Python算法题集_两两交换链表中的节点
- 题24:两两交换链表中的节点
- 1. 示例说明
- 2. 题目解析
- - 题意分解
- - 优化思路
- - 测量工具
- 3. 代码展开
- 1) 标准求解【四节点法】
- 2) 改进版一【列表操作】
- 3) 改进版二【三指针法】
- 4) 改进版三【递归大法】
- 4. 最优算法
本文为Python算法题集之一的代码示例
题24:两两交换链表中的节点
1. 示例说明
-
给你一个链表,两两交换其中相邻的节点,并返回交换后链表的头节点。你必须在不修改节点内部的值的情况下完成本题(即,只能进行节点交换)。
示例 1:
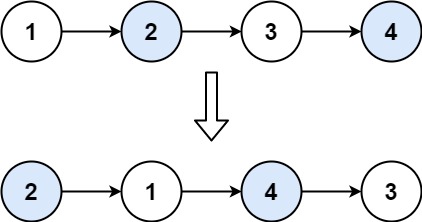
输入:head = [1,2,3,4] 输出:[2,1,4,3]示例 2:
输入:head = [] 输出:[]示例 3:
输入:head = [1] 输出:[1]提示:
- 链表中节点的数目在范围
[0, 100]内 0 <= Node.val <= 100
- 链表中节点的数目在范围
2. 题目解析
- 题意分解
- 本题为两两交换链表中间的节点
- 本题的主要计算是2块,1是链表遍历,2是节点链接调整
- 基本的解法是单层循环,链表1读一遍,过程中执行节点链接调整,所以基本的时间算法复杂度为O(m)
- 优化思路
-
通常优化:减少循环层次
-
通常优化:增加分支,减少计算集
-
通常优化:采用内置算法来提升计算速度
-
分析题目特点,分析最优解
-
标准方法是一次循环,4个节点中,第2个节点链接第1个,第1个节点连接第3个或者第4个【如果第4个存在】
-
可以用列表结构进行节点调整,列表结构简单,方便维护
-
可以用三指针方式一次循环完成
-
此问题可以用嵌套思路,使用递归法
-
- 测量工具
- 本地化测试说明:LeetCode网站测试运行时数据波动很大,因此需要本地化测试解决这个问题
CheckFuncPerf(本地化函数用时和内存占用测试模块)已上传到CSDN,地址:Python算法题集_检测函数用时和内存占用的模块- 本题很难超时,本地化超时测试用例自己生成,详见【最优算法章节】
3. 代码展开
1) 标准求解【四节点法】
一次遍历检查4个节点,完成节点链接调整
出类拔萃,超过85%
import CheckFuncPerf as cfp
class Solution:
@staticmethod
def swapPairs_base(head):
if not head:
return head
if not head.next:
return head
tmpNode1, tmpNode2 = head, head.next
head = tmpNode2
while tmpNode1 and tmpNode2:
tmpNode11 = tmpNode2.next
tmpNode12 = None
tmpNode1.next = tmpNode2.next
tmpNode2.next = tmpNode1
if tmpNode11:
tmpNode12 = tmpNode11.next
if tmpNode12:
tmpNode1.next = tmpNode12
tmpNode1 = tmpNode11
tmpNode2 = tmpNode12
return head
result = cfp.getTimeMemoryStr(Solution.swapPairs_base, ahead)
print(result['msg'], '执行结果 = {}'.format(result['result'].val))
# 运行结果
函数 swapPairs_base 的运行时间为 18.01 ms;内存使用量为 4.00 KB 执行结果 = 1
2) 改进版一【列表操作】
将链表转换为数组,再完成节点链接调整
马马虎虎,超过69%
import CheckFuncPerf as cfp
class Solution:
@staticmethod
def swapPairs_ext1(head):
if not head:
return head
if not head.next:
return head
list_node = []
while head:
list_node.append(head)
head = head.next
iLen = len(list_node)
for iIdx in range(len(list_node) // 2):
if iIdx * 2 + 2 > iLen:
continue
list_node[iIdx*2+1].next = list_node[iIdx*2]
if iIdx * 2 + 3 > iLen:
list_node[iIdx * 2].next = None
elif iIdx * 2 + 4 > iLen:
list_node[iIdx * 2].next = list_node[iIdx * 2 + 2]
else:
list_node[iIdx * 2].next = list_node[iIdx * 2 + 3]
return list_node[1]
result = cfp.getTimeMemoryStr(Solution.swapPairs_ext1, ahead)
print(result['msg'], '执行结果 = {}'.format(result['result'].val))
# 运行结果
函数 swapPairs_ext1 的运行时间为 109.04 ms;内存使用量为 76.00 KB 执行结果 = 1
3) 改进版二【三指针法】
使用三指针结构遍历链表,完成节点链接调整
出类拔萃,超过85%
import CheckFuncPerf as cfp
class Solution:
@staticmethod
def swapPairs_ext2(head):
dummyhead = ListNode(0)
dummyhead.next = head
nodepre = dummyhead
nodeslow = dummyhead.next
if not nodeslow:
return dummyhead.next
nodefast = nodeslow.next
while nodefast:
nodeslow.next = nodefast.next
nodefast.next = nodeslow
nodepre.next = nodefast
nodepre = nodeslow
nodeslow = nodeslow.next
if not nodeslow:
break
nodefast = nodeslow.next
return dummyhead.next
result = cfp.getTimeMemoryStr(Solution.swapPairs_ext2, ahead)
print(result['msg'], '执行结果 = {}'.format(result['result'].val))
# 运行结果
函数 swapPairs_ext2 的运行时间为 17.00 ms;内存使用量为 0.00 KB 执行结果 = 1
4) 改进版三【递归大法】
采用递归方式遍历链表,完成节点链接调整
出神入化,超过96%
import CheckFuncPerf as cfp
class Solution:
@staticmethod
def swapPairs_ext3(head):
def swapnodepair(head):
nodeleft = head
if not nodeleft:
return head
noderight = nodeleft.next
if not noderight:
return head
nodeleft.next = swapnodepair(noderight.next)
noderight.next = nodeleft
return noderight
return swapnodepair(head)
result = cfp.getTimeMemoryStr(Solution.swapPairs_ext3, ahead)
print(result['msg'], '执行结果 = {}'.format(result['result'].val))
# 运行结果
Traceback (most recent call last):
......
[Previous line repeated 991 more times]
RecursionError: maximum recursion depth exceeded
4. 最优算法
根据本地日志分析,最优算法为第3种swapPairs_ext2
nums = [ x for x in range(200000)]
def generateOneLinkedList(data):
head = ListNode()
current_node = head
for num in data:
new_node = ListNode(num)
current_node.next = new_node
current_node = new_node
return head.next
ahead = generateOneLinkedList(nums)
result = cfp.getTimeMemoryStr(Solution.swapPairs_base, ahead)
print(result['msg'], '执行结果 = {}'.format(result['result'].val))
# 算法本地速度实测比较
函数 swapPairs_base 的运行时间为 18.01 ms;内存使用量为 4.00 KB 执行结果 = 1
函数 swapPairs_ext1 的运行时间为 109.04 ms;内存使用量为 76.00 KB 执行结果 = 1
函数 swapPairs_ext2 的运行时间为 17.00 ms;内存使用量为 0.00 KB 执行结果 = 1
Traceback (most recent call last): # 递归法swapPairs_ext3超时
......
[Previous line repeated 991 more times]
RecursionError: maximum recursion depth exceeded
一日练,一日功,一日不练十日空
may the odds be ever in your favor ~