文章目录
- 第二章 chrony服务器
- 1.1安装与配置
- 1.2同步网络时间服务器
- 1.3 配置时间服务器
- 1.4 chronyc 命令
- 1.5常见时区
- 课后练习
- 第一题:第一台机器从阿里云同步时间,第二台机器从第一台机器同步时间
- 第二题:第一台服务器使用系统时间作为第二台服务器的时钟源, 第一台服务器层级设置为6
第二章 chrony服务器
Chrony是一个开源自由的网络时间协议 NTP 的客户端和服务器软软件。它能让计算机保持系统时钟与时钟服务器(NTP)同步,因此让你的计算机保持精确的时间,Chrony也可以作为服务端软件为其他计算机提供时间同步服务。
Chrony由两个程序组成,分别是chronyd和chronyc
chronyd是一个后台运行的守护进程,用于调整内核中运行的系统时钟和时钟服务器同步。它确定计算机增减时间的比率,并对此进行补偿。
chronyc提供了一个用户界面,用于监控性能并进行多样化的配置。它可以在chronyd实例控制的计算机上工作,也可以在一台不同的远程计算机上工作
。
NTP 是网络时间协议(Network Time Protocol)的简称,通过 udp 123 端口进行网络时钟同步。
RHEL7中默认使用chrony作为时间服务器,也支持NTP,需要额外安装。
NTP与chrony不能同时存在,只能用其中一个
1.1安装与配置
#yum -y install chrony
#systemctl enable chronyd
#systemctl start chronyd
Chrony的配置文件是/etc/chrony.conf
# 使用 pool.ntp.org 项目中的公共服务器。以server开,理论上想添加多少时间服务器都可以。
server 0.centos.pool.ntp.org iburst
server 1.centos.pool.ntp.org iburst
server 2.centos.pool.ntp.org iburst
server 3.centos.pool.ntp.org iburst
# 根据实际时间计算出服务器增减时间的比率,然后记录到一个文件中,在系统重启后为系统做出最佳时间补偿调整。
driftfile /var/lib/chrony/drift
# 如果系统时钟的偏移量大于1秒,则允许系统时钟在前三次更新中步进。
# Allow the system clock to be stepped in the first three updates if its offset is larger than 1 second.
makestep 1.0 3
# 启用实时时钟(RTC)的内核同步。
# Enable kernel synchronization of the real-time clock (RTC).
rtcsync
# 通过使用 hwtimestamp 指令启用硬件时间戳
# Enable hardware timestamping on all interfaces that support it.
#hwtimestamp *
# Increase the minimum number of selectable sources required to adjust the system clock.
#minsources 2
# 指定 NTP 客户端地址,以允许或拒绝连接到扮演时钟服务器的机器
# Allow NTP client access from local network.
#allow 192.168.0.0/16
# Serve time even if not synchronized to a time source.
#local stratum 10
# 指定包含 NTP 身份验证密钥的文件。
# Specify file containing keys for NTP authentication.
#keyfile /etc/chrony.keys
# 指定日志文件的目录。
# Specify directory for log files.
logdir /var/log/chrony
# 选择日志文件要记录的信息。
# Select which information is logged.
#log measurements statistics tracking
1.2同步网络时间服务器
授时中心
210.72.145.44 国家授时中心
ntp.aliyun.com 阿里云
s1a.time.edu.cn 北京邮电大学
s1b.time.edu.cn 清华大学
s1c.time.edu.cn 北京大学
s1d.time.edu.cn 东南大学
s1e.time.edu.cn 清华大学
s2a.time.edu.cn 清华大学
s2b.time.edu.cn 清华大学
s2c.time.edu.cn 北京邮电大学
s2d.time.edu.cn 西南地区网络中心
s2e.time.edu.cn 西北地区网络中心
s2f.time.edu.cn 东北地区网络中心
s2g.time.edu.cn 华东南地区网络中心
s2h.time.edu.cn 四川大学网络管理中心
s2j.time.edu.cn 大连理工大学网络中心
s2k.time.edu.cn CERNET桂林主节点
