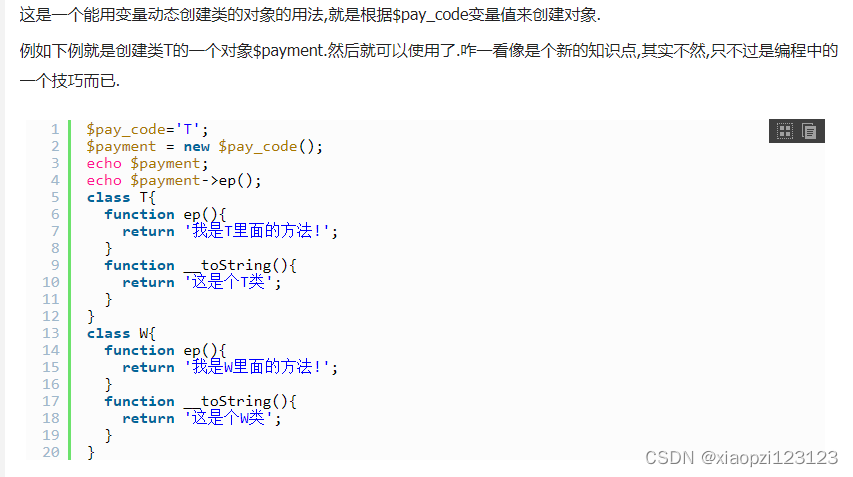
DQN(Deep Q-Network)是深度强化学习(Deep Reinforcement Learning)的开山之作,将深度学习引入强化学习中,构建了 Perception 到 Decision 的 End-to-end 架构。DQN 最开始由 DeepMind 发表在 NIPS 2013,后来将改进的版本发表在 Nature 2015。
NIPS 2013: Playing Atari with Deep Reinforcement Learning
Nature 2015: Human-level control through deep reinforcement learning
DQN 面临着几个挑战:
深度学习需要大量带标签的训练数据;
强化学习从 scalar reward 进行学习,但是 reward 经常是 sparse, noisy, delayed;
深度学习假设样本数据是独立同分布的,但是强化学习中采样的数据是强相关的
因此,DQN 采用经验回放(Experience Replay)机制,将训练过的数据进行储存到 Replay Buffer 中,以便后续从中随机采样进行训练,好处就是:1. 数据利用率高;2. 减少连续样本的相关性,从而减小方差(variance)。
class DeepQNetwork:
def init(
self,
n_actions,
n_features,
learning_rate=0.01,
reward_decay=0.9,
e_greedy=0.9,
replace_target_iter=300,
memory_size=500,
batch_size=32,
e_greedy_increment=None,
output_graph=False,
):
self.n_actions = n_actions
self.n_features = n_features
self.lr = learning_rate
self.gamma = reward_decay
self.epsilon_max = e_greedy
self.replace_target_iter = replace_target_iter
self.memory_size = memory_size
self.batch_size = batch_size
self.epsilon_increment = e_greedy_increment
self.epsilon = 0 if e_greedy_increment is not None else self.epsilon_max
# total learning step
self.learn_step_counter = 0
# initialize zero memory [s, a, r, s_]
self.memory = np.zeros((self.memory_size, n_features * 2 + 2))
# consist of [target_net, evaluate_net]
self._build_net()
t_params = tf.get_collection('target_net_params')
e_params = tf.get_collection('eval_net_params')
self.replace_target_op = [tf.assign(t, e) for t, e in zip(t_params, e_params)]
self.sess = tf.Session()
if output_graph:
# $ tensorboard --logdir=logs
tf.summary.FileWriter("logs/", self.sess.graph)
self.sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
self.cost_his = []
def _build_net(self):
# ------------------ build evaluate_net ------------------
self.s = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, self.n_features], name='s') # input
self.q_target = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, self.n_actions], name='Q_target') # for calculating loss
with tf.variable_scope('eval_net'):
# c_names(collections_names) are the collections to store variables
c_names = ['eval_net_params', tf.GraphKeys.GLOBAL_VARIABLES]
n_l1 = 10
w_initializer = tf.random_normal_initializer(0., 0.3)
b_initializer = tf.constant_initializer(0.1)
# first layer. collections is used later when assign to target net
with tf.variable_scope('l1'):
w1 = tf.get_variable('w1', [self.n_features, n_l1], initializer=w_initializer, collections=c_names)
b1 = tf.get_variable('b1', [1, n_l1], initializer=b_initializer, collections=c_names)
l1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(self.s, w1) + b1)
# second layer. collections is used later when assign to target net
with tf.variable_scope('l2'):
w2 = tf.get_variable('w2', [n_l1, self.n_actions], initializer=w_initializer, collections=c_names)
b2 = tf.get_variable('b2', [1, self.n_actions], initializer=b_initializer, collections=c_names)
self.q_eval = tf.matmul(l1, w2) + b2
with tf.variable_scope('loss'):
self.loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.squared_difference(self.q_target, self.q_eval))
with tf.variable_scope('train'):
self._train_op = tf.train.RMSPropOptimizer(self.lr).minimize(self.loss)
# ------------------ build target_net ------------------
self.s_ = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, self.n_features], name='s_') # input
with tf.variable_scope('target_net'):
# c_names(collections_names) are the collections to store variables
c_names = ['target_net_params', tf.GraphKeys.GLOBAL_VARIABLES]
