- 前言
- 1. 初步认识双向链表
- 1.1 定义
- 1.2 结构
- 1.3 储存
- 2. 双向链表的方法(接口函数)
- 2.1 动态申请空间
- 2.2 创建哨兵位
- 2.3 查找指定数据
- 2.4 指定位置插入
- 2.5 指定位置删除
- 2.6 头部插入
- 2.7 头部删除
- 2.8 尾部插入
- 2.9 尾部删除
- 2.10 计算链表大小
- 2.11 销毁链表
- 3. 双向链表的代码实现
- 结语

↓
上期回顾: 【数据结构|C语言版】顺序表应用
个人主页:C_GUIQU
专栏:【数据结构(C语言版)学习】
↑
前言
各位小伙伴大家好!上期小编给大家讲解了数据结构中的顺序表应用,接下来讲讲数据结构中的双向链表!

1. 初步认识双向链表
1.1 定义
双向链表也叫双链表,是链表的一种,它的每个数据结点中都有两个指针,分别指向直接后继和直接前驱。
1.2 结构
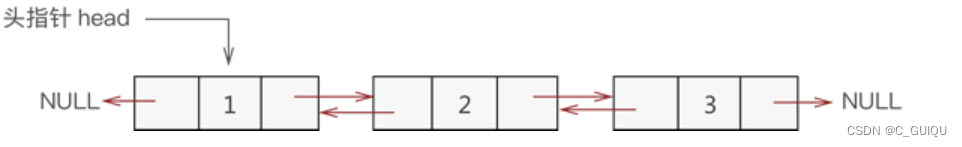
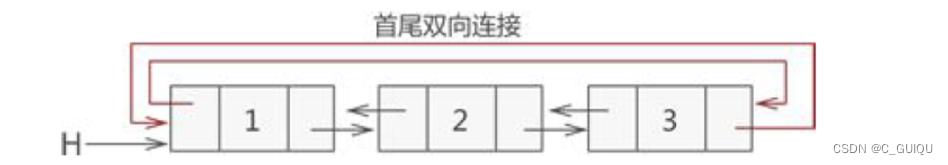
1.3 储存
//双链表节点结构体
typedef struct DoubleLinkNode
{
char data;
struct DoubleLinkNode* prior;
struct DoubleLinkNode* next;
} Node,*NodePtr;
2. 双向链表的方法(接口函数)
2.1 动态申请空间
【本质】动态开辟一块sizeof(ListNode)大小的空间进行存储
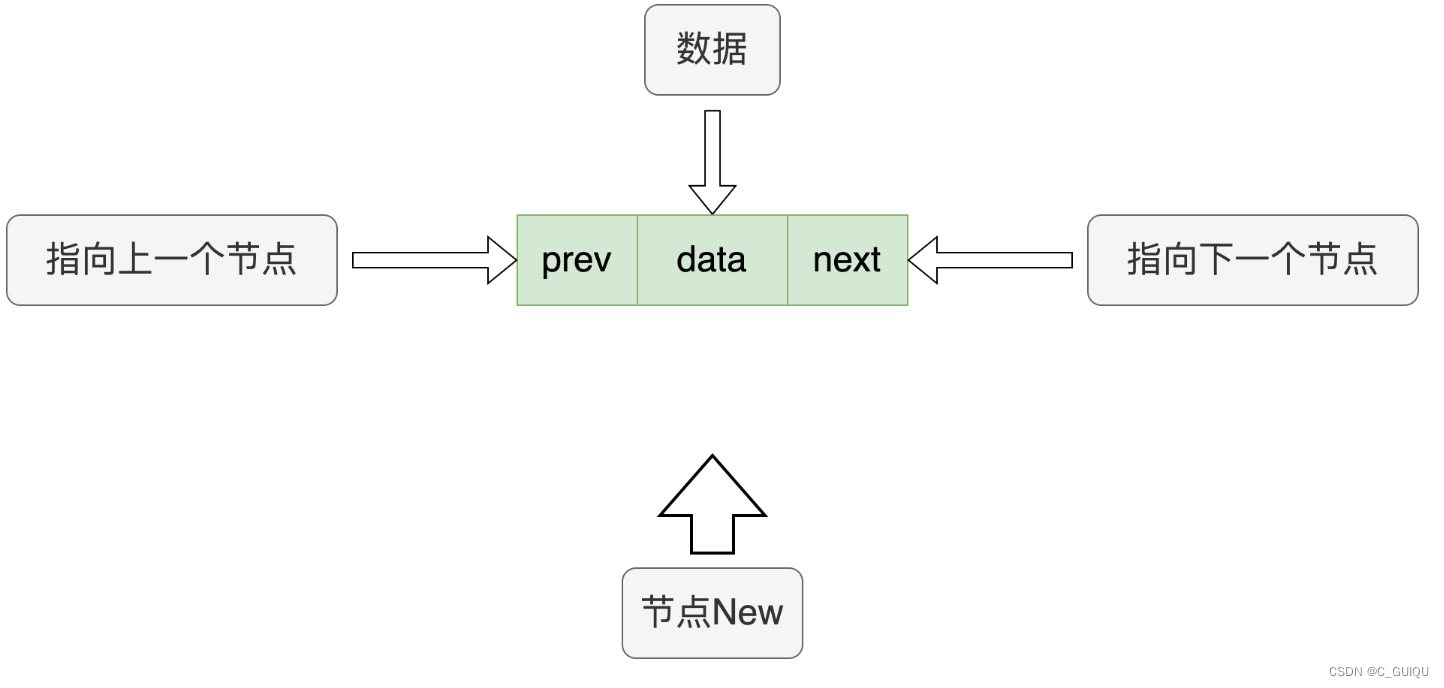
// 动态申请一个结点
ListNode *BuyListNode(LTDateType x) {
ListNode *node = (ListNode *) malloc(sizeof(ListNode));
node->data = x;
node->prev = NULL;
node->next = NULL;
return node;
}
2.2 创建哨兵位
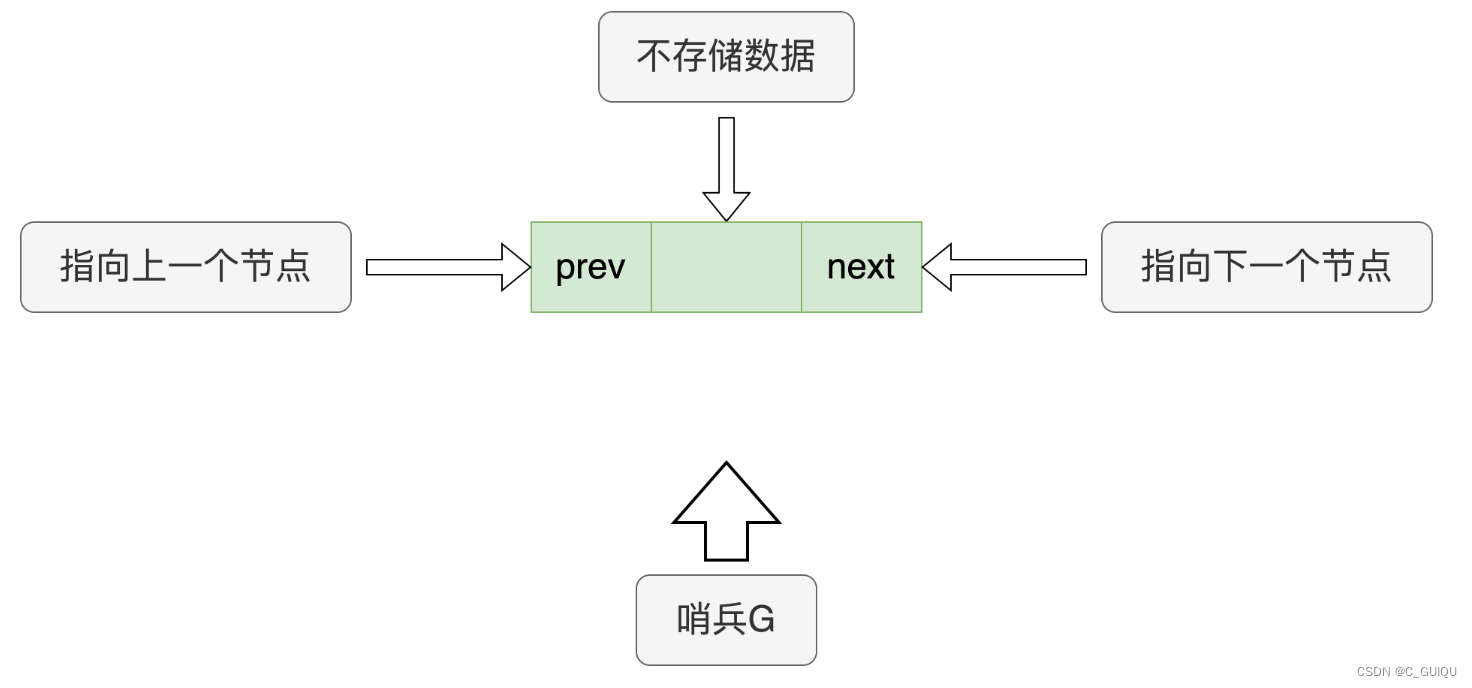
// 创建返回链表的哨兵位
ListNode *ListInit() {
ListNode *pHead = BuyListNode(-1);
pHead->prev = pHead;
pHead->next = pHead;
return pHead;
}
2.3 查找指定数据
// 双向链表查找
ListNode *ListFind(ListNode *pHead, LTDateType x) {
assert(pHead);
ListNode *curr = pHead->next;
while (curr != pHead) {
if (curr->data == x) {
return curr;
}
curr = curr->next;
}
return NULL;
}
2.4 指定位置插入
// 双向链表在pos位置插入x
void ListInsert(ListNode *pos, LTDateType x) {
assert(pos);
ListNode *newNode = BuyListNode(x);
ListNode *prev = pos->prev;
newNode->prev = prev;
newNode->next = pos;
prev->next = newNode;
pos->prev = newNode;
}
2.5 指定位置删除
// 双向链表在pos位置删除
