Kubernetes 给出的解决方案就是:自动伸缩(auto-scaling),通过自动伸缩组件之间的配合,可以 7*24 小时的监控着k8s集群,动态变化负载,以适应用户需求。
1 自动伸缩组件
1.1 自动伸缩类型
1.1.1 水平自动伸缩(Horizontal Pod Autoscaler,HPA)
HPA 可以基于实时的 CPU 利用率自动伸缩 Replication Controller、Deployment 和 Replica Set 中的 Pod 数量。也可以通过搭配 Metrics Server 基于其他的度量指标。
1.1.2 垂直自动伸缩(Vertical Pod Autoscaler,VPA)
VPA 可以基于 Pod 的使用资源来自动设置 Pod 所需资源并且能够在运行时自动调整资源。
1.1.3 集群自动伸缩(Cluster Autoscaler,CA)
CA 是一个可以自动伸缩集群 Node 的组件。如果集群中有未被调度的 Pod,它将会自动扩展 Node 来使 Pod 可用,或是在发现集群中的 Node 资源使用率过低时,删除 Node 来节约资源。
1.2 插件伸缩(Addon Resizer)
Addon Resizer是一个小插件,它以 Sidecar 的形式来垂直伸缩与自己同一个部署中的另一个容器,目前唯一的策略就是根据集群中节点的数量来进行线性扩展。通常与 Metrics Server 配合使用,以保证其可以负担不断扩大的整个集群的 metrics API 服务。
通过 HPA 伸缩无状态应用,VPA 伸缩有状态应用,CA 保证计算资源,它们的配合使用,构成了一个完整的自动伸缩解决方案。
2 Cluster Autoscaler 详细介绍
上面介绍的四个组件中,HPA 是在 kubernetes 代码仓库中的,随着 kubernetes 的版本进行更新发布,不需要部署,可以直接使用。其他的三个组件都在官方社区维护的仓库中,Cluster Autoscaler 的 v1.0(GA) 版本已经随着 kubernetes 1.8 一起发布,剩下两个则还是 beta 版本。
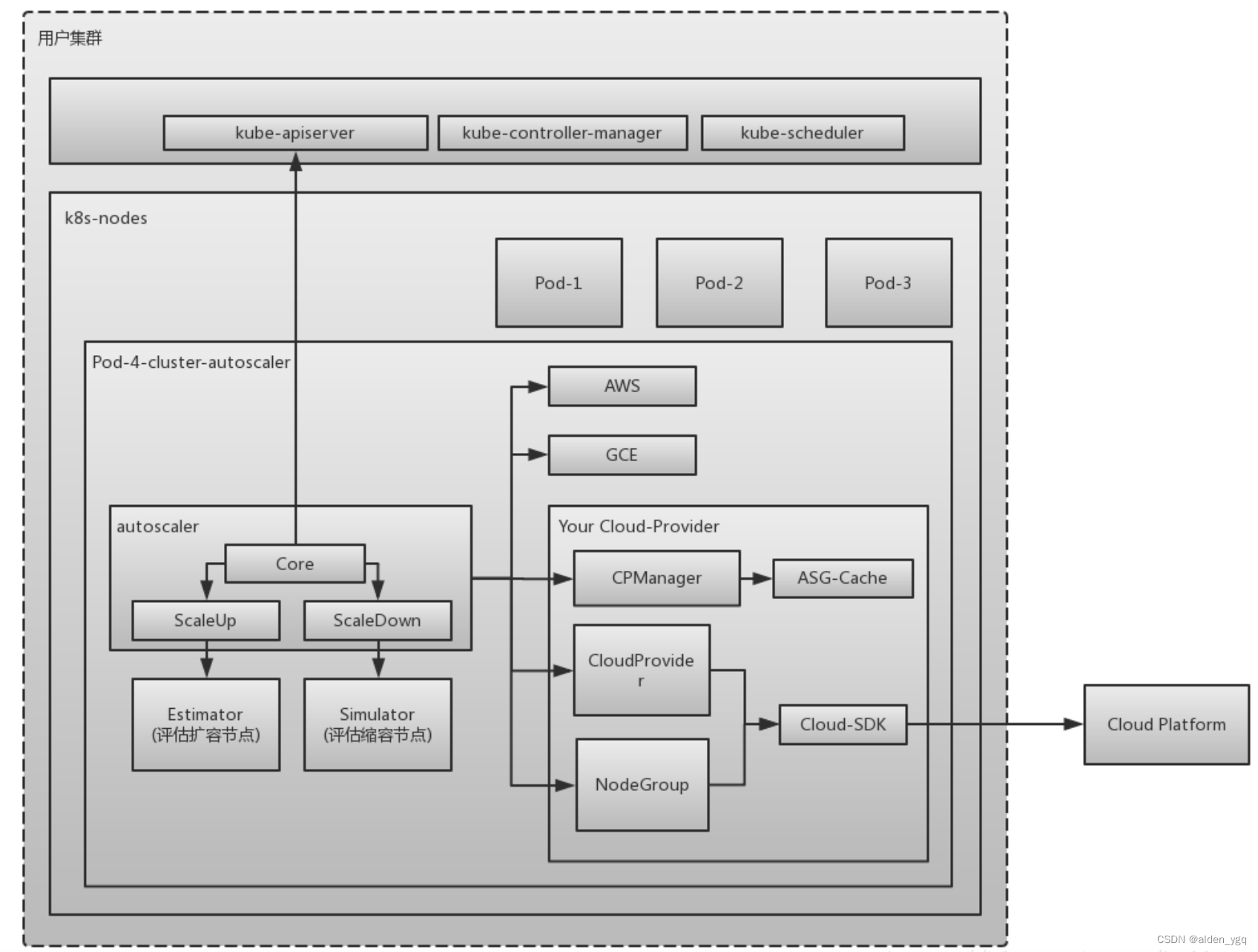
CA由以下几个模块组成:
- autoscaler:核心模块,负责整体扩缩容功能
- Estimator:负责评估计算扩容节点
- Simulator:负责模拟调度,计算缩容节点
- CA Cloud-Provider:与云交互进行节点的增删操作。社区目前仅支持AWS和GCE,其他云厂商需要自己实现CloudProvider和NodeGroup相关接口。
CA的架构如下:
2.1 云厂商
Cluster Autoscaler 通常需要搭配云厂商使用,它提供了 Cloud Provider 接口供各个云厂商接入,云厂商通过伸缩组(Scaling Group)或节点池(Node Pool)的功能对 ECS 类产品节点进行增加删除等操作。
目前(v1.18.1)已接入的云厂商:
Alicloud:https://github.com/kubernetes/autoscaler/blob/master/cluster-autoscaler/cloudprovider/alicloud/README.md
Aws:https://github.com/kubernetes/autoscaler/blob/master/cluster-autoscaler/cloudprovider/aws/README.md
Azure:https://github.com/kubernetes/autoscaler/blob/master/cluster-autoscaler/cloudprovider/azure/README.md
Baiducloud:https://github.com/kubernetes/autoscaler/blob/master/cluster-autoscaler/cloudprovider/baiducloud/README.md
