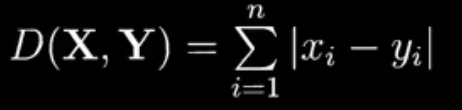一、KNN算法核心思想和原理
1.1、怎么想出来的?
近朱者赤,近墨者黑!
距离决定一切、民主集中制
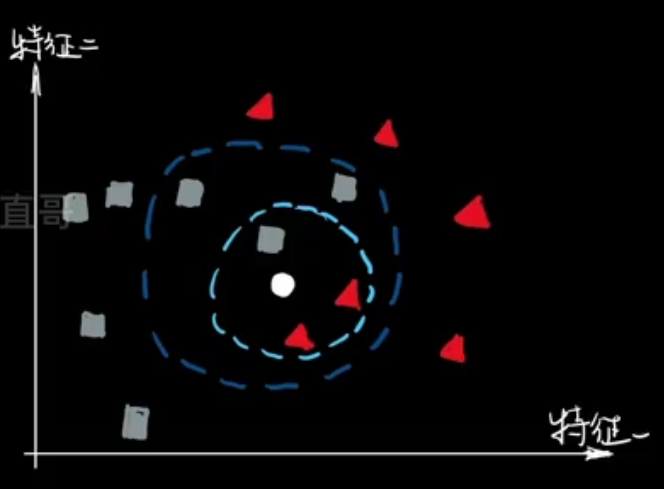
1.2、基本原理 —— 分类
- k个最近的邻居
- 民主集中制投票
- 分类表决与加权分类表决
1.3、基本原理 —— 回归
- 计算未知点的值
- 决策规则不同
- 均值法与加权均值法

1.4、如何选择K值?
- K太小导致“过拟合”(过分相信某个数据),容易把噪声学进来
- K太大导致“欠拟合”,决策效率低
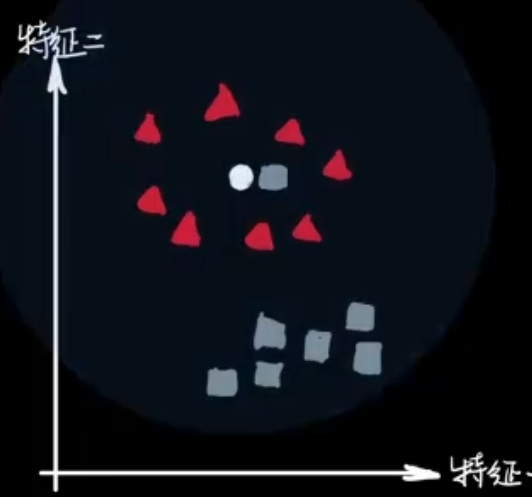
- K不能太小也不能太大
- Fit = 最优拟合(找三五个熟悉的人问问),通过超参数调参实现 ~
1.5、距离的度量
- 明氏距离 Minkowski Distance
- p为距离的阶数,n为特征空间的维度
- p=1时,即曼哈顿距离;p=2时,即欧式距离
- p趋向于无穷时,为切比雪夫距离
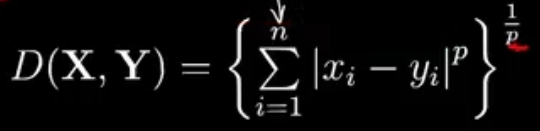
- ·p=1时,曼哈顿距离 Manhattan Distance
- ·p=2时,欧式距离 Euclidean Distance
- 空间中两点的直线距离


1.6、特征归一化的重要性
简单来讲,就是统一坐标轴比例
二、代码实现 KNN 预测
KNN 预测的过程
- 1. 计算新样本点与已知样本点的距离
- 2. 按距离排序
- 3. 确定k值
- 4. 距离最近的k个点投票
若不使用scikit-learn:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from collections import Counter
# 样本特征
data_X = [
[1.3, 6],
[3.5, 5],
[4.2, 2],
[5, 3.3],
[2, 9],
[5, 7.5],
[7.2, 4 ],
[8.1, 8],
[9, 2.5]
]
# 样本标记
data_y = [0,0,0,0,1,1,1,1,1]
# 训练集
X_train = np.array(data_X)
y_train = np.array(data_y)
# 新的样本点
data_new = np.array([4,5])
# 1. 计算新样本点与已知样本点的距离
distance = [np.sqrt(np.sum(data - data_new)**2) for data in X_train]
# 2. 按距离排序
sort_index = np.argsort(distance)
# 3. 确定k值
k = 5
# 4. 距离最近的k个点投票
first_k = [y_train[i] for i in sort_index[:k]]
predict_y = Counter(first_k).most_common(1)[0][0]
print(predict_y)若使用sklearn:
import numpy as np
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier
# 样本特征
data_X = [
[1.3, 6],
[3.5, 5],
[4.2, 2],
[5, 3.3],
[2, 9],
[5, 7.5],
[7.2, 4 ],
[8.1, 8],
[9, 2.5]
]
# 样本标记
data_y = [0,0,0,0,1,1,1,1,1]
# 训练集
X_train = np.array(data_X)
y_train = np.array(data_y)
# 新的样本点
data_new = np.array([4,5])
# 创造类的实例
knn_classifier = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=5)
# fit
knn_classifier.fit(X_train,y_train)
# sklearn支持预测多个数据,而我们只有一个数据,所以需要将其转为二维
data_new.reshape(1,-1)
predict_y = knn_classifier.predict(data_new.reshape(1,-1))
print(predict_y)
三、划分数据集:训练集与预测集
为什么要划分数据集?
