Kubernetes 二进制部署 - easzlab / kubeasz项目部署
- 1. 准备工作
- 1.1 设置防火墙
- 1.2 设置SeLinux
- 1.3 设置时区及时间同步
- 1.4 配置域名解析
- 1.5 确认SSH开启
- 1.6 IP转发
- 1.7 安装docker
- 1.8 关闭swap
- 2. 服务器规划
- 2.1 基本架构图
- 2.2 官方建议
- 2.3 实践服务器规划
- 3. 服务器配置
- 3.1 配置域名及IP
- 3.2 配置hosts
- 3.3 配置部署服务器
- 3.4 配置gitlab服务器
- 3.5 配置haproxy服务器
- 3.6 配置harbor服务器
本次通过Github上的一个开源项目(kubeasz)部署K8s,该项目在生产环境中得到过多次验证,部署的质量有一定的保证
kubeasz简介
一款基于Ansible的Kubernetes安装与运维管理工具,提供自动化部署、集群管理、配置管理等功能。 - 功能:提供自动化部署Kubernetes集群、节点管理、容器管理、存储管理、网络管理等功能。 - 特点:基于Ansible,易于上手;支持离线安装;支持多种Kubernetes版本。
官网 https://github.com/easzlab/kubeasz
国内网址 https://gitcode.com/easzlab/kubeasz/overview
本文是笔者在观看了马哥教育-张士杰讲师的视频后,进行整理实践,本文内容如涉及侵权,请联系笔者删除
下面我们将按照官网流程进行安装
1. 准备工作
本次实践将在虚拟机中进行,所以我们提前配置好一个基础环境,然后进行克隆。
base环境
[root@k8s-master-01 ~]# cat /etc/redhat-release
CentOS Linux release 7.9.2009 (Core)
[root@k8s-master-01 ~]# uname -r
3.10.0-1160.108.1.el7.x86_64
内核版本建议升级到稳定版本,毕竟搭建完成后,再进行内核升级属实是个不小的工程
1.1 设置防火墙
本次实践将关闭防火墙,在某些公司需要打开防火墙,并对防火墙规则及富规则会有明确要求。对某些规则变更或添加端口等等,需要经过严格评审。
systemctl stop firewalld
systemctl disable firewalld
systemctl mask firewalld
[root@k8s-master-01 ~]# systemctl status firewalld
● firewalld.service
Loaded: masked (/dev/null; bad)
Active: inactive (dead)
1.2 设置SeLinux
本次实践将关闭SeLinux功能
[root@k8s-master-01 ~]# getenforce
Disabled
[root@k8s-master-01 ~]# grep SELINUX /etc/selinux/config
# SELINUX= can take one of these three values:
SELINUX=disabled
# SELINUXTYPE= can take one of three values:
SELINUXTYPE=targeted
1.3 设置时区及时间同步
ntpdate ntp1.aliyun.com #同步时间
[root@k8s-master-01 ~]# cat /var/spool/cron/root #添加计划任务
*/5 * * * * root /usr/bin/ntpdate ntp1.aliyun.com &> /dev/null && hwclock -w
ln -sf /usr/share/zoneinfo/Asia/Shanghai /etc/localtime #更改时区
1.4 配置域名解析
[root@k8s-master-01 ~]# cat /etc/resolv.conf
nameserver 8.8.8.8
nameserver 114.114.114.114
1.5 确认SSH开启
[root@k8s-master-01 ~]# systemctl status sshd
● sshd.service - OpenSSH server daemon
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/sshd.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Mon 2024-02-19 18:00:09 CST; 20min ago
...
[root@k8s-master-01 ~]# yum list openssh
...
Installed Packages
openssh.x86_64 7.4p1-23.el7_9 @updates
1.6 IP转发
sysctl -w net.ipv4.ip_forward=1
[root@k8s-master-01 ~]# cat /etc/sysctl.conf
...
net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1
1.7 安装docker
本次的K8s容器使用docker而非默认的containerd,所以可以提前安装docker
参考 https://blog.csdn.net/u010230019/article/details/128624286
yum update
yum install -y yum-utils device-mapper-persistent-data lvm2
yum-config-manager --add-repo https://download.docker.com/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo
yum update
[root@k8s-master-01 ~]# yum list docker-ce
...
