NioServerSocketChannel
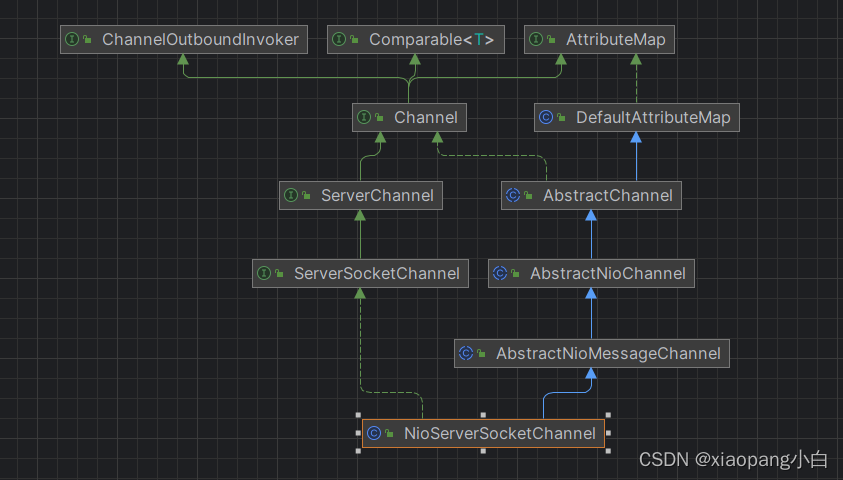
NioServerSocketChannel是netty服务端的channel。在ServerbootStrap的bind方法中,通过反射,实例化对象NioServerSocketChannel。
NioServerSocketChannel对象实例化的过程中。
AbstractChannel中实例化channel的id,unsafe,channelpipeline。AbstractNioChannel保存ServerSocketChannel,并设置感兴趣的事件SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT,设置ServerSocketChannel#configureBlocking为false。NioServerSocketChannel中对NioServerSocketChannelConfig对象进行构建,爆保存到类变量config中。NioServerSocketChannelConfig中包含了当前对象和通过ServerSocketChannel获取到的serverSocket对象。
AbstractNioMessageChannel这个父类中没有对属性赋值。它主要是对AbstractChannel中的抽象方法newUnsafe的实现。Unsafe的落地实现主要是处理NioEventLoop--》run--》processSelectedKeys--》processSelectedKey--》unsafe.read(),其中unsafe是当前channel父类abstractChannel中的unsafe。也就是说,当NioEventLoop中处理IO事件的时候,读取数据的时候,落地实现在AbstractNioMessageChannel的内部类NioMessageUnsafe。
NioMessageUnsafe中的doReadMessages方法,将数据读取到readBuf中。doReadMessages也是一个抽象方法,落地实现是NioServerSocketChannel。主要是做的事情是通过ServerSocketChannel.accept方法获取到SocketChannel,将这个SocketChannel封装成NioSocketChannel,添加到readBuf中。

NioMessageUnsafe中的fireChannelRead方法,将readBuf集合中的数据遍历调用channelPipeline的fireChannelRead方法。readBuf集合中存储的是NioSocketChannel。之前的学习我们知道,NioServerSocketChannel中的channelPipeline的链表结构为:headContext-->ServerBootstrapAcceptor-->tailContext。
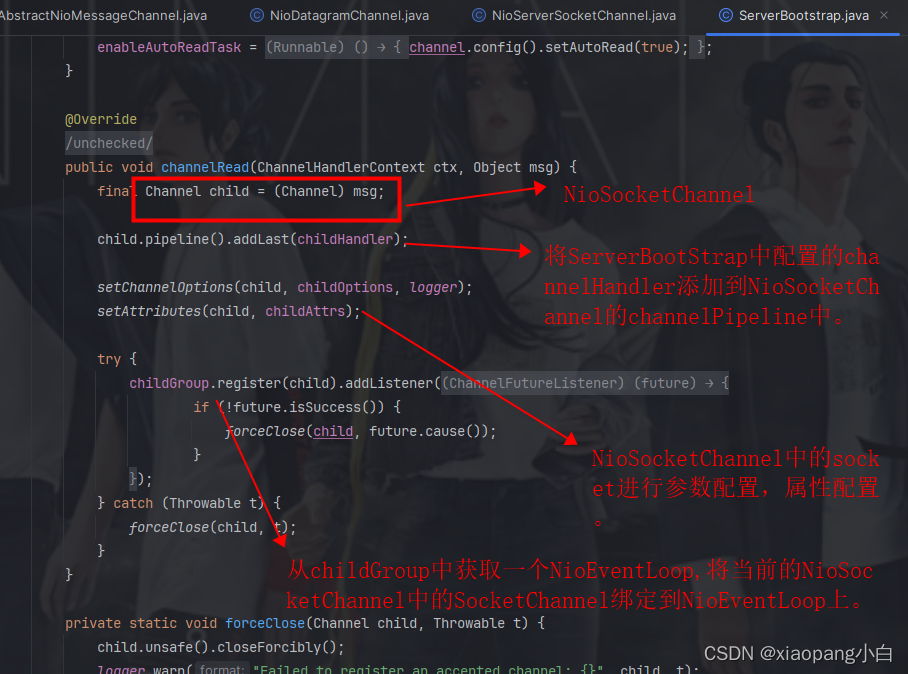
ServerBootstrapAcceptor中的channelRead方法,将客户端的请求socketChannel绑定到childGroup中的一个NioEventLoop上。
下面是AbstractNioMessageChannel 的原代码。
public abstract class AbstractNioMessageChannel extends AbstractNioChannel {
boolean inputShutdown;
/**
* @see AbstractNioChannel#AbstractNioChannel(Channel, SelectableChannel, int)
*/
protected AbstractNioMessageChannel(Channel parent, SelectableChannel ch, int readInterestOp) {
super(parent, ch, readInterestOp);
}
@Override