s2m.time.edu.cn 北京大学
ntp.sjtu.edu.cn 202.120.2.101 上海交通大学
chrony.conf 修改两处
# Use public servers from the pool.ntp.org project.
# Please consider joining the pool (http://www.pool.ntp.org/join.html).
server s1a.time.edu.cn iburst
server ntp.aliyun.com iburst
# Allow NTP client access from local network.
设置开机启动,重启服务
systemctl enable chronyd
systemctl restart chronyd
# 查看时间同步状态
timedatectl status
# 开启网络时间同步
timedatectl set-ntp true
1.3 配置时间服务器
chrony.conf 修改两处
allow 192.168.143.0/24
local stratum 10
设置开机启动,重启服务
systemctl enable chronyd
systemctl restart chronyd
客户端主机查看时间同步状态
vim /etc/chrony.conf
server 192.168.143.111
systemctl restart chronyd
#timedatectl status
开启网络时间同步
timedatectl set-ntp true
1.4 chronyc 命令
查看 ntp_servers
chronyc sources -v
查看 ntp_servers 状态
chronyc sourcestats -v
查看 ntp_servers 是否在线
chronyc activity -v
查看 ntp 详细信息
chronyc tracking -v
强制同步下系统时钟
chronyc -a makestep
1.5常见时区
(1)UTC 整个地球分为二十四时区,每个时区都有自己的本地时间。在国际无线电通信场合,为了统一起见,使用一个统一的时间,称为通用协调时(UTC, Universal Time Coordinated)。
(2)GMT 格林威治标准时间 (Greenwich Mean Time)指位于英国伦敦郊区的×××格林尼治天文台的标准时间,因为本初子午线被定义在通过那里的经线。(UTC与GMT时间基本相同,本文中不做区分)
(3)CST 中国标准时间 (China Standard Time)
GMT + 8 = UTC + 8 = CST
(4)DST夏令时(Daylight Saving Time) 指在夏天太阳升起的比较早时,将时间拨快一小时,以提早日光的使用。(中国不使用)
chronyc sources 输出结果解析
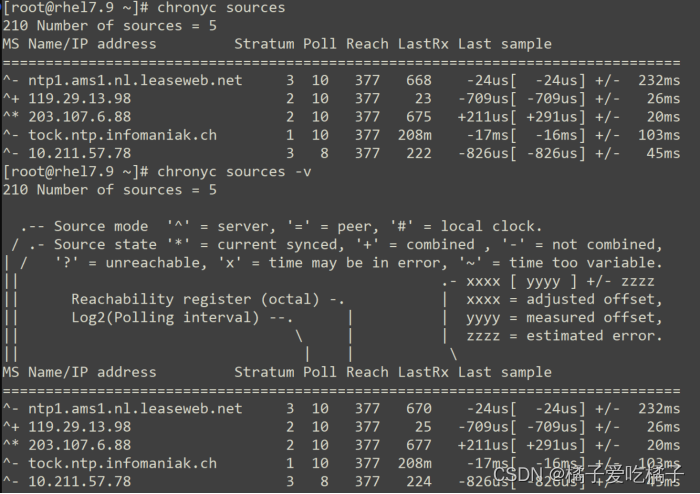
M
这表示信号源的模式。^表示服务器,=表示对等方,#表示本地连接的参考时钟。
S
此列指示源的状态。
• * 表示chronyd当前同步到的源。
• + 表示可接受的信号源,与选定的信号源组合在一起。
• - 表示被合并算法排除的可接受源。
• ? 指示已失去连接性或其数据包未通过所有测试的源。它也显示在启动时,直到从中至少收集了3个样本为止。
• x 表示chronyd认为是虚假行情的时钟(即,其时间与大多数其他来源不一致)。
• 〜 表示时间似乎具有太多可变性的来源。
Name/IP address
这显示了源的名称或IP地址,或参考时钟的参考ID。
Stratum(偏移量)
这显示了来源的层,如其最近收到的样本中所报告的那样。层1表示一台具有本地连接的参考时钟的计算机。与第1层计算机同步的计算机位于第2层。与第2层计算机同步的计算机位于第3层,依此类推。
Poll
这显示轮询源的速率,以秒为单位的时间间隔的以2为底的对数。因此,值为6表示每64秒进行一次测量。chronyd会根据当前情况自动更改轮询速率。
Reach
这显示了源的可达性寄存器以八进制数字打印。寄存器有8位,并在每个从源接收或丢失的数据包上更新。值377表示从最后八次传输中收到了对所有用户的有效答复。
LastRx
此列显示多长时间前从来源接收到了最后一个好的样本(在下一列中显示)。未通过某些测试的测量将被忽略。通常以秒为单位。字母m,h,d或y表示分钟,小时,天或年。
Last sample
此列显示上次测量时本地时钟与源之间的偏移。方括号中的数字表示实际测得的偏移量。可以用ns(表示纳秒),us (表示微秒),ms(表示毫秒)或s(表示秒)作为后缀。方括号左侧的数字表示原始测量值,已调整为允许此后施加于本地时钟的任何摆度。
+/-指示器后面的数字表示测量中的误差范围。正偏移表示本地时钟位于源时钟之前。
[root@rhel7.9 ~]# chronyc add server 10.210.57.78
200 OK
[root@rhel7.9 ~]# chronyc sources -v
210 Number of sources = 5
.-- Source mode '^' = server, '=' = peer, '#' = local clock.
