目录
前言
一、CoapClient对象
1、类定义
2、Client方法调用
二、发送请求
1、构建请求
2、发起请求
3、接收响应
总结
前言
在之前的博客中物联网协议Coap之Californium CoapServer解析,文中简单介绍了CoapServer的实现。在物联网开发环境中,除了Server端需要定义,很多的开发场景是在客户端的开发,这涉及设备端的交互,比如传感器的数据采集,需要通过Client的put方法进行采集数据的提交,同时通过get方法获取服务器端的指令,然后在Client端进行采集。
本次我们简单来看看CoapClient的具体实现,博文将继续采用面向对象分析的方法,结合类图、实际代码、时序图来讲讲解CoapClient类,方便了解和掌握其相关的配置,同时掌握其运行原理。在实际的终端开发中有的放矢。行文仓促,定有不当之处,欢迎各位读者批评指正,再此感谢。
一、CoapClient对象
在Coap的世界中,并不是像http协议一样,只要是浏览器就能发http请求,Coap需要实现对应的CoapClient,以此来跟Server建立通讯,实现数数据的提交,服务的交互。
1、类定义
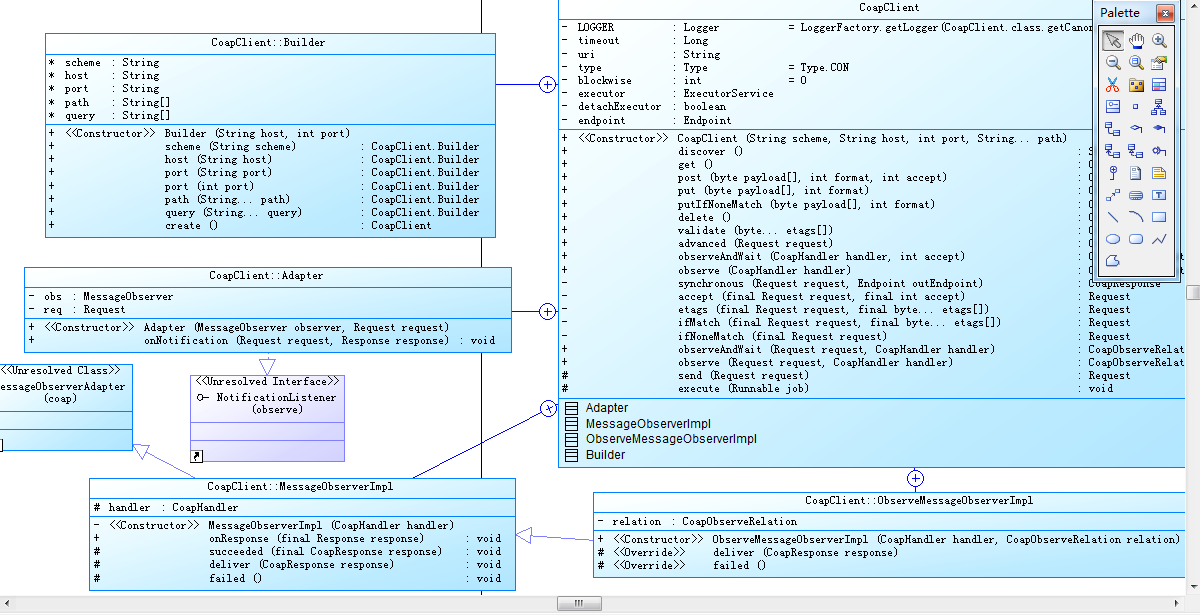
在CoapClient的构造方法中,有三种构造的方式:
/**
* Constructs a new CoapClient that sends requests to the specified URI.
*
* @param uri the uri
*/
public CoapClient(String uri) {
this.uri = uri;
}
/**
* Constructs a new CoapClient that sends request to the specified URI.
*
* @param uri the uri
*/
public CoapClient(URI uri) {
this(uri.toString());
}
/**
* Constructs a new CoapClient with the specified scheme, host, port and
* path as URI.
*
* @param scheme the scheme
* @param host the host
* @param port the port
* @param path the path
*/
public CoapClient(String scheme, String host, int port, String... path) {
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder().append(scheme).append("://").append(host).append(":").append(port);
for (String element : path) {
builder.append("/").append(element);
}
this.uri = builder.toString();
}2、Client方法调用
在CoapClient中,定义了包括get、put、delete、post等方法的定义,在这里只是进行入口函数的编写。下节将重点讲解,在CoapClient中如何进行相应请求的发送。
// Asynchronous GET
/**
* Sends a GET request and invokes the specified handler when a response
* arrives.
*
* @param handler the Response handler
*/
public void get(CoapHandler handler) {
asynchronous(newGet().setURI(uri), handler);
}
/**
* Sends aGET request with the specified Accept option and invokes the
* handler when a response arrives.
*
* @param handler the Response handler
* @param accept the Accept option
*/
public void get(CoapHandler handler, int accept) {
asynchronous(accept(newGet().setURI(uri), accept), handler);
}
// Synchronous POST
/**
* Sends a POST request with the specified payload, the specified content
* format and accept and invokes the specified handler when a response
* arrives.
*
* @param handler the Response handler
* @param payload the payload
* @param format the Content-Format
* @param accept the Accept option
*/
public void post(CoapHandler handler, byte[] payload, int format, int accept) {
asynchronous(accept(format(newPost().setURI(uri).setPayload(payload), format), accept), handler);
}
/**
* Sends a PUT request with the specified payload and the specified content
* format and invokes the specified handler when a response arrives.
*
* @param handler the Response handler
* @param payload the payload
* @param format the Content-Format
*/
public void put(CoapHandler handler, byte[] payload, int format) {
asynchronous(format(newPut().setURI(uri).setPayload(payload), format), handler);
}
/**
* Sends a DELETE request and invokes the specified handler when a response
* arrives.
*
* @param handler the response handler
*/
public void delete(CoapHandler handler) {
asynchronous(newDelete().setURI(uri), handler);
}二、发送请求
在构建好CoapClient对象后,就可以往目标服务器提交请求并获取响应结果了。这里详细讲解在Coap中如何进行请求的发送。下面是之前创建CoapClient以及发送get请求的关键代码:
URI uri = null;
//coap://127.0.0.1:5683/core/time?type=1
uri = new URI("coap://localhost:5683/hello"); // 创建一个资源请求hello资源,注意默认端口为5683
//uri = new URI("coap://127.0.0.1:5683/core/time?type=1");
CoapClient client = new CoapClient(uri);
CoapResponse response = client.get();1、构建请求
通过代码跟踪和时序图,以发送get请求为例,来看看底层究竟是怎么运行的。