Digitalocean:https://github.com/kubernetes/autoscaler/blob/master/cluster-autoscaler/cloudprovider/digitalocean/README.md
GoogleCloud GCE:https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/administer-cluster/cluster-management/#upgrading-google-compute-engine-clusters
GoogleCloud GKE:https://cloud.google.com/kubernetes-engine/docs/concepts/cluster-autoscaler
OpenStack Magnum:https://github.com/kubernetes/autoscaler/blob/master/cluster-autoscaler/cloudprovider/magnum/README.md
Packet:https://github.com/kubernetes/autoscaler/blob/master/cluster-autoscaler/cloudprovider/packet/README.md
启动参数:https://github.com/kubernetes/autoscaler/blob/master/cluster-autoscaler/FAQ.md#what-are-the-parameters-to-ca
部署yaml:
直接在集群中部署即可,简化的yaml如下所示,启动参数按需添加,其中{{MIN}}是最小节点数,{{MAX}}是最大节点数。
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: cluster-autoscaler
labels:
k8s-app: cluster-autoscaler
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
k8s-app: cluster-autoscaler
template:
metadata:
labels:
k8s-app: cluster-autoscaler
spec:
containers:
- image: cluster-autoscaler:latest
name: cluster-autoscaler
command:
- ./cluster-autoscaler
- --nodes={{MIN}}:{{MAX}}:k8s-worker-asg-12.2 工作原理
Cluster Autoscaler 抽象出了一个 NodeGroup 的概念,与之对应的是云厂商的伸缩组服务。Cluster Autoscaler 通过 CloudProvider 提供的 NodeGroup 计算集群内节点资源,以此来进行伸缩。
在启动后,Cluster Autoscaler 会定期(默认 10s)检查未调度的 Pod 和 Node 的资源使用情况,并进行相应的 Scale UP 和 Scale Down 操作。
2.2.1 Scale UP
当 Cluster Autoscaler 发现有 Pod 由于资源不足而无法调度时,就会通过调用 Scale UP 执行扩容操作。
在 Scale UP 中会只会计算在 NodeGroup 中存在的 Node,我们可以将 Worker Node 统一交由伸缩组进行管理。并且由于伸缩组非同步加入的特性,也会考虑到 Upcoming Node。
为了业务需要,集群中可能会有不同规格的 Node,我们可以创建多个 NodeGroup,在扩容时会根据 --expander 选项配置指定的策略,选择一个扩容的节点组,支持如下五种策略:
- random:随机选择一个
NodeGroup。如果未指定,则默认为此策略。 - most-pods:选择能够调度最多 Pod 的
NodeGroup,比如有的 Pod 未调度是因为nodeSelector,此策略会优先选择能满足的NodeGroup来保证大多数的 Pod 可以被调度。 - least-waste:为避免浪费,此策略会优先选择能满足 Pod 需求资源的最小资源类型的
