我们上一起讲了这一期讲存储类和继承,这个难度很大的。
存储类
存储类主要规定了函数和变量的范围,在c++中有这些存储类↓:
৹ auto(自动判断函数是什么类型)
৹ register (常用的变量和inline差不多,但应用于变量)
৹ static (函数调用之间保持局部变量的值)
就像这样:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
void out(){
static int i = 0;
cout<<"hello "<<++i<<'\n';
}
int main(){
int n;
cin >> n;
while(n--) out();
return 0;
}
懂了吗,我们再来看下一个。
৹ extern (就是比如众所周知前面的函数不能访问后面的,但加了这个后只要在前面申明有这个东西就可以了)
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
extern void out_();
int n;
void out(){
static int i = 0;
cout<<"hello "<<++i;
out_();
}
void out_(){
static int j = n+1;
cout<<' '<<j--<<'\n';
}
int main(){
cin >> n;
while(n--) out();
return 0;
}
৹ mutable(被mutable修饰的变量,即使在一个const函数,也可以改变)
৹ thread_local (C++存储期的一种,属于线程存储期)
这些存储类就不多讲了
继承
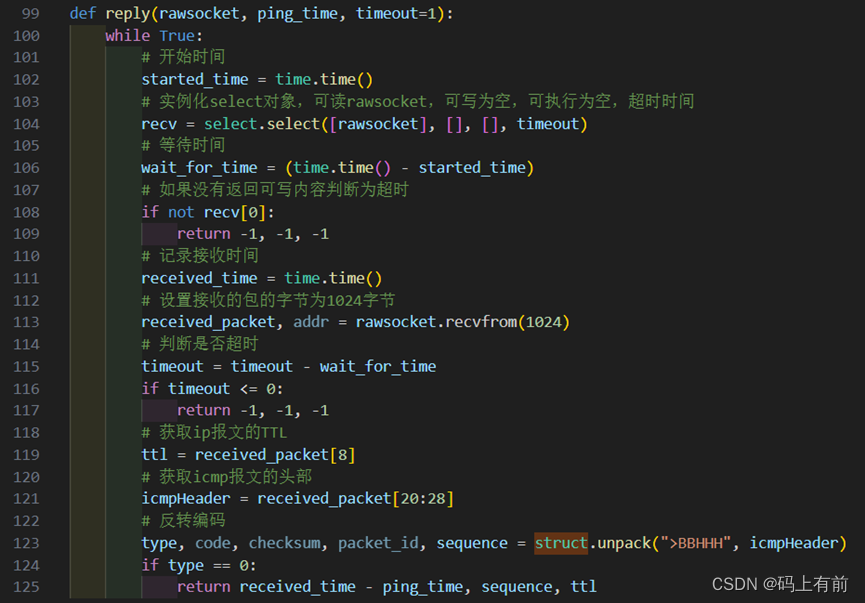
继承我们先来看一个代码再说:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define DB double
class student{
public:
int age; //年龄
string name; //姓名
protected:
DB Chinese, Maths, English; //语文,数学·,英语成绩
private :
DB finalexam; //期末综合成绩
};
class __Final__ : public student{ // 继承(__Final__是一个派生类)
public:
void GetCME_(){ //输入父类中的受保护成员函数
DB C_, M_, E_;
cin >> C_ >> M_ >> E_;
Chinese = C_, Maths = M_, English = E_;
}
DB getFinal(){
return (Chinese + Maths + English) / 3;
}
};
int main(){
__Final__ _S;
cin>>_S.name>>_S.age;
_S.GetCME_();
cout << _S.getFinal();
return 0;
}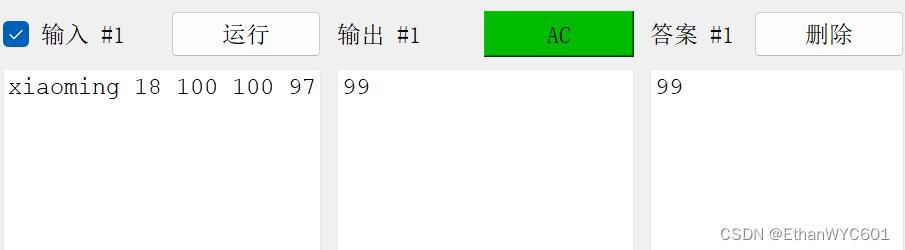
看样例知道这是一个求平均分的。
看一下注释吧。在这里__Final__就是student的派生类。