Available Packages
docker-ce.x86_64 3:25.0.3-1.el7 docker-ce-stable
yum install -y docker-ce
systemctl start docker
systemctl enable docker
像其他工具安装,例如vim等,个人设置,例如alias等,可根据自己具体情况执行。
到这里,我们的基础环境准备完毕
其他的设置,如免密登录,主机名等等,在分配好服务器后再通过ansible进行配置
1.8 关闭swap
[root@k8s-master-01 ~]# swapoff -a
[root@k8s-master-01 ~]# free
total used free shared buff/cache available
Mem: 1862788 224324 207308 9736 1431156 1464188
Swap: 0 0 0
[root@k8s-master-01 ~]# cat /etc/fstab
...
#/dev/mapper/centos-swap swap swap defaults 0 0
2. 服务器规划
2.1 基本架构图

2.2 官方建议
- 高可用集群所需节点配置如下
| 角色 | 数量 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| 部署节点 | 1 | 运行ansible/ezctl命令,一般复用第一个master节点 |
| etcd节点 | 3 | 注意etcd集群需要1,3,5,…奇数个节点,一般复用master节点 |
| master节点 | 2 | 高可用集群至少2个master节点 |
| node节点 | n | 运行应用负载的节点,可根据需要提升机器配置/增加节点数 |
-
机器配置:
- master节点:4c/8g内存/50g硬盘
- worker节点:建议8c/32g内存/200g硬盘以上
注意:默认配置下容器运行时和
kubelet会占用/var的磁盘空间,如果磁盘分区特殊,可以设置config.yml中的容器运行时和kubelet数据目录:CONTAINERD_STORAGE_DIRDOCKER_STORAGE_DIRKUBELET_ROOT_DIR
2.3 实践服务器规划
本次配置以生产环境为目标,所以配置的内容尽量详细

| 角色 | 数量 | IP | 描述 |
|---|---|---|---|
| gitlab | 1 | 192.168.17.191 | 代码库 |
| master | 2 | 192.168.17.200 192.168.17.201 | master-apiserver,高可用至少2个,和ansible主控机混用,通过VIP做主备高可用 |
| etcd | 3+ | 192.168.17.210 192.168.17.211 192.168.17.212 | etcd-server,涉及选举所以需要3个 |
| harbor | 2 | 192.168.17.220 192.168.17.221 | 镜像管理服务器 |
| hproxy | 2 | 192.168.17.230 192.168.17.231 | 高可用etcd代理服务器 |
| ansible | 2 | 192.168.17.200 192.168.17.201 | k8s部署服务器,可以和master混用 |
| node | 2+ | 192.168.17.240 192.168.17.241 | 工作节点,高可用至少2+,后续可以扩容 |
IP掩码建议22位,这样同一个子网允许有1000+个服务器,一般情况下都可以满足需求。当然确定用不到这么多服务器,24位也是可以的,但如果超出子网超出范围再扩容还是很麻烦的
| 类型 | IP | 主机名 | VIP |
|---|---|---|---|
| gitlab-server | 192.168.17.191 | k8s-gitlab-01.xx.net | |
| k8s master1 | 192.168.17.200 | k8s-master-01.xx.net | 192.168.17.188 |
| k8s master2 | 192.168.17.201 | k8s-master-02.xx.net | 192.168.17.188 |
| etcd1 | 192.168.17.210 | k8s-etcd-01.xx.net | |
| etcd2 | 192.168.17.211 | k8s-etcd-02.xx.net | |
| etcd3 | 192.168.17.212 | k8s-etcd-03.xx.net | |
| harbor1 | 192.168.17.220 | k8s-harbor-01.xx.net | |
| harbor2 | 192.168.17.221 | k8s-harbor-02.xx.net | |
| haproxy1 | 192.168.17.230 | k8s-haproxy-01.xx.net | |
| haproxy2 | 192.168.17.231 | k8s-haproxy-02.xx.net | |
| node1 | 192.168.17.240 | k8s-node-01.xx.net | |
| node2 | 192.168.17.241 | k8s-node-02.xx.net |
本次实践一共12台机器,可以根据实际情况自行安排虚拟机配置,gitlab-server建议配置高一点,其他服务器可以适当减配
3. 服务器配置
由于是虚拟机,所以在服务器规划完成后,就可以进行克隆了,等克隆完成后可以根据不同服务器类型进行单独配置
gitlab、harbor和haproxy不属于K8s的部署范畴,但是为了后续CD的实践需要,还是一同部署了
3.1 配置域名及IP
在克隆完成后,根据前面的清单配置每个服务器的域名及IP,如
[root@k8s-master-01 ~]# hostnamectl set-hostname k8s-master-01.xx.net
[root@k8s-master-01 ~]# hostname
k8s-master-01.xx.net
[root@k8s-master-01 ~]# grep IPADDR /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-ens34
IPADDR=192.168.17.200
3.2 配置hosts
我们可以提前把/etc/hosts中的对应关系配置好
[root@k8s-master-01 ~]# cat /etc/hosts
127.0.0.1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost4 localhost4.localdomain4
::1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost6 localhost6.localdomain6
192.168.17.191 k8s-gitlab-01.xx.net gitlab-server
192.168.17.200 k8s-master-01.xx.net k8s-master1
192.168.17.201 k8s-master-02.xx.net k8s-master2
192.168.17.210 k8s-etcd-01.xx.net etcd1
192.168.17.211 k8s-etcd-02.xx.net etcd2
192.168.17.212 k8s-etcd-03.xx.net etcd3
192.168.17.220 k8s-harbor-01.xx.net harbor1
192.168.17.221 k8s-harbor-02.xx.net harbor2
192.168.17.225 k8s-harbor-lb-01.xx.net harborlb1
192.168.17.230 k8s-haproxy-01.xx.net haproxy1
192.168.17.231 k8s-haproxy-02.xx.net haproxy2
