编辑 Hacker_Albert · 202
- linux 启动流程
- module加载
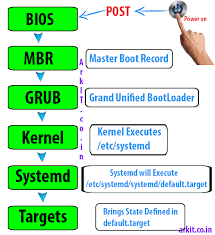
1.启动过程分为三个部分
- BIOS 上电自检(POST)
- 引导装载程序 (GRUB2)
- 内核初始化
- 启动 systemd,其是所有进程之父。
1.1.BIOS 上电自检(POST)
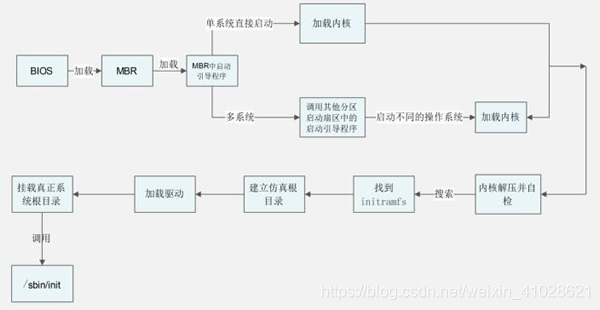
BIOS stands for Basic Input/Output System. In simple terms, the BIOS loads and executes the Master Boot Record (MBR) boot loader.
When you first turn on your computer, the BIOS first performs some integrity checks of the HDD or SSD.
Then, the BIOS searches for, loads, and executes the boot loader program, which can be found in the Master Boot Record (MBR). The MBR is sometimes on a USB stick or CD-ROM such as with a live installation of Linux.
Once the boot loader program is detected, it’s then loaded into memory and the BIOS gives control of the system to it.
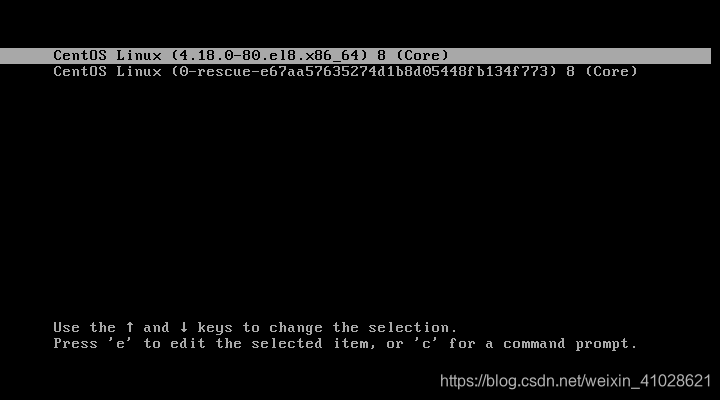
1.2.GRUB2
Once the POST is complete and the coast is clear, the BIOS probes the MBR (Master Boot Record) for the bootloader and disk partitioning information.
The MBR is a 512-byte code that is located on the first sector of the hard drive which is usually /dev/sda or /dev/hda depending on your hard drive architecture. Note, however, that sometimes the MBR can be located on a Live USB or DVD installation of Linux.
There are 3 main types of bootloaders in Linux: LILO, GRUB, and GRUB2. The GRUB2 bootloader is the latest and primary bootloader in modern Linux distributions and informs our decision to leave out the other two which have become antiquated with the passage of time.
GRUB2 stands for GRand Unified Bootloader version 2. Once the BIOS locates the grub2 bootloader, it executes and loads it onto the main memory (RAM).
The grub2 menu allows you to do a couple of things. It allows you to select the Linux kernel version that you’d want to use. If you have been upgrading your system a couple of times, you might see different kernel versions listed. Additionally, it gives you the ability to edit some kernel parameters by pressing a combination of keyboard keys.
Also, in a dual-boot setup where you have multiple OS installations, the grub menu allows you to select which OS to boot into. The grub2 configuration file is the /boot/grub2/grub2.cfg file. GRUB’s main objective is to load the Linux kernel onto the main memory.
