前言
接着前文分析Android T 远程动画显示流程其二
我们通过IRemoteAnimationRunner跨进程通信从系统进程来到了桌面进程,这里是真正动画播放的逻辑。
之后又通过IRemoteAnimationFinishedCallback跨进程通信回到系统进程,处理动画结束时的逻辑。
进入桌面进程启动动画
跨进程通信,实现IRemoteAnimationRunner
代码路径:frameworks/base/packages/SystemUI/shared/src/com/android/systemui/shared/system/RemoteAnimationRunnerCompat.java
public abstract class RemoteAnimationRunnerCompat extends IRemoteAnimationRunner.Stub {
public abstract void onAnimationStart(@WindowManager.TransitionOldType int transit,
RemoteAnimationTarget[] apps, RemoteAnimationTarget[] wallpapers,
RemoteAnimationTarget[] nonApps, Runnable finishedCallback);
@Override
public final void onAnimationStart(@TransitionOldType int transit,
RemoteAnimationTarget[] apps,
RemoteAnimationTarget[] wallpapers,
RemoteAnimationTarget[] nonApps,
final IRemoteAnimationFinishedCallback finishedCallback) {
//调用自身抽象方法onAnimationStart
onAnimationStart(transit, apps, wallpapers,
nonApps, () -> {
try {
finishedCallback.onAnimationFinished();
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Log.e("ActivityOptionsCompat", "Failed to call app controlled animation"
+ " finished callback", e);
}
});
}
......
}
这里传递的参数都是前面RemoteAnimationController.goodToGo方法中获取的值。
transit的值是TRANSIT_OLD_WALLPAPER_CLOSE(12);
app指的是桌面和应用的RemoteAnimationTarget;
wallpapers壁纸的RemoteAnimationTarget;
nonApp非APP类型的RemoteAnimationTarget;
finishedCallback是FinishedCallback对象,这里传递的是调用了其onAnimationFinished()方法。
这方方法调用了自身抽象方法调用自身抽象方法onAnimationStart,onAnimationStart方法真正的实现在LauncherAnimationRunner类中
@TargetApi(Build.VERSION_CODES.P)
public class LauncherAnimationRunner extends RemoteAnimationRunnerCompat {
......
@BinderThread
public void onAnimationStart(
int transit,
RemoteAnimationTarget[] appTargets,
RemoteAnimationTarget[] wallpaperTargets,
RemoteAnimationTarget[] nonAppTargets,
Runnable runnable) {
Runnable r = () -> {
//退出动画的流程,此时mAnimationResult为空,尚未进入该流程
finishExistingAnimation();
//创建AnimationResult,传递了两个runnable
//() -> mAnimationResult = null,把AnimationResult对象置空
//runnable,就是前面传递的IRemoteAnimationFinishedCallback.onAnimationFinished
mAnimationResult = new AnimationResult(() -> mAnimationResult = null, runnable);
//传递从系统侧调用过来的参数创建动画
getFactory().onCreateAnimation(transit, appTargets, wallpaperTargets, nonAppTargets,
mAnimationResult);
};
//根据mStartAtFrontOfQueue的值,执行线程 r
if (mStartAtFrontOfQueue) {
//将Runnable插入到消息队列的前面,以确保它尽快被执行
postAtFrontOfQueueAsynchronously(mHandler, r);
} else {
//将Runnable异步地插入到消息队列中,它将在队列中的其他消息之后执行。
postAsyncCallback(mHandler, r);
}
}
......
}
-
退出动画的流程
finishExistingAnimation();@UiThread private void finishExistingAnimation() { if (mAnimationResult != null) { mAnimationResult.finish(); mAnimationResult = null; } }根据mAnimationResult是否为空执行finish方法,主要就是执行
mASyncFinishRunnable,后续会在动画退出流程中细讲finish方法。 -
创建AnimationResult
mAnimationResult = new AnimationResult(() -> mAnimationResult = null, runnable);public static final class AnimationResult { ...... private AnimationResult(Runnable syncFinishRunnable, Runnable asyncFinishRunnable) { mSyncFinishRunnable = syncFinishRunnable; mASyncFinishRunnable = asyncFinishRunnable; } ...... }AnimationResult主要用来返回当前动画播放结果,以便后续执行动画播放完成时的回调(mASyncFinishRunnable)。
() -> mAnimationResult = null,一个把AnimationResult对象置空的Runnable,保存到mSyncFinishRunnable中;
runnable,就是前面传递的IRemoteAnimationFinishedCallback.onAnimationFinished,保存到mASyncFinishRunnable中。 -
传递从系统侧创建的参数创建动画
getFactory().onCreateAnimation(transit, appTargets, wallpaperTargets, nonAppTargets, mAnimationResult);传递了从系统侧创建的参数,并传递了
mAnimationResult对象。这里调用的是RemoteAnimationFactory接口中的onCreateAnimation方法。/** * Used with LauncherAnimationRunner as an interface for the runner to call back to the * implementation. */ @FunctionalInterface public interface RemoteAnimationFactory { /** * Called on the UI thread when the animation targets are received. The implementation must * call {@link AnimationResult#setAnimation} with the target animation to be run. */ void onCreateAnimation(int transit, RemoteAnimationTarget[] appTargets, RemoteAnimationTarget[] wallpaperTargets, RemoteAnimationTarget[] nonAppTargets, LauncherAnimationRunner.AnimationResult result); ...... }在最开始Launcher.startActivitySafely流程中,QuickstepTransitionManager.getActivityLaunchOptions方法中创建了AppLaunchAnimationRunner对象,并作为RemoteAnimationFactory对象传递到了。
mAppLaunchRunner = new AppLaunchAnimationRunner(v, onEndCallback); RemoteAnimationRunnerCompat runner = new LauncherAnimationRunner( mHandler, mAppLaunchRunner, true /* startAtFrontOfQueue */);因此我们这里RemoteAnimationFactory的实现,就是在QuickstepTransitionManager.AppLaunchAnimationRunner中。
传递从系统侧创建的参数创建动画
代码路径:packages/apps/Launcher3/quickstep/src/com/android/launcher3/QuickstepTransitionManager.java
private class AppLaunchAnimationRunner implements RemoteAnimationFactory {
private final View mV;
private final RunnableList mOnEndCallback;
AppLaunchAnimationRunner(View v, RunnableList onEndCallback) {
mV = v;
mOnEndCallback = onEndCallback;
}
@Override
public void onCreateAnimation(int transit,
RemoteAnimationTarget[] appTargets,
RemoteAnimationTarget[] wallpaperTargets,
RemoteAnimationTarget[] nonAppTargets,
LauncherAnimationRunner.AnimationResult result) {
//创建AnimatorSet
AnimatorSet anim = new AnimatorSet();
//判断桌面的是否已经不在前台
boolean launcherClosing =
launcherIsATargetWithMode(appTargets, MODE_CLOSING);
//检查是否从桌面小部件启动应用
final boolean launchingFromWidget = mV instanceof LauncherAppWidgetHostView;
//检查是否从最近应用列表启动应用
final boolean launchingFromRecents = isLaunchingFromRecents(mV, appTargets);
//决定是否跳过动画的第一帧
final boolean skipFirstFrame;
if (launchingFromWidget) {//从桌面小部件启动应用的动画
composeWidgetLaunchAnimator(anim, (LauncherAppWidgetHostView) mV, appTargets,
wallpaperTargets, nonAppTargets, launcherClosing);
addCujInstrumentation(
anim, InteractionJankMonitorWrapper.CUJ_APP_LAUNCH_FROM_WIDGET);
skipFirstFrame = true;
} else if (launchingFromRecents) {//从最近任务启动应用的动画
composeRecentsLaunchAnimator(anim, mV, appTargets, wallpaperTargets, nonAppTargets,
launcherClosing);
addCujInstrumentation(
anim, InteractionJankMonitorWrapper.CUJ_APP_LAUNCH_FROM_RECENTS);
skipFirstFrame = true;
} else {//点击桌面图标启动应用的动画
composeIconLaunchAnimator(anim, mV, appTargets, wallpaperTargets, nonAppTargets,
launcherClosing);
addCujInstrumentation(anim, InteractionJankMonitorWrapper.CUJ_APP_LAUNCH_FROM_ICON);
skipFirstFrame = false;
}
//桌面不在前台给动画添加一个监听器
if (launcherClosing) {
anim.addListener(mForceInvisibleListener);
}
//设置动画和回调
result.setAnimation(anim, mLauncher, mOnEndCallback::executeAllAndDestroy,
skipFirstFrame);
}
@Override
public void onAnimationCancelled() {
mOnEndCallback.executeAllAndDestroy();
}
}
这里我们主要关注点击桌面图标启动应用的动画逻辑
点击桌面图标启动应用的动画
composeIconLaunchAnimator(anim, mV, appTargets, wallpaperTargets, nonAppTargets,
launcherClosing);
anim一个AnimatorSet对象;
mV这里指的是启动的应用图标,比如com.android.launcher3.BubbleTextView{bace738 VFED..CL. ........ 582,525-859,945 #7f09016a app:id/icon};
appTargets指的是桌面和应用的RemoteAnimationTarget;
wallpaperTargets壁纸的RemoteAnimationTarget;
nonAppTargets非APP类型的RemoteAnimationTarget;
launcherClosing此时桌面的是否已经不在前台,因此值为true
/**
* Compose the animations for a launch from the app icon.
