如何通过互斥锁和条件变量构建线程安全的队列(栈)
在C++并发编程 -2.线程间共享数据 已经介绍过构建线程安全的栈,现在重新回顾。
一.构建线程安全的栈
1.异常发生在接口处
有时候我们可以将对共享数据的访问和修改聚合到一个函数,在函数内加锁保证数据的安全性。但是对于读取类型的操作,即使读取函数是线程安全的,但是返回值抛给外边使用,存在不安全性。比如一个栈对象,我们要保证其在多线程访问的时候是安全的,可以在判断栈是否为空,判断操作内部我们可以加锁,但是判断结束后返回值就不在加锁了,就会存在线程安全问题。
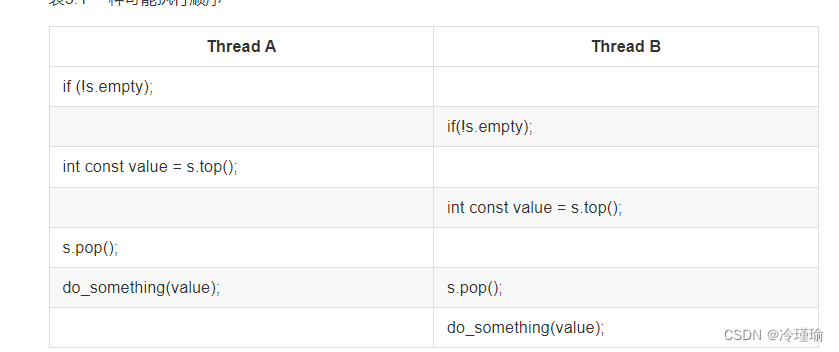
比如我定义了如下栈, 对于多线程访问时判断栈是否为空,此后两个线程同时出栈,可能会造成崩溃,因为两个线程运行顺序可能如下:
template<typename T>
class threadsafe_stack1
{
private:
std::stack<T> data;
mutable std::mutex m;
public:
threadsafe_stack1() {}
threadsafe_stack1(const threadsafe_stack1& other)
{
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(other.m);
data = other.data;
}
threadsafe_stack1& operator=(const threadsafe_stack1&) = delete;
void push(T new_value)
{
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(m);
data.push(std::move(new_value));
}
T pop()
{
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(m);
auto element = data.top();
data.pop();
return element;
}
bool empty() const
{
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(m);
return data.empty();
}
};线程1和线程2先后判断栈都不为空,之后执行出栈操作,可能会造成崩溃。
void test_threadsafe_stack1() {
threadsafe_stack1<int> safe_stack;
safe_stack.push(1);
std::thread t1([&safe_stack]() {
if (!safe_stack.empty()) {
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::seconds(1));
safe_stack.pop();
}
});
std::thread t2([&safe_stack]() {
if (!safe_stack.empty()) {
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::seconds(1));
safe_stack.pop();
}
});
t1.join();
t2.join();
}针对可能造成栈区异常,可以适当抛出异常来提醒。例如定义一个空栈函数,代码优化如下:
struct empty_stack : std::exception
{
const char* what() const throw();
};
T pop()
{
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(m);
if (data.empty()) throw empty_stack();
auto element = data.top();
data.pop();
return element;
}2.异常发生在栈分配
但是现在仍然还有可能存在问题,假设有一个stack<vector<int>>,vector是一个动态容器,当你拷贝一个vetcor,标准库会从堆上分配很多内存来完成这次拷贝。当这个系统处在重度负荷,或有严重的资源限制的情况下,这种内存分配就会失败,所以vector的拷贝构造函数可能会抛出一个std::bad_alloc异常。当vector中存有大量元素时,这种情况发生的可能性更大。当pop()函数返回“弹出值”时(也就是从栈中将这个值移除),会有一个潜在的问题:这个值被返回到调用函数的时候,栈才被改变;值返回会涉及到拷贝数据,此时由于内存空间不够导致拷贝失败,弹出的数据会丢失。
如何解决上述问题?如下
2.1 尽可能减少拷贝
2.1.1 传入引用
void pop(T& value)
{
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(m);
if(data.empty()) throw empty_stack();
value=data.top();
data.pop();
}缺点:既然要传入引用, 大部分情况下需要临时构造出一个堆中类型的实例,用于接收目标值。从时间和资源的角度上来看都不划算。
2.1.2 返回弹出元素的指针
std::shared_ptr<T> pop()
{
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(m);
if(data.empty()) throw empty_stack();
std::shared_ptr<T> const res(std::make_shared<T>(data.top()));
data.pop();
return res;
} 直接pop出智能指针类型,这样在pop函数内部减少了数据的拷贝,防止内存溢出,其实这做法确实是相比之前直接pop固定类型的值更节省内存,运行效率也好很多。
2.2.使用条件变量避免空队列处理
通过添加《传入引用》或《返回弹出元素的指针》来解决上面异常.但是两种方式都存在一定的弊端:
传入引用弊端是需要在函数外部构建临时变量影响效率且需要抛出空栈。