protected AbstractNioUnsafe newUnsafe() {
// 看这里,看这里,看这里。是对AbstractChannel的newUnsafe抽象方法的实现。
return new NioMessageUnsafe();
}
@Override
protected void doBeginRead() throws Exception {
if (inputShutdown) {
return;
}
super.doBeginRead();
}
protected boolean continueReading(RecvByteBufAllocator.Handle allocHandle) {
return allocHandle.continueReading();
}
// 看这里,看这里,看这里。内部类实现Unsafe
private final class NioMessageUnsafe extends AbstractNioUnsafe {
private final List<Object> readBuf = new ArrayList<Object>();
@Override
public void read() {
assert eventLoop().inEventLoop();
final ChannelConfig config = config();
final ChannelPipeline pipeline = pipeline();
final RecvByteBufAllocator.Handle allocHandle = unsafe().recvBufAllocHandle();
allocHandle.reset(config);
boolean closed = false;
Throwable exception = null;
try {
try {
do {
// 看这里,看这里,看这里。doReadMessages也是一个抽象方法,落地实现是NioServerSocketChannel。主要是做的事情是通过ServerSocketChannel.accept方法获取到SocketChannel,将这个SocketChannel封装成NioSocketChannel,添加到readBuf中。
int localRead = doReadMessages(readBuf);
if (localRead == 0) {
break;
}
if (localRead < 0) {
closed = true;
break;
}
allocHandle.incMessagesRead(localRead);
} while (continueReading(allocHandle));
} catch (Throwable t) {
exception = t;
}
int size = readBuf.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i ++) {
readPending = false;
// 看这里,看这里,看这里。调用NioServerSocketChannel的channelPipeline进行事件发布。readBuf里面存的是NioSocketChannel。
pipeline.fireChannelRead(readBuf.get(i));
}
readBuf.clear();
allocHandle.readComplete();
pipeline.fireChannelReadComplete();
if (exception != null) {
closed = closeOnReadError(exception);
pipeline.fireExceptionCaught(exception);
}
if (closed) {
inputShutdown = true;
if (isOpen()) {
close(voidPromise());
}
}
} finally {
// Check if there is a readPending which was not processed yet.
