node *BTreeNode) findMinKey() KeyType {
if node.left == nil {
return node.keys[0]
}
return node.left.findMinKey()
}
func (node *BTreeNode) findPredecessor(key KeyType) *BTreeNode {
if node.parent == nil {
return nil // key not found
}
for {
if node.parent.right == node {
return node.parent
}
if node.key(0) > key {
return node.parent
}
node = node.parent
}
}
// 从root开始查找,返回B树中的最小关键字
func findMinKey(root *BTreeNode) KeyType {
return root.findMinKey()
}
// 从root开始查找,返回值为给定关键字的前驱,如果没有则返回nil
func findPredecessor(root *BTreeNode, key KeyType) *BTreeNode {
return root.findPredecessor(key)
}
请注意,这只是一个大致的框架,并没有包括B树的所有操作和错误处理。在实际应用中,还需要考虑空树或不存在的关键字等情况。
智谱清言:
B 树是一种自平衡的树结构,它维持数据的有序性。在 B 树中查找最小关键字和找到某一给定关键字的前驱(如果存在的话)需要从根节点开始,并沿着树的右侧分支进行搜索。
下面是使用 Go 语言实现的示例代码,说明如何在 B 树中找到最小关键字和给定关键字的前驱:
package main
import (
"fmt"
)
// 定义 B 树节点
type TreeNode struct {
Key int
Children []*TreeNode
IsLeaf bool
NextSibling *TreeNode
}
// 插入关键字到 B 树
func (root *TreeNode) Insert(key int) {
// 插入逻辑,省略...
}
// 在 B 树中查找最小关键字
func (root *TreeNode) FindMin() int {
if root == nil {
return -1 // 树为空
}
if root.IsLeaf {
for i := 0; i < len(root.Children); i++ {
if root.Children[i] == nil {
return root.Key
}
}
return -1 // 如果所有孩子都不为空,则没有最小值
}
return root.Children[0].FindMin() // 最小值在第一个孩子节点中
}
// 查找给定关键字的前驱
func (root *TreeNode) FindPrev(key int) int {
if root == nil {
return -1 // 树为空
}
// 查找最小关键字,如果找到,则返回其父节点的索引
minKey := root.FindMin()
if minKey == key {
return minKey // 最小关键字即为前驱
}
// 递归在左子树中查找
for i, child := range root.Children {
if child != nil {
if child.IsLeaf {
for j := 0; j < len(child.Children); j++ {
if child.Children[j] == nil {
return child.Key
}
}
} else {
prev := child.FindPrev(key)
if prev != -1 {
return prev
}
