https://machinelearningmastery.com/develop-word-embedding-model-predicting-movie-review-sentiment/
https://machinelearningmastery.com/prepare-movie-review-data-sentiment-analysis/
本教程分为 5 个部分;他们是:
- 电影评论数据集
- 数据准备
- 训练嵌入层
- 训练 word2vec 嵌入
- 使用预训练嵌入
数据准备
1.将数据分为训练集和测试集。
2.加载和清理数据以删除标点符号和数字。
3.定义首选单词的词汇表。
在空白处拆分标记。
删除单词中的所有标点符号。
删除所有不完全由字母字符组成的单词。
删除所有已知停用词的单词。
删除长度为 <= 1 个字符的所有单词。
我们可以使用字符串 translate() 函数从标记中过滤掉标点符号。
我们可以通过对每个标记使用 isalpha() 检查来删除只是标点符号或包含数字的标记。
我们可以使用使用 NLTK 加载的列表删除英语停用词。
我们可以通过检查短标记的长度来过滤掉它们。
from string import punctuation
from os import listdir
from collections import Counter
from nltk.corpus import stopwords
# load doc into memory
def load_doc(filename):
# open the file as read only
file = open(filename, 'r')
# read all text
text = file.read()
# close the file
file.close()
return text
# turn a doc into clean tokens
def clean_doc(doc):
# split into tokens by white space
tokens = doc.split()
# remove punctuation from each token
table = str.maketrans('', '', punctuation)
tokens = [w.translate(table) for w in tokens]
# remove remaining tokens that are not alphabetic
tokens = [word for word in tokens if word.isalpha()]
# filter out stop words
stop_words = set(stopwords.words('english'))
tokens = [w for w in tokens if not w in stop_words]
# filter out short tokens
tokens = [word for word in tokens if len(word) > 1]
return tokens
# load doc and add to vocab
def add_doc_to_vocab(filename, vocab):
# load doc
doc = load_doc(filename)
# clean doc
tokens = clean_doc(doc)
# update counts
vocab.update(tokens)
# load all docs in a directory
def process_docs(directory, vocab, is_trian):
# walk through all files in the folder
for filename in listdir(directory):
# skip any reviews in the test set
if is_trian and filename.startswith('cv9'):
continue
if not is_trian and not filename.startswith('cv9'):
continue
# create the full path of the file to open
path = directory + '/' + filename
# add doc to vocab
add_doc_to_vocab(path, vocab)
# define vocab
vocab = Counter()
# add all docs to vocab
process_docs('txt_sentoken/neg', vocab, True)
process_docs('txt_sentoken/pos', vocab, True)
# print the size of the vocab
print(len(vocab))
# print the top words in the vocab
print(vocab.most_common(50))
使用 Counter() 进行统计和去重
保存
# save list to file
def save_list(lines, filename):
# convert lines to a single blob of text
data = '\n'.join(lines)
# open file
file = open(filename, 'w')
# write text
file.write(data)
# close file
file.close()
# save tokens to a vocabulary file
save_list(tokens, 'vocab.txt')
训练嵌入层
https://machinelearningmastery.com/what-are-word-embeddings/
from string import punctuation
from os import listdir
from numpy import array
from keras.preprocessing.text import Tokenizer
from keras.preprocessing.sequence import pad_sequences
from keras.models import Sequential
from keras.layers import Dense
from keras.layers import Flatten
from keras.layers import Embedding
from keras.layers.convolutional import Conv1D
from keras.layers.convolutional import MaxPooling1D
# load doc into memory
def load_doc(filename):
# open the file as read only
file = open(filename, 'r')
# read all text
text = file.read()
# close the file
file.close()
return text
# turn a doc into clean tokens
def clean_doc(doc, vocab):
# split into tokens by white space
tokens = doc.split()
# remove punctuation from each token
table = str.maketrans('', '', punctuation)
