Spring
- 1、简介:
- 2、第一个程序
- 2、set注入
- 2.1 简单数据类型
- 2.2测试
- 2.3 注入Properties
- 2.4 p命名空间注入
- 2.5 c命名空间注入
- 2.6 util注入
- 2.6 引入外部配置文件
1、简介:
自己的理解:spring其实就是一个容器,也可以说是一个框架,主要是控制反转和面向切面编程。
控制反转IOC:是一种思想,就是把new对象的权力交给了spring,也把两个对象之间关系的连接交给了别人。
依赖注入DI:是控制反转的一种实现方式,依赖就是指对象A和对象B之间的关系,注入就是就是一种方式将对象A和对象B关联起来。
依赖注入DI,又包括常见的两种方式:
第一种:set注入(执行set方法给属性赋值)
第二种:构造方法注入(执行构造方法给属性赋值)
注意术语:
OCP:开闭原则(开发原则)
DIP:依赖倒置原则(开发原则)
IoC:控制反转(一种思想,一种新型的设计模式)
DI:依赖注入(控制反转思想的具体实现方式)
2、第一个程序
首先建立一个空项目
给该项目添加上jdk配置,即给该项目下的所有模块都进行了配置。
接着创建一个module模块
创建一个maven模块
在resoureces目录下配置spring xml文件配置,即在这里边进行依赖注入。
配置pom.xml(根据自己的需求)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.cky</groupId>
<artifactId>spring6-demo1</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>17</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>17</maven.compiler.target>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>6.1.5</version>
</dependency>
<!--log4j2的依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.logging.log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j-core</artifactId>
<version>2.19.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.logging.log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j-slf4j2-impl</artifactId>
<version>2.19.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.13.2</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
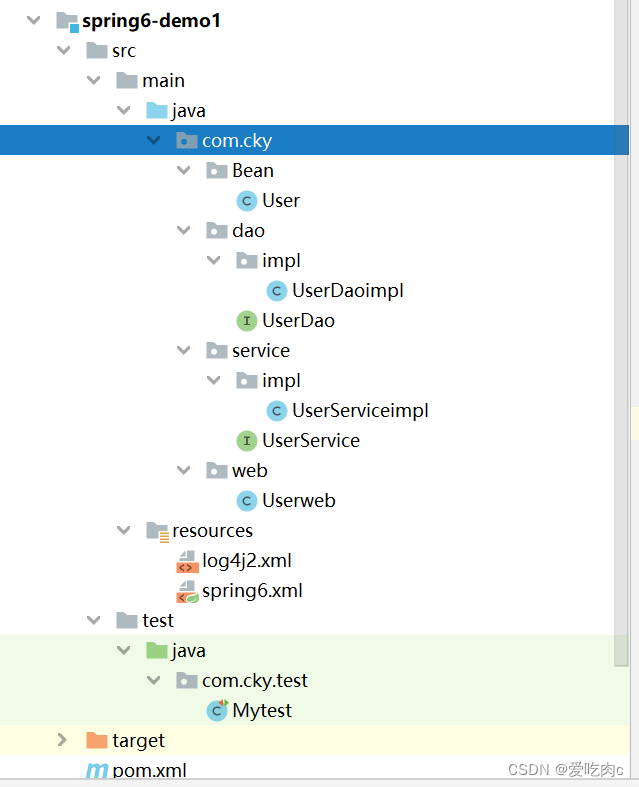
我的项目目录:
我的spring6.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="user" class="com.cky.Bean.User"></bean>
<bean id="userDaoimpl" class="com.cky.dao.impl.UserDaoimpl"></bean>
<bean id="userServiceimpl" class="com.cky.service.impl.UserServiceimpl">
<property name="userDao" ref="userDaoimpl"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="userweb" class="com.cky.web.Userweb">
<property name="userService" ref="userServiceimpl"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
set注入
name是set方法后边的字母(第一个字母小写),ref是要注入bean的id。
set注入是先实例化对象,在注入
构造注入
通过测试得知,通过构造方法注入的时候:
● 可以通过下标 index
● 可以通过参数名 name
● 也可以不指定下标和参数名,可以类型自动推断。
Spring在装配方面做的还是比较健壮的。
构造注入是实例化对象的同时就进行了依赖注入。
2、set注入