*
* @param anim the animation to add to
* @param v the launching view with the icon
* @param appTargets the list of opening/closing apps
* @param launcherClosing true if launcher is closing
*/
private void composeIconLaunchAnimator(@NonNull AnimatorSet anim, @NonNull View v,
@NonNull RemoteAnimationTarget[] appTargets,
@NonNull RemoteAnimationTarget[] wallpaperTargets,
@NonNull RemoteAnimationTarget[] nonAppTargets,
boolean launcherClosing) {
// Set the state animation first so that any state listeners are called
// before our internal listeners.
//setCurrentAnimation(anim)取消任何正在运行的动画,设置新的动画
//即将动画设置为当前状态动画
mLauncher.getStateManager().setCurrentAnimation(anim);
// Note: the targetBounds are relative to the launcher
int startDelay = getSingleFrameMs(mLauncher);
//设置动画参数
Animator windowAnimator = getOpeningWindowAnimators(
v, appTargets, wallpaperTargets, nonAppTargets, launcherClosing);
//设置动画启动延时
windowAnimator.setStartDelay(startDelay);
//设置windowAnimator给AnimatorSet对象
anim.play(windowAnimator);
//如果桌面已经不在最顶层显示
if (launcherClosing) {
// Delay animation by a frame to avoid jank.
//将动画延迟一帧以避免抖动
//创建一个launcherAnimator动画和endListener线程
Pair<AnimatorSet, Runnable> launcherContentAnimator =
getLauncherContentAnimator(true /* isAppOpening */, startDelay, false);
//把launcherAnimator动画放到AnimatorSet
anim.play(launcherContentAnimator.first);
anim.addListener(new AnimatorListenerAdapter() {
@Override
public void onAnimationEnd(Animator animation) {
//运行endListener线程
launcherContentAnimator.second.run();
}
});
}
}
之前最为关键的就是getOpeningWindowAnimators方法
Animator windowAnimator = getOpeningWindowAnimators(
v, appTargets, wallpaperTargets, nonAppTargets, launcherClosing);
这个方法是动画真正的设置部分
设置动画相关参数、监听等
/**
* @return Animator that controls the window of the opening targets from app icons.
*/
private Animator getOpeningWindowAnimators(View v,
RemoteAnimationTarget[] appTargets,
RemoteAnimationTarget[] wallpaperTargets,
RemoteAnimationTarget[] nonAppTargets,
boolean launcherClosing) {
//获取应用方向
int rotationChange = getRotationChange(appTargets);
//获取启动应用的窗口边界
Rect windowTargetBounds = getWindowTargetBounds(appTargets, rotationChange);
//检查appTargets中所有应用目标是否半透明
//areAllTargetsTranslucent方法返回的的是,
//mode值为MODE_OPENING(正在打开的应用)的RemoteAnimationTarget的isTranslucent的值
boolean appTargetsAreTranslucent = areAllTargetsTranslucent(appTargets);
RectF launcherIconBounds = new RectF();
//获取一个浮动图标视图
FloatingIconView floatingView = FloatingIconView.getFloatingIconView(mLauncher, v,
!appTargetsAreTranslucent, launcherIconBounds, true /* isOpening */);
Rect crop = new Rect();
Matrix matrix = new Matrix();
//创建mMode为MODE_OPENING的RemoteAnimationTargets对象
//把app、壁纸和非app类型的RemoteAnimationTarget对象保存到RemoteAnimationTargets中
RemoteAnimationTargets openingTargets = new RemoteAnimationTargets(appTargets,
wallpaperTargets, nonAppTargets, MODE_OPENING);
//创建SurfaceTransactionApplier对象
SurfaceTransactionApplier surfaceApplier =
new SurfaceTransactionApplier(floatingView);
//为了确保动画完成时,释放相关资源
openingTargets.addReleaseCheck(surfaceApplier);
//获取导航栏的RemoteAnimationTarget对象
RemoteAnimationTarget navBarTarget = openingTargets.getNavBarRemoteAnimationTarget();
//DragLayer是一个ViewGroup,协调处理它的子view拖动的容器
//getLocationOnScreen获取DragLayer在屏幕上的绝对位置
int[] dragLayerBounds = new int[2];
mDragLayer.getLocationOnScreen(dragLayerBounds);
//检查是否支持冷启动窗口Splash Screen
final boolean hasSplashScreen;
if (supportsSSplashScreen()) {
int taskId = openingTargets.getFirstAppTargetTaskId();
Pair<Integer, Integer> defaultParams = Pair.create(STARTING_WINDOW_TYPE_NONE, 0);
Pair<Integer, Integer> taskParams =
mTaskStartParams.getOrDefault(taskId, defaultParams);
mTaskStartParams.remove(taskId);
hasSplashScreen = taskParams.first == STARTING_WINDOW_TYPE_SPLASH_SCREEN;
} else {
hasSplashScreen = false;
}
//创建AnimOpenProperties对象,设置应用启动时的动画属性
AnimOpenProperties prop = new AnimOpenProperties(mLauncher.getResources(), mDeviceProfile,
windowTargetBounds, launcherIconBounds, v, dragLayerBounds[0], dragLayerBounds[1],
hasSplashScreen, floatingView.isDifferentFromAppIcon());
//计算裁剪区域的边界
int left = prop.cropCenterXStart - prop.cropWidthStart / 2;
int top = prop.cropCenterYStart - prop.cropHeightStart / 2;
int right = left + prop.cropWidthStart;
int bottom = top + prop.cropHeightStart;
// Set the crop here so we can calculate the corner radius below.
crop.set(left, top, right, bottom);
//创建临时矩形和点对象
RectF floatingIconBounds = new RectF();
RectF tmpRectF = new RectF();
Point tmpPos = new Point();
//设置动画的一些参数和监听
AnimatorSet animatorSet = new AnimatorSet();
ValueAnimator appAnimator = ValueAnimator.ofFloat(0, 1);
appAnimator.setDuration(APP_LAUNCH_DURATION);
//设置动画的插值器为LINEAR。插值器决定了动画的速度曲线。LINEAR意味着动画将匀速进行
appAnimator.setInterpolator(LINEAR);
//为appAnimator添加一个动画监听器floatingView。
//当动画开始、结束、取消或重复时,floatingView上的相应方法将被调用。
appAnimator.addListener(floatingView);
appAnimator.addListener(new AnimatorListenerAdapter() {
@Override
//监听动开始
public void onAnimationStart(Animator animation) {
//获取LauncherTaskbarUIController的实例
LauncherTaskbarUIController taskbarController = mLauncher.getTaskbarUIController();
//检查是否应该调用shouldShowEdu()
if (taskbarController != null && taskbarController.shouldShowEdu()) {
// LAUNCHER_TASKBAR_EDUCATION_SHOWING is set to true here, when the education
// flow is about to start, to avoid a race condition with other components
// that would show something else to the user as soon as the app is opened.