}
}
}
return -1 // 未找到前驱
}
func main() {
// 创建 B 树并插入一些数据,省略...
// 查找最小关键字
minKey := root.FindMin()
fmt.Printf("最小关键字: %d\n", minKey)
// 查找某个给定关键字的前驱
key := 10 // 示例关键字
prevKey := root.FindPrev(key)
fmt.Printf("关键字 %d 的前驱是: %d\n", key, prevKey)
}
注意:上述代码中的 B 树节点结构以及插入逻辑是假设的,并没有完全实现。实际应用中,B 树的实现更为复杂,涉及到节点分裂、合并等操作。此代码段仅提供了在一个已存在的 B 树中查找最小关键字及前驱的基本逻辑。
实际使用时,您需要根据实际需求实现 B 树的其它部分,包括节点的创建、分裂、合并、删除等操作,以确保 B 树能够正确地维护数据的有序性和平衡性。
天工:
在B树中找出最小关键字的步骤如下:
- 从根节点开始。
- 如果当前节点有左子树,则向左子树移动(因为B树的特性是所有左子节点的关键字值都小于等于该节点的关键字值)。
- 如果当前节点没有左子树,那么它就是这棵子树中的最小关键字所在的节点。
找到某一给定关键字的前驱的步骤如下:
- 如果关键字所在的节点有左孩子,那么最小的关键字是这个左孩子节点中的最大关键字。
- 如果关键字所在的节点是其父节点的右孩子,并且父节点也有左孩子,那么最小的关键字是这个父节点中的最小关键字。
- 如果关键字所在的节点是根节点,那么它本身就是整棵树中的最小关键字。
以下是Go语言中实现这些步骤的示例代码:
package main
import (
"fmt"
)
type TreeNode struct {
key int
left *TreeNode
right *TreeNode
}
func findMin(node *TreeNode) int {
for node.left != nil {
node = node.left
}
return node.key
}
func findPredecessor(node, x *TreeNode) *TreeNode {
if node == nil {
return x
} else if x.key <= node.key {
return findPredecessor(node.left, x)
} else {
if node.right != nil {
return findPredecessor(node.right, x)
} else {
return node
}
}
}
func main() {
// 构建一个简单的B树示例
root := &TreeNode{key: 27}
root.left = &TreeNode{key: 14}
root.right = &TreeNode{key: 35}
root.left.left = &TreeNode{key: 10}
root.left.right = &TreeNode{key: 19}
root.right.right = &TreeNode{key: 42}
// 查找最小关键字
minKey := findMin(root)
fmt.Printf("The minimum key in the B-tree is: %d\n", minKey)
// 查找给定关键字的前驱
givenKey := 19 // 可以改变这个值来测试不同的情况
predecessor := findPredecessor(root, root.right)
for predecessor != nil && predecessor.key != givenKey {
if predecessor.right != nil {
predecessor = predecessor.right
} else {