2.1 简单数据类型
public static boolean isSimpleValueType(Class<?> type) {
return (Void.class != type && void.class != type &&
(ClassUtils.isPrimitiveOrWrapper(type) ||
Enum.class.isAssignableFrom(type) ||
CharSequence.class.isAssignableFrom(type) ||
Number.class.isAssignableFrom(type) ||
Date.class.isAssignableFrom(type) ||
Temporal.class.isAssignableFrom(type) ||
URI.class == type ||
URL.class == type ||
Locale.class == type ||
Class.class == type));
}
通过源码分析得知,简单类型包括:
● 基本数据类型
● 基本数据类型对应的包装类
● String或其他的CharSequence子类
● Number子类
● Date子类
● Enum子类
● URI
● URL
● Temporal子类
● Locale
● Class
● 另外还包括以上简单值类型对应的数组类型。
2.2测试
package com.cky.Bean;
public class People {
private String name;
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "People{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
package com.cky.Bean;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
public class User {
private Class aClass;
private String[] names;
private List<People> peoples;
private Map<Integer,String> maps;
private Set<String> sets;
private String nulls;
private String email;
private String p;
public void setP(String p) {
this.p = p;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"aClass=" + aClass +
", names=" + Arrays.toString(names) +
", peoples=" + peoples +
", maps=" + maps +
", sets=" + sets +
", nulls='" + nulls + '\'' +
", email='" + email + '\'' +
", p='" + p + '\'' +
'}';
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
public void setNames(String[] names) {
this.names = names;
}
public void setPeoples(List<People> peoples) {
this.peoples = peoples;
}
public void setMaps(Map<Integer, String> maps) {
this.maps = maps;
}
public void setSets(Set<String> sets) {
this.sets = sets;
}
public void setNulls(String nulls) {
this.nulls = nulls;
}
public void setaClass(Class aClass) {
this.aClass = aClass;
}
public User(){
System.out.println("无参构造执行了");
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!-- private Class aClass;
private String[] names;
private List<People> peoples;
private Map<Integer,String> maps;
private Set<String> sets;
private String nulls;