// This could be for two reasons:
// * The user called Channel.read() or ChannelHandlerContext.read() in channelRead(...) method
// * The user called Channel.read() or ChannelHandlerContext.read() in channelReadComplete(...) method
//
// See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/2254
if (!readPending && !config.isAutoRead()) {
removeReadOp();
}
}
}
}
@Override
protected void doWrite(ChannelOutboundBuffer in) throws Exception {
final SelectionKey key = selectionKey();
final int interestOps = key.interestOps();
int maxMessagesPerWrite = maxMessagesPerWrite();
while (maxMessagesPerWrite > 0) {
Object msg = in.current();
if (msg == null) {
break;
}
try {
boolean done = false;
for (int i = config().getWriteSpinCount() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
if (doWriteMessage(msg, in)) {
done = true;
break;
}
}
if (done) {
maxMessagesPerWrite--;
in.remove();
} else {
break;
}
} catch (Exception e) {
if (continueOnWriteError()) {
maxMessagesPerWrite--;
in.remove(e);
} else {
throw e;
}
}
}
if (in.isEmpty()) {
// Wrote all messages.
if ((interestOps & SelectionKey.OP_WRITE) != 0) {
key.interestOps(interestOps & ~SelectionKey.OP_WRITE);
}
} else {
// Did not write all messages.
if ((interestOps & SelectionKey.OP_WRITE) == 0) {
key.interestOps(interestOps | SelectionKey.OP_WRITE);
}
}
}
/**
* Returns {@code true} if we should continue the write loop on a write error.
*/
protected boolean continueOnWriteError() {
return false;
}
protected boolean closeOnReadError(Throwable cause) {
if (!isActive()) {
// If the channel is not active anymore for whatever reason we should not try to continue reading.
return true;
}
if (cause instanceof PortUnreachableException) {
return false;
}
if (cause instanceof IOException) {
// ServerChannel should not be closed even on IOException because it can often continue
// accepting incoming connections. (e.g. too many open files)
return !(this instanceof ServerChannel);
}