predecessor = predecessor.left
}
}
if predecessor == nil {
fmt.Printf("There is no predecessor for the given key %d in the B-tree.\n", givenKey)
} else {
fmt.Printf("The predecessor of the given key %d in the B-tree is: %d\n", givenKey, predecessor.key)
}
}
请注意,上述代码假设输入的B树是正确构造的,并且已经包含了一些元素。在实际应用中,您需要确保B树的操作(如插入、删除和搜索)是按照B树的算法正确执行的。
灵小智:
在一棵B树中找出最小关键字,可以通过以下步骤实现:
- 从根节点开始,不断往左子节点移动,直到到达叶子节点。
- 返回叶子节点的第一个关键字,即为最小关键字。
以下是用Go语言实现的代码示例:
type BTreeNode struct {
leaf bool
keys []int
children []*BTreeNode
}
// 在B树中找出最小关键字
func findMinKey(root *BTreeNode) int {
if root == nil {
return -1
}
for !root.leaf {
root = root.children[0]
}
return root.keys[0]
}
要找出给定关键字的前驱,在B树中进行以下步骤:
- 从根节点开始,找到该关键字所在的子树。
- 如果该关键字存在于叶子节点中,返回该关键字的前一个关键字。
- 如果该关键字存在于内部节点中,移动到其左子树的最右边叶子节点,返回该叶子节点的最后一个关键字。
以下是用Go语言实现的代码示例:
// 在B树中找出给定关键字的前驱
func findPredecessor(root *BTreeNode, key int) int {
if root == nil {
return -1
}
index := findKeyIndex(root.keys, key)
if index < len(root.keys) && root.keys[index] == key && root.leaf {
// 关键字存在于叶子节点中
if index > 0 {
return root.keys[index-1]
}
} else if !root.leaf {
// 关键字存在于内部节点中
child := root.children[index]
for !child.leaf {
child = child.children[len(child.children)-1]
}
return child.keys[len(child.keys)-1]
}
return -1
}
// 在排序的切片中找到关键字所在的索引
func findKeyIndex(keys []int, key int) int {
index := 0
for index < len(keys) && key > keys[index] {
index++
}
return index
}
请注意,以上代码仅为示例,并不包含完整的B树实现。你需要根据具体的需求和B树结构进行适当的修改。
chatgpt:
在一棵B树中找出最小关键字的操作很简单,只需沿着左子树递归地向下查找直到叶节点即可。以下是用Go语言实现的示例代码:
package main
import (
"fmt"
)
// BTree节点结构定义
type BTreeNode struct {
isLeaf bool
keys []int
children []*BTreeNode
}
// 在BTree中找到最小关键字
func findMinKey(root *BTreeNode) int {
if root == nil {
return -1 // 表示树为空
}