private String email;-->
<bean name="people1" class="com.cky.Bean.People">
<property name="name" value="cui"></property>
</bean>
<bean name="people2" class="com.cky.Bean.People">
<property name="name" value="cky"></property>
</bean>
<bean name="user" class="com.cky.Bean.User">
<!-- 类 -->
<property name="aClass" value="java.lang.String"></property>
<!-- 数组-->
<property name="names">
<array>
<value>a</value>
<value>b</value>
</array>
</property>
<!-- list -->
<property name="peoples">
<list>
<ref bean="people1"></ref>
<ref bean="people2"></ref>
</list>
</property>
<!-- map-->
<property name="maps">
<map>
<entry key="1" value="vui"></entry>
<entry key="2" value="vui"></entry>
</map>
</property>
<!-- set-->
<property name="sets">
<set>
<value>ni</value>
<value>hao</value>
</set>
</property>
<!-- 空第一种形式-->
<!-- <property name="nulls" value=""/>-->
<!-- 第二种形式-->
<property name="nulls">
<value/>
</property>
<!-- null-->
<property name="email"><null/></property>
<!-- 或者只是不赋值 也为null-->
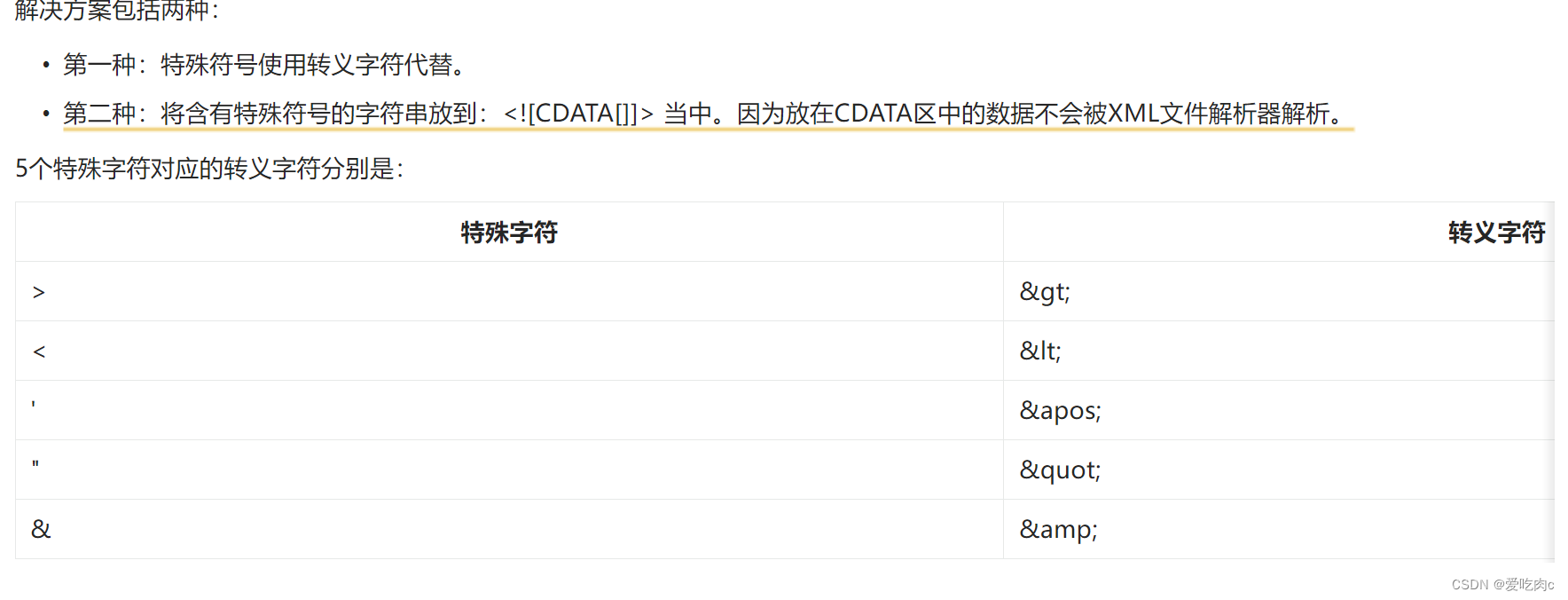
<property name="p">
<!-- 特殊字符-->
<value><![CDATA[2 < 3]]></value>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
package com.cky.test;
import com.cky.Bean.User;
import com.cky.web.Userweb;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class Mytest {
@Test
public void test(){
//获取spring容器
ApplicationContext applicationContext= new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring6_1.xml");
//获取对应的bean
User userweb = applicationContext.getBean("user", User.class);
System.out.println(userweb);
}
}
User{aClass=class java.lang.String, names=[a, b], peoples=[People{name=‘cui’}, People{name=‘cky’}], maps={1=vui, 2=vui}, sets=[ni, hao], nulls=‘’, email=‘null’, p=‘2 < 3’}
2.3 注入Properties
package com.powernode.spring6.beans;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Properties;
import java.util.Set;
/**
* @author 动力节点
* @version 1.0
* @className People
* @since 1.0
**/
public class People {
private Properties properties;
public void setProperties(Properties properties) {
this.properties = properties;
}
//......