1.3.Kernel Initialization
The kernel is the core of any Linux system. It interfaces the PC’s hardware with the underlying processes. The kernel controls all the processes on your Linux system. Once the selected Linux kernel is loaded by the bootloader, it must self extract from its compressed version before undertaking any task. Upon self-extracting, the selected kernel mounts the root file system and initializes the /sbin/init program commonly referred to as init.
Init is always the first program to be executed and is assigned the process ID or PID of 1. It’s the init process that spawns various daemons & mounts all partitions that are specified in the /etc/fstab file.
The kernel then mounts the initial RAM disk (initrd) which is a temporary root filesystem until the real root filesystem is mounted. All kernels are located in the /boot directory together with the initial RAM disk image.
1.3.1.initramfs 文件系统
Linux操作系统首先要将内核加载到内存。内核驻留于操作系统与应用程序的整个活动周期,其中应用程序(软件)在“用户空间”内运行,位于内核控制之下。
为了使加载存储器最小化,一些核心Linux程序转化成可加载核心模块形式,可以动态加载系统中。
initrd系统中的文件在引导阶段可以被核心访问,里面的内容会被挂载成一个loop类型的文件。initrd通常被压缩成gzip类型,在引导的时候由bootloader(LILO、GRUB)来告知核心initrd的位置。在2.6版本内核之后出现了initramfs,它的功能类似initrd,但是它基于CPIO格式,无须挂载就可以展开成一个文件系统。
initramfs是initrd的替代品。initrd是一个被加载的块设备,内部有ext2一类文件系统的存在,于是由于Linux内核的缓存机制,其中的内容还会被缓存到内存上,造成一定的内存空间浪费。而initramfs本身就是一个tmpfs的RAM disk,拥有最小化的设计,绕过了缓存机制,也消除了多余的内存占用。
1.3.2.加载modules
内核完成再次系统自检之后,开始采用动态的方式加载每个硬件的模块,这个动态模块大家可以想象成硬件的驱动(默认 Linux 硬件的驱动是不需要手工安装的,如果是重要的功能,则会直接编译到内核当中;如果是非重要的功能,比如硬件驱动会编译为模块,则在需要时由内核调用。不过,如果没有被内核硬件,要想驱动,就需要手工安装个硬件的硬块了。
模块的全称是动态可加载内核模块,它是具有独立功能的程序,可以被单独编译,但不能独立运行。模块是为内核或其他模块提供功能的代码集合。这些模块可以是 Linux 源码中自带的,也可以是由硬件厂商开发的(可以想象成驱动)。不过内核因为发布时间较长,所以自带的模块可能版本较低,还有一些新硬件可能就不自带模块了,只能由硬件厂商在发布硬件的同时发布新模块。
也就是说,安装模块一般有两种方法:
- 第一种方法在编译内核时,手工调整内核模块功能,加入所需的模块。这种方法有一个问题,就是内核必须支持这个硬件或功能才可以通过编译内核加入模块。如果硬件比内核新,内核本身并不支持硬件,就不能通过重新编译内核来加入新的硬件的支持。
- 第二种方法就是下载厂商发布的新硬件的驱动模块,或下载驱动程序,再编译成驱动模块,然后手工安装。
工具目录:
- /usr/lib/modprobe.d/
- /etc/modprobe.d/
1.3.2.1.管理模块实用程序
- insmod 加载内核模块的简单程序。建议使用modprobe (8), 这更聪明,可以处理模块依赖。
- rmmod 卸载(可卸载内核模块)的简单程序。建议使用(modprobe -r)。
- lsmod 列出当前加载的内核模块,(地格式化/proc/modules的内容).