return true;
}
/**
* Read messages into the given array and return the amount which was read.
*/
protected abstract int doReadMessages(List<Object> buf) throws Exception;
/**
* Write a message to the underlying {@link java.nio.channels.Channel}.
*
* @return {@code true} if and only if the message has been written
*/
protected abstract boolean doWriteMessage(Object msg, ChannelOutboundBuffer in) throws Exception;
}
NioSocketChannel
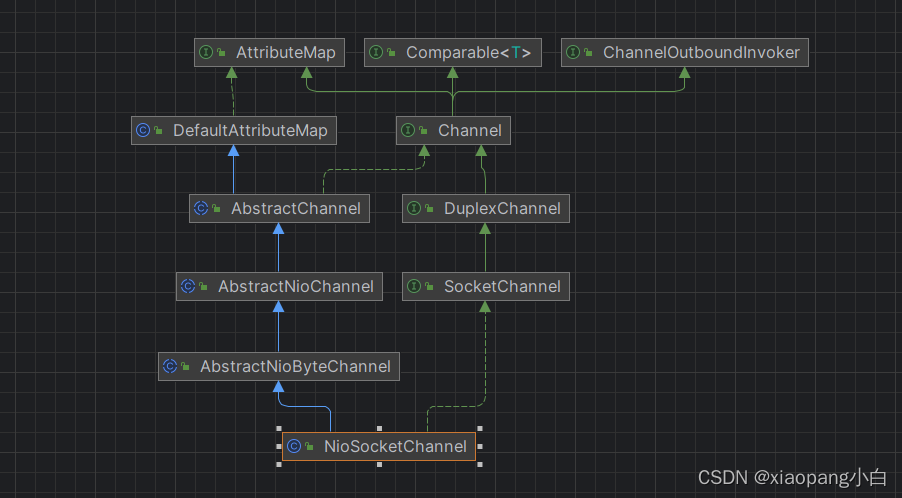
NioSocketChannel是netty封装的客户端请求的channel。
与上面的NioServerSocketChannel相比。继承类中将AbstractNioMessageChannel 替换为了AbstractNioByteChannel。从名称上看,是对字节数据的处理。下面就单独研究一下AbstractNioByteChannel。
AbstractNioByteChannel。同样的,在NioSocketChannel实例化的时候,这个类没有属性赋值。它主要也是实现AbstractChannel中的newUnsafe抽象方法。
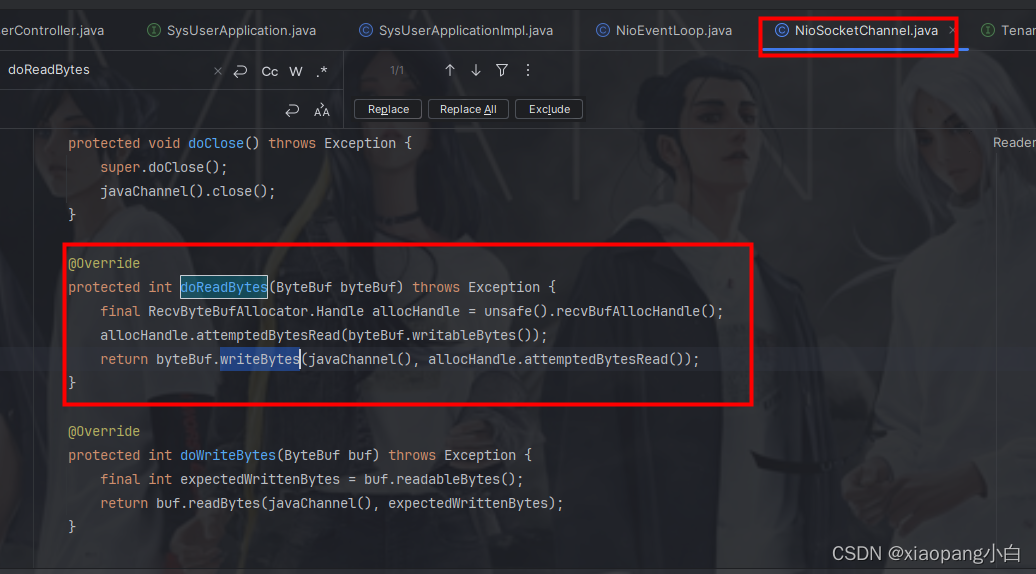
newUnsafe的实现也是AbstractNioByteChannel的内部类NioByteUnsafe 。NioByteUnsafe 读取数据是调用抽象方法doReadBytes。doReadBytes的落地实现在NioSocketChannel中。
以下是AbstractNioByteChannel 的原码。
public abstract class AbstractNioByteChannel extends AbstractNioChannel {
private static final ChannelMetadata METADATA = new ChannelMetadata(false, 16);
private static final String EXPECTED_TYPES =
" (expected: " + StringUtil.simpleClassName(ByteBuf.class) + ", " +
StringUtil.simpleClassName(FileRegion.class) + ')';
private final Runnable flushTask = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
// Calling flush0 directly to ensure we not try to flush messages that were added via write(...) in the
// meantime.
((AbstractNioUnsafe) unsafe()).flush0();
}
};
private boolean inputClosedSeenErrorOnRead;
/**
* Create a new instance
*
* @param parent the parent {@link Channel} by which this instance was created. May be {@code null}
* @param ch the underlying {@link SelectableChannel} on which it operates
*/
protected AbstractNioByteChannel(Channel parent, SelectableChannel ch) {
super(parent, ch, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
}
/**
* Shutdown the input side of the channel.