@Override
public String toString() {
return "People{" +
"properties=" + properties +
", addrs=" + addrs +
", phones=" + phones +
", names=" + names +
'}';
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="peopleBean" class="com.powernode.spring6.beans.People">
<property name="properties">
<props>
<prop key="driver">com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver</prop>
<prop key="url">jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring</prop>
<prop key="username">root</prop>
<prop key="password">123456</prop>
</props>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
2.4 p命名空间注入
本质是set注入,需要提供set方法。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="peo" class="com.cky.Bean.People" p:name="cui"></bean>
</beans>
2.5 c命名空间注入
本质是构造注入,需要提供构造方法。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:c="http://www.springframework.org/schema/c"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!-- <bean name="cat" class="com.cky.Bean.Cat" c:_0="k" c:_1="2"></bean>-->
<!-- 或者-->
<bean id="cat" class="com.cky.Bean.Cat" c:name="3" c:age="2"></bean>
</beans>
2.6 util注入
可以使得内容共享。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util.xsd">
<util:properties id="dogbean">
<prop key="name">k</prop>
<prop key="age">2</prop>
<prop key="sex">男</prop>
</util:properties>
<bean name="dog1" class="com.cky.Bean.Dog">
<property name="properties" ref="dogbean"></property>
</bean>
<bean name="dog2" class="com.cky.Bean.Dog">
<property name="properties" ref="dogbean"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
2.6 引入外部配置文件
比如数据源的driver,password,url等配置,我们想要配置到一个jdbc.properties
文件中,然后通过读取该配置文件的值,为我们的类赋值。
DataSource .java
package com.cky.Bean;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.SQLFeatureNotSupportedException;
import java.util.logging.Logger;
public class DataSource implements javax.sql.DataSource {
private String url;
private String driver;
private String password;
private String username;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "DataSource{" +
"url='" + url + '\'' +
", driver='" + driver + '\'' +
", password='" + password + '\'' +
", username='" + username + '\'' +
'}';
}
public void setUrl(String url) {
this.url = url;
}
public void setDriver(String driver) {
this.driver = driver;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
@Override
public Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
return null;
}
@Override
public Connection getConnection(String username, String password) throws SQLException {
return null;
}
@Override
public PrintWriter getLogWriter() throws SQLException {
return null;
}
@Override
public void setLogWriter(PrintWriter out) throws SQLException {
}
@Override
public void setLoginTimeout(int seconds) throws SQLException {
}
@Override
public int getLoginTimeout() throws SQLException {
return 0;
}
@Override
public Logger getParentLogger() throws SQLFeatureNotSupportedException {
return null;
}
@Override
public <T> T unwrap(Class<T> iface) throws SQLException {
return null;
}
@Override
public boolean isWrapperFor(Class<?> iface) throws SQLException {
return false;
}
}
jdbc.properties
driver=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url=jdbc:mysql//127.0.0.1:3306/spring
username=root
passwoed=123456
spring_pro.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<context:property-placeholder location="jdbc.properties"></context:property-placeholder>
<bean id="datasource" class="com.cky.Bean.DataSource">
<property name="driver" value="${driver}"></property>
<property name="url" value="${url}"></property>
<property name="password" value="${passwoed}"></property>
<property name="username" value="${username}"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
测试类
@Test
public void test4(){
//获取spring容器
ApplicationContext applicationContext= new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring_pro.xml");
DataSource datasource = applicationContext.getBean("datasource", DataSource.class);
System.out.println(datasource);}
}
DataSource{url=‘jdbc:mysql//127.0.0.1:3306/spring’, driver=‘com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver’, password=‘123456’, username=‘10945’}
注意,这里我们读取到的username是系统的名称,使用 ${} 会让我们先获取到的是 系统变量,所以最好加上前缀。
jdbc.driver=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql//127.0.0.1:3306/spring
jdbc.username=root
jdbc.passwoed=123456