栈和队列
- 栈
- 1.1栈的概念和结构
- 1.2栈的实现
- 队列
- 2.1队列的概念及结构
- 2.2队列的实现
- 2.3循环队列
- 栈和队列笔试题
- 3.1[有效的括号](https://leetcode.cn/problems/valid-parentheses/submissions/516297357/)
- 3.2[用队列实现栈](https://leetcode.cn/problems/implement-stack-using-queues/)
- 3.3[栈实现队列](https://leetcode.cn/problems/implement-queue-using-stacks/)
- 3.4[设计循环队列](https://leetcode.cn/problems/design-circular-queue/description/)
栈
1.1栈的概念和结构
栈:一种特殊的线性表,其只允许在固定的一端进行插入和删除元素操作。进行数据插入和删除操作的一端称为栈顶,另一端称为栈底。(先进后出也称之为LIFO)
栈的操作
压栈:栈的插入操作叫做进栈/压栈/入栈,入数据在栈顶
出栈:栈的删除操作叫做出栈,出数据也在栈顶.
1.2栈的实现
栈的实现可用数组或者链表实现,数组的话会更好些,因为在数组尾插尾删代价小
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
typedef int STDataType;
typedef struct Stack
{
STDataType* a;
int top;
int capacity;
}ST;
//初始化
void STInit(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
pst->a = NULL;
pst->top = 0;//top为最后一个元素的下一个位置
pst->capacity = 0;
}
//销毁栈
void STDestroy(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
free(pst->a);
pst->a = NULL;
pst->top = 0;
pst->capacity = 0;
}
//入栈
void STPush(ST* pst,STDataType x)
{
if (pst->top == pst->capacity)
{
int newcapacity = pst->capacity == 0 ? 4 : pst->capacity * 2;
STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(pst->a,sizeof(STDataType) * newcapacity);
if (tmp == NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
return;
}
pst->a = tmp;
pst->capacity = newcapacity;
}
pst->a[pst->top] = x;
pst->top++;
}
//判空
bool STEmpty(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
return pst->top == 0;
}
//出栈
void STPop(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
assert(!STEmpty(pst));
pst->top--;
}
//显示栈顶元素
STDataType STTop(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
assert(!STEmpty(pst));
return pst->a[pst->top - 1];
}
//栈内元素个数
int STSize(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
return pst->top;
}
队列
2.1队列的概念及结构
队列:只允许在一端进行插入数据操作,在另一端进行删除数据操作的特殊线性表,队列具有先进先出(FIFO)
入队列:进行插入操作的一端称为队尾 出队列:进行删除操作的一端称为队头
2.2队列的实现
队列:数组和链表的结构都可以实现,使用链表的结构实现更优一些,因为如果使用数组的结构,出队列在数组头上出数据,效率会比较低。
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
typedef int QDataType;
typedef struct QueueNode
{
struct QueueNode* next;
QDataType data;
}QNode;
typedef struct Queue
{
QNode* phead;
QNode* ptail;
int size;
}Queue;
void QueueInit(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
pq->phead = NULL;
pq->ptail = NULL;
pq->size = 0;
}
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* cur = pq->phead;
while (cur)
{
QNode* next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL;
pq->size = 0;
}
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->size == 0;
}
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
if (newnode == NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail\n");
return;
}
newnode->next = NULL;
newnode->data = x;
if (pq->ptail == NULL)
{
assert(pq->phead == NULL);
pq->phead = pq->ptail = newnode;
}
else
{
pq->ptail->next = newnode;
pq->ptail = newnode;
}
pq->size++;
}
void QueuePop(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
if (pq->phead->next==NULL)
{
assert(pq->ptail->next == NULL);
free(pq->phead);
