什么是Semi-Join半连接
Semi-Join半连接,当外表在内表中找到匹配的记录之后,Semi-Join会返回外表中的记录。但即使在内表中找到多条匹配的记录,外表也只会返回已经存在于外表中的记录。而对于子查询,外表的每个符合条件的元组都要执行一轮子查询,效率比较低下。此时使用半连接操作优化子查询,会减少查询次数,提高查询性能。其主要思路是将子查询上拉到父查询中,这样内表和外表是并列关系,外表的每个符合条件的元组,只需要在内表中找符合条件的元组即可,所以效率会大大提高。
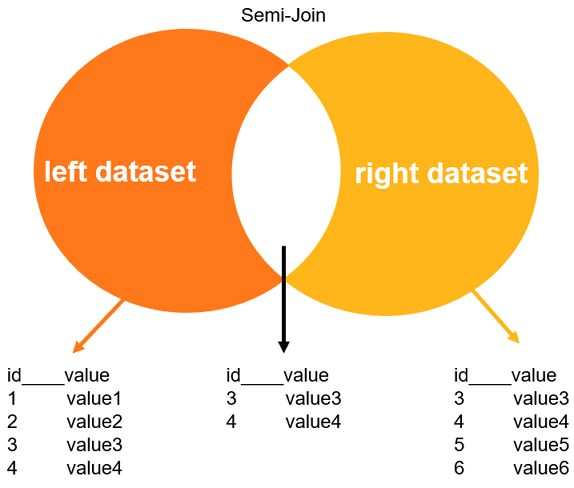
当参与等值JOIN的表达式存在有重复值时, 如果不需要找出该表其他字段的值(也就是仅使用JOIN字段/表达式), 那么JOIN时只需要查每个值的第一条, 然后就可以跳到下一个值. 在数据库中常常被用来优化 in, exists, not exists, = any(), except 等操作(或者逻辑上成立的其他JOIN场景).
还有什么特别的join?PostgreSQL 与关系代数 (Equi-Join , Semi-Join , Anti-Join , Division)
并不是所有数据库都实现了所有场景的semi join, 例如 Oracle中的半连接,MySQL也有半连接
如果未实现, 有什么方法可以模拟semi-join?递归/group by/distinct on/distinct
Semi-Join 例子
准备测试数据
postgres=# create table a (id int, info text, ts timestamp);
CREATE TABLE
postgres=# create table b (like a);
CREATE TABLE
postgres=# insert into a select id, md5(random()::text), now() from generate_series(0,1000000) as t(id);
INSERT 0 1000001
-- b表的100万行记录中b.id只有11个唯一值
postgres=# insert into b select random()*10, md5(random()::text), now() from generate_series(0,1000000) as t(id);
INSERT 0 1000001
postgres=# create index on a (id);
CREATE INDEX
postgres=# create index on b (id);
CREATE INDEX
未优化SQL
select a.* from a where exists (select 1 from b where a.id=b.id);
postgres=# explain analyze select a.* from a where exists (select 1 from b where a.id=b.id);
QUERY PLAN
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Merge Join (cost=18436.17..18436.66 rows=11 width=45) (actual time=226.590..226.598 rows=11 loops=1)
Merge Cond: (a.id = b.id)
-> Index Scan using a_id_idx on a (cost=0.42..27366.04 rows=1000001 width=45) (actual time=0.010..0.013 rows=12 loops=1)
-> Sort (cost=18435.74..18435.77 rows=11 width=4) (actual time=226.576..226.577 rows=11 loops=1)
Sort Key: b.id
Sort Method: quicksort Memory: 25kB
-> HashAggregate (cost=18435.44..18435.55 rows=11 width=4) (actual time=226.568..226.570 rows=11 loops=1)
Group Key: b.id
Batches: 1 Memory Usage: 24kB
-> Index Only Scan using b_id_idx on b (cost=0.42..15935.44 rows=1000001 width=4) (actual time=0.010..77.936 rows=1000001 loops=1)
Heap Fetches: 0
Planning Time: 0.189 ms
Execution Time: 226.630 ms
(13 rows)
以上查询没有使用semi-join, 性能很一般.
由于b表的100万行记录中b.id只有11个唯一值, 可以使用semi-join进行加速.