//将LAUNCHER_TASKBAR_EDUCATION_SHOWING设置为true,以避免与其他组件发生竞争
Settings.Secure.putInt(mLauncher.getContentResolver(),
LAUNCHER_TASKBAR_EDUCATION_SHOWING, 1);
}
}
@Override
//监听动结束
public void onAnimationEnd(Animator animation) {
if (v instanceof BubbleTextView) {
//我们这里v是BubbleTextView类型
//设置控件v保持按下的状态为false
((BubbleTextView) v).setStayPressed(false);
}
//获取LauncherTaskbarUIController的实例
LauncherTaskbarUIController taskbarController = mLauncher.getTaskbarUIController();
if (taskbarController != null) {
//调用shouldShowEdu()
taskbarController.showEdu();
}
//释放所有类型的RemoteAnimationTarget对象
//包含壁纸、app和非app类型的RemoteAnimationTarget对象
openingTargets.release();
}
});
//initialWindowRadius用于设置动画开始时的窗口圆角半径
//supportsRoundedCornersOnWindows(mLauncher.getResources()判断桌面是否支持窗口圆角
final float initialWindowRadius = supportsRoundedCornersOnWindows(mLauncher.getResources())
? Math.max(crop.width(), crop.height()) / 2f
: 0f;
//finalWindowRadius用于设置动画结束时的窗口圆角半径
//mDeviceProfile.isMultiWindowMode检查是否处于多窗口模式
//getWindowCornerRadius(mLauncher)获取桌面窗口的圆角半径
final float finalWindowRadius = mDeviceProfile.isMultiWindowMode
? 0 : getWindowCornerRadius(mLauncher);
//inalShadowRadius用于设置动画结束时的阴影半径
//appTargetsAreTranslucent表示应用目标是否半透明
//mMaxShadowRadius最大阴影半径值
final float finalShadowRadius = appTargetsAreTranslucent ? 0 : mMaxShadowRadius;
MultiValueUpdateListener listener = new MultiValueUpdateListener() {
//mDx:这个属性表示在动画过程中,X轴上的位移变化。
//它从0开始,到prop.dX结束,动画时长为APP_LAUNCH_DURATION,使用mOpeningXInterpolator作为插值器。
FloatProp mDx = new FloatProp(0, prop.dX, 0, APP_LAUNCH_DURATION,
mOpeningXInterpolator);
//这个属性表示在动画过程中,Y轴上的位移变化。
//它从0开始,到prop.dY结束,动画时长为APP_LAUNCH_DURATION,使用mOpeningInterpolator作为插值器。
FloatProp mDy = new FloatProp(0, prop.dY, 0, APP_LAUNCH_DURATION,
mOpeningInterpolator);
//mIconScaleToFitScreen:这个属性表示应用图标在屏幕上的缩放变化。
//它从prop.initialAppIconScale开始,到prop.finalAppIconScale结束,
//动画时长为APP_LAUNCH_DURATION,使用mOpeningInterpolator作为插值器。
FloatProp mIconScaleToFitScreen = new FloatProp(prop.initialAppIconScale,
prop.finalAppIconScale, 0, APP_LAUNCH_DURATION, mOpeningInterpolator);
//mIconAlpha:这个属性表示应用图标的透明度变化。
//它从prop.iconAlphaStart开始,到0结束,
//动画的开始延迟为APP_LAUNCH_ALPHA_START_DELAY,时长为APP_LAUNCH_ALPHA_DURATION,
//使用线性插值器(LINEAR)。
FloatProp mIconAlpha = new FloatProp(prop.iconAlphaStart, 0f,
APP_LAUNCH_ALPHA_START_DELAY, APP_LAUNCH_ALPHA_DURATION, LINEAR);
//mWindowRadius:这个属性表示窗口圆角的半径变化。
//它从initialWindowRadius开始,到finalWindowRadius结束,动画时长为APP_LAUNCH_DURATION,
//使用mOpeningInterpolator作为插值器。
FloatProp mWindowRadius = new FloatProp(initialWindowRadius, finalWindowRadius, 0,
APP_LAUNCH_DURATION, mOpeningInterpolator);
//mShadowRadius:这个属性表示阴影的半径变化。
//它从0开始,到finalShadowRadius结束,动画时长为APP_LAUNCH_DURATION,
//使用mOpeningInterpolator作为插值器。
FloatProp mShadowRadius = new FloatProp(0, finalShadowRadius, 0,
APP_LAUNCH_DURATION, mOpeningInterpolator);
//mCropRectCenterX、mCropRectCenterY、mCropRectWidth、mCropRectHeight
//这些属性分别表示裁剪矩形的中心X坐标、中心Y坐标、宽度和高度的变化。
//它们都有各自的起始值和结束值,动画时长为APP_LAUNCH_DURATION,使用mOpeningInterpolator作为插值器。
FloatProp mCropRectCenterX = new FloatProp(prop.cropCenterXStart, prop.cropCenterXEnd,
0, APP_LAUNCH_DURATION, mOpeningInterpolator);
FloatProp mCropRectCenterY = new FloatProp(prop.cropCenterYStart, prop.cropCenterYEnd,
0, APP_LAUNCH_DURATION, mOpeningInterpolator);
FloatProp mCropRectWidth = new FloatProp(prop.cropWidthStart, prop.cropWidthEnd, 0,
APP_LAUNCH_DURATION, mOpeningInterpolator);
FloatProp mCropRectHeight = new FloatProp(prop.cropHeightStart, prop.cropHeightEnd, 0,
APP_LAUNCH_DURATION, mOpeningInterpolator);
//这个属性表示导航栏的淡出效果。
//它从1开始,到0结束,动画时长为ANIMATION_NAV_FADE_OUT_DURATION,
//使用NAV_FADE_OUT_INTERPOLATOR作为插值器。
FloatProp mNavFadeOut = new FloatProp(1f, 0f, 0, ANIMATION_NAV_FADE_OUT_DURATION,
NAV_FADE_OUT_INTERPOLATOR);
//mNavFadeIn:这个属性表示导航栏的淡入效果。它从0开始,到1结束,
//动画的开始延迟为ANIMATION_DELAY_NAV_FADE_IN,时长为ANIMATION_NAV_FADE_IN_DURATION,
//使用NAV_FADE_IN_INTERPOLATOR作为插值器。
FloatProp mNavFadeIn = new FloatProp(0f, 1f, ANIMATION_DELAY_NAV_FADE_IN,
ANIMATION_NAV_FADE_IN_DURATION, NAV_FADE_IN_INTERPOLATOR);
//动画的更新
@Override
public void onUpdate(float percent, boolean initOnly) {
// Calculate the size of the scaled icon.
//计算缩放图标的大小
float iconWidth = launcherIconBounds.width() * mIconScaleToFitScreen.value;
float iconHeight = launcherIconBounds.height() * mIconScaleToFitScreen.value;
int left = (int) (mCropRectCenterX.value - mCropRectWidth.value / 2);
int top = (int) (mCropRectCenterY.value - mCropRectHeight.value / 2);
int right = (int) (left + mCropRectWidth.value);
int bottom = (int) (top + mCropRectHeight.value);
crop.set(left, top, right, bottom);
final int windowCropWidth = crop.width();
final int windowCropHeight = crop.height();
if (rotationChange != 0) {
Utilities.rotateBounds(crop, mDeviceProfile.widthPx,
mDeviceProfile.heightPx, rotationChange);
}
// Scale the size of the icon to match the size of the window crop.