返回智能指针异常下会导致空指针产生。
这么都不是很友好,所以我们可以通过条件变量完善之前的程序,重新实现一个线程安全队列。
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
#include <stack>
#include <memory>
#include <mutex>
#include <condition_variable>
using namespace std;
template<typename T>
class threadQueue
{
public:
threadQueue(): mutx(), condVar(), stackQueue()
{};
~threadQueue(){};
void push(T value)
{
lock_guard<mutex> lk(mutx);
stackQueue.push(value);
condVar.notify_one();
}
void waitAndpop(T &stackQueue_)
{
unique_lock<mutex> lk(mutx);
/*
wait函数第二个参数确保队列有数据才进行条件变量后续操作,相当于增加一层判断,更加准确
*/
condVar.wait(lk, [this](){return !stackQueue.empty();});
stackQueue_ = stackQueue.top();
stackQueue.pop();
}
shared_ptr<T> waitAndPop()
{
unique_lock<mutex> lk(mutx);
condVar.wait(lk, [this](){return !stackQueue.empty();});
shared_ptr<T> res = make_shared<T>(move(stackQueue.top())); //1
stackQueue.pop();
return res;
}
bool tryPop(T &value)
{
lock_guard<mutex> lk(mutx);
if(stackQueue.empty()){return false;}
value = stackQueue.top();
stackQueue.pop();
return true;
}
shared_ptr<T> tryPop()
{
lock_guard<mutex> lk(mutx);
if (stackQueue.empty())
return std::shared_ptr<T>();
shared_ptr<T> res = make_shared<T>(move(stackQueue.top()));//2
stackQueue.pop();
return res;
}
private:
mutable mutex mutx;
condition_variable condVar;
stack<T> stackQueue;
};
mutex mutxThread;
template<typename T>
void funcProducer(threadQueue<T> &thdQueue)
{
for(;;)
{
for(size_t i = 0; i < __LONG_MAX__; i++)
{
thdQueue.push(i);
lock_guard<mutex> lk(mutxThread);
cout<<"funcProducer:"<<i<<endl;
this_thread::sleep_for(chrono::milliseconds(100));
}
}
}
template<typename T>
void funcWorker1(threadQueue<T> &thdQueue)
{
for(;;)
{
auto data = thdQueue.waitAndPop();
lock_guard<mutex> lk(mutxThread);
cout<<"funcWorker1 waitAndpop:"<<*(data)<<endl;
// this_thread::sleep_for(chrono::milliseconds(500));
}
}
template<typename T>
void funcWorker2(threadQueue<T> &thdQueue)
{
for(;;)
{
auto data = thdQueue.tryPop();
if(data != nullptr)
{
lock_guard<mutex> lk(mutxThread);
cout<<"funcWorker2 waitAndpop:"<<*(data)<<endl;
}
// this_thread::sleep_for(chrono::milliseconds(500));
}
}
int main()
{
threadQueue<int> thdQueue;
thread t1(funcProducer<int>, ref(thdQueue));
thread t2(funcWorker1<int>, ref(thdQueue));
thread t3(funcWorker2<int>, ref(thdQueue));
t1.join();
t2.join();
t3.join();
}2.3 避免异常导致延迟消费
异常一:如果push线程(notifyone)添加数据很快,但是pop线程(cond_wait)处理出局速度很慢,可能导致notify部分丢失,最终导致waitandpop函数阻塞!(第二大节分离数据处理)
异常二:线程t1从wait_and_pop唤醒,但在执行1或2处,因为内存不足引发了异常,虽然对于栈来说是安全的,但是t1异常后,其他线程无法从队列中消费数据,除非push线程再执行一次push。因为我们采用的是notify_one的方式,所以仅有一个线程被激活,如果被激活的线程异常了,就不能保证该数据被其他线程消费了,解决这个问题,可以采用几个方案:
- 将
notify_one改为notify_all,但会引起线程间竞争。 - 通过栈存储智能指针的方式进行。
2.4 使用智能指针避免赋值异常(异常二)
