个人主页:Lei宝啊
愿所有美好如期而遇
目录
第一题
第二题
第三题
第一题
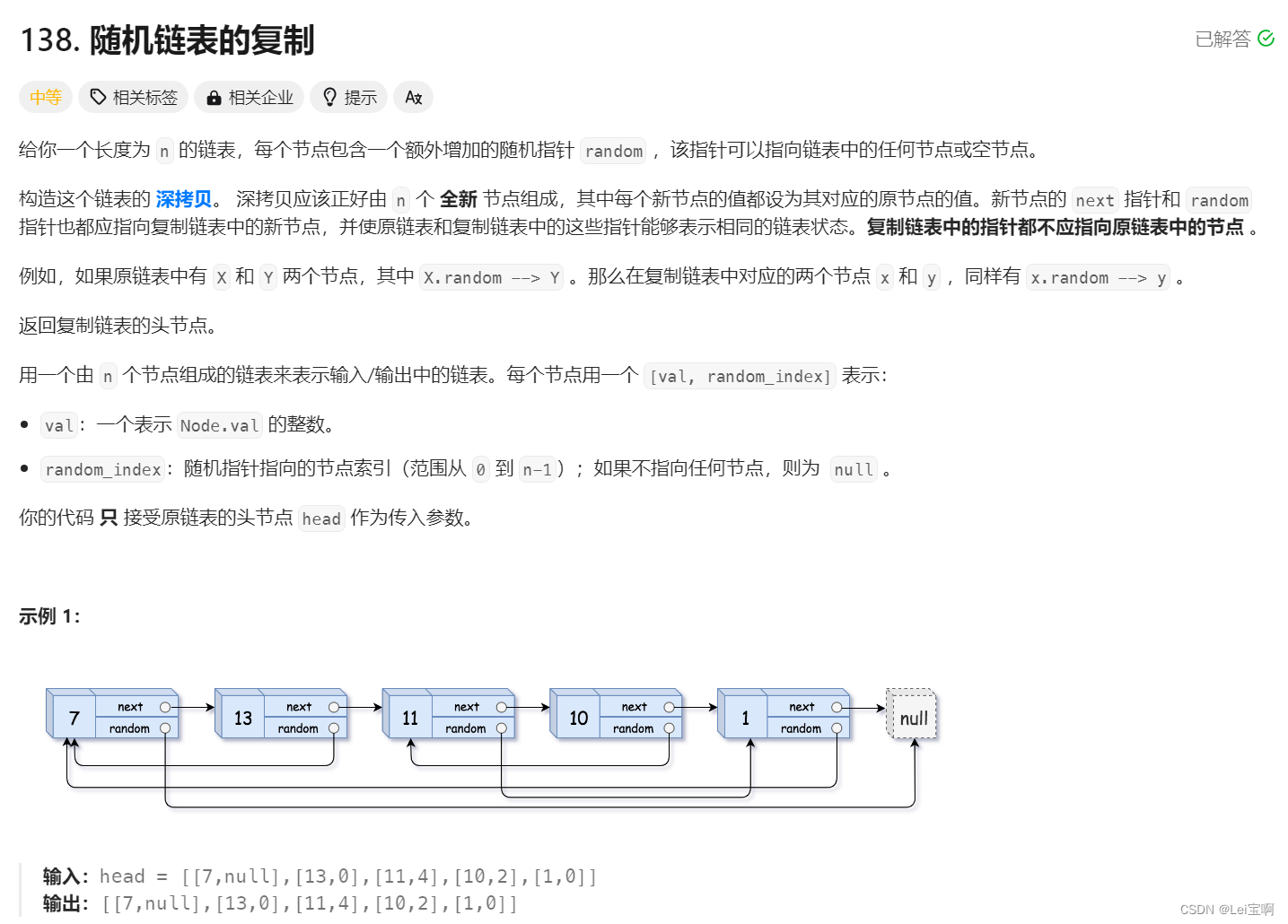
随机链表的复制![]() https://leetcode.cn/problems/copy-list-with-random-pointer/description/
https://leetcode.cn/problems/copy-list-with-random-pointer/description/
思路
首先遍历旧链表,并创建新节点,同时用map将旧节点与新节点存起来建立联系,这样在遍历新链表填充random的时候,就可以这样填Node* copy = m[cur]; copy->random = m[copy->random];
代码
class Solution {
public:
Node* copyRandomList(Node* head)
{
Node* cur = head;
Node* phead = nullptr;
Node* ptail = nullptr;
map<Node*,Node*> m;
while(cur)
{
Node* temp = new Node(cur->val);
if(phead == nullptr)
{
phead = ptail = temp;
}
else
{
ptail->next = temp;
ptail = ptail->next;
}
m[cur] = temp;
cur = cur->next;
}
cur = head;
while(cur)
{
Node* copy = m[cur];
if(cur->random == nullptr)
copy->random = nullptr;
else
copy->random = m[cur->random];
cur = cur->next;
}
return phead;
}
};第二题
前K个高频单词![]() https://leetcode.cn/problems/top-k-frequent-words/description/
https://leetcode.cn/problems/top-k-frequent-words/description/
思路
这道题有两个点,第一个点是按照单词出现频率排序,第二个点是频率相同,按字母的字典序排序。
首先我们可以使用map<string,int>来存单词和他的频率,这样这些单词就先进行了字典序排序,接着将map里的元素拷贝到一个vector<pair<string,int>>中,然后按照频率排序,但是这个排序必须是稳定排序,因为我们一开始在map中就已经按照字典序排好了单词,接下来按照频率排序时,稳定排序不会改变原来频率相同单词的相对顺序,所以这里的排序有两种选择,第一种就是使用库里的stable_sort,这个底层使用的归并排序,是稳定排序,而sort是不稳定排序,底层使用的快排。第二种就是使用sort,改变他的排序方式,有一个参数Compare comp,就是一个仿函数的对象,我们需要自己写一个仿函数,然后传递他的对象。