*/
protected abstract ChannelFuture shutdownInput();
protected boolean isInputShutdown0() {
return false;
}
@Override
protected AbstractNioUnsafe newUnsafe() {
// 看这里,看这里,看这里。实现是内部类NioByteUnsafe
return new NioByteUnsafe();
}
@Override
public ChannelMetadata metadata() {
return METADATA;
}
final boolean shouldBreakReadReady(ChannelConfig config) {
return isInputShutdown0() && (inputClosedSeenErrorOnRead || !isAllowHalfClosure(config));
}
private static boolean isAllowHalfClosure(ChannelConfig config) {
return config instanceof SocketChannelConfig &&
((SocketChannelConfig) config).isAllowHalfClosure();
}
// 看这里,看这里,看这里,实现newUnsafe的内部类
protected class NioByteUnsafe extends AbstractNioUnsafe {
private void closeOnRead(ChannelPipeline pipeline) {
if (!isInputShutdown0()) {
if (isAllowHalfClosure(config())) {
shutdownInput();
pipeline.fireUserEventTriggered(ChannelInputShutdownEvent.INSTANCE);
} else {
close(voidPromise());
}
} else if (!inputClosedSeenErrorOnRead) {
inputClosedSeenErrorOnRead = true;
pipeline.fireUserEventTriggered(ChannelInputShutdownReadComplete.INSTANCE);
}
}
private void handleReadException(ChannelPipeline pipeline, ByteBuf byteBuf, Throwable cause, boolean close,
RecvByteBufAllocator.Handle allocHandle) {
if (byteBuf != null) {
if (byteBuf.isReadable()) {
readPending = false;
pipeline.fireChannelRead(byteBuf);
} else {
byteBuf.release();
}
}
allocHandle.readComplete();
pipeline.fireChannelReadComplete();
pipeline.fireExceptionCaught(cause);
// If oom will close the read event, release connection.
// See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/10434
if (close || cause instanceof OutOfMemoryError || cause instanceof IOException) {
closeOnRead(pipeline);
}
}
// 看这里,看这里,看这里,我们重点看看read()方法。
@Override
public final void read() {
// 获取NioSocketChannelConfig对象
final ChannelConfig config = config();
if (shouldBreakReadReady(config)) {
clearReadPending();
return;
}
// 获取NioSocketChannel的channelPipeline
final ChannelPipeline pipeline = pipeline();
final ByteBufAllocator allocator = config.getAllocator();
final RecvByteBufAllocator.Handle allocHandle = recvBufAllocHandle();
allocHandle.reset(config);
ByteBuf byteBuf = null;
boolean close = false;
try {
do {
byteBuf = allocHandle.allocate(allocator);
// 看这里,看这里,看这里,将数据读取到byteBuf中。doReadBytes
allocHandle.lastBytesRead(doReadBytes(byteBuf));
if (allocHandle.lastBytesRead() <= 0) {
// nothing was read. release the buffer.
byteBuf.release();
byteBuf = null;
close = allocHandle.lastBytesRead() < 0;
if (close) {
// There is nothing left to read as we received an EOF.
readPending = false;
}
break;
}
allocHandle.incMessagesRead(1);
readPending = false;
// 看这里,看这里,看这里,将读取到的数据在pipeline中进行事件传播。
pipeline.fireChannelRead(byteBuf);
byteBuf = null;
} while (allocHandle.continueReading());
allocHandle.readComplete();
pipeline.fireChannelReadComplete();
if (close) {
closeOnRead(pipeline);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
handleReadException(pipeline, byteBuf, t, close, allocHandle);
} finally {
// Check if there is a readPending which was not processed yet.
// This could be for two reasons:
// * The user called Channel.read() or ChannelHandlerContext.read() in channelRead(...) method
// * The user called Channel.read() or ChannelHandlerContext.read() in channelReadComplete(...) method
//
// See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/2254
if (!readPending && !config.isAutoRead()) {
removeReadOp();
}
}
}
}
/**
* Write objects to the OS.
* @param in the collection which contains objects to write.
* @return The value that should be decremented from the write quantum which starts at
* {@link ChannelConfig#getWriteSpinCount()}. The typical use cases are as follows:
* <ul>
* <li>0 - if no write was attempted. This is appropriate if an empty {@link ByteBuf} (or other empty content)
* is encountered</li>
* <li>1 - if a single call to write data was made to the OS</li>
* <li>{@link ChannelUtils#WRITE_STATUS_SNDBUF_FULL} - if an attempt to write data was made to the OS, but no
* data was accepted</li>
* </ul>
* @throws Exception if an I/O exception occurs during write.