智能指针通过引用计数问题避免不必要的拷贝等操作,可以将数据stack<T> stackQueue换为stack<shared_ptr<T>> stackQueue,这样在使用的时候可以将智能指针取出来赋值给一个新的智能指针并返回,避免了拷贝开销。
所有智能指针共享引用计数所以在复制时仅为8字节开销,降低了内存消耗。 关于智能指针的赋值不会引发异常应该是指针在64位机器占用8个字节
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
#include <stack>
#include <memory>
#include <mutex>
#include <condition_variable>
using namespace std;
template<typename T>
class threadQueue
{
public:
threadQueue(): mutx(), condVar(), stackQueue()
{};
~threadQueue(){};
void push(T value)
{
std::shared_ptr<T> data(
std::make_shared<T>(std::move(value)));
lock_guard<mutex> lk(mutx);
stackQueue.push(data);
condVar.notify_one();
}
void waitAndpop(T &stackQueue_)
{
unique_lock<mutex> lk(mutx);
/*
wait函数第二个参数确保队列有数据才进行条件变量后续操作,相当于增加一层判断,更加准确
*/
condVar.wait(lk, [this](){return !stackQueue.empty();});
stackQueue_ = move(*stackQueue.top());
stackQueue.pop();
}
shared_ptr<T> waitAndPop()
{
unique_lock<mutex> lk(mutx);
condVar.wait(lk, [this](){return !stackQueue.empty();});
// shared_ptr<T> res = make_shared<T>(move(*(stackQueue.top()))); //1
shared_ptr<T> res = stackQueue.top(); //1
stackQueue.pop();
return res;
}
bool tryPop(T &value)
{
lock_guard<mutex> lk(mutx);
if(stackQueue.empty()){return false;}
value = move(*stackQueue.top());
stackQueue.pop();
return true;
}
shared_ptr<T> tryPop()
{
lock_guard<mutex> lk(mutx);
if (stackQueue.empty())
return std::shared_ptr<T>();
shared_ptr<T> res =stackQueue.top();//2
stackQueue.pop();
return res;
}
private:
mutable mutex mutx;
condition_variable condVar;
stack<shared_ptr<T>> stackQueue;
};
mutex mutxThread;
template<typename T>
void funcProducer(threadQueue<T> &thdQueue)
{
for(;;)
{
for(size_t i = 0; i < __LONG_MAX__; i++)
{
thdQueue.push(i);
lock_guard<mutex> lk(mutxThread);
cout<<"funcProducer:"<<i<<endl;
this_thread::sleep_for(chrono::milliseconds(100));
}
}
}
template<typename T>
void funcWorker1(threadQueue<T> &thdQueue)
{
for(;;)
{
auto data = thdQueue.waitAndPop();
lock_guard<mutex> lk(mutxThread);
cout<<"funcWorker1 waitAndpop:"<<*(data)<<endl;
// this_thread::sleep_for(chrono::milliseconds(500));
}
}
template<typename T>
void funcWorker2(threadQueue<T> &thdQueue)
{
for(;;)
{
auto data = thdQueue.tryPop();
if(data != nullptr)
{
lock_guard<mutex> lk(mutxThread);
cout<<"funcWorker2 waitAndpop:"<<*(data)<<endl;
}
// this_thread::sleep_for(chrono::milliseconds(500));
}
}
int main()
{
threadQueue<int> thdQueue;
thread t1(funcProducer<int>, ref(thdQueue));
thread t2(funcWorker1<int>, ref(thdQueue));
thread t3(funcWorker2<int>, ref(thdQueue));
t1.join();
t2.join();
t3.join();
}所以推荐大家存储数据放入容器中时尽量用智能指针,这样能保证复制和移动过程中开销较小,也可以实现一定意义的数据共享。
二.分离数据处理提高并发能力
下述文字及图片摘自恋恋风尘 博主比较懒表情😒
队列push和pop时采用的是一个mutex,导致push和pop等操作串行化,我们要考虑的是优化锁的精度,提高并发,避免pop消费过慢造成线程阻塞,那有什么办法吗?