NodeGroup。 - price:根据
CloudProvider提供的价格模型,选择最省钱的NodeGroup。 - priority:通过配置优先级来进行选择,用起来比较麻烦,需要额外的配置,可以看文档。
如果有需要,也可以平衡相似 NodeGroup 中的 Node 数量,避免 NodeGroup 达到 MaxSize 而导致无法加入新 Node。通过 --balance-similar-node-groups 选项配置,默认为 false。
再经过一系列的操作后,最终计算出要扩容的 Node 数量及 NodeGroup,使用 CloudProvider 执行 IncreaseSize 操作,增加云厂商的伸缩组大小,从而完成扩容操作。
文字表达能力不足,如果有不清晰的地方,可以参考下面的 ScaleUP 源码解析。
2.2.2 Scale Down
缩容是一个可选的功能,通过 --scale-down-enabled 选项配置,默认为 true。
在 Cluster Autoscaler 监控 Node 资源时,如果发现有 Node 满足以下三个条件时,就会标记这个 Node 为 unneeded:
- Node 上运行的所有的 Pod 的 Cpu 和内存之和小于该 Node 可分配容量的 50%。可通过
--scale-down-utilization-threshold选项改变这个配置。 - Node 上所有的 Pod 都可以被调度到其他节点。
- Node 没有表示不可缩容的 annotaition。
如果一个 Node 被标记为 unneeded 超过 10 分钟(可通过 --scale-down-unneeded-time 选项配置),则使用 CloudProvider 执行 DeleteNodes 操作将其删除。一次最多删除一个 unneeded Node,但空 Node 可以批量删除,每次最多删除 10 个(通过 ----max-empty-bulk-delete 选项配置)。
实际上并不是只有这一个判定条件,还会有其他的条件来阻止删除这个 Node,比如 NodeGroup 已达到 MinSize,或在过去的 10 分钟内有过一次 Scale UP 操作(通过 --scale-down-delay-after-add 选项配置)等等,更详细可查看文档。
Cluster Autoscaler 的工作机制很复杂,但其中大部分都能通过 flags 进行配置,如果有需要,请详细阅读文档:https://github.com/kubernetes/autoscaler/blob/master/cluster-autoscaler/FAQ.md
2.3 如何实现 CloudProvider
如果使用上述中已实现接入的云厂商,只需要通过 --cloud-provider 选项指定来自哪个云厂商就可以,如果想要对接自己的 IaaS 或有特定的业务逻辑,就需要自己实现 CloudProvider Interface 与 NodeGroupInterface。并将其注册到 builder 中,用于通过 --cloud-provider 参数指定。
builder 在 cloudprovider/builder 中的 builder_all.go 中注册,也可以在其中新建一个自己的 build,通过 go 文件的 +build 编译参数来指定使用的 CloudProvider。
CloudProvider 接口与 NodeGroup 接口在 cloud_provider.go 中定义,其中需要注意的是 Refresh 方法,它会在每一次循环(默认 10 秒)的开始时调用,可在此时请求接口并刷新 NodeGroup 状态,通常的做法是增加一个 manager 用于管理状态。有不理解的部分可参考其他 CloudProvider 的实现。
type CloudProvider interface {
// Name returns name of the cloud provider.
