线程安全的集合
文章目录
- 线程安全的集合
- 1 List 和 Set体系
- Collections中的工具方法
- 1.1 CopyOnWriteArrayList
- 1.2 CopyOnWriteArraySet
- 1.3 ConcurrentHashMap
- 2 CAS算法
- 3 Queue接口(队列)
- 3.1 ConcurrentLinkedQueue
- 3.2 BlockingQueue接口(阻塞队列)
Collection体系集合、以及线程安全集合。
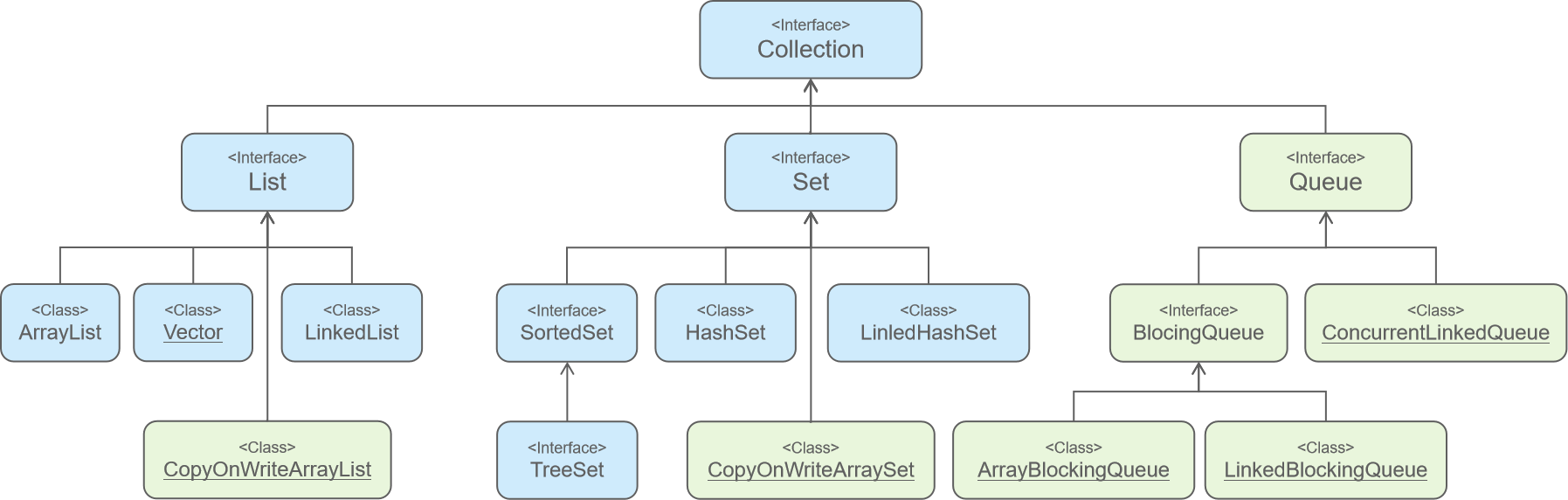
注:下划线代表线程安全集合
1 List 和 Set体系
Collections中的工具方法
Collections工具类中提供了多个可以获得线程安全集合的方法。
- public static Collection synchronizedCollection(Collection c)
- public static List synchronizedList(List list)
- public static Set synchronizedSet(Set s)
- public static <K,V> Map<K,V> synchronizedMap(Map<K,V> m)
- public static SortedSet synchronizedSortedSet(SortedSet s)
- public static <K,V> SortedMap<K,V> synchronizedSortedMap(SortedMap<K,V> m)
JDK1.2提供,接口统一、维护性高,但性能没有提升,均以synchonized实现。
1.1 CopyOnWriteArrayList
- 线程安全的ArrayList,加强版读写分离。
- 写有锁,读无锁,读写之间不阻塞,优于读写锁。
- 写入时,先copy一个容器副本、再添加新元素,最后替换引用。
- 使用方式与ArrayList无异。
1.2 CopyOnWriteArraySet
- 线程安全的Set,底层使用CopyOnWriteArrayList实现。
- 唯一不同在于,使用addIfAbsent()添加元素,会遍历数组
- 如存在元素,则不添加(扔掉副本)。
1.3 ConcurrentHashMap
JDK 1.7
- 初始容量默认为16段(Segment),使用分段锁设计。
- 不对整个Map加锁,而是为每个Segment加锁。
- 当多个对象存入同一个Segment时,才需要互斥。
- 最理想状态为16个对象分别存入16个Segment,并行数量16。
- 使用方式与HashMap无异。
JDK 1.8
- 改为CAS无锁算法。
eg:
public class TestThreadSafe {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//ArrayList<String> list=new ArrayList<>();
//CopyOnWriteArrayList list=new CopyOnWriteArrayList();
//CopyOnWriteArraySet set=new CopyOnWriteArraySet();
ConcurrentHashMap<String,String> hashMap=new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
ExecutorService es = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
es.submit(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int j = 0; j < 10; j++) {
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
hashMap.put(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"..."+j,"xxx");
}
}
});
}
es.shutdown();
while(!es.isTerminated());
System.out.println("元素个数:"+hashMap.size());
}
}
2 CAS算法
CAS:Compare And Swap(比较交换算法)
- 其实现方式是基于硬件平台的汇编指令,是靠硬件来实现的,效率高。
- 并且比较和交换过程是同步的。
- CAS是一种乐观锁。
乐观锁:
- 总是认为是线程安全,不怕别的线程修改变量,如果修改了再重新尝试,直到成功。
- CAS是乐观锁。
悲观锁:
- 总是认为线程不安全,不管什么情况都进行加锁,要是获取锁失败,就阻塞。
- synchronized、ReentrantLock是悲观锁。
CAS比较交换算法,修改的方法包含三个核心参数(V,E,N)
- V:要更新的变量、E:预期值、N:新值。
- 只有当V==E时,V=N;否则表示已被更新过,则取消当前操作,继续判断直到成功。
eg:
使用代码模拟CAS算法
public class TestCAS {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Cas cas=new Cas();
ExecutorService es = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(100);
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
es.submit(() -> {