可以考虑将push和pop操作分化为分别对尾和对首部的操作。对首和尾分别用不同的互斥量管理就可以实现真正意义的并发。
引入虚位节点的概念,表示一个空的节点,没有数据,是一个无效的节点,初始情况下,队列为空,head和tail节点都指向这个虚位节点。

我们push一个数据,比如为MyClass类型的数据后,tail向后移动一个位置,并且仍旧指向这个虚位节点

示例是我自己写的,测试一百万条数据四种代码处理速度
代码一:摘自2.4 小节示例

代码二:沿用2.4小节示例,保留push线程和trypop线程 (毕竟代码一涉及线程上下文切换,速度肯定慢)

代码三:下述示例
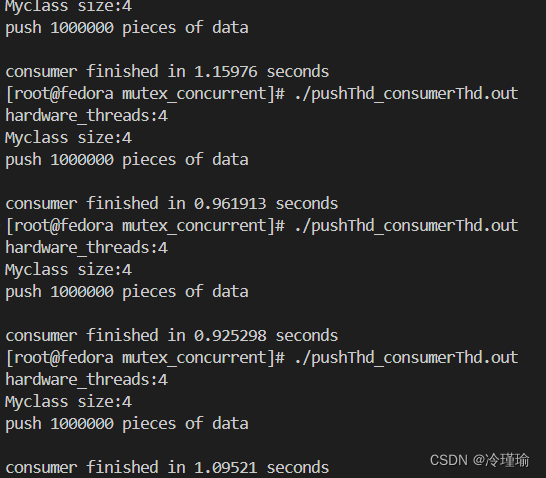
代码四:针对代码三 额外添加三个pop线程消费

先说结论,代码三运行速度最快。跟我预想的差不多表情🤣,
代码一:存在三个线程,共用一把锁,本质还是单线程,而且涉及线程上下文切换,速度最慢毋庸置疑。
代码二:返璞归真,直接上trypop,如此避免互斥锁+条件变量使用导致占用锁时间加长,虽然一定程度引入了异常,但是速度确实变快
代码三:分离节点,pop处理head,push处理tail,真正意义上的并发(pop条件变量判断为空还是会占用锁,使用trypop还会更快)
代码四:分离节点,四个线程 pop处理head,push处理tail。但由于pop四个线程竞争锁,引入线程上下文切换,导致速度不如代码三快(后续做成hash试试,速度应该会起飞)
代码三如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
#include <stack>
#include <memory>
#include <mutex>
#include <condition_variable>
#include <chrono>
#include <vector>
#include <atomic>
#include <future>
/*
设置虚拟节点,进行节点分离,使得pop和push线程分离并发,速度最快(有锁下)
*/
using namespace std;
template<typename T>
class threadsafeQueue
{
private:
struct Node
{
shared_ptr<T> data;
unique_ptr<Node> next;
};
mutable mutex headMutex;
mutable mutex tailMutex;
unique_ptr<Node> head;
Node* tail; //不使用unique_ptr<Node> tail;避免析构异常
condition_variable cond;
public:
threadsafeQueue():head(new Node),tail(head.get())
{}
~threadsafeQueue()
{
while (head)
{
unique_ptr<Node> oldHead = move(head);
head = move(oldHead->next);
}
}
threadsafeQueue(const threadsafeQueue&) = delete;
threadsafeQueue& operator=(const threadsafeQueue&) = delete;
bool try_pop(T &value)
{
if(empty()) return false;
lock_guard<mutex> headLk(headMutex);
unique_ptr<Node> oldHead = move(head);
value = move(*(oldHead->data));
head = head->next;
return true;
}
void wait_and_pop(T &value)
{
unique_lock<mutex> headLk(headMutex);
cond.wait(headLk, [&](){
lock_guard<mutex> tailLk(tailMutex);
return (head.get() != tail);
});
unique_ptr<Node> oldHead = move(head);
value = move(*(oldHead->data));
head = head->next;
}
shared_ptr<T> wait_and_pop()
{
unique_lock<mutex> headLk(headMutex);
cond.wait(headLk, [&](){
lock_guard<mutex> tailLk(tailMutex);
return (head.get() != tail);
});
shared_ptr<Node> oldHead = move(head);
head = move(oldHead->next);
