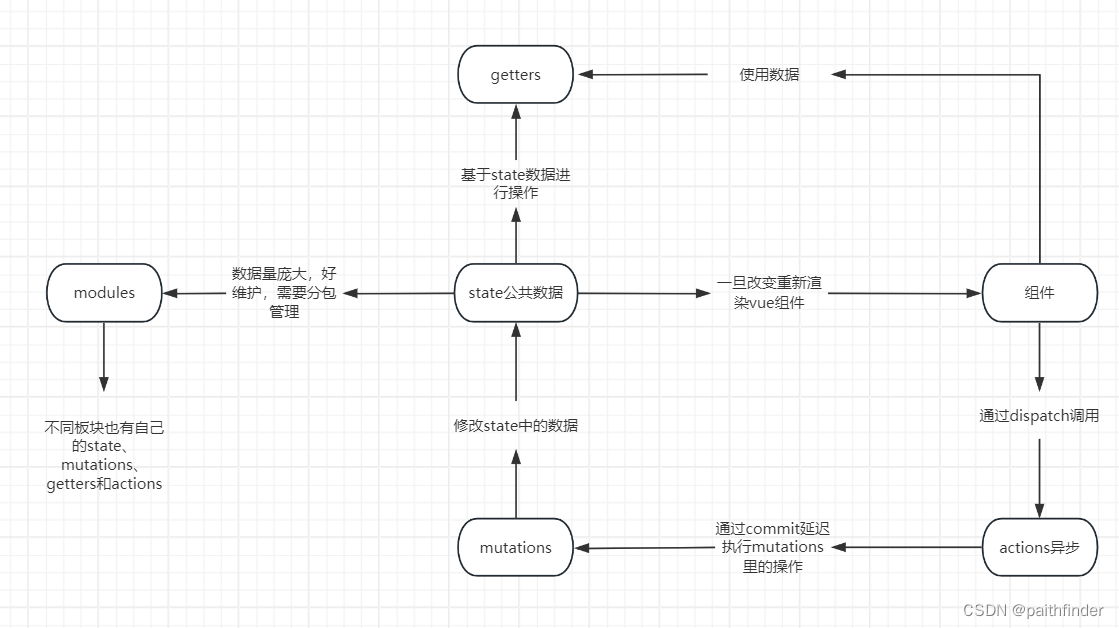
vuex:五大核心概念
- 一、state状态
- 1.state的含义
- 2.如何访问以及使用仓库的数据
- (1)通过store直接访问
- 获取store对象
- (2)通过辅助函数MapState
- 二、mutations
- 1.作用
- 2.严格模式
- 3.操作流程
- 定义 mutations 对象,对象中存放修改 state 的方法
- 组件通过commit调用mutations进行修改
- 4.mutations传参
- mutation 对象中定义带参函数
- 提交调用 mutation
- 5.辅助函数mapMutations
- (1)作用
- (2)操作步骤
- 三、actions
- 1.作用
- 2.操作流程
- 3.辅助函数mapActions
- 作用
- 流程
- 四、getters
- 1.作用
- 2.操作流程
- 3.辅助函数mapGetters
- 五、module(分包管理)
- 1.作用
- 2.创建module模块
- 3.直接使用模块中的数据
- (1)方式一:直接通过模块名访问
- (2)方式二:mapState
- 4.使用模块中getters的数据
- (1)方式一:直接通过模块名访问
- (2)方式二:mapGetters
- 5.调用模块中的mutation
- (1)方式一:直接调用
- (2)方式二:mapMutation
- 6.调用模块中的actions
- (1)方式一:直接调用
- (2)方式二:mapAction
- 六、总结
一、state状态
1.state的含义
是整个应用的仓库,存储共用的数据
2.如何访问以及使用仓库的数据
一般来说,都有直接访问和通过辅助函数进行访问这两种方式
(1)通过store直接访问
获取store对象
| 适用场景 | 语法 |
|---|---|
| Vue 组件内部访问 store 对象 | this.$store |
| 普通的 js 模块中获取 store 对象 | import store from ‘.xxx/store’ |
使用数据
| 适用场景 | 语法 |
|---|---|
| vue模板中 | {{ $store.state.xxx}} |
| Vue组件的js逻辑代码中 | this.$store.state.xxx |
| 普通的 js 模块中 | store.state.xxx |
(2)通过辅助函数MapState
辅助函数能帮助我们简化代码,使用起来更加方便
//store下的index.js文件
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
name:"小美“
}
//在需要使用的组件内导入mapState
import { mapState } from 'vuex'
//用数组方式引入State,用展开运算符进行映射
export default {
computed: mapState(['name']),
}
这样,我们就可以在模板中直接使用 {{ name }} 来获取并展示 name 的值。
二、mutations
1.作用
用于修改仓库里面的数据
原因:在vuex中同样要遵循单项数据流,组件是不能直接修改仓库中的数据的,所以我们需要在用mutations修改数据
2.严格模式
因为vuex不允许组件直接修改仓库里的数据,为了避免某些错误写法可能导致无效的问题,我们可以通过开启严格模式检查问题
//store/index.js
const store =new Vuex.Store({
strict:true,
state:{
xxxxxx
}
})
3.操作流程
定义 mutations 对象,对象中存放修改 state 的方法
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
name:"小美”
},
// 定义mutations对象
mutations: {
// 第一个参数要求是当前store的state属性
changeName (state) {
state.name:"小帅“
}
}
})
组件通过commit调用mutations进行修改
this.$store.commit('changeName')
4.mutations传参
mutation 对象中定义带参函数
mutations: {
changeName (state,name) {
state.name:name
}
}
提交调用 mutation
this.$store.commit('changeName', 小羊)
注意:传参只能传state和一个自定义的参数,不支持传多个参数,但是支持传state和一个对象/数组
5.辅助函数mapMutations
(1)作用
把mutation中定义的方法提取出来,映射在组件中的methods
(2)操作步骤
store/index文件中定义mutation对象的代码不变
//在需要使用的组件内导入mapMutations
import { mapMutations } from 'vuex'
//映射在methodss中
methods: {
...mapMutations(['changeName'])
}
就可以直接调用仓库里的方法,例如,模板里
<button @click="changeName(‘大灰狼’)">点一下我就改名</button>
而在组件js逻辑代码块中用this.changeName(‘大灰狼’)即可调用
三、actions
1.作用
用于处理异步操作
注意:actions处理异步,mutations只能处理同步,actions中的异步操作也是在调用mutations中定义的方法
2.操作流程
下面给出一个一秒后给数组增添一个数的例子:
// store.js
state () {
return {
list: []
}
},
mutations = {
addNumber(state, number) {
state.list.push(number);
}
}
actions = {