//缩放图标的大小以匹配窗口裁剪的大小。
float scaleX = iconWidth / windowCropWidth;
float scaleY = iconHeight / windowCropHeight;
float scale = Math.min(1f, Math.max(scaleX, scaleY));
float scaledCropWidth = windowCropWidth * scale;
float scaledCropHeight = windowCropHeight * scale;
float offsetX = (scaledCropWidth - iconWidth) / 2;
float offsetY = (scaledCropHeight - iconHeight) / 2;
// Calculate the window position to match the icon position.
//计算窗口位置以匹配图标位置。
tmpRectF.set(launcherIconBounds);
tmpRectF.offset(dragLayerBounds[0], dragLayerBounds[1]);
tmpRectF.offset(mDx.value, mDy.value);
Utilities.scaleRectFAboutCenter(tmpRectF, mIconScaleToFitScreen.value);
float windowTransX0 = tmpRectF.left - offsetX - crop.left * scale;
float windowTransY0 = tmpRectF.top - offsetY - crop.top * scale;
// Calculate the icon position.
//计算图标位置
floatingIconBounds.set(launcherIconBounds);
floatingIconBounds.offset(mDx.value, mDy.value);
Utilities.scaleRectFAboutCenter(floatingIconBounds, mIconScaleToFitScreen.value);
floatingIconBounds.left -= offsetX;
floatingIconBounds.top -= offsetY;
floatingIconBounds.right += offsetX;
floatingIconBounds.bottom += offsetY;
if (initOnly) {
// For the init pass, we want full alpha since the window is not yet ready.
//使用floatingView.update方法更新浮动视图的属性,包括透明度、边界、半径等。
floatingView.update(1f, 255, floatingIconBounds, percent, 0f,
mWindowRadius.value * scale, true /* isOpening */);
return;
}
SurfaceTransaction transaction = new SurfaceTransaction();
//遍历桌面和启动应用的RemoteAnimationTarget,获取其leash,分别做处理
for (int i = appTargets.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
RemoteAnimationTarget target = appTargets[i];
SurfaceProperties builder = transaction.forSurface(target.leash);
if (target.mode == MODE_OPENING) {
/**
* 如果目标模式是MODE_OPENING(打开模式),代码会设置一个矩阵(matrix)来进行缩放和平移操作。
* 根据rotationChange的值(可能是表示屏幕旋转的变量),代码会决定如何平移窗口。
* 然后,使用floatingView.update方法更新浮动视图的属性,包括透明度、边界、半径等。
* 接着,通过builder.setMatrix等方法设置窗口的矩阵、裁剪区域、透明度、圆角半径和阴影半径。
*/
matrix.setScale(scale, scale);
if (rotationChange == 1) {
matrix.postTranslate(windowTransY0,
mDeviceProfile.widthPx - (windowTransX0 + scaledCropWidth));
} else if (rotationChange == 2) {
matrix.postTranslate(
mDeviceProfile.widthPx - (windowTransX0 + scaledCropWidth),
mDeviceProfile.heightPx - (windowTransY0 + scaledCropHeight));
} else if (rotationChange == 3) {
matrix.postTranslate(
mDeviceProfile.heightPx - (windowTransY0 + scaledCropHeight),
windowTransX0);
} else {
matrix.postTranslate(windowTransX0, windowTransY0);
}
floatingView.update(mIconAlpha.value, 255, floatingIconBounds, percent, 0f,
mWindowRadius.value * scale, true /* isOpening */);
builder.setMatrix(matrix)
.setWindowCrop(crop)
.setAlpha(1f - mIconAlpha.value)
.setCornerRadius(mWindowRadius.value)
.setShadowRadius(mShadowRadius.value);
} else if (target.mode == MODE_CLOSING) {
/**
* 如果目标模式是MODE_CLOSING(关闭模式),代码会处理关闭动画。
* 首先,根据目标的本地边界或位置设置临时位置(tmpPos)。
* 然后,根据rotationChange的值,可能需要对裁剪区域(crop)和临时位置进行旋转调整。
* 最后,设置窗口的矩阵和裁剪区域,并将透明度设置为1(完全不透明)。
*/
if (target.localBounds != null) {
tmpPos.set(target.localBounds.left, target.localBounds.top);
} else {
tmpPos.set(target.position.x, target.position.y);
}
final Rect crop = new Rect(target.screenSpaceBounds);
crop.offsetTo(0, 0);
if ((rotationChange % 2) == 1) {
int tmp = crop.right;
crop.right = crop.bottom;
crop.bottom = tmp;
tmp = tmpPos.x;
tmpPos.x = tmpPos.y;
tmpPos.y = tmp;
}
matrix.setTranslate(tmpPos.x, tmpPos.y);
builder.setMatrix(matrix)
.setWindowCrop(crop)
.setAlpha(1f);
}
}
/**
* 如果navBarTarget不为空(即存在导航栏目标),代码会为其设置动画和视图属性。
* 根据`mNavFadeIn.value`的值,决定是淡入还是淡出导航栏。如果淡入值大于起始值,则应用淡入动画;
*/
if (navBarTarget != null) {
SurfaceProperties navBuilder =
transaction.forSurface(navBarTarget.leash);
if (mNavFadeIn.value > mNavFadeIn.getStartValue()) {
matrix.setScale(scale, scale);
matrix.postTranslate(windowTransX0, windowTransY0);
navBuilder.setMatrix(matrix)
.setWindowCrop(crop)
.setAlpha(mNavFadeIn.value);
} else {
navBuilder.setAlpha(mNavFadeOut.value);
}
}
surfaceApplier.scheduleApply(transaction);
}
};
appAnimator.addUpdateListener(listener);
// Since we added a start delay, call update here to init the FloatingIconView properly.
//调用MultiValueUpdateListener.update更新动画显示
listener.onUpdate(0, true /* initOnly */);
// If app targets are translucent, do not animate the background as it causes a visible
// flicker when it resets itself at the end of its animation.
//appTargetsAreTranslucent,启动的应用为半透明
//或 !launcherClosing,桌面在最顶层
if (appTargetsAreTranslucent || !launcherClosing) {
//仅设置appAnimator给animatorSet
animatorSet.play(appAnimator);
} else {
//设置appAnimator和getBackgroundAnimator() (背景动画)
//用于并行播放
animatorSet.playTogether(appAnimator, getBackgroundAnimator());
}
return animatorSet;
}
设置一些动画相关参数和监听,通过MultiValueUpdateListener.update方法更新动画显示。
调用setAnimation设置动画和回调
回到QuickstepTransitionManager.AppLaunchAnimationRunner.onCreateAnimation方法中,继续看到setAnimation方法:
result.setAnimation(anim, mLauncher, mOnEndCallback::executeAllAndDestroy,
skipFirstFrame);
前面的在getOpeningWindowAnimators方法中设置的动画,通过anim播放
动画的启动与结束
代码路径:packages/apps/Launcher3/quickstep/src/com/android/launcher3/LauncherAnimationRunner.java
/**
* Sets the animation to play for this app launch
* @param skipFirstFrame Iff true, we skip the first frame of the animation.
* We set to false when skipping first frame causes jank.
*/
@UiThread
public void setAnimation(AnimatorSet animation, Context context,
@Nullable Runnable onCompleteCallback, boolean skipFirstFrame) {
if (mInitialized) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Animation already initialized");
}
mInitialized = true;
mAnimator = animation;
mOnCompleteCallback = onCompleteCallback;
//如果动画为空,直接调用finish方法,走结束动画流程
if (mAnimator == null) {
finish();
} else if (mFinished) {//mFinished为true,表示动画播放结束
// Animation callback was already finished, skip the animation.