/ .- Source state '*' = current synced, '+' = combined , '-' = not combined,
| / '?' = unreachable, 'x' = time may be in error, '~' = time too variable.
|| .- xxxx [ yyyy ] +/- zzzz
|| Reachability register (octal) -. | xxxx = adjusted offset,
|| Log2(Polling interval) --. | | yyyy = measured offset,
|| \ | | zzzz = estimated error.
|| | | \
MS Name/IP address Stratum Poll Reach LastRx Last sample
===============================================================================
^- ntp1.ams1.nl.leaseweb.net 3 10 377 651 -4572us[-4572us] +/- 227ms
^- 119.29.13.98 2 9 377 17 +2553us[+2553us] +/- 26ms
^* 203.107.6.88 2 10 377 656 -1432us[-1106us] +/- 19ms
^- tock.ntp.infomaniak.ch 1 9 377 52m -16ms[ -16ms] +/- 103ms
^? 10.211.57.78 3 6 1 10 +1089us[+1089us] +/- 34ms
[root@rhel7.9 ~]# chronyc sources -v
210 Number of sources = 5
.-- Source mode '^' = server, '=' = peer, '#' = local clock.
/ .- Source state '*' = current synced, '+' = combined , '-' = not combined,
| / '?' = unreachable, 'x' = time may be in error, '~' = time too variable.