Name() string
// NodeGroups returns all node groups configured for this cloud provider.
// 会在一此循环中多次调用此方法,所以不适合每次都请求云厂商服务,可以在 Refresh 时存储状态
NodeGroups() []NodeGroup
// NodeGroupForNode returns the node group for the given node, nil if the node
// should not be processed by cluster autoscaler, or non-nil error if such
// occurred. Must be implemented.
// 同上
NodeGroupForNode(*apiv1.Node) (NodeGroup, error)
// Pricing returns pricing model for this cloud provider or error if not available.
// Implementation optional.
// 如果不使用 price expander 就可以不实现此方法
Pricing() (PricingModel, errors.AutoscalerError)
// GetAvailableMachineTypes get all machine types that can be requested from the cloud provider.
// Implementation optional.
// 没用,不需要实现
GetAvailableMachineTypes() ([]string, error)
// NewNodeGroup builds a theoretical node group based on the node definition provided. The node group is not automatically
// created on the cloud provider side. The node group is not returned by NodeGroups() until it is created.
// Implementation optional.
// 通常情况下,不需要实现此方法,但如果你需要 ClusterAutoscaler 创建一个默认的 NodeGroup 的话,也可以实现。
// 但其实更好的做法是将默认 NodeGroup 写入云端的伸缩组
NewNodeGroup(machineType string, labels map[string]string, systemLabels map[string]string,
taints []apiv1.Taint, extraResources map[string]resource.Quantity) (NodeGroup, error)
// GetResourceLimiter returns struct containing limits (max, min) for resources (cores, memory etc.).
// 资源限制对象,会在 build 时传入,通常情况下不需要更改,除非在云端有显示的提示用户更改的地方,否则使用时会迷惑用户
GetResourceLimiter() (*ResourceLimiter, error)
// GPULabel returns the label added to nodes with GPU resource.
// GPU 相关,如果集群中有使用 GPU 资源,需要返回对应内容。 hack: we assume anything which is not cpu/memory to be a gpu.
GPULabel() string
// GetAvailableGPUTypes return all available GPU types cloud provider supports.
// 同上
GetAvailableGPUTypes() map[string]struct{}
// Cleanup cleans up open resources before the cloud provider is destroyed, i.e. go routines etc.
// CloudProvider 只会在启动时被初始化一次,如果每次循环后有需要清除的内容,在这里处理
Cleanup() error
// Refresh is called before every main loop and can be used to dynamically update cloud provider state.
// In particular the list of node groups returned by NodeGroups can change as a result of CloudProvider.Refresh().
// 会在 StaticAutoscaler RunOnce 中被调用
Refresh() error
}
// NodeGroup contains configuration info and functions to control a set
// of nodes that have the same capacity and set of labels.
type NodeGroup interface {
// MaxSize returns maximum size of the node group.
MaxSize() int
// MinSize returns minimum size of the node group.