return oldHead->data;
}
void pushQueue(T value)
{
shared_ptr<T> newData = make_shared<T>(move(value));
unique_ptr<Node> p(new Node);
{
lock_guard<mutex> tailLk(tailMutex);
Node * const ptr = p.get();
tail->next = move(p);
tail->data = newData;
tail = ptr;
}
cond.notify_one();
}
bool empty() const
{
lock_guard<mutex> headLk(headMutex);
lock_guard<mutex> tailLk(tailMutex);
return (tail == head.get());
}
};
class MyClass
{
public:
MyClass(int data):_data(data){}
MyClass(const MyClass& mc):_data(mc._data){}
MyClass(MyClass&& mc) :_data(mc._data)
{}
friend ostream& operator << (ostream& os, const MyClass& mc)
{
os << mc._data;
return os;
}
private:
int _data;
};
mutex mtx_cout;
condition_variable cond;
void PrintMyClass(string consumer, shared_ptr<MyClass> data)
{
lock_guard<mutex> lock(mtx_cout);
cout << consumer << " pop data success , data is " << (*data) << endl;
}
int main()
{
unsigned long const hardware_threads = thread::hardware_concurrency();
cout <<"hardware_threads:"<<hardware_threads<<endl;
cout<<"Myclass size:"<<sizeof(MyClass)<<endl;
threadsafeQueue<MyClass> thrdQue;
atomic<bool> isFlag(false);
//粗略计算,忽略线程创建开销时间
auto start = chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
thread consumer([&]()
{
for (;;)
{
if(isFlag.load(memory_order_acquire))
{
isFlag.store(false, memory_order_seq_cst); //避免多个线程进去此逻辑
auto end = chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
chrono::duration<double> elapsed = end - start;
lock_guard<mutex> lock(mtx_cout);
{
cout << "consumer finished in " << elapsed.count() << " seconds" << endl;
}
break;
}
shared_ptr<MyClass> data = thrdQue.wait_and_pop();
}
});
thread producer([&]()
{
int i = 0;
for (;;)
{
MyClass mc(i++);
thrdQue.pushQueue(move(mc));
if(i % 1000000 == 0) //一百万条数据
{
isFlag.store(true, memory_order_relaxed);
lock_guard<mutex> lock(mtx_cout);
cout<<"push "<<i<<" pieces of data"<<endl<<endl;
break;
}
}
});
consumer.join();
producer.join();
}
三. 实现线程安全的hash查找表
散列表(Hash table,也叫哈希表),是根据键(Key)而直接访问在存储器存储位置的数据结构。 也就是说,它通过计算出一个键值的函数,将所需查询的数据映射到表中一个位置来让人访问,这加快了查找速度。 这个映射函数称做散列函数,存放记录的数组称做散列表。
举个例子:
假如我们一共有 50 人参加学校的数学竞赛,然后我们为每个学生分配一个编号,依次是 1 到 50.