- depmod 输出适合modprobe实用程序的依赖项列表。(生成modules.dep和映射文件)
- Linux内核模块可以为其它模块提供提供服务(在代码中使用EXPORT_SYMBOL),这种服务被称作”symbols”。若第二个模块使用了这个symbol,则该模块很明显依赖于第一个模块。这些依赖关系是非常繁杂的。
- depmod读取在/lib/modules/version 目录下的所有模块,并检查每个模块导出的symbol和需要的symbol,然后创建一个依赖关系列表。默认地,该列表写入到/lib/moudules /version目录下的modules.dep文件中。若命令中的filename有指定的话,则仅检查这些指定的模块(不是很有用)。若命令中提供了version参数,则会使用version所指定的目录生成依赖,而不是当前内核的版本(uname -r 返回的)。
$ cat /lib/modules/‘uname -r’/modules.dep
- modinfo 显示有关Linux内核模块的信息
- modprobe命令用于智能地向内核中加载模块或者从内核中移除模块。
modprobe可载入指定的个别模块,或是载入一组相依的模块。modprobe会根据depmod所产生的相依关系,决定要载入哪些模块。若在载入过程中发生错误,在modprobe会卸载整组的模块。
1.3.2.2.Kernel module 加载
使用systemd自动加载模块:
所有必要模块的加载均由 udev 自动完成。所以,如果不需要使用任何额外的模块,就没有必要在任何配置文件中添加启动时加载的模块。但是,有些情况下可能需要在系统启动时加载某个额外的模块,或者将某个模块列入黑名单以便使系统正常运行。
内核模块可以在**/etc/modules-load.d/** 下的文件中明确列出,以便systemd在引导过程中加载它们。 每个配置文件都以 /etc/modules-load.d/.conf的样式命名。 配置文件仅包含要加载的内核模块名称列表,以换行符分隔。 空行和第一个非空白字符为#或;的行被忽略。
/etc/modules-load.d/virtio-net.conf: # Load virtio_net.ko at boot virtio_net
手动加载卸载:
-
1.先将.ko文件拷贝到/lib/module/
uname -r/kernel/driver/…目录下,根据具体用途的区别分为net、ide、scsi、usb、video、parport、md、block、ata等等。
-
2.运行depmod -a,更新模块依赖新,主要是更新modules.dep文件
-
3.运行modprobe加载内核模块
sudo modprobe -v etnaviv
配置模块参数:
1.传递参数的基本方式是使用 modprobe 选项,格式是 key=value:# modprobe module_name parameter_name=parameter_value
2.使用 /etc/modprobe.d/中的文件
要通过配置文件传递参数,在 /etc/modprobe.d/ 中放入任意名称 .conf 文件,加入:
/etc/modprobe.d/myfilename.conf
options modname parametername=parametercontents
Modules are stored in /usr/lib/modules/kernel_release. You can use the command uname -r to get your current kernel release version.
黑名单:
只需将module_blacklist=modname1,modname2,modname3 添加到引导加载程序的内核行中即可。This can also be made permanent by editing /etc/default/grub and adding to the GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX_DEFAULT variable. For example, in my /etc/default/grub I have:
GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX_DEFAULT=“quiet splash modprobe.blacklist=nouveau”
1.3.2.3.Kernel module dependencies
Certain kernel modules sometimes depend on one or more other kernel modules. The /lib/modules/<KERNEL_VERSION>/modules.dep file contains a complete list of kernel module dependencies for the respective kernel version.
The dependency file is generated by the depmod program, which is a part of the kmod package. Many of the utilities provided by kmod take module dependencies into account when performing operations so that manual dependency-tracking is rarely necessary.
