总的地址 :
面试经典 150 题 - 学习计划 - 力扣(LeetCode)全球极客挚爱的技术成长平台
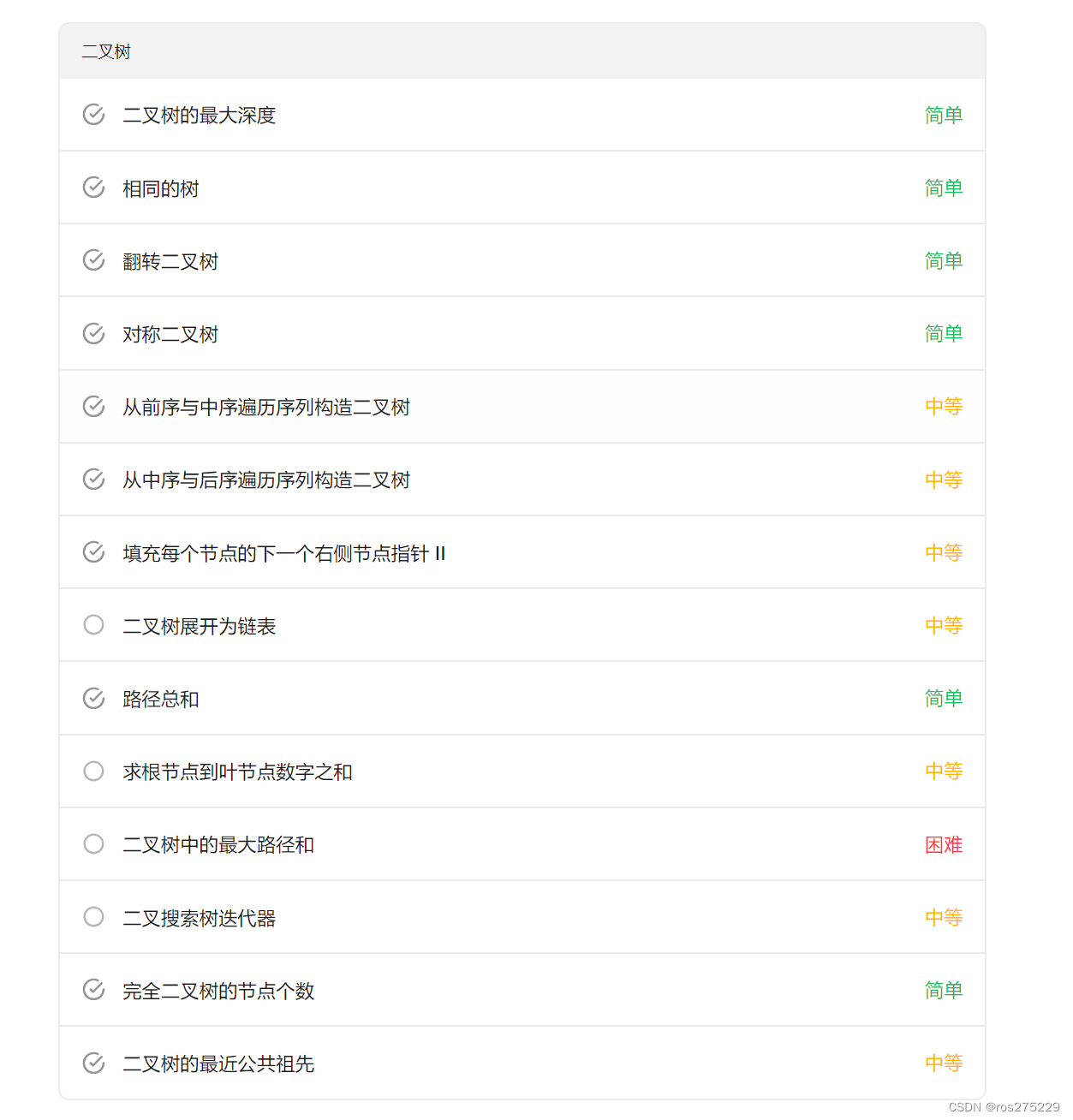
104 . 二叉树的最大深度
104 . 二叉树的最大深度
递归 :
直接用递归访问 , 访问左孩子 和 右孩子 , 如果 存在 , 深度就+1 ;
class Solution {
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return 0 ;
int lm = maxDepth(root.left) ;
int rm = maxDepth(root.right) ;;
return Math.max(lm, rm) + 1 ;
}
}层序遍历
找到一层 就 ans ++ ;
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
int ans = 0;
queue<TreeNode*> que;
if(root != nullptr) que.push(root);
while(!que.empty()){
int size = que.size();
ans ++;
for(int i=0;i<size;i++){
TreeNode* node = que.front();
que.pop();
if(node->left) que.push(node->left);
if(node->right) que.push(node->right);
}
}
return ans;
}
};100 . 相同的树
链接 :
力扣(LeetCode)官网 - 全球极客挚爱的技术成长平台
LeetCode题解链接 :
力扣(LeetCode)官网 - 全球极客挚爱的技术成长平台
[迭代]
> 采用广度优先遍历,用队列先存入两个树的头节点,每次判断队尾的两个结点是不是满足相等,不相等直接返回false,同时为空,继续下一对结点的判断 ;
都不为空且值相等,就依次将两个节点的左孩子 和 右孩子 存入队列中;然后开始下一次的判断 ; 知道两个队列都为空为止 ;
Java :
class Solution {
public boolean isSameTree(TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if(p==null && q==null) return true;
if(p==null || q==null) return false;
if(p.val !=q.val) return false;
Queue<TreeNode> qp = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
Queue<TreeNode> qq = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
qp.offer(p);
qq.offer(q);
while(!qp.isEmpty() && !qq.isEmpty()){
TreeNode cp = qp.poll();
TreeNode cq = qq.poll();
if(cp==null&& cq==null) continue;
if((cp==null || cq==null) || cp.val != cq.val) return false;
qp.offer(cp.left) ;
qq.offer(cq.left) ;
qp.offer(cp.right) ;
qq.offer(cq.right) ;
}
return true ;
}
}cpp
class Solution {
public:
bool isSameTree(TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {
if(p==nullptr && q==nullptr) return true;
if(p==nullptr || q==nullptr) return false;
if(p->val !=q->val) return false;
queue<TreeNode*> qp ;
queue<TreeNode*> qq;
qp.push(p);
qq.push(q);
while(!qp.empty() && !qq.empty()){
TreeNode* cp = qp.front() ; qp.pop();
TreeNode* cq = qq.front() ; qq.pop();
if(cp==nullptr && cq==nullptr) continue;
if((cp==nullptr || cq==nullptr) || cp->val != cq->val) return false;
qp.push(cp->left) ;
qq.push(cq->left) ;
qp.push(cp->right) ;
qq.push(cq->right) ;
}
return true ;
}
};[递归]
> 用递归的思想实现上面迭代的过程,先判断两个根节点是否满足题意,满足就同时递归判断两个节点的左子树和右子树 ;
Java
class Solution {
public boolean isSameTree(TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if(p==null && q==null) return true;
if(p==null || q==null) return false;
if(p.val != q.val) return false;
return isSameTree(p.left,q.left) && isSameTree(p.right,q.right) ;
}
}cpp
class Solution {
public:
bool isSameTree(TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {
if(p==nullptr && q==nullptr) return true;
else if(p==nullptr || q==nullptr) return false;
else if(p->val != q->val) return false;
else return isSameTree(p->left,q->left) && isSameTree(p->right,q->right);
}
};226 . 反转二叉树
链接
226 . 反转二叉树
递归 :
遍历一个结点就继续向下反转其左子树 和 右子树 ;
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* invertTree(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == nullptr) return root ;
swap(root->left,root->right);
invertTree(root->left) ;
invertTree(root->right) ;
return root ;
}
};前序遍历
按照中左右的顺序,先处理中间结点(交换其左右子树),然后将其左子树和右子树加入栈中 ;
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* invertTree(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == NULL) return root;
stack<TreeNode*> st;
st.push(root);
while(!st.empty()) {
TreeNode* node = st.top(); // 中
st.pop();
swap(node->left, node->right);
if(node->right) st.push(node->right); // 右
if(node->left) st.push(node->left); // 左
}
return root;
}
};层序遍历
和前序遍历类似,采用队列queue存放结点 ;
广度优先,在遍历的过程中将每一层的每一个结点的左右孩子结点交换即可;
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* invertTree(TreeNode* root) {
queue<TreeNode*> que;
if (root != NULL) que.push(root);
while (!que.empty()) {
int size = que.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode* node = que.front();
que.pop();
swap(node->left, node->right); // 节点处理
if (node->left) que.push(node->left);
if (node->right) que.push(node->right);
}
}
return root;
}
};101 . 对称二叉树
递归
对于二叉树是否对称,要比较的是根节点的左子树与右子树是不是相互翻转的,理解这一点就知道了其实我们要比较的是两个树(这两个树是根节点的左右子树),所以在递归遍历的过程中,也是要同时遍历两棵树。
我们要通过递归函数的返回值来判断两个子树的内侧节点和外侧节点是否相等。(遍历顺序 : 左右中 / 右左中 , "后序遍历 ")
class Solution {
public:
bool cmp(TreeNode* left,TreeNode* right){
if(left==nullptr && right!=nullptr) return false;
else if(left!=nullptr && right==nullptr) return false;
else if(left==nullptr && right==nullptr) return true;
else if(left->val != right->val) return false;
else return cmp(left->left,right->right) && cmp(left->right,right->left);
}
bool isSymmetric(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == nullptr) return true;
return cmp(root->left,root->right);
}
};迭代
也就是用类似层序遍历的方式来实现递归的步骤 ;
详细请看代码 :
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool isSymmetric(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == nullptr) return true;
queue<TreeNode*> que;
que.push(root->left);
que.push(root->right);
while(!que.empty()){
TreeNode* l = que.front();
que.pop();
TreeNode* r = que.front();
que.pop();
if(!l && !r) continue;//左右结点均为空,直接下一步;
if((l&&!r) || (!l&&r)) return false;//左右结点一个为空,返回false;
if(l->val != r->val) return false;//均不为空但不相等,直接返回false;
que.push(l->left);
que.push(r->right);