MinSize() int
// TargetSize returns the current target size of the node group. It is possible that the
// number of nodes in Kubernetes is different at the moment but should be equal
// to Size() once everything stabilizes (new nodes finish startup and registration or
// removed nodes are deleted completely). Implementation required.
// 响应的是伸缩组的节点数,并不一定与 kubernetes 中的节点数保持一致
TargetSize() (int, error)
// IncreaseSize increases the size of the node group. To delete a node you need
// to explicitly name it and use DeleteNode. This function should wait until
// node group size is updated. Implementation required.
// 扩容的方法,增加伸缩组的节点数
IncreaseSize(delta int) error
// DeleteNodes deletes nodes from this node group. Error is returned either on
// failure or if the given node doesn't belong to this node group. This function
// should wait until node group size is updated. Implementation required.
// 删除的节点一定要在该节点组中
DeleteNodes([]*apiv1.Node) error
// DecreaseTargetSize decreases the target size of the node group. This function
// doesn't permit to delete any existing node and can be used only to reduce the
// request for new nodes that have not been yet fulfilled. Delta should be negative.
// It is assumed that cloud provider will not delete the existing nodes when there
// is an option to just decrease the target. Implementation required.
// 当 ClusterAutoscaler 发现 kubernetes 节点数与伸缩组的节点数长时间不一致,会调用此方法来调整
DecreaseTargetSize(delta int) error
// Id returns an unique identifier of the node group.
Id() string
// Debug returns a string containing all information regarding this node group.
Debug() string
// Nodes returns a list of all nodes that belong to this node group.
// It is required that Instance objects returned by this method have Id field set.
// Other fields are optional.
// This list should include also instances that might have not become a kubernetes node yet.
// 返回伸缩组中的所有节点,哪怕它还没有成为 kubernetes 的节点
Nodes() ([]Instance, error)
// TemplateNodeInfo returns a schedulernodeinfo.NodeInfo structure of an empty
// (as if just started) node. This will be used in scale-up simulations to
// predict what would a new node look like if a node group was expanded. The returned
// NodeInfo is expected to have a fully populated Node object, with all of the labels,
// capacity and allocatable information as well as all pods that are started on
// the node by default, using manifest (most likely only kube-proxy). Implementation optional.
// ClusterAutoscaler 会将节点信息与节点组对应,来判断资源条件,如果是一个空的节点组,那么就会通过此方法来虚拟一个节点信息。
TemplateNodeInfo() (*schedulernodeinfo.NodeInfo, error)
// Exist checks if the node group really exists on the cloud provider side. Allows to tell the
// theoretical node group from the real one. Implementation required.
Exist() bool
// Create creates the node group on the cloud provider side. Implementation optional.
// 与 CloudProvider.NewNodeGroup 配合使用
Create() (NodeGroup, error)
// Delete deletes the node group on the cloud provider side.
// This will be executed only for autoprovisioned node groups, once their size drops to 0.
// Implementation optional.
Delete() error
// Autoprovisioned returns true if the node group is autoprovisioned. An autoprovisioned group
// was created by CA and can be deleted when scaled to 0.
Autoprovisioned() bool
}
2.4 ScaleUP 源码解析
func ScaleUp(context *context.AutoscalingContext, processors *ca_processors.AutoscalingProcessors, clusterStateRegistry *clusterstate.ClusterStateRegistry, unschedulablePods []*apiv1.Pod, nodes []*apiv1.Node, daemonSets []*appsv1.DaemonSet, nodeInfos map[string]*schedulernodeinfo.NodeInfo, ignoredTaints taints.TaintKeySet) (*status.ScaleUpStatus, errors.AutoscalerError) {
......