如果我们想要快速知道编号对应学生的信息,我们就可以用一个数组来存放学生的信息,编号为 1 的放到数组下标为 1 的位置,编号为 2 的放到数组下标为 2 的位置,依次类推。
现在如果我们想知道编号为 20 的学生的信息,我们只需要把数组下标为 20 的元素取出来就可以了,时间复杂度为 O(1),是不是效率非常高呢。
但是这些学生肯定来自不同的年级和班级,为了包含更详细的信息,我们在原来编号前边加上年级和班级的信息,比如 030211 ,03 表示年级,02 表示班级,11 原来的编号,这样我们该怎么存储学生的信息,才能够像原来一样使用下标快速查找学生的信息呢?
思路还是和原来一样,我们通过编号作为下标来储存,但是现在编号多出了年级和班级的信息怎么办呢,我们只需要截取编号的后两位作为数组下标来储存就可以了。
这个过程就是典型的散列思想。其中,参赛学生的编号我们称之为键(key),我们用它来标识一个学生。然后我们通过一个方法(比如上边的截取编号最后两位数字)把编号转变为数组下标,这个方法叫做散列函数(哈希函数),通过散列函数得到的值叫做散列值(哈希值)。
我们自己在设计散列函数的函数时应该遵循什么规则呢?
- 得到的散列值是一个非负整数
- 两个相同的键,通过散列函数计算出的散列值也相同
- 两个不同的键,计算出的散列值不同
虽然我们在设计的时候要求满足以上三条要求,但对于第三点很难保证所有不同的建都被计算出不同的散列值。有可能不同的建会计算出相同的值,这叫做哈希冲突。最常见的一些解决哈希冲突的方式是开放寻址法和链表法,我们这里根据链表法,将散列函数得到相同的值的key放到同一个链表中。
如下图
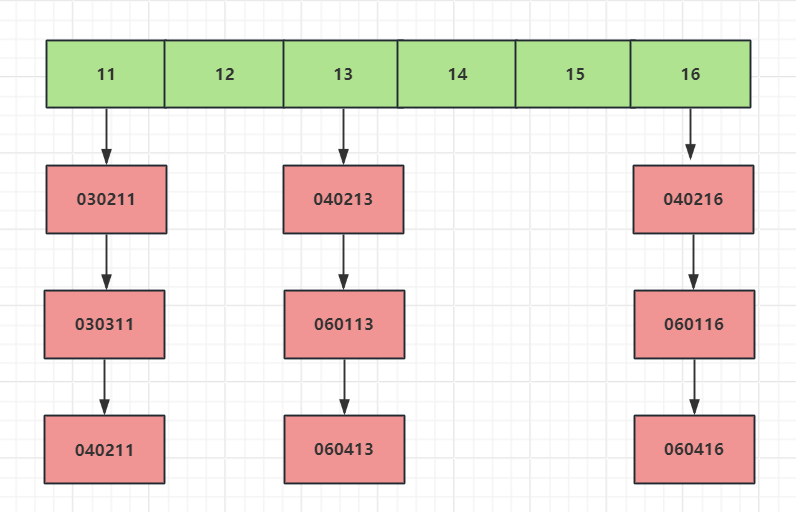
当我们根据key值的后两位计算编号,将编号相同的放入一个链表,比如030211和030311是一个编号,所以将其放入一个链表。
同样的道理040213和060113是一个编号,放入一个链表
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
#include <vector>
#include <list>
#include <memory>
#include <mutex>
#include <shared_mutex>
#include <iterator>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iomanip>
#include <future>
#define max_buckets 10
#define max_datas 10000
using namespace std;
template<typename Key, typename Value, typename Hash = std::hash<Key>>
class threadsafe_lookup_table
{
public:
// 桶类型
class bucket_type
{
friend class threadsafe_lookup_table;
private:
//存储元素的类型为pair,由key和value构成
typedef std::pair<Key, Value> bucket_value;
//由链表存储元素构
typedef std::list<bucket_value> bucket_data;
//链表的迭代器
typedef typename bucket_data::iterator bucket_iterator;
//链表数据
bucket_data data;
//改用共享锁
mutable std::shared_mutex mutex;
//查找操作,在list中找到匹配的key值,然后返回迭代器
bucket_iterator find_entry_for(const Key & key)
{
return std::find_if(data.begin(), data.end(),
[&](bucket_value const& item)
{return item.first == key; });
}
public:
//查找key值,找到返回对应的value,未找到则返回默认值
Value value_forr(Key const& key, Value const& default_value)
{
std::shared_lock<std::shared_mutex> lock(mutex);
bucket_iterator const found_entry = find_entry_for(key);
return (found_entry == data.end()) ?