//调用mAnimator.start()和mAnimator.end()来跳过动画
mAnimator.start();
mAnimator.end();
if (mOnCompleteCallback != null) {
mOnCompleteCallback.run();
}
} else {
// Start the animation
//添加动画监听
mAnimator.addListener(new AnimatorListenerAdapter() {
@Override
//动画结束时的监听,调用finish()方法
public void onAnimationEnd(Animator animation) {
finish();
}
});
//开始播放动画
mAnimator.start();
//如果skipFirstFrame为true
if (skipFirstFrame) {
// Because t=0 has the app icon in its original spot, we can skip the
// first frame and have the same movement one frame earlier.
//调用mAnimator.setCurrentPlayTime()来设置动画的当前播放时间,
//该时间为动画总时长与getSingleFrameMs(context)的较小值。
//这可以使得应用图标从原始位置开始的移动提前一帧,
//因为t=0时应用图标位于其原始位置。
mAnimator.setCurrentPlayTime(
Math.min(getSingleFrameMs(context), mAnimator.getTotalDuration()));
}
}
}
}
这个方法主要是通过mAnimator.start();启动动画的播放。当动画播放结束时,使用finish();方法进入动画结束播放流程。
动画播放结束
动画播放结束时,调用finish方法进入结束动画流程
代码路径:packages/apps/Launcher3/quickstep/src/com/android/launcher3/LauncherAnimationRunner.java
public static final class AnimationResult {
......
@UiThread
private void finish() {
if (!mFinished) {
//运行的是 () -> mAnimationResult = null
//即把AnimationResult对象置空
mSyncFinishRunnable.run();
UI_HELPER_EXECUTOR.execute(() -> {
//运行的是IRemoteAnimationFinishedCallback.onAnimationFinished
mASyncFinishRunnable.run();
if (mOnCompleteCallback != null) {
MAIN_EXECUTOR.execute(mOnCompleteCallback);
}
});
//mFinished标志位置为true,表示动画播放完成。
mFinished = true;
}
}
......
}
前面跨进程通信时,对AnimationResult构造方法进行了初始化
private AnimationResult(Runnable syncFinishRunnable, Runnable asyncFinishRunnable) {
mSyncFinishRunnable = syncFinishRunnable;
mASyncFinishRunnable = asyncFinishRunnable;
}
并且onAnimationStart方法中给创建了AnimationResult对象,传递了两个runnable。
mAnimationResult = new AnimationResult(() -> mAnimationResult = null, runnable);
这里传递的runnable就是跨进程通信传递过来的动画完成时回调。
即mSyncFinishRunnable表示的就是() -> mAnimationResult = null,置空AnimationResult对象;
mASyncFinishRunnable表示的就是IRemoteAnimationFinishedCallback.onAnimationFinished方法,即跨进程调用结束动画流程。
跨进程通信进入动画结束流程
代码路径:frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/IRemoteAnimationFinishedCallback.aidl
/**
* Interface to be invoked by the controlling process when a remote animation has finished.
*
* @see IRemoteAnimationRunner
* {@hide}
*/
oneway interface IRemoteAnimationFinishedCallback {
@UnsupportedAppUsage
void onAnimationFinished();
}
IRemoteAnimationFinishedCallback的实现在RemoteAnimationController.FinishedCallback类中
进入系统进程结束动画
跨进程通信,实现IRemoteAnimationFinishedCallback
代码路径:frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/RemoteAnimationController.java
private static final class FinishedCallback extends IRemoteAnimationFinishedCallback.Stub {
RemoteAnimationController mOuter;
FinishedCallback(RemoteAnimationController outer) {
mOuter = outer;
}
@Override
public void onAnimationFinished() throws RemoteException {
ProtoLog.d(WM_DEBUG_REMOTE_ANIMATIONS, "app-onAnimationFinished(): mOuter=%s", mOuter);
final long token = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
try {
if (mOuter != null) {
mOuter.onAnimationFinished();
// In case the client holds on to the finish callback, make sure we don't leak
// RemoteAnimationController which in turn would leak the runner on the client.
mOuter = null;
}
} finally {
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(token);
}
}
/**
* Marks this callback as not be used anymore by releasing the reference to the outer class
* to prevent memory leak.
*/
void release() {
ProtoLog.d(WM_DEBUG_REMOTE_ANIMATIONS, "app-release(): mOuter=%s", mOuter);
mOuter = null;
}
};
这段代码的关键就是调用mOuter.onAnimationFinished();
onAnimationFinished方法的实现
private void onAnimationFinished() {
ProtoLog.d(WM_DEBUG_REMOTE_ANIMATIONS, "onAnimationFinished(): mPendingAnimations=%d",
mPendingAnimations.size());
//移除超时回调
mHandler.removeCallbacks(mTimeoutRunnable);
synchronized (mService.mGlobalLock) {
//解除绑定IRemoteAnimationRunner
unlinkToDeathOfRunner();
//释放绑定的IRemoteAnimationFinishedCallback
releaseFinishedCallback();
//开启事务
mService.openSurfaceTransaction();
try {
ProtoLog.d(WM_DEBUG_REMOTE_ANIMATIONS,
"onAnimationFinished(): Notify animation finished:");
//app类型动画结束时回调
//调用桌面和启动应用的动画结束时回调
for (int i = mPendingAnimations.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
final RemoteAnimationRecord adapters = mPendingAnimations.get(i);
if (adapters.mAdapter != null) {
adapters.mAdapter.mCapturedFinishCallback
.onAnimationFinished(adapters.mAdapter.mAnimationType,
adapters.mAdapter);
}
if (adapters.mThumbnailAdapter != null) {
adapters.mThumbnailAdapter.mCapturedFinishCallback
.onAnimationFinished(adapters.mThumbnailAdapter.mAnimationType,
adapters.mThumbnailAdapter);
}
mPendingAnimations.remove(i);
ProtoLog.d(WM_DEBUG_REMOTE_ANIMATIONS, "\tcontainer=%s",
adapters.mWindowContainer);
}
//壁纸类型动画结束时回调
for (int i = mPendingWallpaperAnimations.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
final WallpaperAnimationAdapter adapter = mPendingWallpaperAnimations.get(i);
adapter.getLeashFinishedCallback().onAnimationFinished(
adapter.getLastAnimationType(), adapter);
mPendingWallpaperAnimations.remove(i);
ProtoLog.d(WM_DEBUG_REMOTE_ANIMATIONS, "\twallpaper=%s", adapter.getToken());
}
//非App类型动画结束时回调
for (int i = mPendingNonAppAnimations.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
final NonAppWindowAnimationAdapter adapter = mPendingNonAppAnimations.get(i);
adapter.getLeashFinishedCallback().onAnimationFinished(
adapter.getLastAnimationType(), adapter);
mPendingNonAppAnimations.remove(i);
ProtoLog.d(WM_DEBUG_REMOTE_ANIMATIONS, "\tnonApp=%s",
adapter.getWindowContainer());
}
} catch (Exception e) {
Slog.e(TAG, "Failed to finish remote animation", e);
throw e;
} finally {
mService.closeSurfaceTransaction("RemoteAnimationController#finished");
}
// Reset input for all activities when the remote animation is finished.
