前言
本文为大家带来的是 lionsoul2014 开发的 ip2region 项目,一种高效的离线 IP 地址定位库。ip2region 提供了10微秒级别的查询效率,支持多种主流编程语言,是一种理想的 IP 定位解决方案。
这个开源项目可以实现 IP 地址到地理位置的精确映射,包括国家、省份、城市、运营商等信息,对于需要地理定位功能的应用程序来说,它是非常有用的。
别的不说,最近在项目中就运用上了它!!!
项目地址:https://github.com/lionsoul2014/ip2region
项目概览
ip2region 是一个跨语言的 IP 定位库,它提供了一个紧凑、高效的数据结构来存储 IP 定位数据,并且支持快速查询。这使得 ip2region 在需要快速准确获取 IP 地址地理位置信息的场合中,如网络分析、广告定向、内容定制等领域,显得尤为重要。
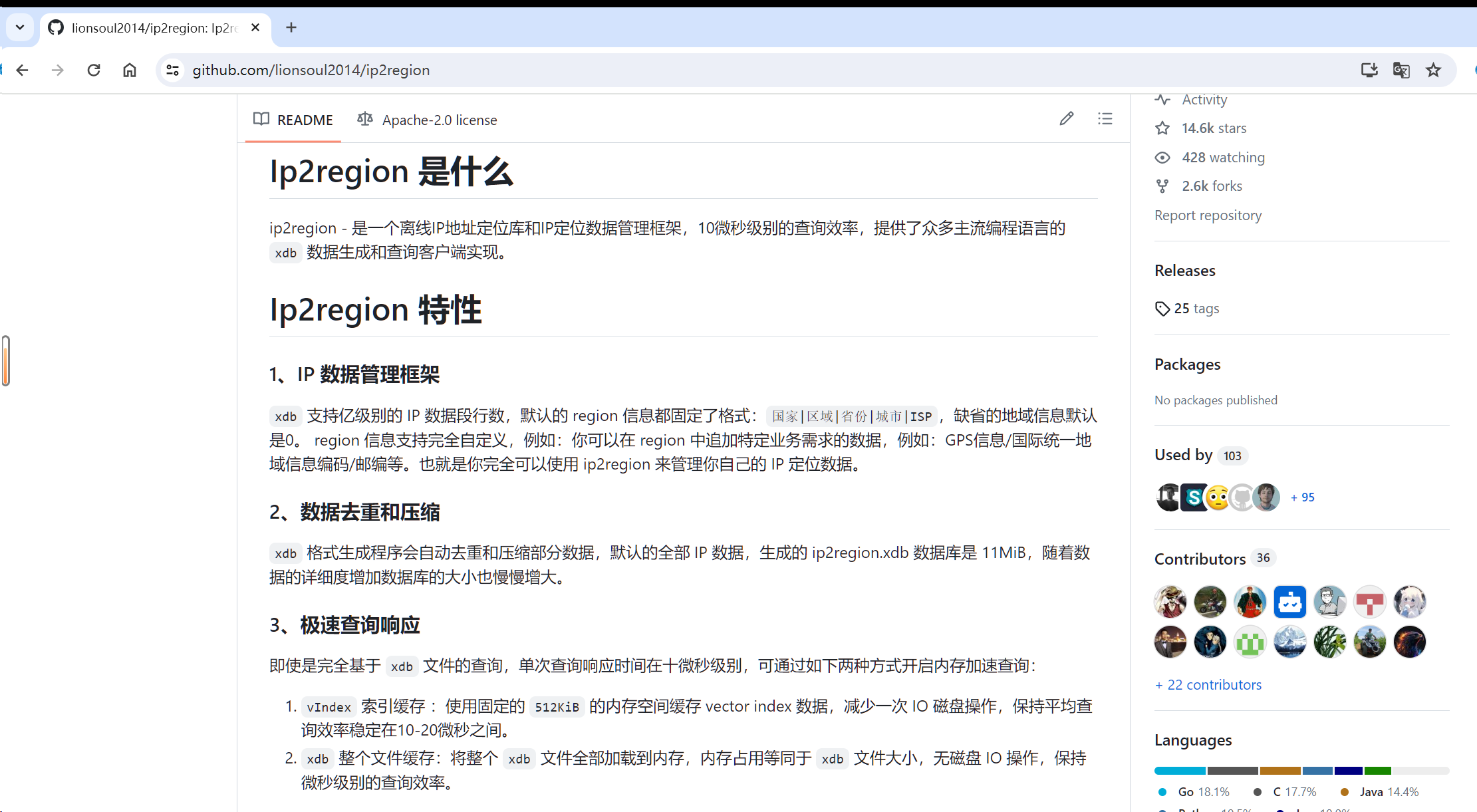
可以看到项目支持多种编程语言去查询。

克隆项目
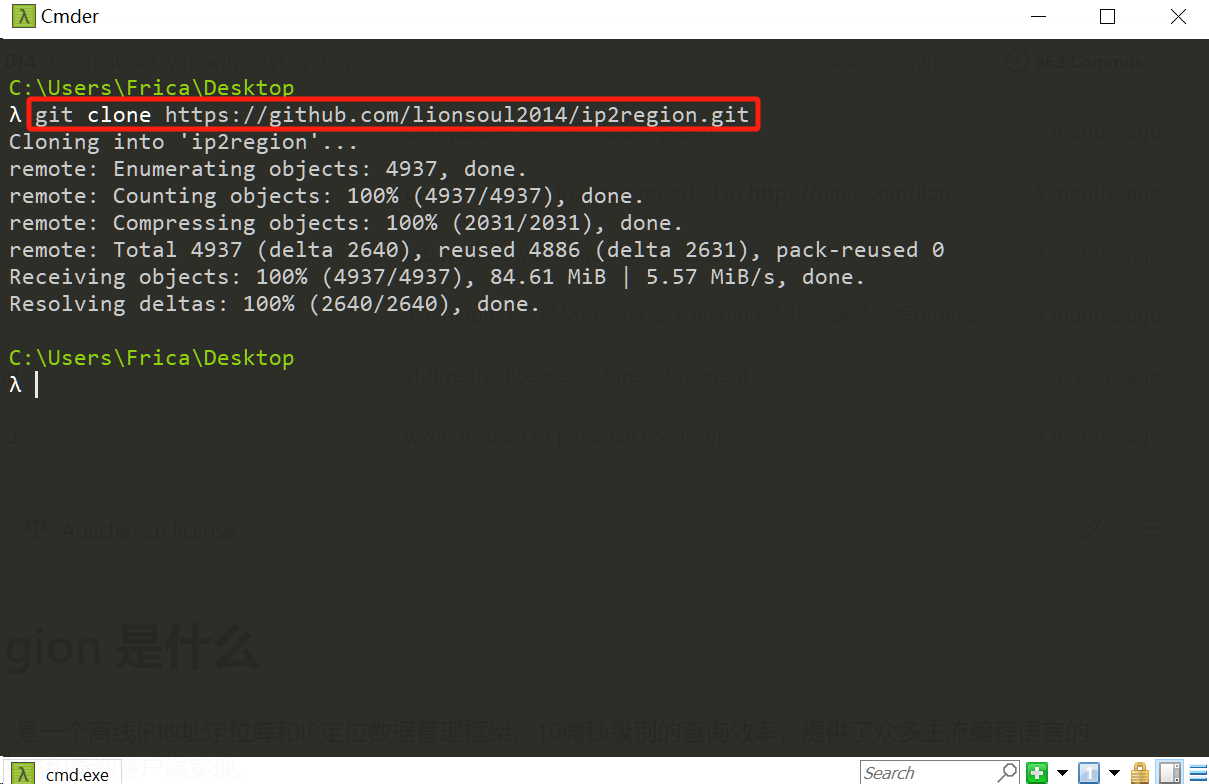
git clone