current := root
for !current.isLeaf {
current = current.children[0]
}
return current.keys[0]
}
// 在BTree中找到给定关键字的前驱(假设关键字唯一)
func findPredecessor(root *BTreeNode, key int) int {
if root == nil {
return -1 // 表示树为空
}
predecessor := -1 // 默认设置为-1,表示不存在前驱
current := root
for true {
i := 0
for i < len(current.keys) && key > current.keys[i] { // 找到第一个大于等于key的索引i
i++
}
if i > 0 { // 如果当前节点存在小于key的关键字,则将其设置为前驱,并继续向左子树搜索
predecessor = current.keys[i-1]
current = current.children[i]
continue
}
if !current.isLeaf { // 当前节点不是叶节点,继续向左子树搜索
current = current.children[i]
} else {
break // 当前节点是叶节点,退出循环
}
}
return predecessor
}
func main() {
root := &BTreeNode{
isLeaf: true,
keys: []int{2, 4, 6, 8},
children: nil,
}
minKey := findMinKey(root)
fmt.Println("最小关键字:", minKey)
key := 5
predecessor := findPredecessor(root, key)
fmt.Printf("关键字 %d 的前驱:", key)
if predecessor == -1 {
fmt.Println("不存在")
} else {
fmt.Println(predecessor)
}
}
这段代码中,我们使用了一个简化的BTree结构(每个节点的关键字数量为3)。你可以根据实际情况修改代码来适应更复杂的BTree。
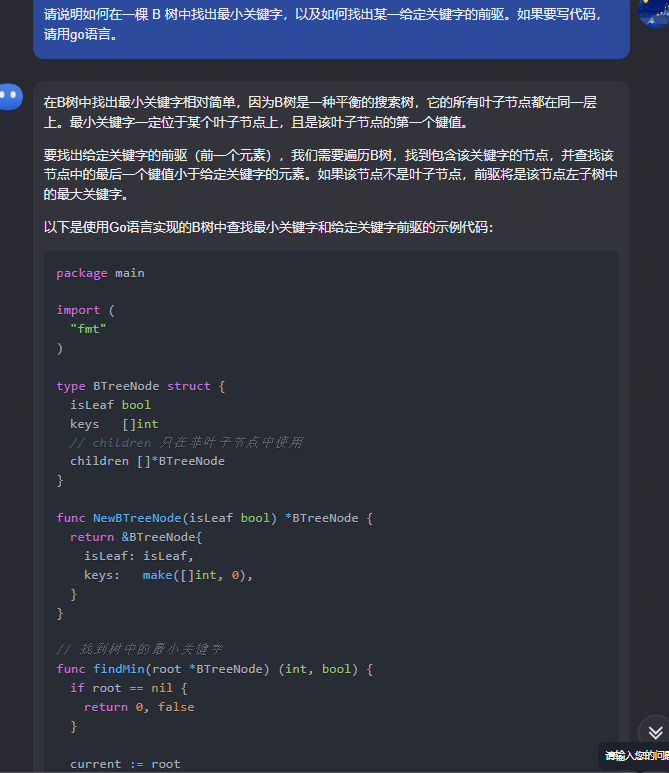
kimi:
在B树中找出最小关键字相对简单,因为B树是一种平衡的搜索树,它的所有叶子节点都在同一层上。最小关键字一定位于某个叶子节点上,且是该叶子节点的第一个键值。
要找出给定关键字的前驱(前一个元素),我们需要遍历B树,找到包含该关键字的节点,并查找该节点中的最后一个键值小于给定关键字的元素。如果该节点不是叶子节点,前驱将是该节点左子树中的最大关键字。
以下是使用Go语言实现的B树中查找最小关键字和给定关键字前驱的示例代码:
package main
import (
"fmt"
)
type BTreeNode struct {
isLeaf bool
keys []int
// children 只在非叶子节点中使用
children []*BTreeNode
}
func NewBTreeNode(isLeaf bool) *BTreeNode {
return &BTreeNode{
isLeaf: isLeaf,
keys: make([]int, 0),
}
}
// 找到树中的最小关键字
func findMin(root *BTreeNode) (int, bool) {
if root == nil {
return 0, false
}
current := root
for !current.isLeaf {
current = current.children[0]
}
return current.keys[0], true
}
// 找到给定关键字的前驱
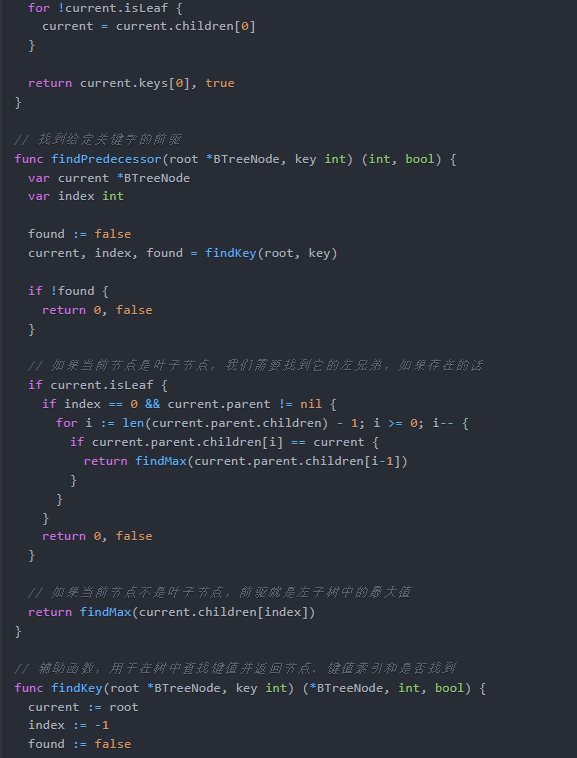