用法参考: 《用PostgreSQL找回618秒逝去的青春 - 递归收敛优化》
使用递归模拟SEMI-JOIN, 只需要 0.171 ms 既可得出b表 11个值的结果.
with recursive tmp as (
select min(id) as id from b
union all
select (select min(b.id) from b where b.id > tmp.id) from tmp where tmp.id is not null
)
select * from tmp where tmp.id is not null;
id
----
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
(11 rows)
执行计划如下
postgres=# explain analyze with recursive tmp as (
select min(id) as id from b
union all
select (select min(b.id) from b where b.id > tmp.id) from tmp where tmp.id is not null
)
select * from tmp where tmp.id is not null;
QUERY PLAN
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
CTE Scan on tmp (cost=50.07..52.09 rows=100 width=4) (actual time=0.028..0.134 rows=11 loops=1)
Filter: (id IS NOT NULL)
Rows Removed by Filter: 1
CTE tmp
-> Recursive Union (cost=0.44..50.07 rows=101 width=4) (actual time=0.025..0.126 rows=12 loops=1)
-> Result (cost=0.44..0.45 rows=1 width=4) (actual time=0.024..0.025 rows=1 loops=1)
InitPlan 3 (returns $1)
-> Limit (cost=0.42..0.44 rows=1 width=4) (actual time=0.021..0.022 rows=1 loops=1)
-> Index Only Scan using b_id_idx on b b_1 (cost=0.42..18435.44 rows=1000001 width=4) (actual time=0.020..0.020 rows=1 loops=1)
Index Cond: (id IS NOT NULL)
Heap Fetches: 0
-> WorkTable Scan on tmp tmp_1 (cost=0.00..4.76 rows=10 width=4) (actual time=0.007..0.007 rows=1 loops=12)
Filter: (id IS NOT NULL)
Rows Removed by Filter: 0
SubPlan 2
-> Result (cost=0.45..0.46 rows=1 width=4) (actual time=0.007..0.007 rows=1 loops=11)
InitPlan 1 (returns $3)
-> Limit (cost=0.42..0.45 rows=1 width=4) (actual time=0.006..0.006 rows=1 loops=11)
-> Index Only Scan using b_id_idx on b (cost=0.42..6979.51 rows=333334 width=4) (actual time=0.006..0.006 rows=1 loops=11)
Index Cond: ((id IS NOT NULL) AND (id > tmp_1.id))
Heap Fetches: 0
Planning Time: 0.177 ms
Execution Time: 0.171 ms
(23 rows)
使用递归模拟semi-join, SQL改写如下:
select a.* from a where exists (select 1 from b where a.id=b.id);
改写成
select a.* from a where exists (select 1 from
(
with recursive tmp as (
select min(id) as id from b
union all
select (select min(b.id) from b where b.id > tmp.id) from tmp where tmp.id is not null
)
select * from tmp where tmp.id is not null
) b
where a.id=b.id);
改写后速度从226.630 ms 提升到 0.246 ms
postgres=# explain analyze select a.* from a where exists (select 1 from
(
with recursive tmp as (
select min(id) as id from b
union all
select (select min(b.id) from b where b.id > tmp.id) from tmp where tmp.id is not null
)
select * from tmp where tmp.id is not null
) b
where a.id=b.id);
QUERY PLAN
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Nested Loop (cost=53.76..318.49 rows=100 width=45) (actual time=0.154..0.189 rows=11 loops=1)
-> HashAggregate (cost=53.34..54.34 rows=100 width=4) (actual time=0.144..0.149 rows=11 loops=1)
Group Key: tmp.id
Batches: 1 Memory Usage: 24kB
-> CTE Scan on tmp (cost=50.07..52.09 rows=100 width=4) (actual time=0.027..0.139 rows=11 loops=1)
Filter: (id IS NOT NULL)
Rows Removed by Filter: 1
CTE tmp
-> Recursive Union (cost=0.44..50.07 rows=101 width=4) (actual time=0.024..0.130 rows=12 loops=1)
-> Result (cost=0.44..0.45 rows=1 width=4) (actual time=0.023..0.024 rows=1 loops=1)
InitPlan 3 (returns $1)
-> Limit (cost=0.42..0.44 rows=1 width=4) (actual time=0.020..0.021 rows=1 loops=1)
-> Index Only Scan using b_id_idx on b b_1 (cost=0.42..18435.44 rows=1000001 width=4) (actual time=0.019..0.019 rows=1 loops=1)
Index Cond: (id IS NOT NULL)
Heap Fetches: 0
-> WorkTable Scan on tmp tmp_1 (cost=0.00..4.76 rows=10 width=4) (actual time=0.008..0.008 rows=1 loops=12)
Filter: (id IS NOT NULL)
Rows Removed by Filter: 0
SubPlan 2
-> Result (cost=0.45..0.46 rows=1 width=4) (actual time=0.007..0.007 rows=1 loops=11)
InitPlan 1 (returns $3)
-> Limit (cost=0.42..0.45 rows=1 width=4) (actual time=0.006..0.006 rows=1 loops=11)
-> Index Only Scan using b_id_idx on b (cost=0.42..6979.51 rows=333334 width=4) (actual time=0.006..0.006 rows=1 loops=11)
Index Cond: ((id IS NOT NULL) AND (id > tmp_1.id))
Heap Fetches: 0
-> Index Scan using a_id_idx on a (cost=0.42..2.63 rows=1 width=45) (actual time=0.003..0.003 rows=1 loops=11)
Index Cond: (id = tmp.id)
Planning Time: 0.295 ms
Execution Time: 0.246 ms
(29 rows)