Linux 中所有的模块都存放在 /lib/modules/kernel_release/modules.dep 文件中,在安装模块时,依赖这个文件査找所有的模块,所以不需要指定模块所在位置的绝对路径,而且也依靠这个文件来解决模块的依赖性。如果这个文件丢失了怎么办?不用担心,使用 depmod 命令会自动扫描系统中已有的模块,并生成 modules.dep 文件。命令格式如下:
[root@localhost ~]# depmod [选项] #不加选项,depmod命令会扫描系统中的内核模块,并写入modules.dep文件 选项: -a:扫描所有模块; -A:扫描新模块,只有有新模块时,才会更新modules.dep文件; -n:把扫描结果不写入modules.dep文件,而是输出到屏幕上;
depmod(depend module)可检测模块的相依性,供modprobe在安装模块时使用。depmod 命令会扫描系统中所有的内核模块,然后把扫描结果放入 modules.dep 文件。后续的模块安装或删除就依赖这个文件中的内容。也就是说,如果我们要手工安装一个模块,则需要先把模块复制到指定位置,一般复制至 /lib/modules/kernel_release/kernel/ 目录中,使用 depmod 命令扫描之后,才能继续安装。
1.3.2.3.常用命令:
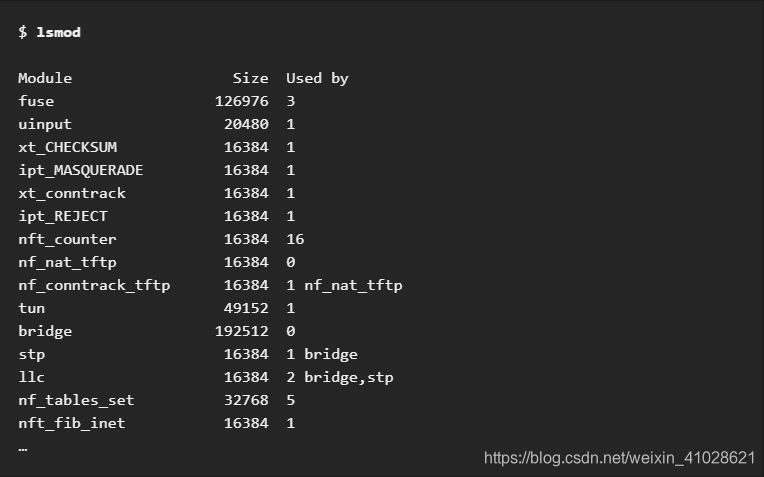
To show what kernel modules are currently loaded:
- The first column provides the names of currently loaded modules.
- The second column displays the amount of memory per module in kilobytes.
- The last column shows the number, and optionally the names of modules that are dependent on a particular module.
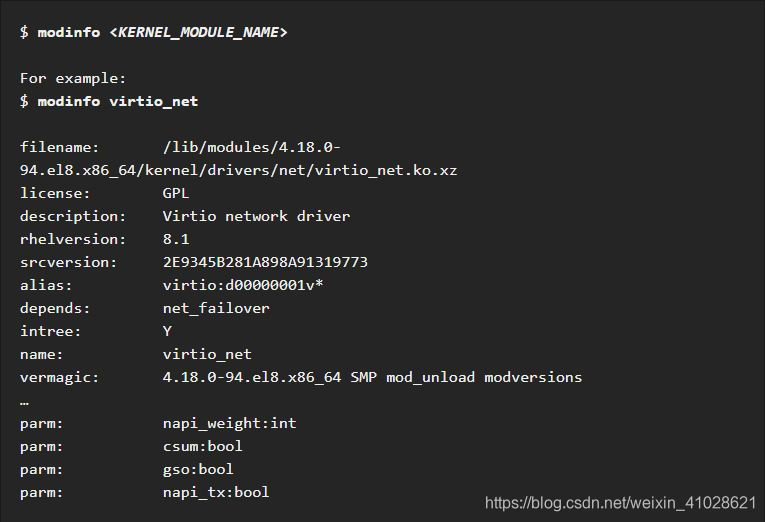
Displaying information about kernel modules:
Loading kernel modules at system runtime:
首先需要把模块复制到指定位置,一般复制到/lib/module/uname -r/kernel目录中,模块的扩展名一般是 *.ko;然后需要执行 depmod 命令扫描这些新模块,并写入 modules.dep 文件;最后就可以利用 modprobe 命令安装这些模块了。命令格式如下:
[root@localhost ~]# modprobe [选项] 模块名
选项:
-f:强制加载模块;
-r:删除模块;
Unloading kernel modules at system runtime
Unload the relevant kernel module: # modprobe -r <MODULE_NAME>
Loading kernel modules automatically at system boot time
Select a kernel module you want to load during the boot process. The modules are located in the /lib/modules/$(uname -r)/kernel/<SUBSYSTEM>/ directory. Create a configuration file for the module: # echo <MODULE_NAME> > /etc/modules-load.d/<MODULE_NAME>.conf
1.3.2.4.调试
使用 strace 追踪 modprobe 的调用过程,发现 modprobe 并不会使用 modules.dep 文件。可以看到它访问了 modules.dep.bin、modules.alias.bin、modules.symbols.bin、modules.builtin.bin 等文件,它并没有访问 modules.dep 文件。
uos@uos-PC:~$ strace /sbin/modprobe etnaviv 2>&1 | grep open openat(AT_FDCWD, "/etc/ld.so.cache", O_RDONLY|O_CLOEXEC) = 3 openat(AT_FDCWD, "/lib/mips64el-linux-gnuabi64/liblzma.so.5", O_RDONLY|O_CLOEXEC) = 3 openat(AT_FDCWD, "/lib/mips64el-linux-gnuabi64/libcrypto.so.1.1", O_RDONLY|O_CLOEXEC) = 3 openat(AT_FDCWD, "/lib/mips64el-linux-gnuabi64/libc.so.6", O_RDONLY|O_CLOEXEC) = 3 openat(AT_FDCWD, "/lib/mips64el-linux-gnuabi64/libpthread.so.0", O_RDONLY|O_CLOEXEC) = 3 openat(AT_FDCWD, "/lib/mips64el-linux-gnuabi64/libdl.so.2", O_RDONLY|O_CLOEXEC) = 3 openat(AT_FDCWD, "/etc/modprobe.d", O_RDONLY|O_NONBLOCK|O_CLOEXEC|O_DIRECTORY) = 3 