que.push(l->right);
que.push(r->left);
}
return true;
}
};105. 从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
详细请看代码 :
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* traversal(vector<int>& preorder,vector<int>& inorder){
if(preorder.size() == 0) return nullptr;
int num = preorder[0];
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(num);
// 叶子节点
if(preorder.size() == 1) return root;
// 找到切割下标
int splitIndex;
for(splitIndex=0;splitIndex<inorder.size();splitIndex++){
if(inorder[splitIndex] == num)
break;
}
//切割中序数组
vector<int> leftVecI(inorder.begin(),inorder.begin()+splitIndex);
vector<int> rightVecI(inorder.begin()+splitIndex+1,inorder.end());
// 去掉前序数组中的第一个元素
preorder.erase(preorder.begin());
// 切割前序数组
vector<int> leftVecP(preorder.begin(),preorder.begin()+leftVecI.size());
vector<int> rightVecP(preorder.begin()+leftVecI.size(),preorder.end());
root->left = traversal(leftVecP,leftVecI);
root->right = traversal(rightVecP,rightVecI);
return root;
}
TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& preorder, vector<int>& inorder) {
if(!preorder.size() || !inorder.size()) return nullptr;
return traversal(preorder,inorder);
}
};106. 从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
详细请看代码 :
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
private:
// 中序区间:[inorderBegin, inorderEnd),后序区间[postorderBegin, postorderEnd)
TreeNode* traversal (vector<int>& inorder, int inorderBegin, int inorderEnd, vector<int>& postorder, int postorderBegin, int postorderEnd) {
if (postorderBegin == postorderEnd) return NULL;
int rootValue = postorder[postorderEnd - 1];
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(rootValue);
if (postorderEnd - postorderBegin == 1) return root;
int delimiterIndex;
for (delimiterIndex = inorderBegin; delimiterIndex < inorderEnd; delimiterIndex++) {
if (inorder[delimiterIndex] == rootValue) break;
}
// 切割中序数组
// 左中序区间,左闭右开[leftInorderBegin, leftInorderEnd)
int leftInorderBegin = inorderBegin;
int leftInorderEnd = delimiterIndex;
// 右中序区间,左闭右开[rightInorderBegin, rightInorderEnd)
int rightInorderBegin = delimiterIndex + 1;
int rightInorderEnd = inorderEnd;
// 切割后序数组
// 左后序区间,左闭右开[leftPostorderBegin, leftPostorderEnd)
int leftPostorderBegin = postorderBegin;
int leftPostorderEnd = postorderBegin + delimiterIndex - inorderBegin; // 终止位置是 需要加上 中序区间的大小size
// 右后序区间,左闭右开[rightPostorderBegin, rightPostorderEnd)
int rightPostorderBegin = postorderBegin + (delimiterIndex - inorderBegin);
int rightPostorderEnd = postorderEnd - 1; // 排除最后一个元素,已经作为节点了
root->left = traversal(inorder, leftInorderBegin, leftInorderEnd, postorder, leftPostorderBegin, leftPostorderEnd);
