输出
一.Array.prototype.sort()
1.默认排序 sort()
sort() 方法就地对数组的元素进行排序,并返回对相同数组的引用。默认排序是将元素转换为字符串,然后按照它们的 UTF-16 码元值升序排序。
由于它取决于具体实现,因此无法保证排序的时间和空间复杂度。
如果想要不改变原数组的排序方法,可以使用 toSorted()。
说明:两个重点。1、会改变原数组。2、默认按将元素转换为字符串排序。
const months = ['March', 'Jan', 'Feb', 'Dec'];
months.sort();
console.log(months);
// Expected output: Array ["Dec", "Feb", "Jan", "March"]
const array1 = [1, 30, 4, 21, 100000];
array1.sort();
console.log(array1);
// Expected output: Array [1, 100000, 21, 30, 4]2.比较函数 sort(compareFn)
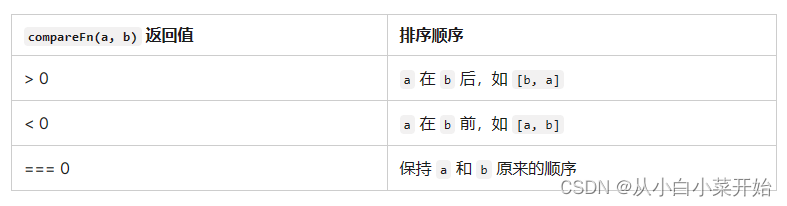
定义排序顺序的函数。返回值应该是一个数字,其符号表示两个元素的相对顺序:如果 a 小于 b,返回值为负数,如果 a 大于 b,返回值为正数,如果两个元素相等,返回值为 0。NaN 被视为 0。
说明:自定义比较函数返回一个数值。一般为1,-1,0.
function compareFn(a, b) {
if (根据排序标准,a 小于 b) {
return -1;
}
if (根据排序标准,a 大于 b) {
return 1;
}
// a 一定等于 b
return 0;
}
const stringArray = ["Blue", "Humpback", "Beluga"];
const numberArray = [40, 1, 5, 200];
const numericStringArray = ["80", "9", "700"];
const mixedNumericArray = ["80", "9", "700", 40, 1, 5, 200];
function compareNumbers(a, b) {
return a - b;
}
stringArray.sort(); // ['Beluga', 'Blue', 'Humpback']
numberArray.sort(compareNumbers); // [1, 5, 40, 200]
numericStringArray.sort(); // ['700', '80', '9']
numericStringArray.sort(compareNumbers); // ['9', '80', '700']
mixedNumericArray.sort(compareNumbers); // [1, 5, '9', 40, '80', 200, '700']
二.对象数组
let arr = [
{ name: 'Zhang', age: 25, score: 85 },
{ name: 'Li', age: 20, score: 90 },
{ name: 'Wang', age: 22, score: 80 },
{ name: 'Zhao', age: 22, score: 92 }
];
// 按 age 升序排序,如果 age 相同则按 score 降序排序
arr.sort((a, b) => {
if (a.age !== b.age) {
return a.age - b.age; // 按 age 升序排序
} else {
return b.score - a.score; // 如果 age 相同,按 score 降序排序
}
});
console.log(arr);[
{ name: 'Li', age: 20, score: 90 },
{ name: 'Wang', age: 22, score: 80 },
{ name: 'Zhao', age: 22, score: 92 },
{ name: 'Zhang', age: 25, score: 85 }
]三.通用方法
1.指定单一对象元素属性
function sortObjectsByProperty(array, property) {
return array.sort(function(a, b) {
if (a[property] < b[property]) {
return -1;
} else if (a[property] > b[property]) {
return 1;
} else {
return 0;
}
});
}
var objects = [
{ name: 'Apple', price: 15 },
{ name: 'Banana', price: 10 },
{ name: 'Cherry', price: 20 }
];
var sortedObjects = sortObjectsByProperty(objects, 'price');
console.log(sortedObjects);
输出:
[
{ name: 'Banana', price: 10 },
{ name: 'Apple', price: 15 },
{ name: 'Cherry', price: 20 }
]2.指定对象元素多属性
function sortObjectsByProperties(array, ...properties) {
return array.sort((a, b) => {
for (const property of properties) {
if (a[property] < b[property]) {
return -1;
} else if (a[property] > b[property]) {
return 1;
}
// 如果属性相等,则继续比较下一个属性
}
// 所有属性都相等
return 0;
});
}
// 示例对象数组
const employees = [
{ name: 'Alice', age: 30, salary: 50000 },
{ name: 'Bob', age: 25, salary: 60000 },
{ name: 'Charlie', age: 35, salary: 55000 },
];
// 使用剩余参数传入多个属性进行排序
const sortedEmployees = sortObjectsByProperties(employees, 'age', 'salary');
console.log(sortedEmployees);输出:
[
{ name: 'Bob', age: 25, salary: 60000 }, // 年龄最小
{ name: 'Alice', age: 30, salary: 50000 }, // 年龄次小,但薪水低于Charlie
{ name: 'Charlie', age: 35, salary: 55000 } // 年龄最大,薪水也最高(在同龄人中)
]四. 对象数组汉字按拼音排序
1.使用stringObject.localeCompare(target)
const chinesePeople = [
{ name: '张三', age: 30 },
{ name: '李四', age: 25 },
{ name: '王五', age: 35 },
{ name: '赵六', age: 40 },
];
// 使用 localeCompare 对名字属性进行排序
chinesePeople.sort((a, b) => a.name.localeCompare(b.name, 'zh-CN'));
console.log(chinesePeople);输出:
[
{ name: '李四', age: 25 },
{ name: '王五', age: 35 },
{ name: '张三', age: 30 },
{ name: '赵六', age: 40 }
]2.使用第三方库
如果你想要根据汉字拼音对对象数组进行排序,你需要先将汉字转换为拼音,然后根据拼音进行排序。这通常需要使用到第三方库来实现汉字到拼音的转换,比如 pinyin 库。
npm install pinyinconst pinyin = require('pinyin');
function sortObjectsByChinesePinyin(array, propertyName) {
return array.sort((a, b) => {
const aPinyin = pinyin(a[propertyName], { style: pinyin.STYLE_NORMAL, heteronym: false }).join('');
const bPinyin = pinyin(b[propertyName], { style: pinyin.STYLE_NORMAL, heteronym: false }).join('');
return aPinyin.localeCompare(bPinyin);
});
}
// 示例对象数组
const chineseNames = [
{ name: '张三', age: 30 },
{ name: '李四', age: 25 },
{ name: '王五', age: 35 },
];
// 使用汉字拼音对名字进行排序
const sortedChineseNames = sortObjectsByChinesePinyin(chineseNames, 'name');
console.log(sortedChineseNames);输出:
[
{ name: '李四', age: 25 }, // 'lǐ sì'
{ name: '王五', age: 35 }, // 'wáng wǔ'
{ name: '张三', age: 30 } // 'zhāng sān'
]强调:如果用VS调试,别忘记了在luanch.jsion文件中添加 "console": "integratedTerminal",这句话,不然会报错。还看不到运行结果。