192.168.17.240 k8s-node-01.xx.net node1
192.168.17.241 k8s-node-02.xx.net node2
[root@k8s-master-01 ~]# ping k8s-master-02.xx.net
PING k8s-master-02.xx.net (192.168.17.201) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from k8s-master-02.xx.net (192.168.17.201): icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=0.351 ms
64 bytes from k8s-master-02.xx.net (192.168.17.201): icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=0.417 ms
[root@k8s-master-01 ~]# ping k8s-master1
PING k8s-master-01.xx.net (192.168.17.200) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from k8s-master-01.xx.net (192.168.17.200): icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=0.029 ms
64 bytes from k8s-master-01.xx.net (192.168.17.200): icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=0.084 ms
3.3 配置部署服务器
- python环境确认
由于本次使用Ansibleeaszlab / kubeasz项目部署,该项目依赖python环境,所以确认python环境
[root@k8s-master-01 ~]# python -V
Python 2.7.5
如果没有,需要自行安装
- 安装ansible
yum install epel-release
yum list ansible
[root@k8s-master-01 ~]# ansible --version
ansible 2.9.27
- 免密登录
[root@k8s-master-01 ansible]# ssh-keygen -t rsa
Generating public/private rsa key pair.
Enter file in which to save the key (/root/.ssh/id_rsa):
Enter passphrase (empty for no passphrase):
Enter same passphrase again:
Your identification has been saved in /root/.ssh/id_rsa.
Your public key has been saved in /root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub.
The key fingerprint is:
SHA256:vpCfdo/3ASX/R3Oo5kDS/eNRlxgMmx6Jd+Ia9k8V/ck root@k8s-master-01.xx.net
The key's randomart image is:
+---[RSA 2048]----+
| . |
| . * .|
| . B.+...|
| .+.+++.=|
| Soooo.oE*|
| o.o+ +.++|
| o ....o.= o|
| o.o.=+. +.|
| .+..oooo |
+----[SHA256]-----+
[root@k8s-master-01 ansible]# ssh-copy-id k8s-master2
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: Source of key(s) to be installed: "/root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub"
The authenticity of host 'k8s-master2 (192.168.17.201)' can't be established.
ECDSA key fingerprint is SHA256:4nnztXLWowGhpbgty9XumjujsHbrQXnyYCX3kTYuSJI.
ECDSA key fingerprint is MD5:f3:d3:c8:50:c5:61:ee:4b:df:d6:b5:03:c4:12:fc:32.
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)? yes
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: attempting to log in with the new key(s), to filter out any that are already installed
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: 1 key(s) remain to be installed -- if you are prompted now it is to install the new keys
root@k8s-master2's password:
Number of key(s) added: 1
Now try logging into the machine, with: "ssh 'k8s-master2'"
and check to make sure that only the key(s) you wanted were added.
[root@k8s-master-01 ansible]# ssh k8s-master2
Last login: Mon Feb 19 23:29:00 2024 from gateway
[root@k8s-master-02 ~]# exit
logout
Connection to k8s-master2 closed.
我们可以通过sshpass -p yurq ssh-copy-id gitlab-server进行批量服务器免密操作
[root@k8s-master-01 ansible]# cat ssh-cp.sh
#!/usr/bin/env bash
passwd=xxx
cat /etc/hosts | while read ipaddr hostname1 hostname2
do
echo $passwd,$ipaddr
sshpass -p $passwd ssh-copy-id $ipaddr
done
- 资产清单
这里我们配置下/etc/ansible/hosts,便于管理
[master]
192.168.17.200
192.168.17.201
[etcd]
192.168.17.210
192.168.17.211
192.168.17.212
[harbor]
192.168.17.220
192.168.17.221
[haproxy]
192.168.17.230
192.168.17.231
[node]
192.168.17.240
192.168.17.241
[gitlab]
192.168.17.191
[k8s-server:children]
master
etcd
node
验证下该配置文件
[root@k8s-master-01 ansible]# ansible all -m ping
192.168.17.241 | SUCCESS => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
...