tokens = [w.translate(table) for w in tokens]
# filter out tokens not in vocab
tokens = [w for w in tokens if w in vocab]
tokens = ' '.join(tokens)
return tokens
# load all docs in a directory
def process_docs(directory, vocab, is_trian):
documents = list()
# walk through all files in the folder
for filename in listdir(directory):
# skip any reviews in the test set
if is_trian and filename.startswith('cv9'):
continue
if not is_trian and not filename.startswith('cv9'):
continue
# create the full path of the file to open
path = directory + '/' + filename
# load the doc
doc = load_doc(path)
# clean doc
tokens = clean_doc(doc, vocab)
# add to list
documents.append(tokens)
return documents
# load the vocabulary
vocab_filename = 'vocab.txt'
vocab = load_doc(vocab_filename)
vocab = vocab.split()
vocab = set(vocab)
# load all training reviews
positive_docs = process_docs('txt_sentoken/pos', vocab, True)
negative_docs = process_docs('txt_sentoken/neg', vocab, True)
train_docs = negative_docs + positive_docs
# create the tokenizer
tokenizer = Tokenizer()
# fit the tokenizer on the documents
tokenizer.fit_on_texts(train_docs)
# sequence encode
encoded_docs = tokenizer.texts_to_sequences(train_docs)
# pad sequences
max_length = max([len(s.split()) for s in train_docs])
Xtrain = pad_sequences(encoded_docs, maxlen=max_length, padding='post')
# define training labels
ytrain = array([0 for _ in range(900)] + [1 for _ in range(900)])
# load all test reviews
positive_docs = process_docs('txt_sentoken/pos', vocab, False)
negative_docs = process_docs('txt_sentoken/neg', vocab, False)
test_docs = negative_docs + positive_docs
# sequence encode
encoded_docs = tokenizer.texts_to_sequences(test_docs)
# pad sequences
Xtest = pad_sequences(encoded_docs, maxlen=max_length, padding='post')
# define test labels
ytest = array([0 for _ in range(100)] + [1 for _ in range(100)])
# define vocabulary size (largest integer value)
vocab_size = len(tokenizer.word_index) + 1
# define model
model = Sequential()
model.add(Embedding(vocab_size, 100, input_length=max_length))
model.add(Conv1D(filters=32, kernel_size=8, activation='relu'))
model.add(MaxPooling1D(pool_size=2))
model.add(Flatten())
model.add(Dense(10, activation='relu'))
model.add(Dense(1, activation='sigmoid'))
print(model.summary())
# compile network
model.compile(loss='binary_crossentropy', optimizer='adam', metrics=['accuracy'])
# fit network
model.fit(Xtrain, ytrain, epochs=10, verbose=2)
# evaluate
loss, acc = model.evaluate(Xtest, ytest, verbose=0)
print('Test Accuracy: %f' % (acc*100))
训练 word2vec 嵌入
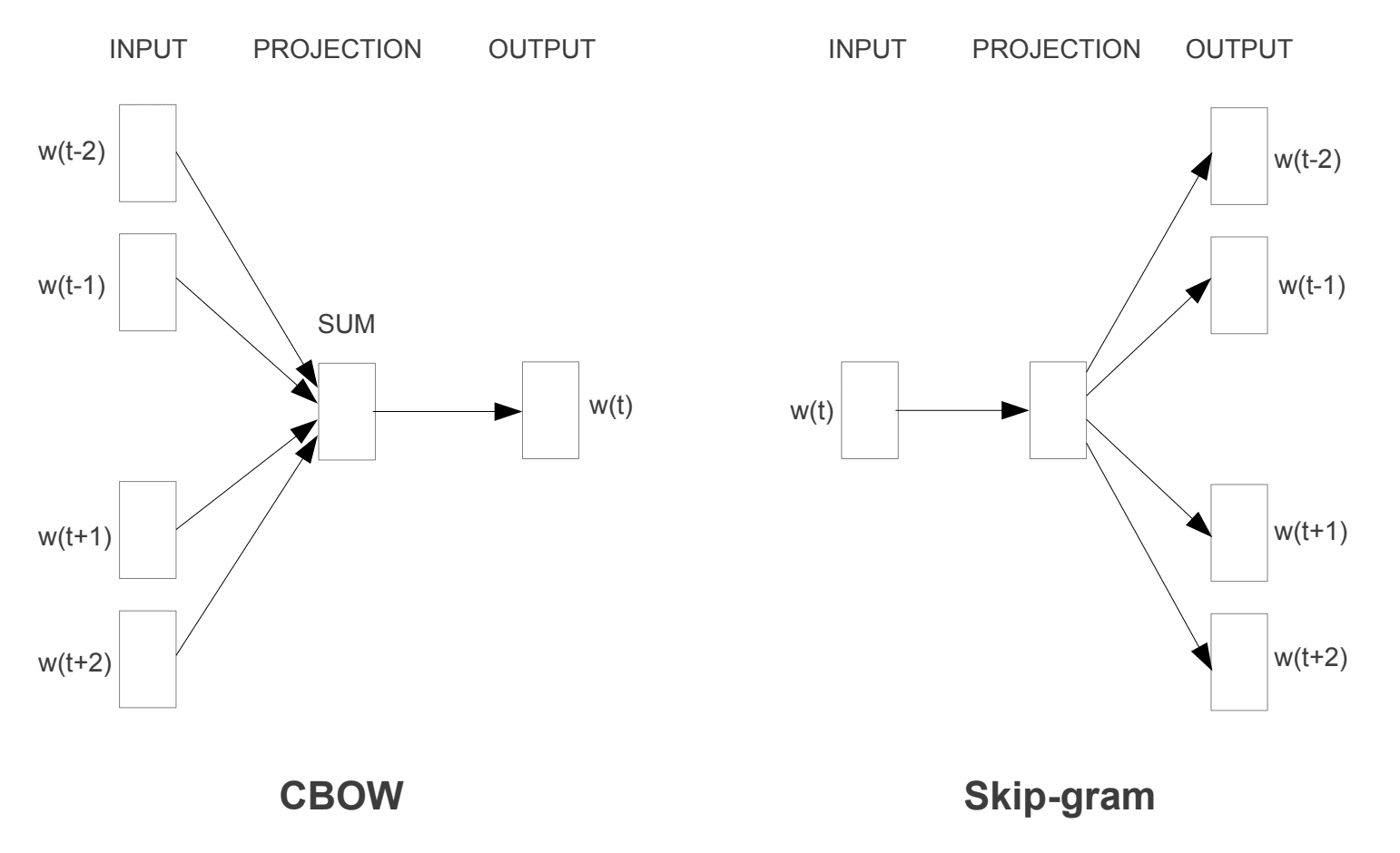
word2vec 算法逐句处理文档。这意味着我们将在清理过程中保留基于句子的结构。
from string import punctuation
from os import listdir
from gensim.models import Word2Vec
# load doc into memory
def load_doc(filename):
# open the file as read only
file = open(filename, 'r')
# read all text
text = file.read()
# close the file
file.close()
return text
# turn a doc into clean tokens
def doc_to_clean_lines(doc, vocab):
clean_lines = list()
lines = doc.splitlines()
for line in lines:
# split into tokens by white space
tokens = line.split()
# remove punctuation from each token
table = str.maketrans('', '', punctuation)
tokens = [w.translate(table) for w in tokens]
# filter out tokens not in vocab
tokens = [w for w in tokens if w in vocab]
clean_lines.append(tokens)
return clean_lines
# load all docs in a directory
def process_docs(directory, vocab, is_trian):