最简单的,在命令行工具数据以下命令即可,如下图所示:
git clone https://github.com/lionsoul2014/ip2region.git
Download ZIP
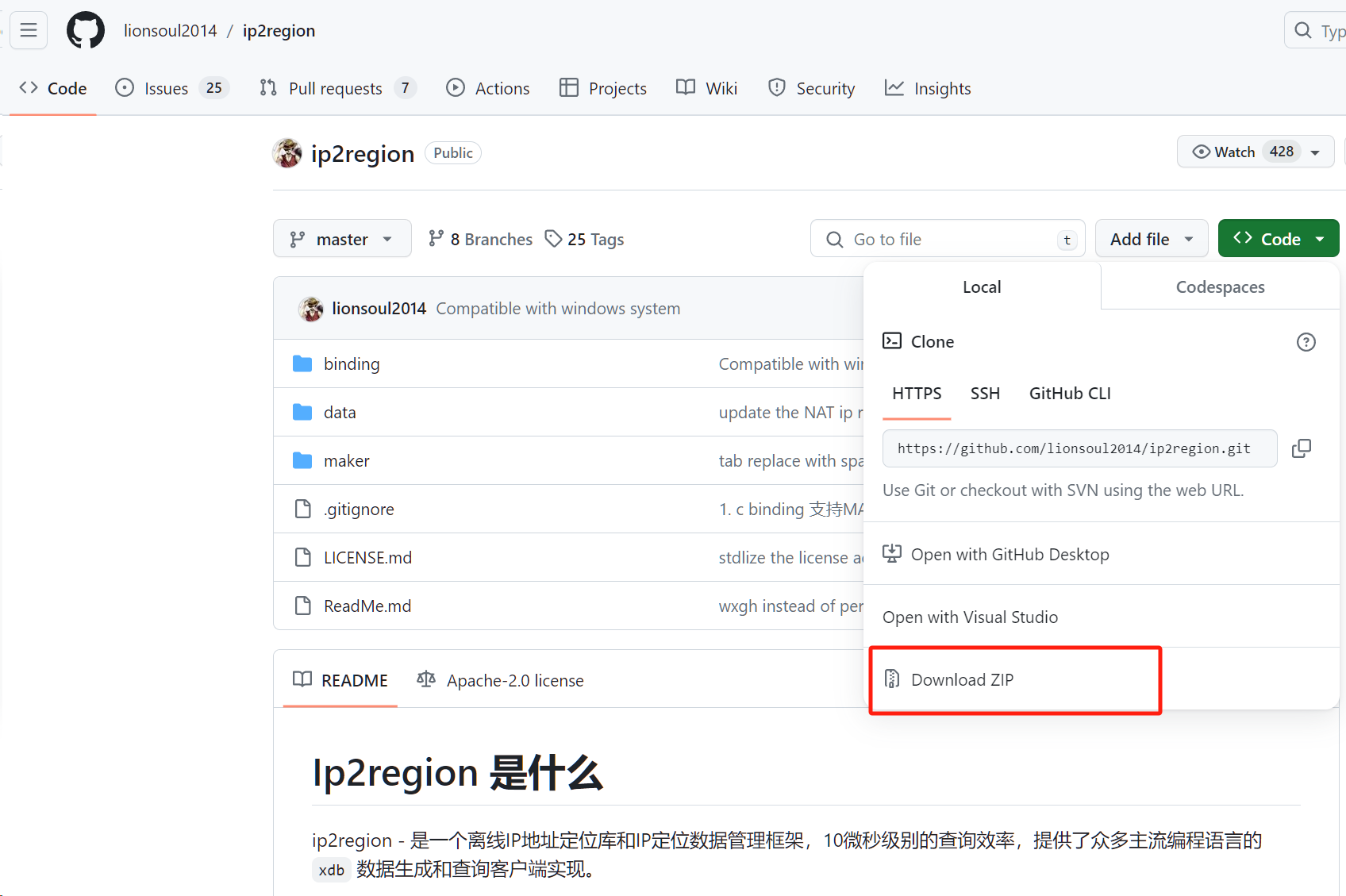
当然,使用 Download ZIP 也是个不错的下载方式。
使用指南
为了展示 ip2region 的使用方法,下面将使用 Python 语言进行演示。Python 版本的 ip2region 使用方法可以在下面的链接中找到:
Python 文档:https://github.com/lionsoul2014/ip2region/tree/master/binding/python
我们将通过一个实例演示如何将大量 IP 地址转换为地理位置信息,并将结果保存为 Excel 文件,以便于测试它的速度有多快。
我准备了一份 19万+ 的 IP 用于测试。

实现代码
以下使用代码来自官方的 Python 文档,但
- 我添加了一个计时器的装饰器
- 从 CSV 文件中读取 IP 地址。
- 将查询结果保存为 Excel 文件。
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# @Author : Frica01
# @Time : 2023-12-20 22:32
# @Name : demo.py
import time
from collections import defaultdict
import pandas as pd
from binding.python.xdbSearcher import XdbSearcher
output_dict = defaultdict(list)
def timer(func):
"""任务计时装饰器,用于测量函数执行时间"""
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
start_time = time.time() # 开始时间
result = func(*args, **kwargs) # 执行函数
end_time = time.time() # 结束时间
print(f"{func.__name__}任务执行耗时 {end_time - start_time:.4f} 秒.")