// 验证当前集群中所有 ready node 是否来自于 nodeGroups,取得所有非组内的 node
nodesFromNotAutoscaledGroups, err := utils.FilterOutNodesFromNotAutoscaledGroups(nodes, context.CloudProvider)
if err != nil {
return &status.ScaleUpStatus{Result: status.ScaleUpError}, err.AddPrefix("failed to filter out nodes which are from not autoscaled groups: ")
}
nodeGroups := context.CloudProvider.NodeGroups()
gpuLabel := context.CloudProvider.GPULabel()
availableGPUTypes := context.CloudProvider.GetAvailableGPUTypes()
// 资源限制对象,会在 build cloud provider 时传入
// 如果有需要可在 CloudProvider 中自行更改,但不建议改动,会对用户造成迷惑
resourceLimiter, errCP := context.CloudProvider.GetResourceLimiter()
if errCP != nil {
return &status.ScaleUpStatus{Result: status.ScaleUpError}, errors.ToAutoscalerError(
errors.CloudProviderError,
errCP)
}
// 计算资源限制
// nodeInfos 是所有拥有节点组的节点与示例节点的映射
// 示例节点会优先考虑真实节点的数据,如果 NodeGroup 中还没有真实节点的部署,则使用 Template 的节点数据
scaleUpResourcesLeft, errLimits := computeScaleUpResourcesLeftLimits(context.CloudProvider, nodeGroups, nodeInfos, nodesFromNotAutoscaledGroups, resourceLimiter)
if errLimits != nil {
return &status.ScaleUpStatus{Result: status.ScaleUpError}, errLimits.AddPrefix("Could not compute total resources: ")
}
// 根据当前节点与 NodeGroups 中的节点来计算会有多少节点即将加入集群中
// 由于云服务商的伸缩组 increase size 操作并不是同步加入 node,所以将其统计,以便于后面计算节点资源
upcomingNodes := make([]*schedulernodeinfo.NodeInfo, 0)
for nodeGroup, numberOfNodes := range clusterStateRegistry.GetUpcomingNodes() {
......
}
klog.V(4).Infof("Upcoming %d nodes", len(upcomingNodes))
// 最终会进入选择的节点组
expansionOptions := make(map[string]expander.Option, 0)
......
// 出于某些限制或错误导致不能加入新节点的节点组,例如节点组已达到 MaxSize
skippedNodeGroups := map[string]status.Reasons{}
// 综合各种情况,筛选出节点组
for _, nodeGroup := range nodeGroups {
......
}
if len(expansionOptions) == 0 {
klog.V(1).Info("No expansion options")
return &status.ScaleUpStatus{
Result: status.ScaleUpNoOptionsAvailable,
PodsRemainUnschedulable: getRemainingPods(podEquivalenceGroups, skippedNodeGroups),
ConsideredNodeGroups: nodeGroups,
}, nil
}
......
// 选择一个最佳的节点组进行扩容,expander 用于选择一个合适的节点组进行扩容,默认为 RandomExpander,flag: expander
// random 随机选一个,适合只有一个节点组
// most-pods 选择能够调度最多 pod 的节点组,比如有 noSchedulerPods 是有 nodeSelector 的,它会优先选择此类节点组以满足大多数 pod 的需求
// least-waste 优先选择能满足 pod 需求资源的最小资源类型的节点组
// price 根据价格模型,选择最省钱的
// priority 根据优先级选择
bestOption := context.ExpanderStrategy.BestOption(options, nodeInfos)
if bestOption != nil && bestOption.NodeCount > 0 {
......
newNodes := bestOption.NodeCount
// 考虑到 upcomingNodes, 重新计算本次新加入节点
if context.MaxNodesTotal > 0 && len(nodes)+newNodes+len(upcomingNodes) > context.MaxNodesTotal {
klog.V(1).Infof("Capping size to max cluster total size (%d)", context.MaxNodesTotal)
newNodes = context.MaxNodesTotal - len(nodes) - len(upcomingNodes)
if newNodes < 1 {
return &status.ScaleUpStatus{Result: status.ScaleUpError}, errors.NewAutoscalerError(
errors.TransientError,
"max node total count already reached")
}
}
createNodeGroupResults := make([]nodegroups.CreateNodeGroupResult, 0)
// 如果节点组在云服务商端处不存在,会尝试创建根据现有信息重新创建一个云端节点组
// 但是目前所有的 CloudProvider 实现都没有允许这种操作,这好像是个多余的方法
// 云服务商不想,也不应该将云端节点组的创建权限交给 ClusterAutoscaler
if !bestOption.NodeGroup.Exist() {
oldId := bestOption.NodeGroup.Id()
createNodeGroupResult, err := processors.NodeGroupManager.CreateNodeGroup(context, bestOption.NodeGroup)
......