lines = list()
# walk through all files in the folder
for filename in listdir(directory):
# skip any reviews in the test set
if is_trian and filename.startswith('cv9'):
continue
if not is_trian and not filename.startswith('cv9'):
continue
# create the full path of the file to open
path = directory + '/' + filename
# load and clean the doc
doc = load_doc(path)
doc_lines = doc_to_clean_lines(doc, vocab)
# add lines to list
lines += doc_lines
return lines
# load the vocabulary
vocab_filename = 'vocab.txt'
vocab = load_doc(vocab_filename)
vocab = vocab.split()
vocab = set(vocab)
# load training data
positive_docs = process_docs('txt_sentoken/pos', vocab, True)
negative_docs = process_docs('txt_sentoken/neg', vocab, True)
sentences = negative_docs + positive_docs
print('Total training sentences: %d' % len(sentences))
# train word2vec model
model = Word2Vec(sentences, size=100, window=5, workers=8, min_count=1)
# summarize vocabulary size in model
words = list(model.wv.vocab)
print('Vocabulary size: %d' % len(words))
# save model in ASCII (word2vec) format
filename = 'embedding_word2vec.txt'
model.wv.save_word2vec_format(filename, binary=False)
from string import punctuation
from os import listdir
from numpy import array
from numpy import asarray
from numpy import zeros
from keras.preprocessing.text import Tokenizer
from keras.preprocessing.sequence import pad_sequences
from keras.models import Sequential
from keras.layers import Dense
from keras.layers import Flatten
from keras.layers import Embedding
from keras.layers.convolutional import Conv1D
from keras.layers.convolutional import MaxPooling1D
# load doc into memory
def load_doc(filename):
# open the file as read only
file = open(filename, 'r')
# read all text
text = file.read()
# close the file
file.close()
return text
# turn a doc into clean tokens
def clean_doc(doc, vocab):
# split into tokens by white space
tokens = doc.split()
# remove punctuation from each token
table = str.maketrans('', '', punctuation)
tokens = [w.translate(table) for w in tokens]
# filter out tokens not in vocab
tokens = [w for w in tokens if w in vocab]
tokens = ' '.join(tokens)
return tokens
# load all docs in a directory
def process_docs(directory, vocab, is_trian):
documents = list()
# walk through all files in the folder
for filename in listdir(directory):
# skip any reviews in the test set
if is_trian and filename.startswith('cv9'):
continue
if not is_trian and not filename.startswith('cv9'):
continue
# create the full path of the file to open
path = directory + '/' + filename
# load the doc
doc = load_doc(path)
# clean doc
tokens = clean_doc(doc, vocab)
# add to list
documents.append(tokens)
return documents
# load embedding as a dict
def load_embedding(filename):
# load embedding into memory, skip first line
file = open(filename,'r')
lines = file.readlines()[1:]
file.close()
# create a map of words to vectors
embedding = dict()
for line in lines:
parts = line.split()
# key is string word, value is numpy array for vector
embedding[parts[0]] = asarray(parts[1:], dtype='float32')
return embedding
# create a weight matrix for the Embedding layer from a loaded embedding
def get_weight_matrix(embedding, vocab):
# total vocabulary size plus 0 for unknown words
vocab_size = len(vocab) + 1
# define weight matrix dimensions with all 0
weight_matrix = zeros((vocab_size, 100))