pq->phead = NULL;
pq->ptail = NULL;
}
else
{
QNode* cur = pq->phead->next;
free(pq->phead);
pq->phead = cur;
}
pq->size--;
}
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
return pq->phead->data;
}
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
return pq->ptail->data;
}
int QueueSize(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->size;
}
2.3循环队列
环形队列可以使用数组实现,也可以使用循环链表实现。
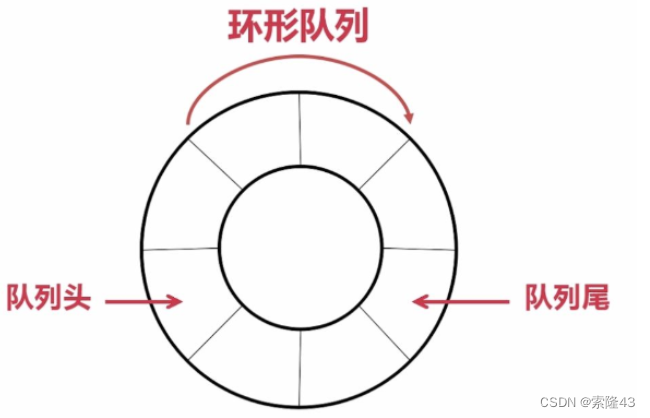
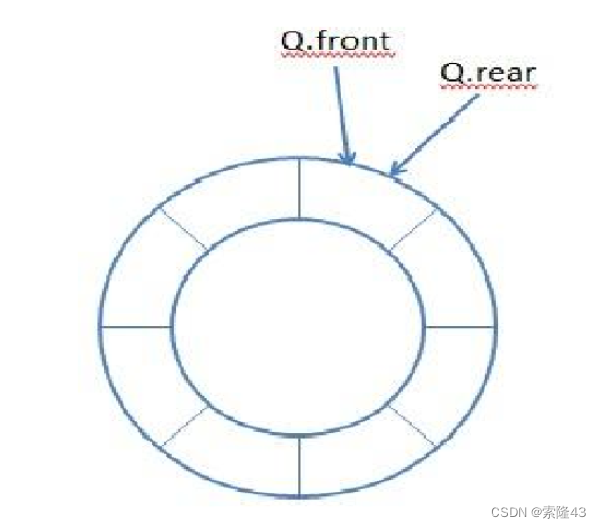
空:front ==rear
满:rear+1 ==front
栈和队列笔试题
3.1有效的括号

//C语言写的话,手撕栈是必不可少的,紧接着这道题是思路是将左括号入栈,遇到右括号则出栈,如果说有一个不匹配的就返回false,直到栈为空,才返回true,如果说左括号配对完了,但右括号仍还有,则栈为空,返回false
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
typedef int STDataType;
typedef struct Stack
{
STDataType* a;
int top;
int capacity;
}ST;
//初始化
void STInit(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
pst->a = NULL;
pst->top = 0;//top为最后一个元素的下一个位置
pst->capacity = 0;
}
//销毁栈
void STDestroy(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
free(pst->a);
pst->a = NULL;
pst->top = 0;
pst->capacity = 0;
}
//入栈
void STPush(ST* pst,STDataType x)
{
if (pst->top == pst->capacity)
{
int newcapacity = pst->capacity == 0 ? 4 : pst->capacity * 2;
STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(pst->a,sizeof(STDataType) * newcapacity);
if (tmp == NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
return;
}
pst->a = tmp;
pst->capacity = newcapacity;
}
pst->a[pst->top] = x;
pst->top++;
}
//判空
bool STEmpty(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
return pst->top == 0;
}
//出栈
void STPop(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
assert(!STEmpty(pst));
pst->top--;
}
//显示栈顶元素
STDataType STTop(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
assert(!STEmpty(pst));
return pst->a[pst->top - 1];
}
//栈内元素个数
int STSize(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
return pst->top;
}
bool isValid(char * s)
{
ST st;
STInit(&st);
while(*s)
{
if(*s=='('||*s=='['||*s=='{')
{
STPush(&st,*s);
}
else
{
if(STEmpty(&st))
{
STDestroy(&st);
return false;
}
char top=STTop(&st);
STPop(&st);
if((*s==')'&&top!='(')||(*s==']'&&top!='[')||(*s=='}'&&top!='{'))
{
STDestroy(&st);
return false;
}
}
s++;
}
bool ret=STEmpty(&st);
STDestroy(&st);
return ret;
}
3.2用队列实现栈

//还是一样,用c语言写首先得会手撕栈,然后本题的思路是,创建两个队列,将其初始化,入栈的逻辑是两个队列谁不是空就往哪个队列上插入,出栈的逻辑是先判断哪个队列是空,哪个不是空,将不是空的队列入为空的队列里去(入完之后还得将元素pop),且不为空的队列只留下最后一个元素,将其记录下来作为返回值(也要记得pop),而显示栈顶元素的逻辑是看哪个队列不为空,就返回该队列的最后一个元素,栈判空的逻辑是两个队列都要为空才为空,栈释放空间的逻辑是先销毁队列,然后再销毁存储两队列地址的结构体
#include<stdio.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
typedef int QDataType;
typedef struct QueueNode
{
struct QueueNode* next;
QDataType data;
}QNode;
typedef struct Queue
{
QNode* phead;
QNode* ptail;
int size;
}Queue;
void QueueInit(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
pq->phead = NULL;
pq->ptail = NULL;
pq->size = 0;
}
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* cur = pq->phead;
while (cur)
{
QNode* next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL;
pq->size = 0;
}
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->size == 0;