|| .- xxxx [ yyyy ] +/- zzzz
|| Reachability register (octal) -. | xxxx = adjusted offset,
|| Log2(Polling interval) --. | | yyyy = measured offset,
|| \ | | zzzz = estimated error.
|| | | \
MS Name/IP address Stratum Poll Reach LastRx Last sample
===============================================================================
^- ntp1.ams1.nl.leaseweb.net 3 10 377 843 -4572us[-4572us] +/- 227ms
^- 119.29.13.98 2 9 377 208 +2553us[+2553us] +/- 26ms
^* 203.107.6.88 2 10 377 847 -1432us[-1106us] +/- 19ms
^- tock.ntp.infomaniak.ch 1 9 377 56m -16ms[ -16ms] +/- 103ms
^- 10.211.57.78 3 6 17 6 +1225us[+1225us] +/- 37ms
上面示例中刚加入的NTP部分显示是 ?即不可达的,过了两分钟再查看状态变成了 -
课后练习
第一题:第一台机器从阿里云同步时间,第二台机器从第一台机器同步时间
第一台机子:
step1、vim /etc/chrony.conf 编辑chrony配置信息,在里面插入
server ntp.aliyun.com iburst,并在allow里面设置允许的主机IP---allow 192.168.231.134/16
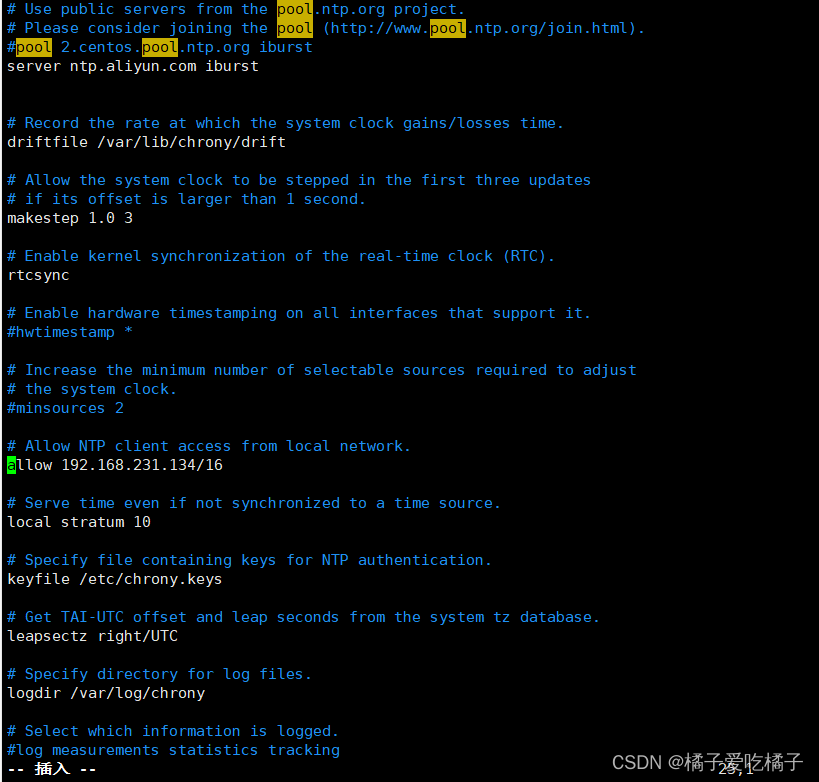
step2、systemctl restart chronyd.service 重启chrony服务器
在第一台服务器上ping ntp. aliyun.com,看能不能ping通,如果能那么就没得啥问题
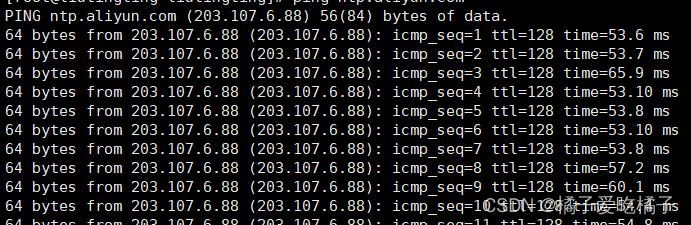
step3、timedatectl set-ntp true:开启网络时间同步