void ListErase(ListNode *pos) {
assert(pos);
assert(pos != pos->next);
pos->next->prev = pos->prev;
pos->prev->next = pos->next;
free(pos);
}
2.6 头部插入
// 双向链表头插
void ListPushFront(ListNode *pHead, LTDateType x) {
ListInsert(pHead->next, x);
}
2.7 头部删除
// 双向链表头删
void ListPopFront(ListNode *pHead) {
ListErase(pHead->next);
}
2.8 尾部插入
// 双向链表尾插
void ListPushBack(ListNode *pHead, LTDateType x) {
ListInsert(pHead, x);
}
2.9 尾部删除
// 双向链表尾删
void ListPopBack(ListNode *pHead) {
ListErase(pHead->prev);
}
2.10 计算链表大小
// 计算大小
int ListSize(ListNode *pHead) {
ListNode *curr = pHead->next;
int size = 0;
while (curr != pHead) {
size++;
curr = curr->next;
}
return size;
}
2.11 销毁链表
// 销毁(手动置空)
void ListDestory(ListNode *pHead) {
ListNode *curr = pHead->next;
while (curr != pHead) {
ListNode *next = curr->next;
free(curr);
curr = next;
}
free(pHead);
}
3. 双向链表的代码实现
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int Linklength;
//双链表节点结构体
typedef struct DoubleLinkNode
{
char data;
struct DoubleLinkNode* prior;
struct DoubleLinkNode* next;
} Node,*NodePtr;
//初始化
NodePtr initLinkList()
{
NodePtr LinkHeader = (NodePtr)malloc(sizeof(Node));
LinkHeader->data = '\0';
LinkHeader->next = NULL;
LinkHeader->prior = NULL;
Linklength = 0;
return LinkHeader;
}
//寻找尾节点
NodePtr tailNodeSearch(NodePtr LinkHeader)
{
NodePtr p = LinkHeader;
while(p->next)
{
p = p->next;
}
return p;
}
//正向打印
void printListByHead(NodePtr LinkHeader)
{
NodePtr p = LinkHeader->next;
while (p)
{
printf("%c",p->data);
p = p->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