openat(AT_FDCWD, "/lib/modprobe.d", O_RDONLY|O_NONBLOCK|O_CLOEXEC|O_DIRECTORY) = 3 openat(AT_FDCWD, "/etc/modprobe.d/8821ce.conf", O_RDONLY|O_CLOEXEC) = 3 openat(AT_FDCWD, "/lib/modprobe.d/aliases.conf", O_RDONLY|O_CLOEXEC) = 3 openat(AT_FDCWD, "/etc/modprobe.d/deepin-screen-recorder.conf", O_RDONLY|O_CLOEXEC) = 3 openat(AT_FDCWD, "/lib/modprobe.d/fbdev-blacklist.conf", O_RDONLY|O_CLOEXEC) = 3 openat(AT_FDCWD, "/etc/modprobe.d/iwlwifi.conf", O_RDONLY|O_CLOEXEC) = 3 openat(AT_FDCWD, "/lib/modules/4.19.0-loongson-3-desktop/modules.softdep", O_RDONLY|O_CLOEXEC) = 3 openat(AT_FDCWD, "/lib/modprobe.d/systemd.conf", O_RDONLY|O_CLOEXEC) = 3 openat(AT_FDCWD, "/proc/cmdline", O_RDONLY|O_CLOEXEC) = 3 openat(AT_FDCWD, "/lib/modules/4.19.0-loongson-3-desktop/modules.dep.bin", O_RDONLY|O_CLOEXEC) = 3 openat(AT_FDCWD, "/lib/modules/4.19.0-loongson-3-desktop/modules.alias.bin", O_RDONLY|O_CLOEXEC) = 3 openat(AT_FDCWD, "/lib/modules/4.19.0-loongson-3-desktop/modules.symbols.bin", O_RDONLY|O_CLOEXEC) = 3 openat(AT_FDCWD, "/lib/modules/4.19.0-loongson-3-desktop/modules.builtin.bin", O_RDONLY|O_CLOEXEC) = 3 openat(AT_FDCWD, "/sys/module/etnaviv/initstate", O_RDONLY|O_CLOEXEC) = -1 ENOENT (没有那个文件或目录) openat(AT_FDCWD, "/sys/module/gpu_sched/initstate", O_RDONLY|O_CLOEXEC) = 3 openat(AT_FDCWD, "/sys/module/etnaviv/initstate", O_RDONLY|O_CLOEXEC) = -1 ENOENT (没有那个文件或目录) openat(AT_FDCWD, "/lib/modules/4.19.0-loongson-3-desktop/kernel/drivers/gpu/drm/etnaviv/etnaviv.ko", O_RDONLY|O_CLOEXEC) = 3
-
/sys/module
这里有系统中所有模块的信息,不论这些模块是以内联(inlined)方式编译到内核映像文件(vmlinuz)中还是编译为外部模块(ko文件),都可能会出现在 /sys/module 中:编译为外部模块(ko文件)在加载后会出现对应的 /sys/module/<module_name>/, 并且在这个目录下会出现一些属性文件和属性目录来表示此外部模块的一些信息,如版本号、加载状态、所提供的驱动程序等;
编译为内联方式的模块则只在当它有非0属性的模块参数时会出现对应的 /sys/module/<module_name>, 这些模块的可用参数会出现在 /sys/modules//parameters/<param_name> 中,如 /sys/module/printk/parameters/time 这个可读写参数控制着内联模块 printk 在打印内核消息时是否加上时间前缀;所有内联模块的参数也可以由 “<module_name>.<param_name>=” 的形式写在内核启动参数上,如启动内核时加上参数 “printk.time=1” 与 向 “/sys/module/printk/parameters/time” 写入1的效果相同;没有非0属性参数的内联模块不会出现于此。
1.4.Starting Systemd
The kernel finally loads Systemd, which is the replacement of the old SysV init. Systemd is the mother of all Linux processes and manages among other things mounting of file systems, starting and stopping services to mention just a few.
Systemd uses the /etc/systemd/system/default.target file to determine the state or target that the Linux system should boot into.
For a desktop workstation (with a GUI) the default target value is 5 which is the equivalent of run level 5 for the old SystemV init.