step4、timedatectl:查看同步时钟状态
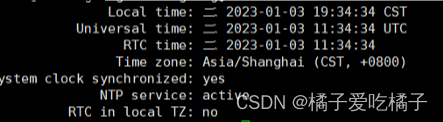
Step5:,chronyc sources查看时钟源

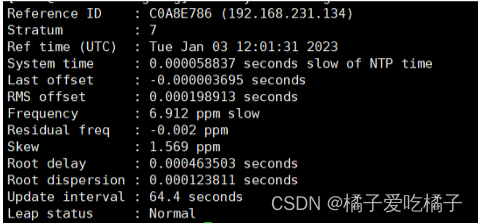
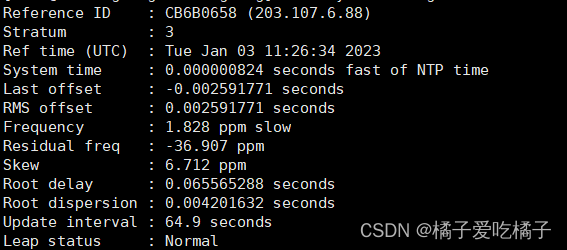
Step6:使用 chrony tracking,查看详细信息,可以看出我们这里已经成功使用阿里云同步时间了
第二台机器:
step1、vim /etc/chrony.conf 编辑chrony配置信息,在里面插入
server 192.168.231.134 iburst(因为是同步第一台机子信息),并在allow里面设置允许的主机IP---allow 192.168.231.134/16
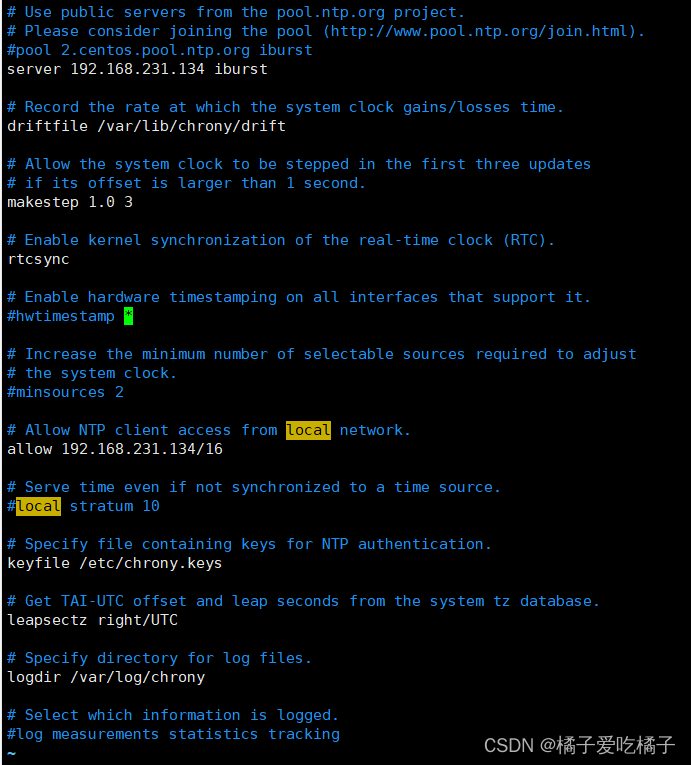
step2、systemctl restart chronyd.service:重启服务器
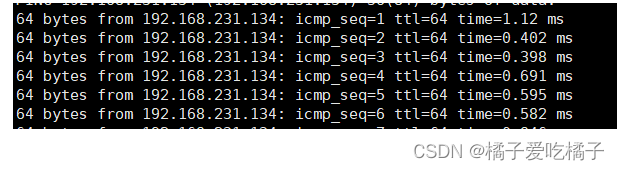
step3、ping 192.168.231.134:检测刚刚配置是否成功
step4、查看timedatectl状态:timedatectl status ,看是否同步成功
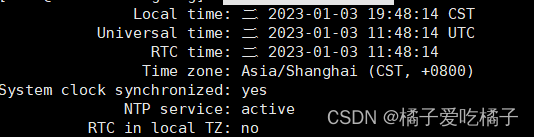
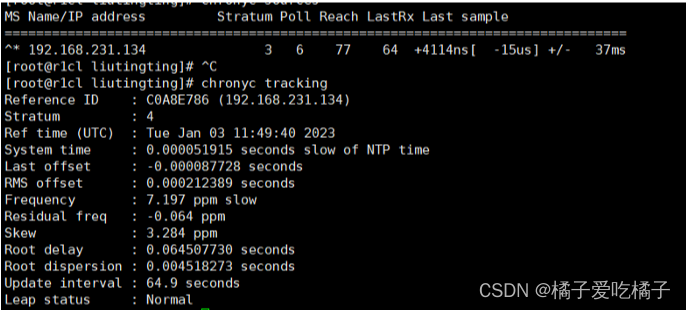
step5、chronyc sources查看时钟源

step6、chrony tracking,查看详细信息,这里我们可以看出stratum的层级由2变成3了,说明同步成功了
第二题:第一台服务器使用系统时间作为第二台服务器的时钟源, 第一台服务器层级设置为6
step1、vim /etc/chrony.conf 编辑chrony配置信息,在里面插入
server 192.168.231.134 iburst(因为是同步第一台机子信息),并在将local stratum改为6
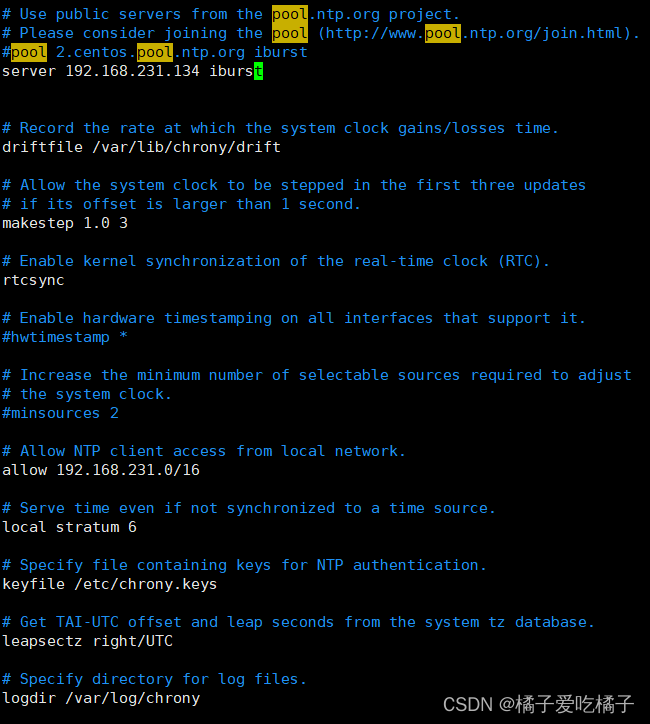
systemctl restart chronyd.service :重启服务
第二台机子进行查看
chronyc tracking:查看详细信息,这个的层级数由6变成7,说明第一台机子配置成功