//反向打印
void printListByTail(NodePtr LinkHeader)
{
NodePtr tail = tailNodeSearch(LinkHeader);
NodePtr p = tail;
while (p)
{
printf("%c",p->data);
p = p->prior;
}
printf("\n");
}
//在某位置插入
void ListInsert(NodePtr LinkHeader, int InsertPosition, char InsertChar)
{
if(InsertPosition < 0 || InsertPosition > Linklength)
{
printf("The position %d out of range of linked list!\n",InsertPosition);
return ;
}
NodePtr p,q,r,tail;
p = LinkHeader;
for(int i = 0; i < InsertPosition; ++i)
{
p = p->next;
if(!p)
{
printf("The position %d out of range of linked list!\n",InsertPosition);
return ;
}
}
q = (NodePtr)malloc(sizeof(Node));
q->data = InsertChar;
r = p->next;
q->prior = p;
q->next = r;
p->next = q;
if(r)
{
r->prior = q;
}
Linklength++;
}
//删除第一个数据域为x的节点
void ListDeleteByData(NodePtr LinkHeader, char DeleteChar)
{
NodePtr p,q,r;
p = LinkHeader;
while(p->next && p->next->data != DeleteChar)
{
p = p->next;
}
if(!(p->next))
{
printf("The char '%c' does't exist.\n",DeleteChar);
return ;
}
q = p->next;
r = q->next;
p->next = r;
if(r)
{
r->prior = p;
}
free(q);
Linklength--;
}
//删除第Position个节点
void ListDeleteByPosition(NodePtr LinkHeader, int Position)
{
NodePtr p,q,r,tail;
int j = 0;
tail = tailNodeSearch(LinkHeader);
p = LinkHeader;
while(p->next && j < Position)
{
p = p->next;
++j;
}
if(!(p->next) || j > Position)
{
printf("Can't delete it!\n");
return ;
}
q = p->next;
r = q->next;
p->next = r;
if(r)
{
r->prior = p;
}
free(q);
Linklength--;
}
//链表节点的读取(打印链表中第position个数据元素的值)
void GetElement(NodePtr LinkHeader, int position)
{
NodePtr p,q,r;