default_value : found_entry->second;
}
//添加key和value,找到则更新,没找到则添加
void add_or_update_mapp(Key const& key, Value const& value)
{
std::unique_lock<std::shared_mutex> lock(mutex);
bucket_iterator const found_entry = find_entry_for(key);
if (found_entry == data.end())
{
data.push_back(bucket_value(key, value));
}
else
{
found_entry->second = value;
}
}
std::shared_mutex& get_mutex()
{
return mutex;
}
bucket_data& get_data()
{
return data;
}
};
//用vector存储桶类型
std::vector<std::unique_ptr<bucket_type>> buckets;
//hash<Key> 哈希表 用来根据key生成哈希值
Hash hasher;
//根据key生成数字,并对桶的大小取余得到下标,根据下标返回对应的桶智能指针
bucket_type& get_buckett(Key const& key) const
{
std::size_t const bucket_index = hasher(key) % buckets.size();
return *buckets[bucket_index];
}
public:
threadsafe_lookup_table(
unsigned num_buckets = max_buckets, Hash const& hasher_ = Hash()) :
buckets(num_buckets), hasher(hasher_)
{
for (unsigned i = 0; i < num_buckets; ++i)
{
buckets[i].reset(new bucket_type);
}
}
~threadsafe_lookup_table()
{
for (unsigned i = 0; i < buckets.size(); ++i)
{
std::unique_lock<std::shared_mutex> lock(buckets[i]->mutex);
buckets[i]->data.clear(); // 清空桶中的数据
}
}
threadsafe_lookup_table(threadsafe_lookup_table const& other) = delete;
threadsafe_lookup_table& operator=(
threadsafe_lookup_table const& other) = delete;
Value value_for(Key const& key,
Value const& default_value = Value())
{
return get_buckett(key).value_forr(key, default_value);
}
void add_or_update_mapping(Key const& key, Value const& value)
{
get_buckett(key).add_or_update_mapp(key, value);
}
bucket_type& get_bucket(Key const& key) const
{
std::size_t const bucket_index = hasher(key) % buckets.size();
return *buckets[bucket_index];
}
void print_buckets_data()
{
for (unsigned i = 0; i < buckets.size(); ++i)
{
std::shared_lock<std::shared_mutex> lock(buckets[i]->mutex);
std::cout << "Bucket " << i << " data:" << std::endl;
for (auto& entry : buckets[i]->data)
{
std::cout << std::setw(8) << std::right << "Key: " << entry.first << ", Value: " << *(entry.second) << std::endl;
}
}
}
};
class MyClass
{
public:
MyClass(int i):_data(i){}
friend std::ostream& operator << (std::ostream& os, const MyClass& mc){
os << mc._data;
return os;
}
int get_data()
{
return _data;
}
private:
int _data;
};
int main()
{
std::vector<int> readVec;
readVec.reserve(max_datas * 2);
threadsafe_lookup_table<int, std::shared_ptr<MyClass>> table;
mutex mut;
std::thread writer([&]() {
std::cout<<"will write data to hashTable"<<std::endl;