root->right = traversal(inorder, rightInorderBegin, rightInorderEnd, postorder, rightPostorderBegin, rightPostorderEnd);
return root;
}
public:
TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& inorder, vector<int>& postorder) {
if (inorder.size() == 0 || postorder.size() == 0) return NULL;
// 左闭右开的原则
return traversal(inorder, 0, inorder.size(), postorder, 0, postorder.size());
}
};117. 填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针 II
链接 :
. - 力扣(LeetCode)
层序遍历 , 借助一个pre结点 来 将每一层的结点的next指针指向右边的结点 ;
class Solution {
public:
Node* connect(Node* root) {
// 层序遍历
queue<Node*> que ;
if(root!=nullptr) que.push(root) ;
while(!que.empty()){
int size = que.size() ;
Node* pre ;
Node* cur ;
for(int i=0;i<size;i++){
if(i==0){
pre = que.front() ;
cur = pre ;
que.pop() ;
}else {
cur = que.front() ;
que.pop() ;
pre -> next = cur ;
pre = cur ;
}
if(cur->left) que.push(cur->left);
if(cur->right) que.push(cur->right);
}
}
return root ;
}
};114 . 二叉树展开成链表
其实就是一个递归的过程 ;
详细请看lc大佬的题解 :
- 力扣(LeetCode)bt
题中函数实现的三个步骤 :
将root的左子树展开成链表,将root的右子树展开成链表,将root的左子树链表插到右子树链表头节点前 ;(注意清空左指针)
然后给出递归代码 :
class Solution {
public:
void flatten(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == nullptr) return ;
flatten(root->left) ;
flatten(root->right) ;
TreeNode* tmp = root->right ;
root->right = root->left ;
root->left = nullptr ;
while(root->right != nullptr) root = root -> right ;
root->right = tmp ;
}
};112 . 路径总和
深度优先遍历,查找每一条路径是否能够和为targetSum;
用递归实现 ;
具体请看代码+注释 :
class Solution {
public:
bool dfs(TreeNode* root ,int t){
// 1 . 递归终止条件编写 :
// 左右子树全空,且t=0,表示找到一条路径和为t
if(!root->left && !root->right && t==0) return true ;
// 左右子树全空 , 但t!=0,直接返回false;
if(!root->left && !root->right) return false;
// 2 . 编写递归逻辑 :
if(root->left){
if(dfs(root->left , t - root->left->val))
return true ;
}
if(root -> right){
if(dfs(root->right , t - root->right->val))
return true ;
}
return false ;
}
bool hasPathSum(TreeNode* root, int t) {
if(!root) return false ;
return dfs(root , t - root->val) ;
}
};129 . 求根节点到叶子结点的数字之和
深度优先
采取先序遍历的方式 ,找到每一个叶子节点 ,然后返回其和 ,先处理root的数据,然后遍历左子树和右子树 ;
class Solution {
public:
int dfs(TreeNode* root,int k){
if(root == nullptr) return 0 ;
// 深度优先 , 中左右 --> 先序遍历
int sum = k * 10 + root -> val ;
if(!root->left && !root->right) return sum ;
return dfs(root->left,sum) + dfs(root->right,sum) ;
}
int sumNumbers(TreeNode* root) {
return dfs(root , 0) ;
}
};124 . 二叉树中的最大路径和
采用动态规划的思想 :
// 思考从下到上的顺序
// 一个结点如果作为根节点 , 那么ress(贡献) = root->val + max(max_left,max_right)
// 那么它对自己根节点的贡献也就是res ;
// 结点作为路径的子节点,那么ans = max(ans,root->val+max_left+max_right)
// 递归 , 在遍历每个节点的过程中 ,跟新最大值 即可