final Consumer<ActivityRecord> updateActivities =
activity -> activity.setDropInputForAnimation(false);
mDisplayContent.forAllActivities(updateActivities);
}
setRunningRemoteAnimation(false);
ProtoLog.i(WM_DEBUG_REMOTE_ANIMATIONS, "Finishing remote animation");
}
我们这里主要关注的是App类型的动画结束流程,这里通过循环,把桌面和启动的应用动画结束时流程逐个调用。这个循环是反向遍历,因此先走的是桌面动画结束时的回调。
adapters.mAdapter.mCapturedFinishCallback
.onAnimationFinished(adapters.mAdapter.mAnimationType,
adapters.mAdapter);
mCapturedFinishCallback是RemoteAnimationAdapterWrapper对象,它其实就是SurfaceAnimator.getFinishedCallback方法。
在创建动画leash的流程中,SurfaceAnimator.startAnimation方法中有调用mAnimation.startAnimation(mLeash, t, type, mInnerAnimationFinishedCallback);,这里把mInnerAnimationFinishedCallback赋值给了RemoteAnimationAdapterWrapper的mCapturedFinishCallback,mInnerAnimationFinishedCallback在SurfaceAnimator的构造方法初始化的值是getFinishedCallback(staticAnimationFinishedCallback),即动画完成时的回调mCapturedFinishCallback对应的就是getFinishedCallback(staticAnimationFinishedCallback)。
所以这里mCapturedFinishCallback.onAnimationFinished调用的,实际是调用就是SurfaceAnimator.getFinishedCallback中匿名的(type, anim) -> {......}
回调处理动画完成的逻辑
这里的流程与本地动画流程相似
代码路径:frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/SurfaceAnimator.java
private OnAnimationFinishedCallback getFinishedCallback(
@Nullable OnAnimationFinishedCallback staticAnimationFinishedCallback) {
return (type, anim) -> {
synchronized (mService.mGlobalLock) {
//移除AnimationAdapter对应的SurfaceAnimator,并将这个SurfaceAnimator返回给target
//mAnimationTransferMap属于启动窗口的动画场景,这里我们不涉及
final SurfaceAnimator target = mService.mAnimationTransferMap.remove(anim);
if (target != null) {
//递归调用onAnimationFinished(type, anim),即return (type, anim) -> {......}
//直到所有的SurfaceAnimator移除完
target.mInnerAnimationFinishedCallback.onAnimationFinished(type, anim);
return;
}
//检查动画是否已被新动画替换,如果当前动画 (anim) 不等于之前存储的动画 (mAnimation),则不执行后续操作
if (anim != mAnimation) {
return;
}
//定义一个名为 resetAndInvokeFinish 的 Runnable
final Runnable resetAndInvokeFinish = () -> {
// We need to check again if the animation has been replaced with a new
// animation because the animatable may defer to finish.
//再次检查动画是否已被新动画替换,因为可设置动画可能会延迟到完成。
if (anim != mAnimation) {
return;
}
//mSurfaceAnimationFinishedCallback是在WindowContainer.startAnimation中赋值的
//其传递值为null,最终SurfaceAnimator.startAnimation赋值给mSurfaceAnimationFinishedCallback
final OnAnimationFinishedCallback animationFinishCallback =
mSurfaceAnimationFinishedCallback;
//重置与动画相关的状态
reset(mAnimatable.getSyncTransaction(), true /* destroyLeash */);
//WindowContainer构造方法中给SurfaceAnimator构造方法传递了staticAnimationFinishedCallback
if (staticAnimationFinishedCallback != null) {
//当一个Surface上的动画结束或取消且不重新启动时,这个回调将被执行。
//这是一个静态回调,它对通过这个 SurfaceAnimator 启动的所有动画都有效。
//回调WindowContainer.onAnimationFinished方法
staticAnimationFinishedCallback.onAnimationFinished(type, anim);
}
//mSurfaceAnimationFinishedCallback的值为null,因此animationFinishCallback的值为null
if (animationFinishCallback != null) {
//当一个Surface上的动画结束或取消且不重新启动时,这个回调将被执行。
//这个回调是每个动画(即每个 AnimationAdapter)特有的。
//如果在WindowContainer.startAnimation方法中有赋值,
//则回调WindowContainer.onAnimationFinished方法
animationFinishCallback.onAnimationFinished(type, anim);
}
};
// If both the Animatable and AnimationAdapter requests to be deferred, only the
// first one will be called.
//如果 mAnimatable 或动画本身请求延迟动画完成,并且它们都没有被延迟,
//那么直接执行 resetAndInvokeFinish.run()。否则,延迟执行。
if (!(mAnimatable.shouldDeferAnimationFinish(resetAndInvokeFinish)
|| anim.shouldDeferAnimationFinish(resetAndInvokeFinish))) {
resetAndInvokeFinish.run();
}
//设置动画完成标志,将 mAnimationFinished 设置为 true
mAnimationFinished = true;
}
};
}
这个方法主要做了这几件事:
- 通过递归的方式移除所有AnimationAdapter对应的SurfaceAnimator
其中的mAnimationTransferMap在启动窗口流程中,ActivityRecord.addStartingWindow中有调用transferStartingWindow方法,逐步调用到SurfaceAnimator.transferAnimation中进行添加mService.mAnimationTransferMap.put(mAnimation, this);,这里我们不涉及,因此target的值为null - 使用
shouldDeferAnimationFinish方法(默认返回false)用来判断是否需要延迟完成动画 - 执行
resetAndInvokeFinish.run(),调用reset(mAnimatable.getSyncTransaction(), true /* destroyLeash */);重置动画相关状态 - 最后调用回调通过
staticAnimationFinishedCallback.onAnimationFinished(type, anim);,调用WindowContainer.onAnimationFinished方法处理和响应动画完成的逻辑
重置动画相关状态并移除leash
reset(mAnimatable.getSyncTransaction(), true /* destroyLeash */);
代码路径:frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/SurfaceAnimator.java
private void reset(Transaction t, boolean destroyLeash) {
//移除AnimationAdapter对应的SurfaceAnimator
mService.mAnimationTransferMap.remove(mAnimation);
mAnimation = null;
mSurfaceAnimationFinishedCallback = null;
//动画类型置为空
mAnimationType = ANIMATION_TYPE_NONE;
//屏幕冻结时的快照
final SurfaceFreezer.Snapshot snapshot = mSnapshot;
mSnapshot = null;
if (snapshot != null) {
// Reset the mSnapshot reference before calling the callback to prevent circular reset.
//如果有屏幕冻结时的快照,取消该动画。
//最终会调用到SurfaceAnimationRunner.onAnimationCancelled
snapshot.cancelAnimation(t, !destroyLeash);
}
if (mLeash == null) {
return;
}
//使用leash存储动画图层mLeash
SurfaceControl leash = mLeash;
//把动画图层置为空
mLeash = null;
//移除leash
final boolean scheduleAnim = removeLeash(t, mAnimatable, leash, destroyLeash);
//将mAnimationFinished设置为false
mAnimationFinished = false;
if (scheduleAnim) {
//leash成功移除后,在WMS中会通过WindowAnimator调度动画,协调各个窗口
mService.scheduleAnimationLocked();
}
}
移除leash
调用removeLeash方法移除leash
final boolean scheduleAnim = removeLeash(t, mAnimatable, leash, destroyLeash);
传递的mAnimatable表示当前窗口,leash就是动画图层,destroyLeash在前面getFinishedCallback流程中传递的值为true
static boolean removeLeash(Transaction t, Animatable animatable, @NonNull SurfaceControl leash,
boolean destroy) {
/* log add start*/
Slog.i("WindowManager:","removeLeash leash = " + leash , new Exception());
/* log add end*/
//scheduleAnim一个标志位,初始值为false
//为true时,走前面reset方法中的mService.scheduleAnimationLocked()流程
boolean scheduleAnim = false;
//获取当前窗口的SurfaceControl
final SurfaceControl surface = animatable.getSurfaceControl();
//获取当前窗口的父窗口的SurfaceControl
final SurfaceControl parent = animatable.getParentSurfaceControl();
//获取动画图层
final SurfaceControl curAnimationLeash = animatable.getAnimationLeash();
// If the surface was destroyed or the leash is invalid, we don't care to reparent it back.
// Note that we also set this variable to true even if the parent isn't valid anymore, in
// order to ensure onAnimationLeashLost still gets called in this case.
// If the animation leash is set, and it is different from the removing leash, it means the
// surface now has a new animation surface. We don't want to reparent for that.
