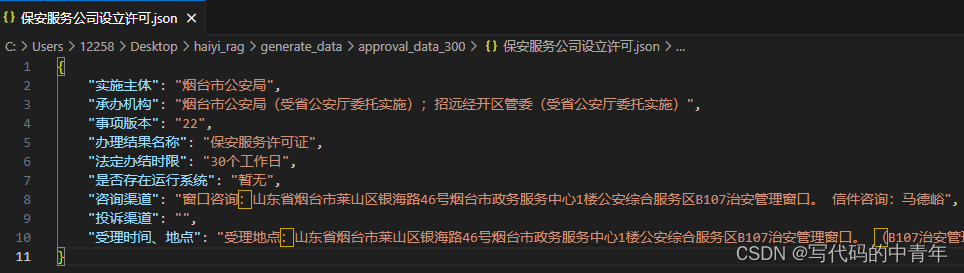
大模型相关目录
大模型,包括部署微调prompt/Agent应用开发、知识库增强、数据库增强、知识图谱增强、自然语言处理、多模态等大模型应用开发内容
从0起步,扬帆起航。
- 大模型应用向开发路径及一点个人思考
- 大模型应用开发实用开源项目汇总
- 大模型问答项目问答性能评估方法
- 大模型数据侧总结
文章目录
- 大模型相关目录
- 一、大模型数据类型
- 二、大模型数据集构建示例
- 三、总结
一、大模型数据类型
从数据内容上
自我认知数据集,顾名思义,使模型在被问及模型名称和研发出处时可准确回答的数据集。一般数据集规模小,内容固定,微调或训练后与一定的prompt配合使用能起到较好的效果。
通用数据集,使模型在微调后能够保持自身对通用问题推理能力水平的数据集。一般数据集规模大,内容丰富,质量要求高。
专业领域数据集,一般在进行垂直领域的大模型开发时所需的数据集,使模型对指定垂直领域进行学习。数据集规模、数据集格式、数据集内容根据垂直领域内容不同而不同。值得注意的是垂直领域的大模型开发所用数据集尽量领域方向固定单一,实践说明多方向数据集会使得模型垂直领域问答能力变弱。
从数据格式上
指令微调数据集
QA数据集
其他格式数据集:包括json、word、pdf、txt等
二、大模型数据集构建示例
大模型数据集构建方法众多,如在已有数据集上设计脚本修改数据集内容、如令大模型自问自答或在一定prompt约束下生成问题和答案…
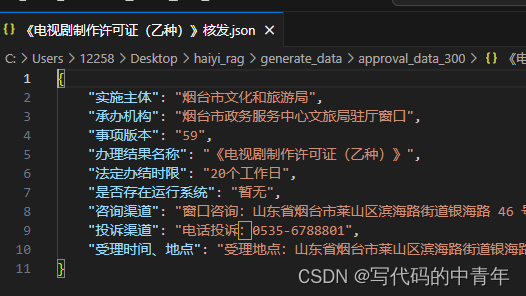
本次示例以一定的json数据为基础,利用大模型能力,设计prompt约束,产生可用于实际应用的问答数据集。
需要注意的是,在上述示例思路下产生数据集,为保证数据质量,在每一次生成问答数据集时,都应颗粒度具体到json的字段(而不仅仅只是每一个json文件)。

from llm_ask.ask_Tongyi import *
import os
# 获取指定目录下所有文件的绝对路径列表
def get_files_in_directory(directory):
result = []
# 遍历指定目录下的所有文件和文件夹
for root, dirs, files in os.walk(directory):
# 只处理文件,不处理文件夹
for file in files:
# 获取文件的完整路径
file_path = os.path.join(root, file)
# 打印文件路径或进行其他操作
# print(file_path)
result.append(file_path)
return result
# 由json文件绝对路径读取单个json文件获取其文件名称和标题
def read_single_json(json_file_path:str)->str:
title = json_file_path.split('\\')[-1][:-5]
with open(json_file_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as file:
data = str(json.load(file))
return title,data
# 以追加方式向指定的txt文件存入内容
def wirte_txt(txt_file_path,data):
with open(txt_file_path,'a',encoding='utf-8') as f:
f.write(data)
f.write('\n\n')
# 对llm返回的结果进行处理
def adjust_result(llm_result):
llm_result_text = llm_result['text']
return llm_result_text
prompt_modules = [
'''
你是一个问答数据生成专家,可以就上述json数据生成问答数据。
本次提问关注json格式中的 {ziduan} 字段,该字段是指{ziduan_describe}。
生成的每条问题要全面清晰,注明政策规范或办理结果名称,不能用这项、这个、上述地点指代有效信息。
生成的回答应将对应的的信息详细以口语形式描述出来。
最后强调,以不同的角度和方式生成3条问答数据以上。
问题及答案符合口语习惯,采取如下格式:
根据{zhengce}请回答问题1:回答1\n\n根据{zhengce}请回答问题2:回答2\\n\\n...]。
'''
]
ziduans = [
'办理结果名称','承办机构','法定办结时限','受理时间、地点','咨询渠道','投诉渠道'
]
ziduan_describes = [
'所要办理的文件','办理该事项的政府机关部门名称',
'办理该文件所需的最大时限','办理该文件时,机关部门的工作地点和工作时间段',
'该事项相关的咨询渠道','该事项相关的投诉渠道'
]
ziduan_indexs = range(len(ziduans))
# exe
ask_tyqw = TongyiAPI()
directory = r'C:\...\generate_data\approval_data_300' # 目录路径
file_paths = get_files_in_directory(directory)
for file_path in file_paths[2:]:
title, json_data = read_single_json(file_path)
prompt_data = json_data
for index in ziduan_indexs:
prompt_module = prompt_modules[0].format(zhengce=title,ziduan=ziduans[index],ziduan_describe=ziduan_describes[index])
prompt = prompt_data + '\n' + prompt_module
llm_result = ask_tyqw.get_one_response_by_prompt(prompt)
print(llm_result)
llm_adjust_result = adjust_result(llm_result)
mid = directory.replace('approval_data_300','approval_data_300_ask_txt')+'\\'+title+'.txt'
wirte_txt(mid, llm_adjust_result)
import requests
import json
import dashscope
from dashscope import Generation
from http import HTTPStatus
class TongyiAPI:
def __init__(self):
API_KEY = 'sk-0000000000000000000000000000' #自己的API_KEY
dashscope.api_key = API_KEY
self.gen = Generation()
def get_one_response_by_prompt(self, prompt):
response = self.gen.call(
model=dashscope.Generation.Models.qwen_turbo,
prompt=prompt
)
# The response status_code is HTTPStatus.OK indicate success,
# otherwise indicate request is failed, you can get error code
# and message from code and message.
if response.status_code == HTTPStatus.OK:
# print(response.output) # The output text
print(response.usage) # The usage information
return response.output
else:
print(response.code) # The error code.
print(response.message) # The error message.
三、总结
上述即是大模型数据侧的一点总结内容,包括数据类型的两个维度划分以及大模型数据集生成方法和注意事项。
完结,撒花!