while(true) {
int old = cas.getV();
boolean b = cas.compareAndSwap(old, new Random().nextInt(100));
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"..."+b);
if(b){
break;
}
}
});
}
es.shutdown();
}
static class Cas{
private int V;//更新的变量
//获取V的值
public int getV(){
return V;
}
public synchronized boolean compareAndSwap(int E,int N){
if(E==V){
V=N;
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
}
3 Queue接口(队列)
Collection的子接口,表示队列FIFO(First In First Out)
常用方法:
- 抛出异常:
- boolean add(E e) //顺序添加一个元素(到达上限后,再添加则会抛出异常)
- E remove() //获得第一个元素并移除(如果队列没有元素时,则抛异常)
- E element() //获得第一个元素但不移除(如果队列没有元素时,则抛异常)
- 返回特殊值:推荐使用
- boolean offer(E e) //顺序添加一个元素 (到达上限后,再添加则会返回false)
- E poll() //获得第一个元素并移除 (如果队列没有元素时,则返回null)
- E peek() //获得第一个元素但不移除 (如果队列没有元素时,则返回null)
3.1 ConcurrentLinkedQueue
线程安全、可高效读写的队列,高并发下性能最好的队列。
- 采用CAS比较交换算法
eg:
public class TestQueue {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Queue<String> queue=new LinkedList<>();
Queue<String> queue=new ConcurrentLinkedQueue<>();
//入队
// queue.offer("aaa");
// queue.offer("bbb");
// queue.offer("ccc");
ExecutorService es = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
es.submit(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
queue.offer(Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
});
}
//出队
es.shutdown();
while(!es.isTerminated());
int count=queue.size();
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
System.out.println(queue.poll());
}
}
}
3.2 BlockingQueue接口(阻塞队列)
Queue的子接口,阻塞的队列,增加了两个线程状态为无限期等待的方法。
方法:
- void put(E e) //将指定元素插入此队列中,如果没有可用空间,则等待。
- E take() //获取并移除此队列头部元素,如果没有可用元素,则等待。
- 可用于解决生产者、消费者问题。
实现类:
- ArrayBlockingQueue:数组结构实现,有界队列。(手工固定上限)
- LinkedBlockingQueue:链表结构实现,有界队列。(默认上限Integer.MAX_VALUE)
eg:
package StageOne.day21.demo02;
import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingQueue;
/**
* @author 胡昊龙
* @version 1.0
* @description: TODO
* @date 2024/1/16 14:32
*/
public class TestBlockingQueue {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建阻塞队列
BlockingQueue<String> queue = new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(6);
//创建线程池
ExecutorService es = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
//提交任务
es.submit(()->{
for (int i = 0; i < 30; i++) {
try {
queue.put("面包"+i);
System.out.println("生产了"+i);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
});
es.submit(()->{
for (int i = 0; i < 30; i++) {
try {
String take = queue.take();
System.out.println("消费了"+take);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
});
es.shutdown();
}
}