For a server, the default target is multi-user.target which corresponds to run level 3 in SysV init.
Here’s a breakdown of the systemd targets:
poweroff.target (runlevel 0): Poweroff or Shutdown the system. rescue.target (runlevel 1): launches a rescue shell session. multi-user.target (runlevel 2,3,4): Configures the system to a non-graphical (console) multi-user system. graphical.target (runlevel 5): Set the system to use a graphical multi-user interface with network services. reboot.target (runlevel 6): reboots the system.
1.4.1.systemd-modules-load.service
It is an early boot service that loads kernel modules. It reads static configuration from files in /usr/ and /etc/, but also runtime configuration from /run/ and the kernel command line.
- /usr/lib/systemd/system/systemd-modules-load.service
[Unit] Description=Load Kernel Modules Documentation=man:systemd-modules-load.service(8) man:modules-load.d(5) DefaultDependencies=no Conflicts=shutdown.target Before=sysinit.target shutdown.target ConditionCapability=CAP_SYS_MODULE ConditionDirectoryNotEmpty=|/lib/modules-load.d ConditionDirectoryNotEmpty=|/usr/lib/modules-load.d ConditionDirectoryNotEmpty=|/usr/local/lib/modules-load.d ConditionDirectoryNotEmpty=|/etc/modules-load.d ConditionDirectoryNotEmpty=|/run/modules-load.d ConditionKernelCommandLine=|modules-load ConditionKernelCommandLine=|rd.modules-load [Service] Type=oneshot RemainAfterExit=yes ExecStart=/lib/systemd/systemd-modules-load TimeoutSec=90s
2.systemd-modules-load.service启动失败问题排查
- 首先,查看哪些服务启动失败:
uos@uos-PC:~$ sudo systemctl --failed UNIT LOAD ACTIVE SUB DESCRIPTION ● lmt-poll.service loaded failed failed Laptop Mode Tools - Battery Polling Service ● NetworkManager-wait-online.service loaded failed failed Network Manager Wait Online ● systemd-modules-load.service loaded failed failed Load Kernel Modules
- journalctl -fp err
uos@uos-PC:~$ sudo journalctl -fp err -- Logs begin at Mon 2022-01-24 17:07:35 CST. -- 1月 25 09:54:14 uos-PC systemd[1]: Failed to start Laptop Mode Tools - Battery Polling Service. 1月 25 09:54:27 uos-PC lightdm[960]: gkr-pam: couldn't unlock the login keyring. 1月 25 09:54:50 uos-PC wpa_supplicant[388]: dbus: wpa_dbus_property_changed: no property SessionLength in object /fi/w1/wpa_supplicant1/Interfaces/1 1月 25 09:55:56 uos-PC wpa_supplicant[388]: dbus: wpa_dbus_property_changed: no property SessionLength in object /fi/w1/wpa_supplicant1/Interfaces/3 1月 25 09:56:52 uos-PC systemd[1]: Failed to start Laptop Mode Tools - Battery Polling Service. 