第一步,在调用get()方法时,进入以下函数:

第二步,进入核心的请求函数

默认情况下,我们没有给请求设置超时时间,因此它会根据配置文件加载默认的超时时间。然后根据请求方式和携带的参数,都封装到request对象中。
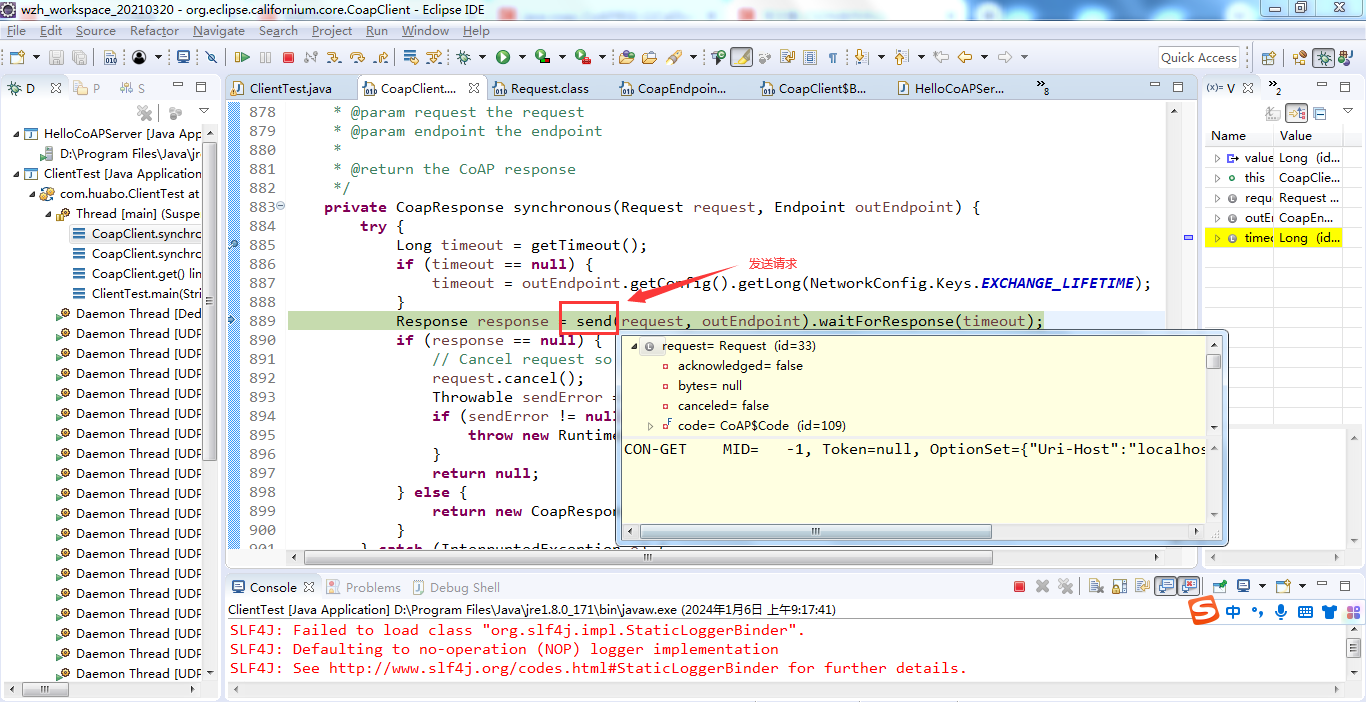
这里可以看到get请求携带的参数如下:
CON-GET MID= -1, Token=null, OptionSet={"Uri-Host":"localhost", "Uri-Path":"hello"}, no payload2、发起请求