}
// 得到最佳节点组的示例节点
nodeInfo, found := nodeInfos[bestOption.NodeGroup.Id()]
if !found {
// This should never happen, as we already should have retrieved
// nodeInfo for any considered nodegroup.
klog.Errorf("No node info for: %s", bestOption.NodeGroup.Id())
return &status.ScaleUpStatus{Result: status.ScaleUpError, CreateNodeGroupResults: createNodeGroupResults}, errors.NewAutoscalerError(
errors.CloudProviderError,
"No node info for best expansion option!")
}
// 根据 CPU、Memory及可能存在的 GPU 资源(hack: we assume anything which is not cpu/memory to be a gpu.),计算出需要多少个 Nodes
newNodes, err = applyScaleUpResourcesLimits(context.CloudProvider, newNodes, scaleUpResourcesLeft, nodeInfo, bestOption.NodeGroup, resourceLimiter)
if err != nil {
return &status.ScaleUpStatus{Result: status.ScaleUpError, CreateNodeGroupResults: createNodeGroupResults}, err
}
// 需要平衡的节点组
targetNodeGroups := []cloudprovider.NodeGroup{bestOption.NodeGroup}
// 如果需要平衡节点组,根据 balance-similar-node-groups flag 设置。
// 检测相似的节点组,并平衡它们之间的节点数量
if context.BalanceSimilarNodeGroups {
......
}
// 具体平衡策略可以看 (b *BalancingNodeGroupSetProcessor) BalanceScaleUpBetweenGroups 方法
scaleUpInfos, typedErr := processors.NodeGroupSetProcessor.BalanceScaleUpBetweenGroups(context, targetNodeGroups, newNodes)
if typedErr != nil {
return &status.ScaleUpStatus{Result: status.ScaleUpError, CreateNodeGroupResults: createNodeGroupResults}, typedErr
}
klog.V(1).Infof("Final scale-up plan: %v", scaleUpInfos)
// 开始扩容,通过 IncreaseSize 扩容
for _, info := range scaleUpInfos {
typedErr := executeScaleUp(context, clusterStateRegistry, info, gpu.GetGpuTypeForMetrics(gpuLabel, availableGPUTypes, nodeInfo.Node(), nil), now)
if typedErr != nil {
return &status.ScaleUpStatus{Result: status.ScaleUpError, CreateNodeGroupResults: createNodeGroupResults}, typedErr
}
}
......
}
......
}2.5 使用场景
在以下情况下,集群自动扩容或者缩放:
- 扩容:由于资源不足,某些Pod无法在任何当前节点上进行调度
- 缩容: Node节点资源利用率较低时,且此node节点上存在的pod都能被重新调度到其他node节点上运行。
2.6 什么时候集群节点不会被 CA 删除?
- 节点上有pod被 PodDisruptionBudget 控制器限制。
- 节点上有命名空间是 kube-system 的pods。
- 节点上的pod不是被控制器创建,例如不是被deployment, replica set, job, stateful set创建。
- 节点上有pod使用了本地存储
- 节点上pod驱逐后无处可去,即没有其他node能调度这个pod
- 节点有注解:"cluster-autoscaler.kubernetes.io/scale-down-disabled": "true"(在CA 1.0.3或更高版本中受支持)
2.7 Horizontal Pod Autoscaler 如何与 Cluster Autoscaler 一起使用?
Horizontal Pod Autoscaler 会根据当前CPU负载更改部署或副本集的副本数。如果负载增加,则HPA将创建新的副本,集群中可能有足够的空间,也可能没有足够的空间。如果没有足够的资源,CA将尝试启动一些节点,以便HPA创建的Pod可以运行。如果负载减少,则HPA将停止某些副本。结果,某些节点可能变得利用率过低或完全为空,然后CA将终止这些不需要的节点。