1月 25 09:59:24 uos-PC systemd[1]: Failed to start Laptop Mode Tools - Battery Polling Service. 1月 25 10:02:14 uos-PC systemd[1]: Failed to start Laptop Mode Tools - Battery Polling Service. 1月 25 10:04:44 uos-PC systemd[1]: Failed to start Laptop Mode Tools - Battery Polling Service. 1月 25 10:07:34 uos-PC systemd[1]: Failed to start Laptop Mode Tools - Battery Polling Service. 1月 25 10:10:07 uos-PC systemd[1]: Failed to start Laptop Mode Tools - Battery Polling Service.
- systemctl status systemd-modules-load.service
uos@uos-PC:~$ sudo systemctl status systemd-modules-load.service
● systemd-modules-load.service - Load Kernel Modules
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/systemd-modules-load.service; static; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: failed (Result: exit-code) since Tue 2022-01-25 09:21:56 CST; 49min ago
Docs: man:systemd-modules-load.service(8)
man:modules-load.d(5)
Process: 256 ExecStart=/lib/systemd/systemd-modules-load (code=exited, status=1/FAILURE)
Main PID: 256 (code=exited, status=1/FAILURE)
Warning: Journal has been rotated since unit was started. Log output is incomplete or unavailable.
- journalctl _PID=256 //
uos@uos-PC:~$ sudo journalctl _PID=256 -- Logs begin at Mon 2022-01-24 17:07:35 CST, end at Tue 2022-01-25 10:11:52 CST. -- 1月 25 09:21:56 uos-PC systemd-modules-load[256]: Failed to find module 'lightcherry' 1月 25 09:21:56 uos-PC systemd-modules-load[256]: Failed to find module 'lightorange' 1月 25 09:21:56 uos-PC systemd-modules-load[256]: Inserted module 'uos_resources' uos@uos-PC:~$ Connection to 10.10.53.31 closed by remote host.
- journalctl _SYSTEMD_UNIT=systemd-modules-load.service //除了使用Process ID进行筛选,还可以直接使用服务名进行筛选。
- journalctl -xe
如果不知道这些日志筛选方法,也可以直接用-xe选项来查看,然后肉眼筛选:
1.5.自动加载模块
打开/lib/systemd/system/rc-local.service文件,找到如下内容: 找到: After=network.target 改为: After=timers.target 找到: Type=forking 改为: Type=simple 在/etc目录增加一个rc.local脚本,在里面写如下内容: #!/bin/bash sleep 10 udevadm trigger --type=subsystems --action=add udevadm trigger --type=devices -S block -S drm -S dri -S tty -S input --action=add udevadm settle 设置rc.local脚本可执行权限: sudo chmod 777 /etc/rc.local
refer to
- https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/the-linux-booting-process-6-steps-described-in-detail/
- https://www.tecmint.com/linux-boot-process/
- http://c.biancheng.net/view/1016.html
- https://www.cnblogs.com/sztom/p/11107485.html


![[mysql 基于C++实现数据库连接池 连接池的使用] 持续更新中](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/4a9a02ef547d45dcb9e5094eb407ae6e.png)