# step vocab, store vectors using the Tokenizer's integer mapping
for word, i in vocab.items():
weight_matrix[i] = embedding.get(word)
return weight_matrix
# load the vocabulary
vocab_filename = 'vocab.txt'
vocab = load_doc(vocab_filename)
vocab = vocab.split()
vocab = set(vocab)
# load all training reviews
positive_docs = process_docs('txt_sentoken/pos', vocab, True)
negative_docs = process_docs('txt_sentoken/neg', vocab, True)
train_docs = negative_docs + positive_docs
# create the tokenizer
tokenizer = Tokenizer()
# fit the tokenizer on the documents
tokenizer.fit_on_texts(train_docs)
# sequence encode
encoded_docs = tokenizer.texts_to_sequences(train_docs)
# pad sequences
max_length = max([len(s.split()) for s in train_docs])
Xtrain = pad_sequences(encoded_docs, maxlen=max_length, padding='post')
# define training labels
ytrain = array([0 for _ in range(900)] + [1 for _ in range(900)])
# load all test reviews
positive_docs = process_docs('txt_sentoken/pos', vocab, False)
negative_docs = process_docs('txt_sentoken/neg', vocab, False)
test_docs = negative_docs + positive_docs
# sequence encode
encoded_docs = tokenizer.texts_to_sequences(test_docs)
# pad sequences
Xtest = pad_sequences(encoded_docs, maxlen=max_length, padding='post')
# define test labels
ytest = array([0 for _ in range(100)] + [1 for _ in range(100)])
# define vocabulary size (largest integer value)
vocab_size = len(tokenizer.word_index) + 1
# load embedding from file
raw_embedding = load_embedding('embedding_word2vec.txt')
# get vectors in the right order
embedding_vectors = get_weight_matrix(raw_embedding, tokenizer.word_index)
# create the embedding layer
embedding_layer = Embedding(vocab_size, 100, weights=[embedding_vectors], input_length=max_length, trainable=False)
# define model
model = Sequential()
model.add(embedding_layer)
model.add(Conv1D(filters=128, kernel_size=5, activation='relu'))
model.add(MaxPooling1D(pool_size=2))
model.add(Flatten())
model.add(Dense(1, activation='sigmoid'))
print(model.summary())
# compile network
model.compile(loss='binary_crossentropy', optimizer='adam', metrics=['accuracy'])
# fit network
model.fit(Xtrain, ytrain, epochs=10, verbose=2)
# evaluate
loss, acc = model.evaluate(Xtest, ytest, verbose=0)
print('Test Accuracy: %f' % (acc*100))
预训练嵌入
from string import punctuation
from os import listdir
from numpy import array
from numpy import asarray
from numpy import zeros
from keras.preprocessing.text import Tokenizer
from keras.preprocessing.sequence import pad_sequences
from keras.models import Sequential
from keras.layers import Dense
from keras.layers import Flatten
from keras.layers import Embedding
from keras.layers.convolutional import Conv1D
from keras.layers.convolutional import MaxPooling1D
# load doc into memory
def load_doc(filename):
# open the file as read only
file = open(filename, 'r')
# read all text
text = file.read()
# close the file
file.close()
return text
# turn a doc into clean tokens
def clean_doc(doc, vocab):
# split into tokens by white space
tokens = doc.split()
# remove punctuation from each token
table = str.maketrans('', '', punctuation)
tokens = [w.translate(table) for w in tokens]
# filter out tokens not in vocab
tokens = [w for w in tokens if w in vocab]
tokens = ' '.join(tokens)
return tokens
# load all docs in a directory
def process_docs(directory, vocab, is_trian):
documents = list()