- 把
/etc/hosts和/etc/resolv.conf分发给各机器
可以通过上面的脚本修改,或者ansible
ansible all -m copy -a "src=/etc/hosts dest=/etc/"
ansible all -m copy -a "src=/etc/resolv.conf dest=/etc/"
ansible all -m shell -a "cat /etc/hosts"
重启下所有服务器,因为前面改完主机名一直没重启
ansible etcd -m shell -a "reboot"
这里注意要分组单独重启,如果all的话,可能有些服务器不能重启哦
测试联通性
[root@k8s-master-01 ansible]# cat ssh-host.sh
#!/usr/bin/env bash
passwd=yurq
cat /etc/hosts | while read ipaddr hostname1 hostname2
do
ping $hostname1 -c 1 -W 1 &> /dev/null
if [ $? == 0 ];then
echo $hostname1 connected
fi
done
[root@k8s-master-01 ansible]# sh ssh-host.sh
localhost connected
localhost connected
k8s-gitlab-01.xx.net connected
k8s-master-01.xx.net connected
k8s-master-02.xx.net connected
k8s-etcd-01.xx.net connected
k8s-etcd-02.xx.net connected
k8s-etcd-03.xx.net connected
k8s-harbor-01.xx.net connected
k8s-harbor-02.xx.net connected
k8s-haproxy-01.xx.net connected
k8s-haproxy-02.xx.net connected
k8s-node-01.xx.net connected
k8s-node-02.xx.net connected
3.4 配置gitlab服务器
参考官网 https://packages.gitlab.com/gitlab/gitlab-ce
curl -s https://packages.gitlab.com/install/repositories/gitlab/gitlab-ce/script.rpm.sh | sudo bash
yum install gitlab-ce-16.9.0-ce.0.el7.x86_64
[root@k8s-gitlab-01 ~]# grep external_url /etc/gitlab/gitlab.rb
##! For more details on configuring external_url see:
external_url 'http://k8s-gitlab-01.xx.net' #修改下URL
...
gitlab-ctl reconfigure
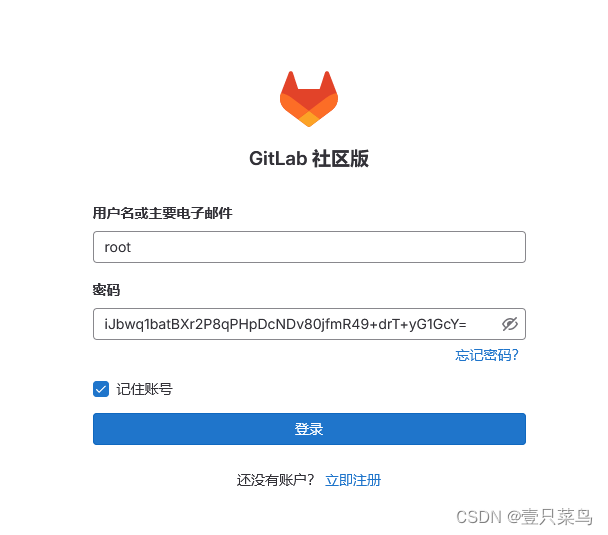
[root@k8s-gitlab-01 ~]# cat /etc/gitlab/initial_root_password
# WARNING: This value is valid only in the following conditions
# 1. If provided manually (either via `GITLAB_ROOT_PASSWORD` environment variable or via `gitlab_rails['initial_root_password']` setting in `gitlab.rb`, it was provided before database was seeded for the first time (usually, the first reconfigure run).
# 2. Password hasn't been changed manually, either via UI or via command line.
#
# If the password shown here doesn't work, you must reset the admin password following https://docs.gitlab.com/ee/security/reset_user_password.html#reset-your-root-password.
Password: iJbwq1batBXr2P8qPHpDcNDv80jfmR49+drT+yG1GcY=
# NOTE: This file will be automatically deleted in the first reconfigure run after 24 hours.
gitlab常用管理命令:
gitlab-ctl --help
gitlab-ctl restart
gitlab-ctl start
gitlab-ctl stop
gitlab-ctl status
3.5 配置haproxy服务器
配置haproxy服务器,需要安装keepalived和haproxy
- keepalived
参考 https://blog.csdn.net/u010230019/article/details/129284821
可以在部署服务器通过ansible安装,或在haproxy服务器手动安装
ansible haproxy -m yum -a "name=keepalived state=installed"
k8s-haproxy-01.xx.net服务器修改配置文件/etc/keepalived/keepalived.conf,作为主节点
[root@k8s-haproxy-01 ~]# cat /etc/keepalived/keepalived.conf
! Configuration File for keepalived
vrrp_instance VI_1 {
state MASTER
interface ens34
virtual_router_id 1
priority 100
advert_int 1
unicast_src_ip 192.168.17.230
unicast_peer {
192.168.17.231
}
authentication {
auth_type PASS
auth_pass 1111
}
virtual_ipaddress {
192.168.17.188 dev ens34 label ens34:1
}
}
k8s-haproxy-02.xx.net服务器修改配置文件/etc/keepalived/keepalived.conf,作为备节点
[root@k8s-haproxy-02 ~]# cat /etc/keepalived/keepalived.conf
! Configuration File for keepalived
vrrp_instance VI_1 {
state BACKUP
interface ens34
virtual_router_id 1
priority 80
advert_int 1
unicast_src_ip 192.168.17.231
unicast_peer {
192.168.17.230
}
authentication {
auth_type PASS
auth_pass 1111
}
virtual_ipaddress {
192.168.17.188 dev ens34 label ens34:1
}
}
达到的效果
[root@k8s-haproxy-01 ~]# ip a
...
3: ens34: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast state UP group default qlen 1000
link/ether 00:0c:29:b5:c2:71 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 192.168.17.230/24 brd 192.168.17.255 scope global noprefixroute ens34
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet 192.168.17.188/32 scope global ens34:1
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 fe80::20c:29ff:feb5:c271/64 scope link
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
...
[root@k8s-master-01 ansible]# ping 192.168.17.188
PING 192.168.17.188 (192.168.17.188) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 192.168.17.188: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=0.750 ms
^C
--- 192.168.17.188 ping statistics ---
1 packets transmitted, 1 received, 0% packet loss, time 0ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 0.750/0.750/0.750/0.000 ms
[root@k8s-master-01 ansible]# ansible haproxy -m shell -a "systemctl enable keepalived"
[WARNING]: Invalid characters were found in group names but not replaced, use -vvvv to see details
192.168.17.231 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/keepalived.service to /usr/lib/systemd/system/keepalived.service.
192.168.17.230 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/keepalived.service to /usr/lib/systemd/system/keepalived.service.
- haproxy
参考 https://blog.csdn.net/coolpale/article/details/79773429
ansible haproxy -m yum -a "name=haproxy state=installed"
修改配置文件/etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg,在后面添加如下内容
[root@k8s-haproxy-01 haproxy]# tail /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg
...
listen k8s_api_6443
bind 192.168.17.188:6443
mode tcp
server 192.168.17.200 192.168.17.200:6443 check inter 2000 fall 3 rise 5
server 192.168.17.201 192.168.17.201:6443 check inter 2000 fall 3 rise 5
启动服务并设置开机自启
systemctl start haproxy
systemctl enable haproxy
查看是否监听
[root@k8s-haproxy-01 haproxy]# ss -lntpu|grep 6443
tcp LISTEN 0 128 192.168.17.188:6443 *:* users:(("haproxy",pid=6459,fd=5))
当我们在haproxy2服务器,安装配置完成后,可能发现该服务无法启动
Starting proxy k8s_api_6443: cannot bind socket [192.168.17.188:6443]
这是由于系统默认无法监听不在本机的端口
[root@k8s-haproxy-02 ~]# sysctl -a |grep bind
net.ipv4.ip_nonlocal_bind = 0
...
做如下修改
[root@k8s-haproxy-02 ~]# sysctl -w net.ipv4.ip_nonlocal_bind=1
net.ipv4.ip_nonlocal_bind = 1
[root@k8s-haproxy-02 ~]# tail -2 /etc/sysctl.conf
net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1
net.ipv4.ip_nonlocal_bind = 1
此时,haproxy2服务器也正常启动haproxy服务了
[root@k8s-haproxy-02 ~]# systemctl status haproxy
● haproxy.service - HAProxy Load Balancer
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/haproxy.service; disabled; vendor preset: disabled)
Active: active (running) since Wed 2024-02-21 01:13:17 CST; 6s ago
...
3.6 配置harbor服务器
参考 https://blog.csdn.net/u010230019/article/details/136261147