在这里,通过endPoint对象来进行发送。org.eclipse.californium.core.network.CoapEndpoint中的sendRequest方法。最终的请求参数如下:
@Override
public void sendRequest(final Request request) {
// create context, if not already set
request.prepareDestinationContext();
// always use endpoint executor
runInProtocolStage(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
coapstack.sendRequest(request);
}
});
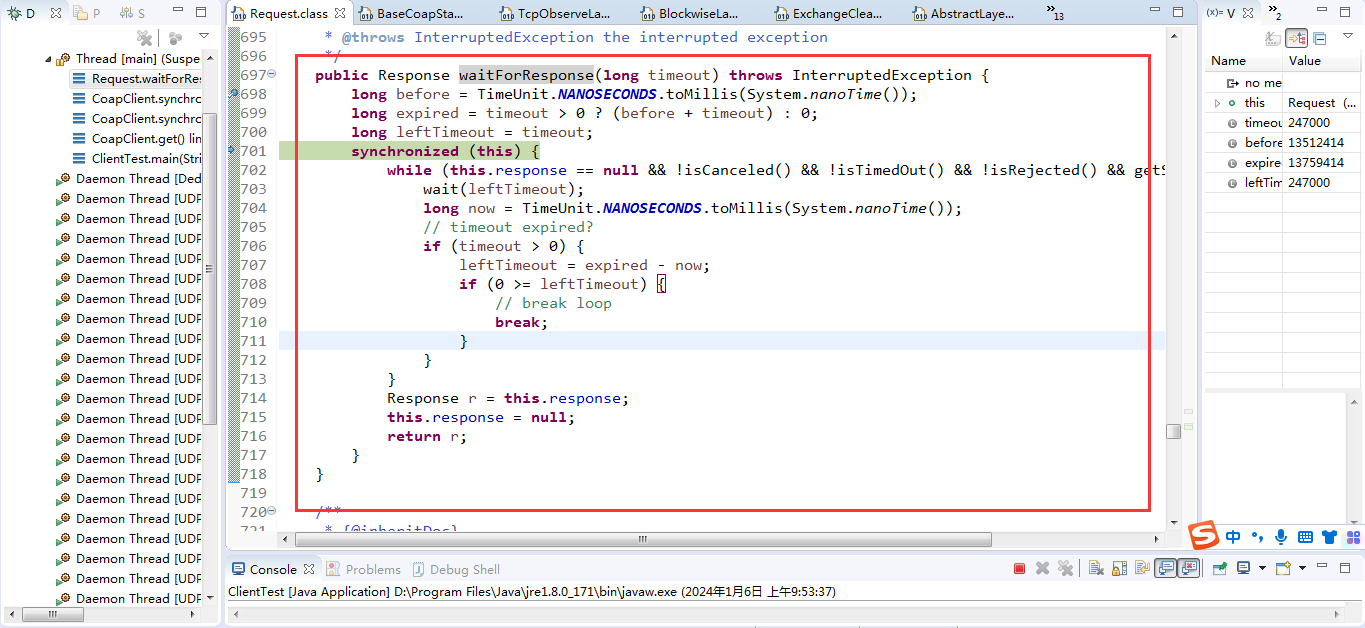
}可以看到,在发送请求的时候,是开启了一个线程池来进行请求发送。

在org.eclipse.californium.core.network.stack.BaseCoapStack

3、接收响应
ACK-2.05 MID=20132, Token=[643cec40ed6f22c6], OptionSet={"Content-Format":"text/plain"}, "Hello CoAP!This is from ".. 40 bytes可以看到,通过response对象就可以正常获取从服务端返回的响应信息。
总结
以上就是本文的主要内容,本文将继续采用面向对象分析的方法,结合类图、实际代码、时序图来讲讲解CoapClient类,方便了解和掌握其相关的配置,同时掌握其运行原理。在实际的终端开发中有的放矢。





![2024年阿里云、腾讯云、华为云、LightNode、硅云服务器如何选?怎么买最划算?[最新价格表]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/6b3427a0bc6aaa7006f6a808f6b04dcf.png)