func findPredecessor(root *BTreeNode, key int) (int, bool) {
var current *BTreeNode
var index int
found := false
current, index, found = findKey(root, key)
if !found {
return 0, false
}
// 如果当前节点是叶子节点,我们需要找到它的左兄弟,如果存在的话
if current.isLeaf {
if index == 0 && current.parent != nil {
for i := len(current.parent.children) - 1; i >= 0; i-- {
if current.parent.children[i] == current {
return findMax(current.parent.children[i-1])
}
}
}
return 0, false
}
// 如果当前节点不是叶子节点,前驱就是左子树中的最大值
return findMax(current.children[index])
}
// 辅助函数,用于在树中查找键值并返回节点、键值索引和是否找到
func findKey(root *BTreeNode, key int) (*BTreeNode, int, bool) {
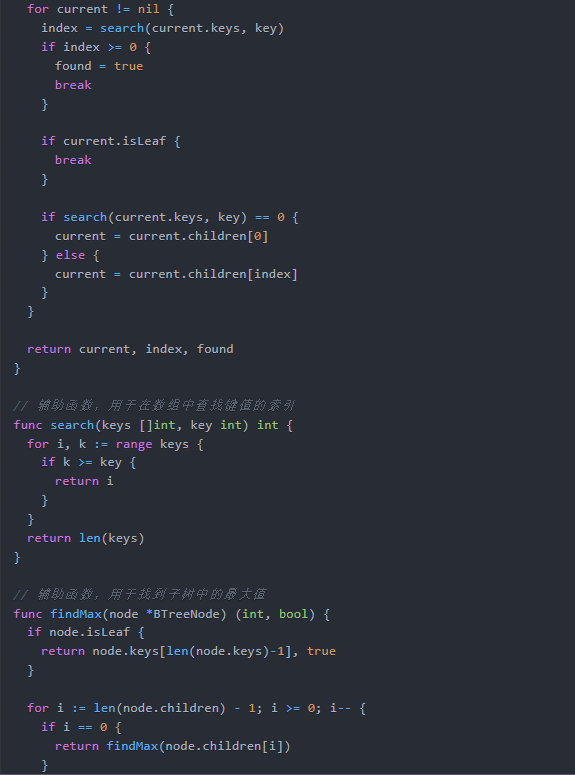
current := root
index := -1
found := false
for current != nil {
index = search(current.keys, key)
if index >= 0 {
found = true
break
}
if current.isLeaf {
break
}
if search(current.keys, key) == 0 {
current = current.children[0]
} else {
current = current.children[index]
}
}
return current, index, found
}
// 辅助函数,用于在数组中查找键值的索引
func search(keys []int, key int) int {
for i, k := range keys {
if k >= key {
return i
}
}
return len(keys)
}
// 辅助函数,用于找到子树中的最大值
func findMax(node *BTreeNode) (int, bool) {
if node.isLeaf {
return node.keys[len(node.keys)-1], true
}
for i := len(node.children) - 1; i >= 0; i-- {
if i == 0 {
return findMax(node.children[i])
}
_, found := findMax(node.children[i])
if found {
return node.keys[i-1], true
}
}
return 0, false
}
func main() {
// 示例:构建一个简单的 B 树并查找最小关键字和前驱
// 注意:这里的代码没有实现 B 树的构建和插入逻辑,只是用于演示查找操作
root := NewBTreeNode(true)
// 假设 root 已经被构建并包含了一些键值
minKey, found := findMin(root)
if found {
fmt.Printf("Minimum key is: %d\n", minKey)
} else {
fmt.Println("Minimum key not found")
}
