题目:
给你一棵树,树上有 n 个节点,按从 0 到 n-1 编号。树以父节点数组的形式给出,其中 parent[i] 是节点 i 的父节点。树的根节点是编号为 0 的节点。
树节点的第 k 个祖先节点是从该节点到根节点路径上的第 k 个节点。
实现 TreeAncestor 类:
TreeAncestor(int n, int[] parent)对树和父数组中的节点数初始化对象。getKthAncestor(int node, int k)返回节点node的第k个祖先节点。如果不存在这样的祖先节点,返回-1。
示例 1:
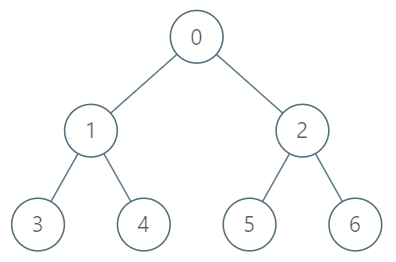
输入: ["TreeAncestor","getKthAncestor","getKthAncestor","getKthAncestor"] [[7,[-1,0,0,1,1,2,2]],[3,1],[5,2],[6,3]] 输出: [null,1,0,-1] 解释: TreeAncestor treeAncestor = new TreeAncestor(7, [-1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 2, 2]); treeAncestor.getKthAncestor(3, 1); // 返回 1 ,它是 3 的父节点 treeAncestor.getKthAncestor(5, 2); // 返回 0 ,它是 5 的祖父节点 treeAncestor.getKthAncestor(6, 3); // 返回 -1 因为不存在满足要求的祖先节点
提示:
1 <= k <= n <= 5 * 10^4parent[0] == -1表示编号为0的节点是根节点。- 对于所有的
0 < i < n,0 <= parent[i] < n总成立 0 <= node < n- 至多查询
5 * 10^4次
思路:
倍增,
倍增的思路类似于动态规划,定义 ancestors[i][j] 表示节点 i 的第 2^j个祖先。此题中,树最多有 50000个节点,因此 ancestors的第二维度的最大值可以设为 16。根据定义,ancestors[i][0]=parent[i]。状态转移方程是 ancestors[i][j]=ancestors[ancestors[i][j−1]][j−1], 即当前节点的第 2^j个祖先,是他的第 2^{j-1}个祖先的第2^{j-1}个祖先。当第 2^j个祖先不存在时,记为 −1。
查询时,需要将 k 的二进制表示从最低位到最高位依次进行判断,如果第 j 位为 1,则节点 node 需要进行转移到 ancestors[node][j],表示 node向祖先方向移动了 2^j次。直至遍历完 k 所有位或者 node变为 −1
java代码:
class TreeAncestor {
static final int LOG = 16;
int[][] ancestors;
public TreeAncestor(int n, int[] parent) {
ancestors = new int[n][LOG];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
Arrays.fill(ancestors[i], -1);
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
ancestors[i][0] = parent[i];
}
for (int j = 1; j < LOG; j++) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (ancestors[i][j - 1] != -1) {
ancestors[i][j] = ancestors[ancestors[i][j - 1]][j - 1];
}
}
}
}
public int getKthAncestor(int node, int k) {
for (int j = 0; j < LOG; j++) {
if (((k >> j) & 1) != 0) {
node = ancestors[node][j];
if (node == -1) {
return -1;
}
}
}
return node;
}
}
/**
* Your TreeAncestor object will be instantiated and called as such:
* TreeAncestor obj = new TreeAncestor(n, parent);
* int param_1 = obj.getKthAncestor(node,k);
*/





![[WIP]Sora相关工作汇总VQGAN、MAGVIT、VideoPoet](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/22aa1d0fcceb4c4081e72bd8d52d6907.png)