//1.surface不为空
//2.curAnimationLeash不为空,且curAnimationLeash等于leash
//因此reparent值为true
final boolean reparent = surface != null && (curAnimationLeash == null
|| curAnimationLeash.equals(leash));
if (reparent) {
ProtoLog.i(WM_DEBUG_ANIM, "Reparenting to original parent: %s for %s",
parent, animatable);
// We shouldn't really need these isValid checks but we do
// b/130364451
//判断当前窗口的surface是否有效,以及该窗口的父窗口的图层不为空且有效
if (surface.isValid() && parent != null && parent.isValid()) {
//把当前窗口图层和其父窗口的图层重新建立父子关系
t.reparent(surface, parent);
//scheduleAnim置为true
scheduleAnim = true;
}
}
//destroy传递过来值为true
if (destroy) {
//移除图层
t.remove(leash);
//scheduleAnim置为true
scheduleAnim = true;
}
if (reparent) {
// Make sure to inform the animatable after the surface was reparented (or reparent
// wasn't possible, but we still need to invoke the callback)
//1.移除和leash相关联的窗口和surface(这个只在前面requiresEdgeExtension为true时逻辑中有涉及)
//2.调整surface
animatable.onAnimationLeashLost(t);
//scheduleAnim置为true
scheduleAnim = true;
}
return scheduleAnim;
}
-
获取当前窗口的图层
final SurfaceControl surface = animatable.getSurfaceControl();
代码路径:frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/WindowContainer.java/** * @return The SurfaceControl for this container. * The SurfaceControl must be valid if non-null. */ @Override public SurfaceControl getSurfaceControl() { return mSurfaceControl; }直接返回一个SurfaceControl。
-
获取当前窗口父窗口的图层
代码路径:frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/WindowContainer.java/* * @return The SurfaceControl parent for this containers SurfaceControl. * The SurfaceControl must be valid if non-null. */ @Override public SurfaceControl getParentSurfaceControl() { final WindowContainer parent = getParent(); if (parent == null) { return null; } return parent.getSurfaceControl(); } @Override final protected WindowContainer getParent() { return mParent; }先获取当前窗口的父窗口,在获取父窗口的SurfaceControl。
-
获取动画图层
代码路径:frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/WindowContainer.java@Override public SurfaceControl getAnimationLeash() { return mAnimationLeash; }mAnimationLeash是前面SurfaceAnimator的startAnimation方法中的mAnimatable.onAnimationLeashCreated(t, mLeash);,把mLeash赋值给了mAnimationLeash,因此这个方法获取的是动画图层。 -
当前窗口图层和其父窗口的图层重新建立父子关系
t.reparent(surface, parent);
桌面的SurfaceControl重新认DefaultTaskDsiplayArea的SurfaceControl为父。
代码路径:frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/SurfaceControl.java/** * Re-parents a given layer to a new parent. Children inherit transform (position, scaling) * crop, visibility, and Z-ordering from their parents, as if the children were pixels within the * parent Surface. * * @param sc The SurfaceControl to reparent * @param newParent The new parent for the given control. * @return This Transaction */ @NonNull public Transaction reparent(@NonNull SurfaceControl sc, @Nullable SurfaceControl newParent) { //检查传入的SurfaceControl对象是否满足某些预设条件 checkPreconditions(sc); long otherObject = 0; if (newParent != null) { //检查新父对象是否被释放。如果已经被释放,那么它会抛出异常。 newParent.checkNotReleased(); //新父对象不为null且未被释放,那么将新父对象的Native对象赋值给otherObject。 otherObject = newParent.mNativeObject; } //传入了三个参数:1.当前对象的Native对象 2.被重新设置父对象的SurfaceControl的Native对象 3.新父对象的Native对象。 //用于实现重新设置父对象的具体操作。 nativeReparent(mNativeObject, sc.mNativeObject, otherObject); //把被重新设置父对象的SurfaceControl和新父对象存储到mReparentedSurfaces这个map中。 mReparentedSurfaces.put(sc, newParent); return this; }前面说过
reparent方法中通过mReparentedSurfaces这个ArrayMap临时存储父子关系,key值存储SurfaceControl对象,value为其父SurfaceControl对象(当前窗口的父窗口的SurfaceControl,即DefaultTaskDsiplayArea的SurfaceControl)
此时leash还没有被释放,DefaultTaskDsiplayArea的SurfaceControl有两个儿子SurfaceControl,(以桌面为例)关系如下图所示:
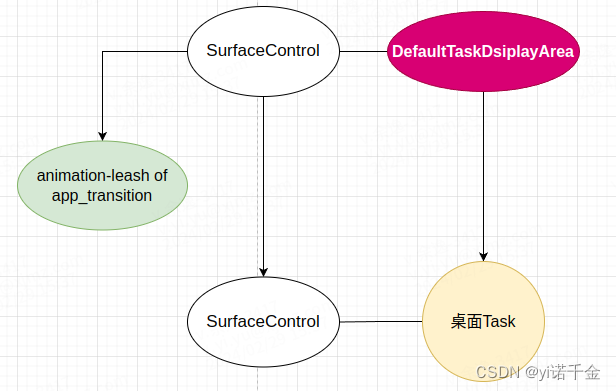
此时leash逐渐发现不对劲,但是假装不知道
假如我们后面不执行移除leash图层的操作,那么这个图层一直会保持这个状态挂在DefaultTaskDsiplayArea上和桌面Task共享父亲。 -
移除动画图层
t.remove(leash);/** * Equivalent to reparent with a null parent, in that it removes * the SurfaceControl from the scene, but it also releases * the local resources (by calling {@link SurfaceControl#release}) * after this method returns, {@link SurfaceControl#isValid} will return * false for the argument. * * @param sc The surface to remove and release. * @return This transaction * @hide */ @NonNull public Transaction remove(@NonNull SurfaceControl sc) { reparent(sc, null); sc.release(); return this; }同样调用了
reparent方法,先把需要remove的图层的父图层置空,然后释放。
过程如下所示:
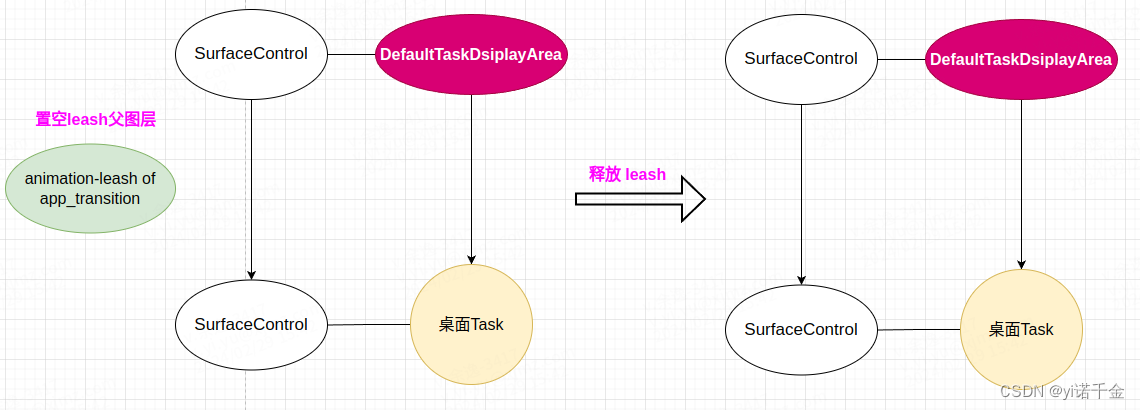
leash:原来我才是多余的那个,悠悠苍天,何薄于我! -
移除和leash相关联的窗口和surface并调整surface
animatable.onAnimationLeashLost(t);
代码路径:frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/WindowContainer.java@Override public void onAnimationLeashLost(Transaction t) { mLastLayer = -1; //调用mWmService中的mSurfaceAnimationRunner对象的onAnimationLeashLost方法 //用于移除和leash相关联的窗口,这个只在前面requiresEdgeExtension为true时逻辑中有涉及 mWmService.mSurfaceAnimationRunner.onAnimationLeashLost(mAnimationLeash, t); //mAnimationLeash置为空 mAnimationLeash = null; mNeedsZBoost = false; //调整其所有child的z-order reassignLayer(t); //更新Surface位置 updateSurfacePosition(t); }其中
mWmService.mSurfaceAnimationRunner.onAnimationLeashLost(mAnimationLeash, t);的mAnimationLeash前面说过就是动画图层。这个只在前面SurfaceAnimationRunner的startAnimation方法中requiresEdgeExtension为true时逻辑中有涉及,其为true时才会操作mEdgeExtensions这个ArrayList,这里不讨论。
协调动画显示
在SurfaceAnimator.reset()方法最后调用了mService.scheduleAnimationLocked();
代码路径:frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/WindowManagerService.java
void scheduleAnimationLocked() {
mAnimator.scheduleAnimation();
}
void scheduleAnimation() {
if (!mAnimationFrameCallbackScheduled) {
//mAnimationFrameCallbackScheduled 设置为 true,表示动画帧回调已经安排
mAnimationFrameCallbackScheduled = true;
//每一帧被绘制时,回调mAnimationFrameCallback
mChoreographer.postFrameCallback(mAnimationFrameCallback);
}
}
这个方法的主要作用是确保动画帧回调被正确地安排,以便在每一帧绘制时执行,可以确保动画在每一帧都被调用,从而平滑地更新和显示动画。
处理和响应动画完成的逻辑
回到SurfaceAnimator.getFinishedCallback中匿名的onAnimationFinished方法中有调用staticAnimationFinishedCallback.onAnimationFinished(type, anim);处理和响应动画完成的逻辑。
这里的staticAnimationFinishedCallback也是在SurfaceAnimator构造方法中初始化的
SurfaceAnimator(Animatable animatable,
@Nullable OnAnimationFinishedCallback staticAnimationFinishedCallback,
WindowManagerService service) {
mAnimatable = animatable;
mService = service;
mStaticAnimationFinishedCallback = staticAnimationFinishedCallback;
mInnerAnimationFinishedCallback = getFinishedCallback(staticAnimationFinishedCallback);
}
在WindowContainer构造方法中初始化mSurfaceAnimator = new SurfaceAnimator(this, this::onAnimationFinished, wms);,因此staticAnimationFinishedCallback.onAnimationFinished对应的就是WindowContainer.onAnimationFinished方法
代码路径:frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/WindowContainer.java
/**
* Called when an animation has finished running.