# first layer. collections is used later when assign to target net
with tf.variable_scope('l1'):
w1 = tf.get_variable('w1', [self.n_features, n_l1], initializer=w_initializer, collections=c_names)
b1 = tf.get_variable('b1', [1, n_l1], initializer=b_initializer, collections=c_names)
l1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(self.s_, w1) + b1)
# second layer. collections is used later when assign to target net
with tf.variable_scope('l2'):
w2 = tf.get_variable('w2', [n_l1, self.n_actions], initializer=w_initializer, collections=c_names)
b2 = tf.get_variable('b2', [1, self.n_actions], initializer=b_initializer, collections=c_names)
self.q_next = tf.matmul(l1, w2) + b2
def store_transition(self, s, a, r, s_):
if not hasattr(self, 'memory_counter'):
self.memory_counter = 0
transition = np.hstack((s, [a, r], s_))
# replace the old memory with new memory
index = self.memory_counter % self.memory_size
self.memory[index, :] = transition
self.memory_counter += 1
def choose_action(self, observation):
# to have batch dimension when feed into tf placeholder
observation = observation[np.newaxis, :]
if np.random.uniform() < self.epsilon:
# forward feed the observation and get q value for every actions
actions_value = self.sess.run(self.q_eval, feed_dict={self.s: observation})
action = np.argmax(actions_value)
else:
action = np.random.randint(0, self.n_actions)
return action
def learn(self):
# check to replace target parameters
if self.learn_step_counter % self.replace_target_iter == 0:
self.sess.run(self.replace_target_op)
print('\ntarget_params_replaced\n')
# sample batch memory from all memory
if self.memory_counter > self.memory_size:
sample_index = np.random.choice(self.memory_size, size=self.batch_size)
else:
sample_index = np.random.choice(self.memory_counter, size=self.batch_size)
batch_memory = self.memory[sample_index, :]
q_next, q_eval = self.sess.run(
[self.q_next, self.q_eval],
feed_dict={
self.s_: batch_memory[:, -self.n_features:], # fixed params
self.s: batch_memory[:, :self.n_features], # newest params
})
# change q_target w.r.t q_eval's action
q_target = q_eval.copy()
batch_index = np.arange(self.batch_size, dtype=np.int32)
eval_act_index = batch_memory[:, self.n_features].astype(int)
reward = batch_memory[:, self.n_features + 1]
q_target[batch_index, eval_act_index] = reward + self.gamma * np.max(q_next, axis=1)
"""
For example in this batch I have 2 samples and 3 actions:
q_eval =
[[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6]]
q_target = q_eval =
[[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6]]
Then change q_target with the real q_target value w.r.t the q_eval's action.
For example in:
sample 0, I took action 0, and the max q_target value is -1;
sample 1, I took action 2, and the max q_target value is -2:
q_target =
[[-1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, -2]]
So the (q_target - q_eval) becomes:
[[(-1)-(1), 0, 0],
[0, 0, (-2)-(6)]]
We then backpropagate this error w.r.t the corresponding action to network,
leave other action as error=0 cause we didn't choose it.
"""
# train eval network
_, self.cost = self.sess.run([self._train_op, self.loss],
feed_dict={self.s: batch_memory[:, :self.n_features],
self.q_target: q_target})
self.cost_his.append(self.cost)
# increasing epsilon
self.epsilon = self.epsilon + self.epsilon_increment if self.epsilon < self.epsilon_max else self.epsilon_max
self.learn_step_counter += 1

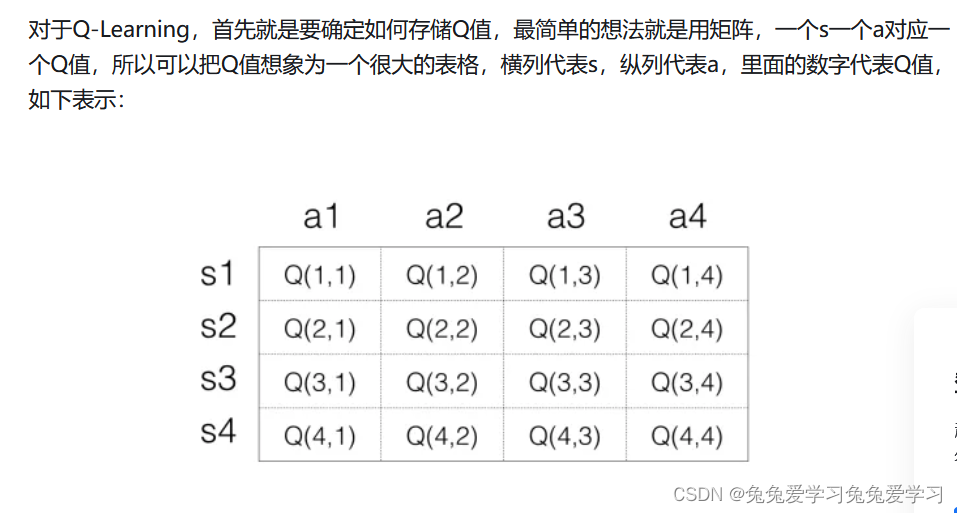
在DQN中增强学习Q-Learning算法和深度学习的SGD训练是同步进行的!
通过Q-Learning获取无限量的训练样本,然后对神经网络进行训练。
样本的获取关键是计算y,也就是标签。