}
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
if (newnode == NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail\n");
return;
}
newnode->next = NULL;
newnode->data = x;
if (pq->ptail == NULL)
{
assert(pq->phead == NULL);
pq->phead = pq->ptail = newnode;
}
else
{
pq->ptail->next = newnode;
pq->ptail = newnode;
}
pq->size++;
}
void QueuePop(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
if (pq->phead->next==NULL)
{
assert(pq->ptail->next == NULL);
free(pq->phead);
pq->phead = NULL;
pq->ptail = NULL;
}
else
{
QNode* cur = pq->phead->next;
free(pq->phead);
pq->phead = cur;
}
pq->size--;
}
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
return pq->phead->data;
}
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
return pq->ptail->data;
}
int QueueSize(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->size;
}
typedef struct {
Queue q1;
Queue q2;
} MyStack;
MyStack* myStackCreate() {
MyStack* obj=(MyStack*)malloc(sizeof(MyStack));
if(obj==NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
return NULL;
}
QueueInit(&obj->q1);
QueueInit(&obj->q2);
return obj;
}
void myStackPush(MyStack* obj, int x) {
if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1))
{
QueuePush(&obj->q1,x);
}
else
{
QueuePush(&obj->q2,x);
}
}
int myStackPop(MyStack* obj) {
Queue* pEmptyQ=&obj->q1;
Queue*pNonEmptyQ=&obj->q2;
if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1))
{
pEmptyQ=&obj->q2;
pNonEmptyQ=&obj->q1;
}
while(QueueSize(pNonEmptyQ)>1)
{
QueuePush(pEmptyQ,QueueFront(pNonEmptyQ));
QueuePop(pNonEmptyQ);
}
int top=QueueFront(pNonEmptyQ);
QueuePop(pNonEmptyQ);
return top;
}
int myStackTop(MyStack* obj) {
if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1))
{
return QueueBack(&obj->q1);
}
else
{
return QueueBack(&obj->q2);
}
}
bool myStackEmpty(MyStack* obj) {
return QueueEmpty(&obj->q1)&&QueueEmpty(&obj->q2);
}
void myStackFree(MyStack* obj) {
QueueDestroy(&obj->q1);
QueueDestroy(&obj->q2);
free(obj);
}
3.3栈实现队列

//还是一样,C语言写这题首先要会手撕栈,然后本题的思路是先创建两个栈,将其初始化,入队列的逻辑是将元素入pushst栈,函数peek的逻辑是popst栈如果没有元素则将pushst栈所以元素入popst栈,并弹出pushst栈所有元素,然后返回popst栈的栈顶元素,所以出队列的逻辑其实就是将peek函数的返回值记录下来,弹出被记录下来的值,然后再返回被记录下来的值,队列判空的逻辑是两个栈均为空才为空,队列释放空间的逻辑是先释放两个栈的空间,然后再释放保存两个栈地址的结构体
#include<stdio.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
typedef int STDataType;
typedef struct Stack
{
STDataType* a;
int top;
int capacity;
}ST;
//初始化
void STInit(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
pst->a = NULL;
pst->top = 0;//top为最后一个元素的下一个位置
pst->capacity = 0;
}
//销毁栈
void STDestroy(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
free(pst->a);
pst->a = NULL;
pst->top = 0;
pst->capacity = 0;
}
//入栈
void STPush(ST* pst,STDataType x)
{
if (pst->top == pst->capacity)
{
int newcapacity = pst->capacity == 0 ? 4 : pst->capacity * 2;
STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(pst->a,sizeof(STDataType) * newcapacity);
if (tmp == NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
return;
}
pst->a = tmp;
pst->capacity = newcapacity;
}
pst->a[pst->top] = x;
pst->top++;
}
//判空