# walk through all files in the folder
for filename in listdir(directory):
# skip any reviews in the test set
if is_trian and filename.startswith('cv9'):
continue
if not is_trian and not filename.startswith('cv9'):
continue
# create the full path of the file to open
path = directory + '/' + filename
# load the doc
doc = load_doc(path)
# clean doc
tokens = clean_doc(doc, vocab)
# add to list
documents.append(tokens)
return documents
# load embedding as a dict
def load_embedding(filename):
# load embedding into memory, skip first line
file = open(filename,'r')
lines = file.readlines()
file.close()
# create a map of words to vectors
embedding = dict()
for line in lines:
parts = line.split()
# key is string word, value is numpy array for vector
embedding[parts[0]] = asarray(parts[1:], dtype='float32')
return embedding
# create a weight matrix for the Embedding layer from a loaded embedding
def get_weight_matrix(embedding, vocab):
# total vocabulary size plus 0 for unknown words
vocab_size = len(vocab) + 1
# define weight matrix dimensions with all 0
weight_matrix = zeros((vocab_size, 100))
# step vocab, store vectors using the Tokenizer's integer mapping
for word, i in vocab.items():
vector = embedding.get(word)
if vector is not None:
weight_matrix[i] = vector
return weight_matrix
# load the vocabulary
vocab_filename = 'vocab.txt'
vocab = load_doc(vocab_filename)
vocab = vocab.split()
vocab = set(vocab)
# load all training reviews
positive_docs = process_docs('txt_sentoken/pos', vocab, True)
negative_docs = process_docs('txt_sentoken/neg', vocab, True)
train_docs = negative_docs + positive_docs
# create the tokenizer
tokenizer = Tokenizer()
# fit the tokenizer on the documents
tokenizer.fit_on_texts(train_docs)
# sequence encode
encoded_docs = tokenizer.texts_to_sequences(train_docs)
# pad sequences
max_length = max([len(s.split()) for s in train_docs])
Xtrain = pad_sequences(encoded_docs, maxlen=max_length, padding='post')
# define training labels
ytrain = array([0 for _ in range(900)] + [1 for _ in range(900)])
# load all test reviews
positive_docs = process_docs('txt_sentoken/pos', vocab, False)
negative_docs = process_docs('txt_sentoken/neg', vocab, False)
test_docs = negative_docs + positive_docs
# sequence encode
encoded_docs = tokenizer.texts_to_sequences(test_docs)
# pad sequences
Xtest = pad_sequences(encoded_docs, maxlen=max_length, padding='post')
# define test labels
ytest = array([0 for _ in range(100)] + [1 for _ in range(100)])
# define vocabulary size (largest integer value)
vocab_size = len(tokenizer.word_index) + 1
# load embedding from file
raw_embedding = load_embedding('glove.6B.100d.txt')
# get vectors in the right order
embedding_vectors = get_weight_matrix(raw_embedding, tokenizer.word_index)
# create the embedding layer
embedding_layer = Embedding(vocab_size, 100, weights=[embedding_vectors], input_length=max_length, trainable=False)
# define model
model = Sequential()
model.add(embedding_layer)
model.add(Conv1D(filters=128, kernel_size=5, activation='relu'))
model.add(MaxPooling1D(pool_size=2))
model.add(Flatten())
model.add(Dense(1, activation='sigmoid'))
print(model.summary())
# compile network
model.compile(loss='binary_crossentropy', optimizer='adam', metrics=['accuracy'])
# fit network
model.fit(Xtrain, ytrain, epochs=10, verbose=2)
# evaluate
loss, acc = model.evaluate(Xtest, ytest, verbose=0)
print('Test Accuracy: %f' % (acc*100))