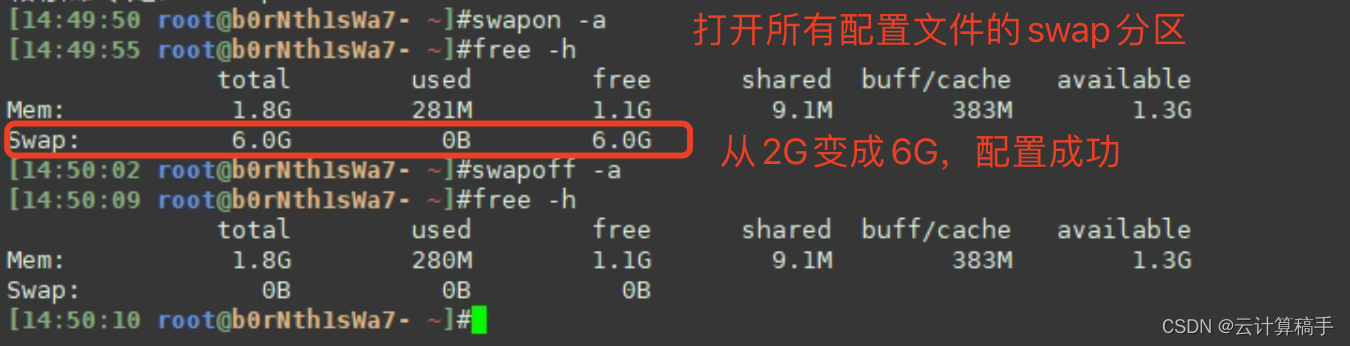
迭代器模式提供一种方法访问一个容器对象中各个元素,而又不需暴露该对象的内部细节。
设计模式,一定要敲代码理解

抽象迭代器
/**
* 迭代抽象
* */
public interface Iterator<A> {
A next();
boolean hasNext();
}
迭代器实现
/**
* @author ggbond
* @date 2024年04月13日 09:08
*/
public class MyIterator<T> implements Iterator<T>{
private MyCollection<T> myCollection;
private int size;
private int index; //索引游标
public MyIterator(MyCollection<T> myCollection) {
this.myCollection = myCollection;
this.index = 0;
this.size = myCollection.getSize();
}
@Override
public T next() {
if (index < size) {
return myCollection.getNext(index++);
}
return null;
}
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
return index < size;
}
}
抽象集合
/**
* 定义集合
* */
public interface Collection<A> {
boolean add(A a);
boolean remove(A a);
Iterator<A> createIterator();
}
集合实现
/**
* @author ggbond
* @date 2024年04月13日 09:12
*/
public class MyCollection<T> implements Collection<T>{
private ArrayList<T> list=new ArrayList<T>();
public int getSize() {
return list.size();
}
@Override
public boolean add(T t) {
return list.add(t);
}
@Override
public boolean remove(T t) {
return list.remove(t);
}
@Override
public Iterator createIterator() {
return new MyIterator(this);
}
public T getNext(int i) {
return list.get(i);
}
}
迭代对象
/**
* @author ggbond
* @date 2024年04月13日 09:29
*/
public class Person {
String name;
String cardID;
public Person(String name, String cardID) {
this.name = name;
this.cardID = cardID;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getCardID() {
return cardID;
}
public void setCardID(String cardID) {
this.cardID = cardID;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", cardID='" + cardID + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
测试与结果
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person p1= new Person("ggbond1","001");
Person p2= new Person("ggbond2","002");
Person p3= new Person("ggbond3","003");
Person p4= new Person("ggbond4","004");
Collection<Person> collection=new MyCollection<>();
collection.add(p1);
collection.add(p2);
collection.add(p3);
collection.add(p4);
Iterator<Person> iterator = collection.createIterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
}
}
Person{name='ggbond1', cardID='001'}
Person{name='ggbond2', cardID='002'}
Person{name='ggbond3', cardID='003'}
Person{name='ggbond4', cardID='004'}
总结
迭代器模式将数据存储和数据遍历的职责进行分离。但针对不同结构的迭代对象,迭代方式需进行添加。
代码下载
代码下载

![[大模型]Yi-6B-chat WebDemo 部署](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/d43df42102a341b4a443cece5c7e214a.png#pic_center)