class Solution {
public:
// 思考从下到上的顺序
// 一个结点如果作为根节点 , 那么ress(贡献) = root->val + max(max_left,max_right)
// 那么它对自己根节点的贡献也就是res ;
// 结点作为路径的子节点,那么ans = max(ans,root->val+max_left+max_right)
// 递归 , 在遍历每个节点的过程中 ,跟新最大值 即可
int ans = INT_MIN ;
int get(TreeNode* root){
if(root == nullptr) return 0 ;
// 递归计算左右结点的最大贡献值
int leftGain = max(get(root->left),0);
int rightGain = max(get(root->right),0);
// 计算作为子节点的最大路径和
int ansP = root->val + leftGain + rightGain ;
// 更新答案
ans = max(ans , ansP) ;
// 返回作为根节点的最大贡献
int res = root->val + max(leftGain , rightGain) ;
return res ;
}
int maxPathSum(TreeNode* root) {
// 调用递归函数
int k = get(root) ;
return ans ;
}
};173 . 二叉搜索树迭代器
先中序遍历 , 按顺序将所有结点的值存起来;
然后按照题目要求模拟 ;
class BSTIterator {
private:
void inorder(TreeNode* root, vector<int>& res) {
if (!root) {
return;
}
inorder(root->left, res);
res.push_back(root->val);
inorder(root->right, res);
}
vector<int> inorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> res;
inorder(root, res);
return res;
}
vector<int> arr;
int idx;
public:
BSTIterator(TreeNode* root): idx(0), arr(inorderTraversal(root)) {}
int next() {
return arr[idx++];
}
bool hasNext() {
return (idx < arr.size());
}
};222 . 完全二叉树的结点个数
层序遍历 :
遍历每一层 , 将每一层的节点数加入ans中 ;
class Solution {
public:
int countNodes(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == nullptr) return 0 ;
queue<TreeNode*> que ;
que.push(root) ;
int ans = 0 ;
while(!que.empty()){
int size = que.size() ;
ans += size ;
for(int i=0;i<size;i++){
TreeNode* node = que.front();
que.pop();
if(node->left) que.push(node->left) ;
if(node->right) que.push(node->right) ;
}
}
return ans ;
}
};递归
一个结点 如果 作为根节点 , 那么总结点数 也就是 1 + 左子树结点数 + 右子树节点数 ;
这样用递归就好 ;
class Solution {
public:
int getSum(TreeNode* node){
if(node == nullptr) return 0 ;
int l = getSum(node->left) ;
int r = getSum(node->right) ;
return l + r + 1 ;
}
int countNodes(TreeNode* root) {
int ans = getSum(root);
return ans ;
}
};236 . 二叉树的最近公共祖先
详细参考 : 代码随想录
采用后序遍历的思想 , 回溯解决 ;
根据题目定义 :
若 root是 p,q的 最近公共祖先 ,则只可能为以下情况之一:
1 . p和 q在 root的子树中,且分列 root的 异侧(即分别在左、右子树中);
2 . p=root ,且 q 在 root的左或右子树中;
3 . q=root,且 p 在 root 的左或右子树中;
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {
if(root == nullptr || root == p || root == q) return root;
TreeNode *left = lowestCommonAncestor(root->left, p, q);
TreeNode *right = lowestCommonAncestor(root->right, p, q);
if(left == nullptr) return right;
if(right == nullptr) return left;
return root;
}
};
参考 :
- https://programmercarl.com/%E4%BA%8C%E5%8F%89%E6%A0%91%E7%90%86%E8%AE%BA%E5%9F%BA%E7%A1%80.html#%E7%AE%97%E6%B3%95%E5%85%AC%E5%BC%80%E8%AF%BE
- 二叉树基础知识总结-CSDN博客
- 二叉树遍历总结 -- 基于LeetCode-CSDN博客