*/
protected final int doWrite0(ChannelOutboundBuffer in) throws Exception {
Object msg = in.current();
if (msg == null) {
// Directly return here so incompleteWrite(...) is not called.
return 0;
}
return doWriteInternal(in, in.current());
}
private int doWriteInternal(ChannelOutboundBuffer in, Object msg) throws Exception {
if (msg instanceof ByteBuf) {
ByteBuf buf = (ByteBuf) msg;
if (!buf.isReadable()) {
in.remove();
return 0;
}
final int localFlushedAmount = doWriteBytes(buf);
if (localFlushedAmount > 0) {
in.progress(localFlushedAmount);
if (!buf.isReadable()) {
in.remove();
}
return 1;
}
} else if (msg instanceof FileRegion) {
FileRegion region = (FileRegion) msg;
if (region.transferred() >= region.count()) {
in.remove();
return 0;
}
long localFlushedAmount = doWriteFileRegion(region);
if (localFlushedAmount > 0) {
in.progress(localFlushedAmount);
if (region.transferred() >= region.count()) {
in.remove();
}
return 1;
}
} else {
// Should not reach here.
throw new Error();
}
return WRITE_STATUS_SNDBUF_FULL;
}
@Override
protected void doWrite(ChannelOutboundBuffer in) throws Exception {
int writeSpinCount = config().getWriteSpinCount();
do {
Object msg = in.current();
if (msg == null) {
// Wrote all messages.
clearOpWrite();
// Directly return here so incompleteWrite(...) is not called.
return;
}
writeSpinCount -= doWriteInternal(in, msg);
} while (writeSpinCount > 0);
incompleteWrite(writeSpinCount < 0);
}
@Override
protected final Object filterOutboundMessage(Object msg) {
if (msg instanceof ByteBuf) {
ByteBuf buf = (ByteBuf) msg;
if (buf.isDirect()) {
return msg;
}
return newDirectBuffer(buf);
}
if (msg instanceof FileRegion) {
return msg;
}
throw new UnsupportedOperationException(
"unsupported message type: " + StringUtil.simpleClassName(msg) + EXPECTED_TYPES);
}
protected final void incompleteWrite(boolean setOpWrite) {
// Did not write completely.
if (setOpWrite) {
setOpWrite();
} else {
// It is possible that we have set the write OP, woken up by NIO because the socket is writable, and then
// use our write quantum. In this case we no longer want to set the write OP because the socket is still
// writable (as far as we know). We will find out next time we attempt to write if the socket is writable
// and set the write OP if necessary.
clearOpWrite();
// Schedule flush again later so other tasks can be picked up in the meantime
eventLoop().execute(flushTask);
}
}
/**
* Write a {@link FileRegion}
*
* @param region the {@link FileRegion} from which the bytes should be written
* @return amount the amount of written bytes
*/
protected abstract long doWriteFileRegion(FileRegion region) throws Exception;
/**
* Read bytes into the given {@link ByteBuf} and return the amount.
*/
protected abstract int doReadBytes(ByteBuf buf) throws Exception;
/**
* Write bytes form the given {@link ByteBuf} to the underlying {@link java.nio.channels.Channel}.
* @param buf the {@link ByteBuf} from which the bytes should be written
* @return amount the amount of written bytes
*/
protected abstract int doWriteBytes(ByteBuf buf) throws Exception;
protected final void setOpWrite() {
final SelectionKey key = selectionKey();
// Check first if the key is still valid as it may be canceled as part of the deregistration
// from the EventLoop
// See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/2104
if (!key.isValid()) {
return;
}
final int interestOps = key.interestOps();
if ((interestOps & SelectionKey.OP_WRITE) == 0) {
key.interestOps(interestOps | SelectionKey.OP_WRITE);
}
}
protected final void clearOpWrite() {
final SelectionKey key = selectionKey();
// Check first if the key is still valid as it may be canceled as part of the deregistration
// from the EventLoop
// See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/2104
if (!key.isValid()) {
return;
}
final int interestOps = key.interestOps();
if ((interestOps & SelectionKey.OP_WRITE) != 0) {
key.interestOps(interestOps & ~SelectionKey.OP_WRITE);
}
}
}