代码
class Solution {
public:
class Compare
{
public:
bool operator()(const pair<string,int>& k, const pair<string,int>& v)
{
return k.second > v.second || (k.second == v.second && k.first < v.first);
}
};
vector<string> topKFrequent(vector<string>& words, int k)
{
//去重并按照字典顺序排序
map<string,int> m;
for(auto &e : words)
{
m[e]++;
}
//按照频率排序,并在频率相同时按照字典序排序
vector<pair<string,int>> v(m.begin(),m.end());
sort(v.begin(),v.end(),Compare());
vector<string> ret;
for(auto &e : v)
{
ret.push_back(e.first);
k--;
if(k == 0) break;
}
return ret;
}
};第三题
两个数组的交集![]() https://leetcode.cn/problems/intersection-of-two-arrays/description/
https://leetcode.cn/problems/intersection-of-two-arrays/description/
思路
这里需要使输出结果的每个元素唯一,那么我们需要对原来的容器中的元素进行去重,这里我们可以使用set,第一种方式,我们使用set去重后,使用迭代器遍历其中一个set,然后在另一个set中找是否存在,存在就push_back进我们的vector中。第二种方式,我们使用迭代器遍历两个set,然后使*it1和*it2中小的++,大的继续往后走,相等的就push_back,这种方法的好处是不仅可以取交集,还可以取差集(相等跳过,不相等留下)。
代码
class Solution
{
public:
vector<int> intersection(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2)
{
set<int> st1(nums1.begin(),nums1.end());
set<int> st2(nums2.begin(),nums2.end());
vector<int> v;
set<int>::iterator it1 = st1.begin();
set<int>::iterator it2 = st2.begin();
while(it1 != st1.end() && it2 != st2.end())
{
if(*it1 < *it2) it1++;
else if(*it1 > *it2) it2++;
else
{
v.push_back(*it1);
it1++;
it2++;
}
}
return v;
}
};