predKey, found := findPredecessor(root, 20)
if found {
fmt.Printf("Predecessor of 20 is: %d\n", predKey)
} else {
fmt.Println("Predecessor not found")
}
}
在这个Go语言程序中,我们定义了 BTreeNode 结构体来表示 B 树的节点,并提供了 findMin 和 findPredecessor 函数来查找最小关键字和给定关键字的前驱。findKey 函数是一个辅助函数,用于在树中查找键值并返回节点、键值索引和是否找到。search 函数用于在数组中查找键值的索引,findMax 函数用于找到子树中的最大值。
请注意,这个程序没有实现 B 树的构建和插入逻辑,只是用于演示如何在 B 树中查找最小关键字和前驱。在实际应用中,B 树的实现会更加复杂,并且需要考虑磁盘I/O优化。
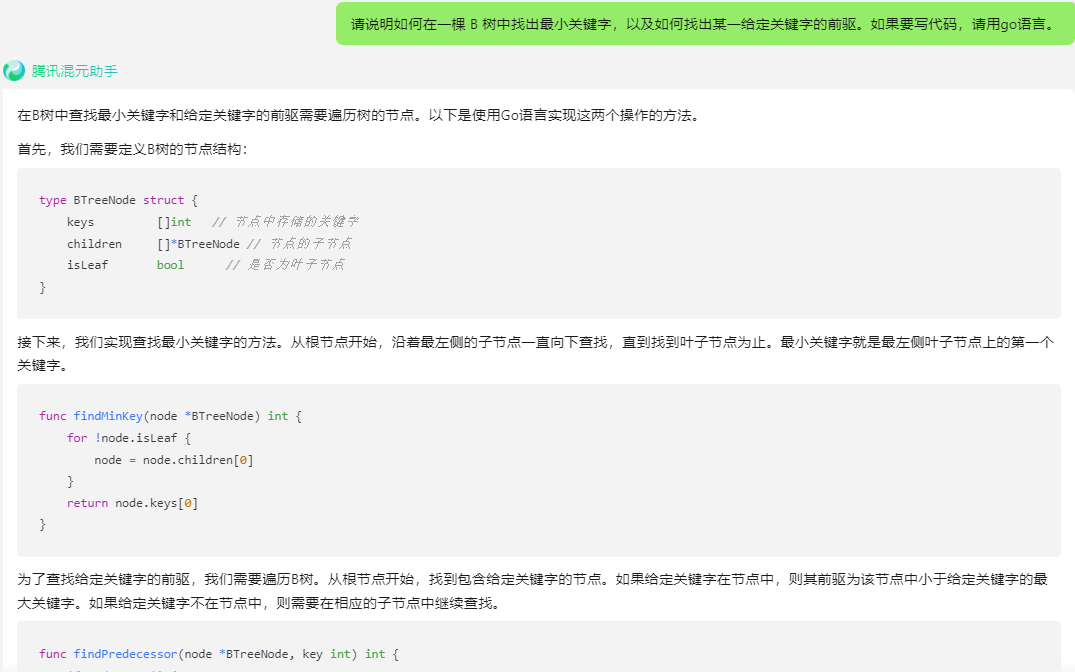
混元:
在B树中查找最小关键字和给定关键字的前驱需要遍历树的节点。以下是使用Go语言实现这两个操作的方法。
首先,我们需要定义B树的节点结构:
type BTreeNode struct {
keys []int // 节点中存储的关键字
children []*BTreeNode // 节点的子节点
isLeaf bool // 是否为叶子节点
}
接下来,我们实现查找最小关键字的方法。从根节点开始,沿着最左侧的子节点一直向下查找,直到找到叶子节点为止。最小关键字就是最左侧叶子节点上的第一个关键字。
func findMinKey(node *BTreeNode) int {
for !node.isLeaf {
node = node.children[0]
}
return node.keys[0]
}
为了查找给定关键字的前驱,我们需要遍历B树。从根节点开始,找到包含给定关键字的节点。如果给定关键字在节点中,则其前驱为该节点中小于给定关键字的最大关键字。如果给定关键字不在节点中,则需要在相应的子节点中继续查找。
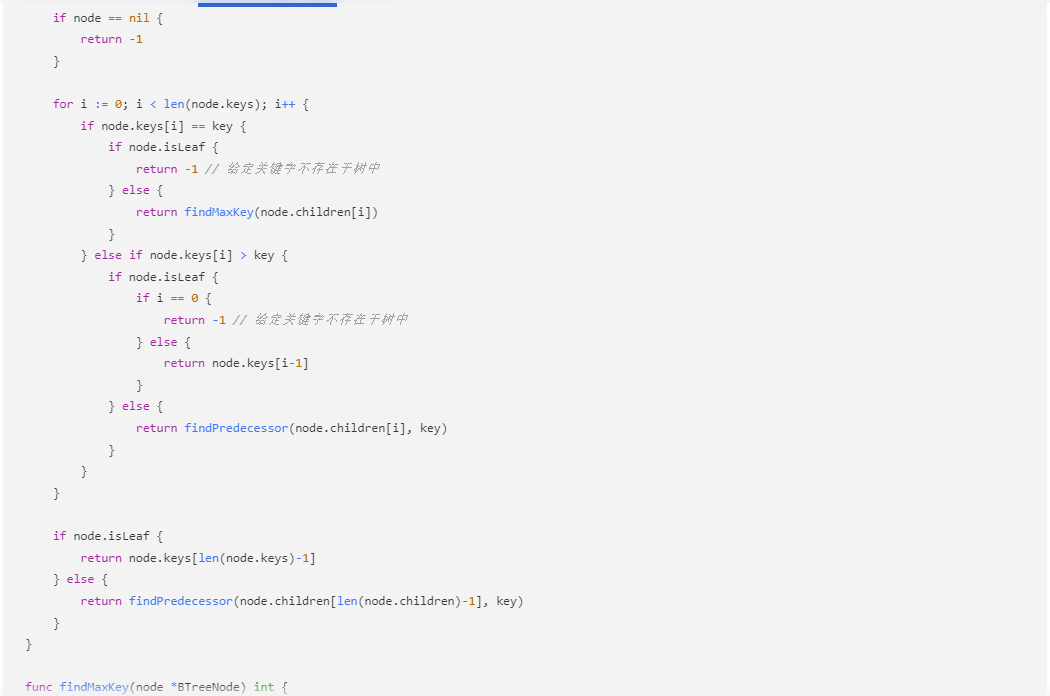
func findPredecessor(node *BTreeNode, key int) int {
if node == nil {
return -1
}
for i := 0; i < len(node.keys); i++ {
if node.keys[i] == key {
if node.isLeaf {
return -1 // 给定关键字不存在于树中
} else {
return findMaxKey(node.children[i])
}
} else if node.keys[i] > key {
if node.isLeaf {
if i == 0 {
return -1 // 给定关键字不存在于树中
} else {
return node.keys[i-1]
}
} else {
return findPredecessor(node.children[i], key)
}
}
}
if node.isLeaf {
return node.keys[len(node.keys)-1]
} else {
return findPredecessor(node.children[len(node.children)-1], key)
}
}
func findMaxKey(node *BTreeNode) int {
for !node.isLeaf {
node = node.children[len(node.children)-1]
}
return node.keys[len(node.keys)-1]
}
这样,我们就实现了在B树中查找最小关键字和给定关键字的前驱的方法。注意,这里的实现假设了B树中的关键字是唯一的。如果B树中存在重复关键字,需要根据具体需求进行相应的调整。