if(position <= Linklength/2)
{
p = LinkHeader->next;
int j = 0;
while(p && j < position)
{
p = p->next;
++j;
}
if(!p || j > position)
{
printf("Can't get it !\n");
return ;
}
printf("The element at its %d-th position is %c\n",position,p->data);
}else
{
p = tailNodeSearch(LinkHeader);
int j = 0;
while(p->prior && j < Linklength-position-1)
{
p = p->prior;
++j;
}
if(!p || j > Linklength-position-1)
{
printf("Can't get it !\n");
return ;
}
printf("The element at its %d-th position is %c\n",position,p->data);
}
}
//测试
void insertDeleteTest()
{
printf("---------------Initialize bidirectional linked list--------------\n");
NodePtr tempList = initLinkList();
printListByHead(tempList);
printListByTail(tempList);
printf("---------------Inserts a node at the specified location--------------\n");
ListInsert(tempList,0,'H');
ListInsert(tempList,1,'e');
ListInsert(tempList,2,'l');
ListInsert(tempList,3,'l');
ListInsert(tempList,4,'o');
printListByHead(tempList);
printListByTail(tempList);
printf("---------------Gets the node data field at the specified location--------------\n");
GetElement(tempList,0);
GetElement(tempList,4);
GetElement(tempList,5);
printf("---------------Delete the first node whose data field is X--------------\n");
ListDeleteByData(tempList,'e');
printListByHead(tempList);
printListByTail(tempList);
printf("---------------Delete the position node--------------\n");
ListDeleteByPosition(tempList,3);
printListByHead(tempList);
printListByTail(tempList);
}
int main()
{
insertDeleteTest();
}
结语
以上就是小编对双向链表的讲解。
如果觉得小编讲的还可以,还请一键三连。互三必回!
持续更新中~!