for(int i = 0; i < max_datas; i++)
{
auto class_ptr = std::make_shared<MyClass>(i);
table.add_or_update_mapping(i, class_ptr);
}
std::cout<<"write data to hashTable over"<<std::endl;
});
writer.join();
this_thread::sleep_for(chrono::microseconds(10));
auto start = chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
thread reader1([&]() {
int local = 0;
for(int j = 0; j < (max_buckets / 2); j++)
{
typename threadsafe_lookup_table<int, std::shared_ptr<MyClass>>::bucket_type& bucket = table.get_bucket(j); // 获取需要读取的桶的引用
std::shared_lock<std::shared_mutex> lock(bucket.get_mutex()); // 使用共享锁锁定该桶
for (auto& entry : bucket.get_data())
{
// cout<<"th1 readVec.size():"<<readVec.size()<<endl;
readVec.insert(readVec.begin() + local ,entry.first); // 将桶中的数据的key存储到readSet中
local++;
this_thread::sleep_for(chrono::microseconds(100)); //执行一些耗时操作
if(readVec.size() >= (max_datas / 2))
{
lock_guard<mutex> lk(mut);
auto end = chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
chrono::duration<double> elapsed = end - start;
cout << "reader1 finished in " << elapsed.count() << " seconds" << endl;
this_thread::sleep_for(chrono::microseconds(1000));
exit(0);
}
}
}
std::cout<<"readVec1.size()"<<readVec.size()<<std::endl;
});
thread reader2([&]() {
int local = max_datas / 2;
for(int j = (max_buckets / 2); j < max_buckets; j++)
{
typename threadsafe_lookup_table<int, std::shared_ptr<MyClass>>::bucket_type& bucket = table.get_bucket(j); // 获取需要读取的桶的引用
std::shared_lock<std::shared_mutex> lock(bucket.get_mutex()); // 使用共享锁锁定该桶
for (auto& entry : bucket.get_data())
{
// cout<<"th2 readVec.size()"<<readVec.size()<<endl;
readVec.insert(readVec.begin() + local ,entry.first); // 将桶中的数据的key存储到readSet中
local++;
this_thread::sleep_for(chrono::microseconds(100)); //执行一些耗时操作
if(readVec.size() >= (max_datas / 2))
{
lock_guard<mutex> lk(mut);
auto end = chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
chrono::duration<double> elapsed = end - start;
cout << "reader2 finished in " << elapsed.count() << " seconds" << endl;
this_thread::sleep_for(chrono::microseconds(1000));
exit(0);
}
}
}
std::cout<<"readVec2.size()"<<readVec.size()<<std::endl;
});
reader2.join();
reader1.join();
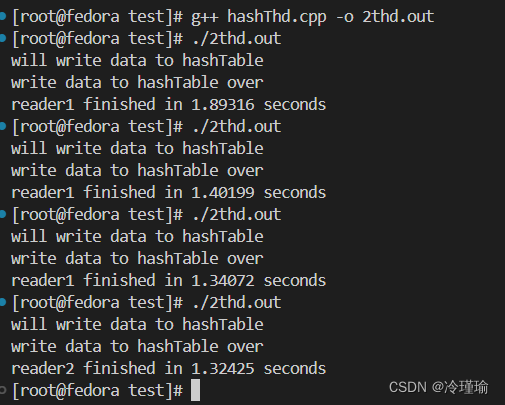
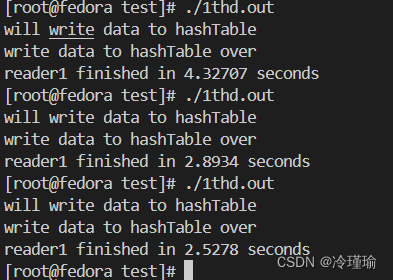
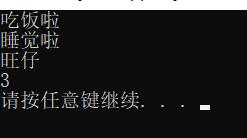
}测试结果如下:
双线程下: 单线程下:
四. 通过链表优化hash查找表
后续补充


![[LeetCode][239]【学习日记】滑动窗口最大值——O(n)单调队列](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/fe2a4da2470c432c82c603eedda06a0b.png)