bool STEmpty(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
return pst->top == 0;
}
//出栈
void STPop(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
assert(!STEmpty(pst));
pst->top--;
}
//显示栈顶元素
STDataType STTop(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
assert(!STEmpty(pst));
return pst->a[pst->top - 1];
}
//栈内元素个数
int STSize(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
return pst->top;
}
typedef struct {
ST pushst;
ST popst;
} MyQueue;
MyQueue* myQueueCreate() {
MyQueue* obj=(MyQueue*)malloc(sizeof(MyQueue));
if(obj==NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
return NULL;
}
STInit(&obj->pushst);
STInit(&obj->popst);
return obj;
}
void myQueuePush(MyQueue* obj, int x) {
STPush(&obj->pushst,x);
}
int myQueuePop(MyQueue* obj) {
int front=myQueuePeek(obj);
STPop(&obj->popst);
return front;
}
int myQueuePeek(MyQueue* obj) {
if(STEmpty(&obj->popst))
{
while(!STEmpty(&obj->pushst))
{
STPush(&obj->popst,STTop(&obj->pushst));
STPop(&obj->pushst);
}
}
return STTop(&obj->popst);
}
bool myQueueEmpty(MyQueue* obj) {
return STEmpty(&obj->pushst)&&STEmpty(&obj->popst);
}
void myQueueFree(MyQueue* obj) {
STDestroy(&obj->pushst);
STDestroy(&obj->popst);
free(obj);
}
3.4设计循环队列

//该题的思路是:用一个顺序表实现的循环队列,队列结构体中包含首元素下标front,尾元素的下一个位置的下标rear,还有记录顺序表中元素个数的k,以及指向顺序表地址的a,然后将其开辟空间,初始化,循环队列判空的逻辑是front等于rear,判满的逻辑本应该是rear+1等于front,但是这个是以k+1为空间下标的循环,所以rear+1还得对k+1取模等于front,从队尾插入元素时,要先判断队列是否已满,插入之后要更新rear的位置(照样也要取模),删除对头元素时,要判断队列是否为空,然后更新front的位置(也要取模),取对头数据先判断队列是否为空,不为空直接取,取队尾数据先判断队列是否为空,由于rear时尾元素的下一个元素的下标,所以取尾元素的时候要注意rear因为减一导致访问越界,所以换成rear先加k再模k+1,释放队列时先释放a指向的开辟空间,然后再释放循环队列结构体
typedef struct {
int front;
int rear;
int k;
int* a;
} MyCircularQueue;
MyCircularQueue* myCircularQueueCreate(int k) {
MyCircularQueue* obj=(MyCircularQueue*)malloc(sizeof(MyCircularQueue));
obj->a=(int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*(k+1));
obj->front=0;
obj->rear=0;
obj->k=k;
return obj;
}
bool myCircularQueueIsEmpty(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
return obj->front==obj->rear;
}
bool myCircularQueueIsFull(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
return obj->front==(obj->rear+1)%(obj->k+1);
}
bool myCircularQueueEnQueue(MyCircularQueue* obj, int value) {
if(myCircularQueueIsFull(obj))
{
return false;
}
obj->a[obj->rear]=value;
obj->rear++;
obj->rear=obj->rear%(obj->k+1);
return true;
}
bool myCircularQueueDeQueue(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
if(myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj))
{
return false;
}
obj->front++;
obj->front%=(obj->k+1);
return true;
}
int myCircularQueueFront(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
if(myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj))
{
return -1;
}
return obj->a[obj->front];
}
int myCircularQueueRear(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
if(myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj))
{
return -1;
}
return obj->a[(obj->rear+obj->k)%(obj->k+1)];
}
void myCircularQueueFree(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
free(obj->a);
obj->a=NULL;
free(obj);
}