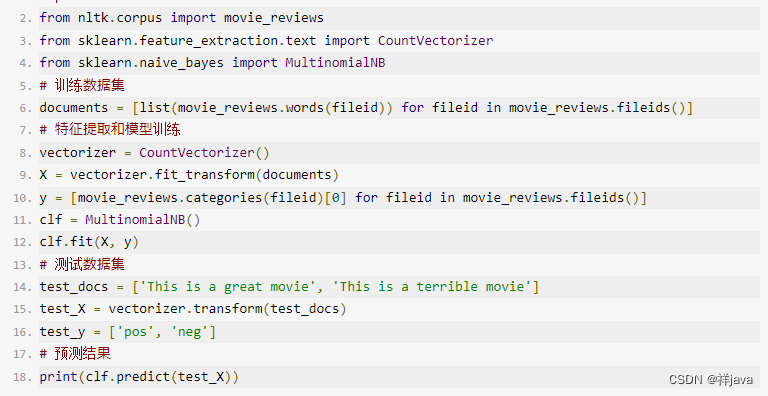
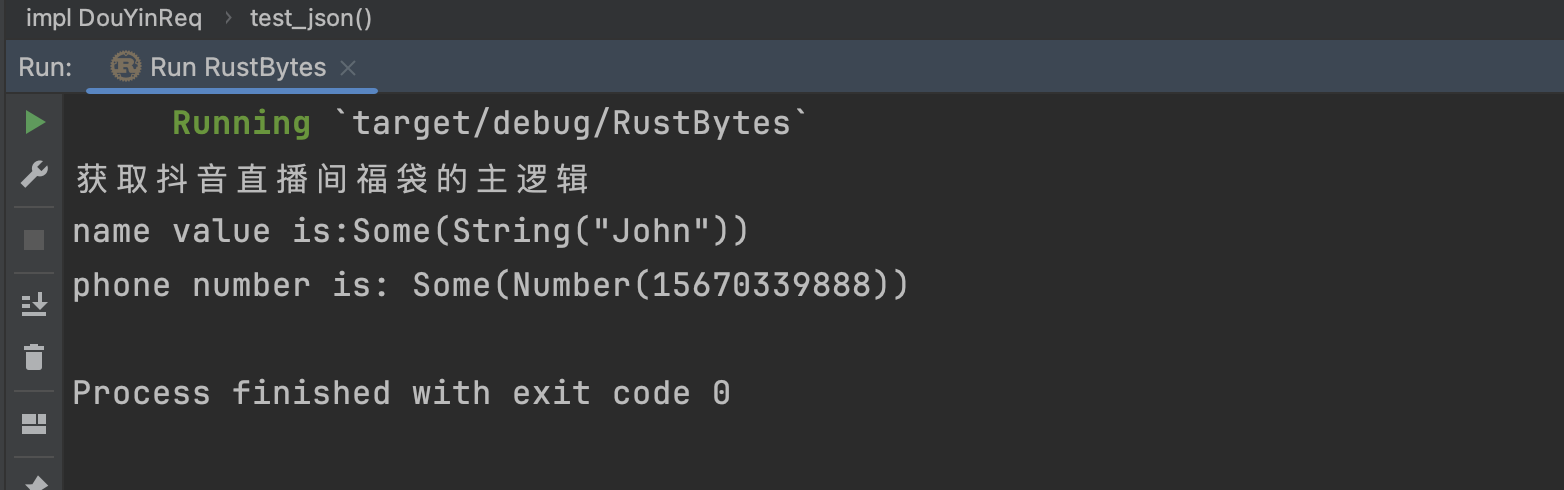
104 二叉树的最大深度
给定一个二叉树 root ,返回其最大深度。
二叉树的 最大深度 是指从根节点到最远叶子节点的最长路径上的节点数。
示例 1:
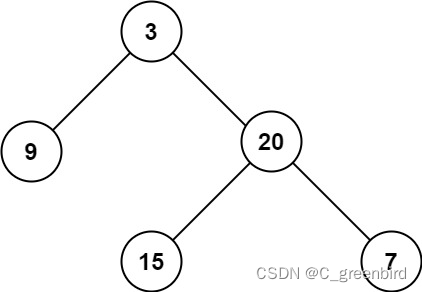
输入:root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
输出:3
示例 2:
输入:root = [1,null,2]
输出:2
提示:
树中节点的数量在
[
0
,
1
0
4
]
[0, 10^4]
[0,104] 区间内。
−
100
<
=
N
o
d
e
.
v
a
l
<
=
100
-100 <= Node.val <= 100
−100<=Node.val<=100
思路
(1)深度优先遍历DFS:
按深度往下遍历,先遍历左子树计算其深度l,再遍历右子树计算其深度r,那么该二叉树的最大深度就是max(l,r)+1。左右子树的深度也是如此计算,故用递归计算左右子树的最大深度+1即可。
(2)广度优先遍历BFS:
即二叉树的层次遍历,因为计算层数就可知道深度。不同于普通的层次遍历每次只取一个队列中的一个节点,计算深度需要每次取当前队列中的所有节点进行遍历。用ans记录深度。
代码
法一:
//DFS
class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == nullptr) {
return 0;
}
return max(maxDepth(root->left), maxDepth(root->right)) + 1;
}
};
法二:
// BFS
class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == nullptr) {
return 0;
}
queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push(root);
int ans = 0;
while (!q.empty()) {
int n = q.size();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
TreeNode* now = q.front();
q.pop();
if (now->left) {
q.push(now->left);
}
if (now->right) {
q.push(now->right);
}
}
ans++;
}
return ans;
}
};