return result
return wrapper
@timer
def searchWithFile():
"""完全基于文件的查询"""
# 1. 创建查询对象
dbPath = "./data/ip2region.xdb"
searcher = XdbSearcher(dbfile=dbPath)
# 2. 执行查询
df = pd.read_csv('test_ip.csv')
for idx, item in df.iterrows():
ip = item['ip']
output_dict['ip'].append(ip)
output_dict['region'].append(searcher.searchByIPStr(ip))
# 3. 关闭searcher
searcher.close()
# 4. 保存为excel文件
pd.DataFrame(data=output_dict).to_excel('result.xlsx', index=False)
@timer
def searchWithVectorIndex():
"""缓存 VectorIndex 索引"""
# 1. 预先加载整个 xdb
dbPath = "./data/ip2region.xdb"
vi = XdbSearcher.loadVectorIndexFromFile(dbfile=dbPath)
# 2. 使用上面的缓存创建查询对象, 同时也要加载 xdb 文件
searcher = XdbSearcher(dbfile=dbPath, vectorIndex=vi)
# 3. 执行查询
df = pd.read_csv('test_ip.csv')
for idx, item in df.iterrows():
ip = item['ip']
output_dict['ip'].append(ip)
output_dict['region'].append(searcher.search(ip))
# 4. 关闭searcher
searcher.close()
# 5. 保存为excel文件
pd.DataFrame(data=output_dict).to_excel('result.xlsx', index=False)
@timer
def searchWithContent():
"""缓存整个 xdb 数据"""
# 1. 预先加载整个 xdb
dbPath = "./data/ip2region.xdb"
cb = XdbSearcher.loadContentFromFile(dbfile=dbPath)
# 2. 仅需要使用上面的全文件缓存创建查询对象, 不需要传源 xdb 文件
searcher = XdbSearcher(contentBuff=cb)
# 3. 执行查询
df = pd.read_csv('test_ip.csv')
for idx, item in df.iterrows():
ip = item['ip']
output_dict['ip'].append(ip)
output_dict['region'].append(searcher.search(ip))
# 4. 关闭searcher
searcher.close()
# 5. 保存为excel文件
pd.DataFrame(data=output_dict).to_excel('result.xlsx', index=False)
if __name__ == '__main__':
searchWithFile()
# searchWithVectorIndex()
# searchWithContent()
测试
不同模式的执行速度如下表所示:
- 它们分别转换了
19万+的 IP ,并将结果保存为excel文件。
| 模式 | 耗时/秒 | 速度 |
|---|---|---|
| 完全基于文件的查询 | 10.2 | ⭐ |
缓存 VectorIndex 索引 | 9.6 | ⭐⭐ |
缓存整个 xdb 数据 | 6.0 | ⭐⭐⭐ |
影响速度的原因
在项目
README.md的末尾,有关于 VectorIndex 和 xdb 等原理的介绍,有需要的读者可以进一步查阅。
VectorIndex 和 xdb 文件是 ip2region 项目中用于存储 IP 地址数据和加速查询的关键组件:
- 索引效率:
VectorIndex提供了一种高效的查找方法,减少了查询时需要扫描的数据量。这种优化的索引方法可以快速定位到数据库中的特定区域,从而加快查询速度。 - xdb数据访问方式:当数据直接从内存中读取时,查询速度要快于从硬盘读取。因此,将整个
xdb文件加载到内存中可以显著提高查询速度。
总的来说,通过使用高效的索引(如 VectorIndex)和将数据加载到内存中,ip2region 能够实现快速、准确的 IP 定位查询,这对于处理大量 IP 地址查询尤其重要。
总结
本文详细介绍了 ip2region 项目,这是一个高效的离线 IP 地址定位库,能够将 IP 地址映射到地理位置。通过对项目的细致解读,本文提供了关于如何使用 ip2region 的全面指南,特别是针对 Python 用户。
文章的重点在于演示如何使用不同的查询模式(完全基于文件的查询、缓存 VectorIndex 索引、缓存整个 xdb 数据)来处理大量的 IP 地址,并比较了这些方法在性能上的差异。通过这些实验,我们能够清楚地看到不同方法对于查询速度的影响,这对于选择合适的查询策略是非常有帮助的。
后话
本次分享到此结束,
see you~~🎈🎈




![[电子榨菜] js中的闭包closure](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/f6e701719f2d4b24b38a479e6078d633.png)