async addNumberWithDelay(context,number) {
setTimeout(()=>{
context.commit('addNumber',number)
},1000)
}
}
页面中用dispatch调用actions的方法:
this.$store.dispatch('addNumberWithDelay', 666)
3.辅助函数mapActions
作用
把在actions中的方法提取出来,映射在组件中的methods方法里
流程
在需要使用的组件里直接导入:
import { mapActions } from 'vuex'
methods: {
...mapActions(['addNumberWithDelay'])
}
在组件js逻辑代码块中用this.addNumberWithDelay(666’)即可调用
四、getters
1.作用
基于state里的数据进行一些操作
类似于computed计算属性
2.操作流程
例如,我们要对state里面定义好的一个数组进行筛选,筛选得到一个全是正数的列表
// store.js
const state = {
numbers: [1, -2, 3, -4, 5]
};
const getters = {
positiveNumbers: state => {
return state.numbers.filter(num => num > 0);
}
};
在需要的组件中得到该方法筛选后的数组
return this.$store.getters.positiveNumbers
3.辅助函数mapGetters
同样也是提取getters中的方法,映射在computed中
import { mapGetters } from 'vuex'
methods: {
...mapGetters(['positiveNumbers'])
}
在组件js逻辑代码块中用this.positiveNumbers即可调用
注意:如果是在模板中调用是{{ positiveNumbers }},具体语法在上文表格中已经提到过:点我跳转查看
五、module(分包管理)
1.作用
在 Vuex 中,使用 module 可以把 store 分割成多个小模块,每个模块都有自己的 state、mutations、actions、getters 等属性,从而使得 Vuex 管理较为复杂的应用程序变得更加方便和灵活
因为一个应用会涉及到很多板块的数据,为了防止store特别膨胀复杂,管理起来更加麻烦,所以我们需要进行拆分,这样方便后续进行维护、扩展和升级等等……
2.创建module模块
大致思路是在store文件目录下新建modules文件夹,再创建不同板块的js文件。各个板块的文件中都有属于自己的state,mutations,actions和gettters.
下面举一个user的例子:
// store/modules/user.js
const state = {
userInfo: {
name:‘敲代码的小乐最快乐’,
isLoggedIn: false
}
}
const mutations = {}
const actions = {}
const getters = {}
export default {
state,
mutations,
actions,
getters
}
接着再导入注册user板块就大功告成:
import user from './modules/user'
const store = new Vuex.Store({
modules: {
user
}
})
3.直接使用模块中的数据
当使用 Vuex 存储数据时,即使将数据拆分到不同的模块中,实际上子模块的状态仍然会被挂载在根级别的状态下,并且属性名就是模块名。
(1)方式一:直接通过模块名访问
你可以使用 $store.state.模块名.xxx 的方式直接访问模块中的数据。
(2)方式二:mapState
mapState 映射根级别的状态:mapState(['xxx'])。
映射子模块的状态:子模块需要开启命名空间namespaced:true,使用mapState('模块名', ['xxx'])进行访问。
export default {
namespaced: true,
state,
mutations,
actions,
getters
}
4.使用模块中getters的数据
(1)方式一:直接通过模块名访问
你可以使用$store.getters['模块名/xxx '] 的方式直接访问
(2)方式二:mapGetters
mapGetters 映射根级别的状态:mapGetters([ 'xxx' ])。
映射子模块的状态:子模块需要开启命名空间,使用mapGetters('模块名', ['xxx'])进行访问。
5.调用模块中的mutation
(1)方式一:直接调用
你可以直接通过 store 调用: $store.commit('模块名/xxx ', 额外参数)
(2)方式二:mapMutation
mapMutations 映射根级别的状态:mapMutations([ 'xxx' ])。
映射子模块的状态:子模块需要开启命名空间,通过mapMutations('模块名', ['xxx']))调用。
6.调用模块中的actions
(1)方式一:直接调用
你可以直接通过 store 调用: $store.dispatch('模块名/xxx ', 额外参数)
(2)方式二:mapAction
mapActions 映射根级别的状态:mapActions([ 'xxx' ])。
映射子模块的状态:子模块需要开启命名空间,通过mapActions('模块名', ['xxx']))调用。
六、总结
vuex的前四大核心概念:state、mutations、getters和actions都有自己的“mapxxx”函数,它都是把其本身的方法提取出来,以映射在组件的方式访问(state和getters是映射在computed中)或者调用(mutations和actions映射在methods中)。
最后的一个核心概念是modules,它存在的意义在于对跟级别的store进行分包管理。
关系图: