目录
- 一、程序及输出
- 1.1 数组类头文件
- 1.2 数组类.cpp
- 1.3 主程序
- 二、分析与总结
一、程序及输出
1.1 数组类头文件
myArray.h
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class MyArray
{
public:
MyArray(); //默认构造 可以给100容量
MyArray(int capacity); //有参构造
MyArray(const MyArray & arr); //拷贝构造
//尾插法
void pushBack(int val);
//根据位置设置数据
void setData(int pos, int val);
//根据位置获取数据
int getData(int pos);
//获取数组容量
int getCapcity();
//获取数组大小
int getSize();
//析构
~MyArray();
//重载[]运算符
int& operator[](int index);
private:
int m_Capacity; //数组容量
int m_Size; //数组大小
int *pAddress; //真实在堆区开辟的数组的指针
};
1.2 数组类.cpp
MyArray.cpp
#include "myArray.h"
MyArray::MyArray()
{
cout << "默认构造函数调用" << endl;
this->m_Capacity = 100;
this->m_Size = 0;
this->pAddress = new int[this->m_Capacity];
}
MyArray::MyArray(int capacity)
{
cout << "有参构造函数调用" << endl;
this->m_Capacity = capacity;
this->m_Size = 0;
this->pAddress = new int[this->m_Capacity];
}
MyArray::MyArray(const MyArray & arr)
{
cout << "拷贝构造函数调用" << endl;
this->m_Capacity = arr.m_Capacity;
this->m_Size = arr.m_Size;
//this->pAddress = arr.pAddress;
this->pAddress = new int[arr.m_Capacity];
for (int i = 0; i < m_Size;i++)
{
this->pAddress[i] = arr.pAddress[i];
}
}
//尾插法
void MyArray::pushBack(int val)
{
this->pAddress[this->m_Size] = val;
this->m_Size++;
}
//根据位置设置数据
void MyArray::setData(int pos, int val)
{
this->pAddress[pos] = val;
}
//根据位置获取数据
int MyArray::getData(int pos)
{
return this->pAddress[pos];
}
//获取数组容量
int MyArray::getCapcity()
{
return this->m_Capacity;
}
//获取数组大小
int MyArray::getSize()
{
return this->m_Size;
}
//析构
MyArray::~MyArray()
{
if (this->pAddress != NULL)
{
cout << "析构函数调用" << endl;
delete [] this->pAddress;
this->pAddress = NULL;
}
}
int& MyArray::operator[](int index)
{
return this->pAddress[index];
}
1.3 主程序
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include "myArray.h"
void test01()
{
MyArray arr;
for (int i = 0; i < 10;i++)
{
arr.pushBack(i);
}
for (int i = 0; i < arr.getSize(); i ++)
{
cout << arr.getData(i) << endl;
}
MyArray arr2(arr);
for (int i = 0; i < arr2.getSize(); i++)
{
cout << arr2.getData(i) << endl;
}
arr.setData(0, 1000);
cout << "arr 0号位置数据为: " << arr.getData(0) << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
cout << arr.getData(i) << endl;
}
cout << "数组容量为: " << arr.getCapcity() << endl;
cout << "数组大小为: " << arr.getSize() << endl;
//小任务: 利用[]方式去索引数组中的元素,可读可写
cout << "---------------------" << endl;
arr[0] = 10000;
cout << arr[0] << endl;
}
int main(){
test01();
system("pause");
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
输出:
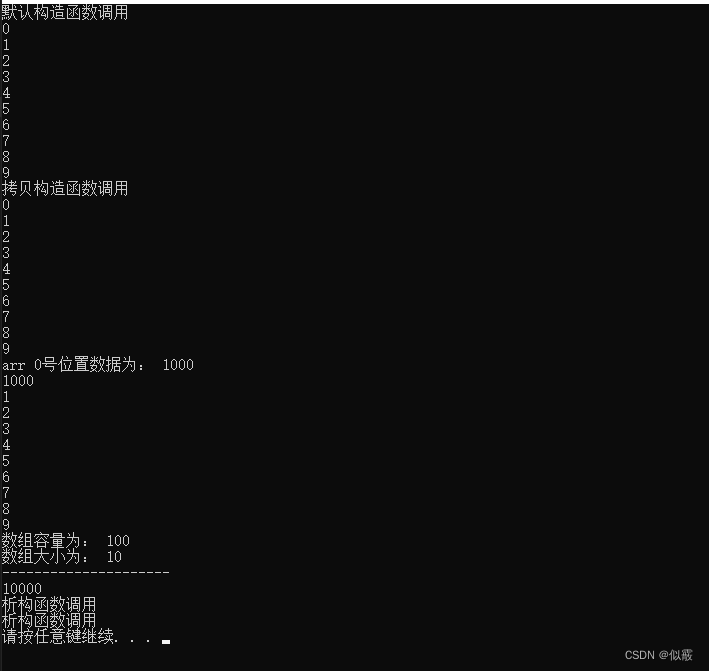
二、分析与总结
在 C++ 中,数组类的封装是指将数组数据结构封装到一个类中,并提供合适的接口以操作数组元素。这种封装可以提高代码的可读性、可维护性和安全性。
私有数据成员:数组类通常会将数组元素作为私有数据成员存储在类中,这样可以限制对数组元素的直接访问,从而提高数据的安全性。
构造函数:数组类通常会提供构造函数来初始化数组,可以包括默认构造函数、带参数的构造函数和复制构造函数等。
析构函数:如果数组类动态分配了内存,通常会提供析构函数来释放内存,防止内存泄漏。
访问器方法:数组类通常会提供访问器方法(getter 和 setter)来访问和修改数组元素。这些方法可以对访问进行限制或验证,确保数组的正确使用。
操作符重载:数组类通常会重载一些操作符,如 [] 运算符,以便可以像使用普通数组一样访问数组元素。
成员函数:数组类通常会提供各种成员函数来实现数组的常见操作,如插入元素、删除元素、查找元素等。






![[嵌入式系统-24]:RT-Thread -11- 内核组件编程接口 - 网络组件 - TCP/UDP Socket编程](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/e610af54ab5f40b7b529f1dd49cc76a9.png)