*/
protected void onAnimationFinished(@AnimationType int type, AnimationAdapter anim) {
//主要用于 清空 mSurfaceAnimationSources 列表
doAnimationFinished(type, anim);
//WindowManagerService中实现onAnimationFinished()
//用于唤醒所有等待mGlobalLock对象的线程,确保多个线程能够正确地执行任务
mWmService.onAnimationFinished();
//将 mNeedsZBoost 设置为 false,表示不再需要Z轴增强
mNeedsZBoost = false;
}
这个里面又调用了另一个doAnimationFinished(type, anim);
private void doAnimationFinished(@AnimationType int type, AnimationAdapter anim) {
for (int i = 0; i < mSurfaceAnimationSources.size(); ++i) {
//mSurfaceAnimationSources中每个容器,做对应的onAnimationFinished
mSurfaceAnimationSources.valueAt(i).onAnimationFinished(type, anim);
}
//清除动画源列表
mSurfaceAnimationSources.clear();
if (mDisplayContent != null) {
//调用DisplayContent的onWindowAnimationFinished方法
//从当前源码上看,主要是针对输入法相关做了一些操作
mDisplayContent.onWindowAnimationFinished(this, type);
}
}
WindowContainer.cancelAnimation方法中调用的doAnimationFinished也是这个方法。
我们这里mSurfaceAnimationSources是保存的是需要做动画的ActivityRecord,即桌面ActivityRecord和启动应用的ActivityRecord。
mSurfaceAnimationSources的值是在前面系统侧动画启动流程中WindowContainer.applyAnimationUnchecked方法中添加的。
mSurfaceAnimationSources.valueAt(i).onAnimationFinished(type, anim);调用了不同容器onAnimationFinished方法,在ActivityRecord和WindowState中都重写了这个方法。我们这里是远程动画,主要调用的就是ActivityRecord中重写的onAnimationFinished方法。
代码路径:frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/ActivityRecord.java
@Override
protected void onAnimationFinished(@AnimationType int type, AnimationAdapter anim) {
super.onAnimationFinished(type, anim);
Trace.traceBegin(TRACE_TAG_WINDOW_MANAGER, "AR#onAnimationFinished");
//更新标志位
mTransit = TRANSIT_OLD_UNSET;
mTransitFlags = 0;
//更新应用的布局变化
setAppLayoutChanges(FINISH_LAYOUT_REDO_ANIM | FINISH_LAYOUT_REDO_WALLPAPER,
"ActivityRecord");
//清除缩略图
clearThumbnail();
//更新应用的可见性状态
setClientVisible(isVisible() || mVisibleRequested);
getDisplayContent().computeImeTargetIfNeeded(this);
ProtoLog.v(WM_DEBUG_ANIM, "Animation done in %s"
+ ": reportedVisible=%b okToDisplay=%b okToAnimate=%b startingDisplayed=%b",
this, reportedVisible, okToDisplay(), okToAnimate(),
isStartingWindowDisplayed());
// clean up thumbnail window
if (mThumbnail != null) {
mThumbnail.destroy();
mThumbnail = null;
}
// WindowState.onExitAnimationDone might modify the children list, so make a copy and then
// traverse the copy.
//通知子窗口动画结束
final ArrayList<WindowState> children = new ArrayList<>(mChildren);
children.forEach(WindowState::onExitAnimationDone);
// The starting window could transfer to another activity after app transition started, in
// that case the latest top activity might not receive exit animation done callback if the
// starting window didn't applied exit animation success. Notify animation finish to the
// starting window if needed.
//通知启动窗口动画结束
if (task != null && startingMoved) {
final WindowState transferredStarting = task.getWindow(w ->
w.mAttrs.type == TYPE_APPLICATION_STARTING);
if (transferredStarting != null && transferredStarting.mAnimatingExit
&& !transferredStarting.isSelfAnimating(0 /* flags */,
ANIMATION_TYPE_WINDOW_ANIMATION)) {
transferredStarting.onExitAnimationDone();
}
}
//通知应用过渡动画结束
getDisplayContent().mAppTransition.notifyAppTransitionFinishedLocked(token);
//协调动画显示
scheduleAnimation();
// Schedule to handle the stopping and finishing activities which the animation is done
// because the activities which were animating have not been stopped yet.
// 如果需要,调度处理停止和结束活动的任务。这是必要的,因为正在动画的活动可能还没有被停止。
mTaskSupervisor.scheduleProcessStoppingAndFinishingActivitiesIfNeeded();
Trace.traceEnd(TRACE_TAG_WINDOW_MANAGER);
}
协调动画显示
和前面在SurfaceAnimator.reset()方法最后调用了mService.scheduleAnimationLocked();相似,
这里我们调用的scheduleAnimation();
代码路径:frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/WindowContainer.java
/**
* Trigger a call to prepareSurfaces from the animation thread, such that pending transactions
* will be applied.
*/
void scheduleAnimation() {
mWmService.scheduleAnimationLocked();
}
代码路径:frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/WindowManagerService.java
void scheduleAnimationLocked() {
mAnimator.scheduleAnimation();
}
最终调用到了WindowAnimator.scheduleAnimation()
代码路径:frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/WindowAnimator.java
void scheduleAnimation() {
if (!mAnimationFrameCallbackScheduled) {
//mAnimationFrameCallbackScheduled 设置为 true,表示动画帧回调已经安排
mAnimationFrameCallbackScheduled = true;
//每一帧被绘制时,回调mAnimationFrameCallback
mChoreographer.postFrameCallback(mAnimationFrameCallback);
}
}
这个方法的主要作用是确保动画帧回调被正确地安排,以便在每一帧绘制时执行,可以确保动画在每一帧都被调用,从而平滑地更新和显示动画。