评价模型性能
防止过拟合
提升泛化能力
3.1、划分数据集代码实现
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from sklearn.datasets import make_blobsx, y = make_blobs(
n_samples = 300, # 样本总数
n_features = 2,
centers = 3,
cluster_std = 1, # 类內标准差
center_box = (-10, 10),
random_state = 233,
return_centers = False
)plt.scatter(x[:,0], x[:,1], c = y,s = 15)
plt.show()
划分数据集
index = np.arange(20)indexarray([ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16,
17, 18, 19])
np.random.shuffle(index)indexarray([13, 16, 2, 19, 7, 14, 9, 0, 1, 11, 8, 6, 15, 10, 4, 18, 3,
12, 17, 5])
np.random.permutation(20)array([12, 19, 6, 7, 11, 10, 4, 8, 16, 3, 2, 15, 18, 5, 9, 0, 1,
14, 13, 17])
np.random.seed(233)
shuffle = np.random.permutation(len(x))shufflearray([ 23, 86, 204, 287, 206, 170, 234, 94, 146, 180, 263, 22, 3,
264, 194, 290, 229, 177, 208, 202, 10, 188, 262, 120, 148, 121,
98, 160, 267, 136, 294, 2, 34, 142, 271, 133, 127, 12, 29,
49, 112, 218, 36, 57, 45, 11, 25, 151, 212, 289, 157, 19,
275, 176, 144, 82, 161, 77, 51, 152, 135, 16, 65, 189, 298,
279, 37, 187, 44, 210, 178, 165, 6, 162, 66, 32, 198, 43,
108, 211, 67, 119, 284, 90, 89, 56, 217, 158, 228, 248, 191,
47, 296, 123, 181, 200, 40, 87, 232, 97, 113, 122, 220, 153,
173, 68, 99, 61, 273, 269, 281, 209, 4, 110, 259, 95, 205,
288, 8, 283, 231, 291, 171, 111, 242, 216, 285, 54, 100, 38,
185, 235, 174, 201, 107, 223, 222, 196, 268, 114, 147, 166, 85,
39, 58, 256, 258, 74, 251, 15, 150, 137, 70, 91, 52, 14,
169, 21, 184, 207, 238, 128, 219, 125, 293, 134, 27, 265, 96,
270, 18, 109, 126, 203, 88, 249, 92, 213, 60, 227, 5, 59,
9, 138, 236, 280, 124, 199, 225, 149, 145, 246, 192, 102, 48,
73, 20, 31, 63, 237, 78, 62, 233, 118, 277, 28, 50, 64,
117, 197, 140, 7, 105, 252, 71, 190, 76, 103, 93, 183, 72,
0, 278, 79, 172, 214, 182, 292, 139, 260, 30, 195, 13, 244,
240, 297, 257, 245, 143, 186, 243, 266, 286, 168, 179, 81, 215,
129, 167, 106, 261, 42, 276, 69, 224, 253, 247, 155, 154, 17,
132, 24, 141, 239, 80, 101, 75, 159, 116, 46, 272, 226, 83,
156, 33, 115, 282, 299, 55, 250, 221, 254, 255, 41, 130, 104,
26, 53, 84, 274, 1, 163, 230, 35, 241, 164, 193, 175, 131,
295])
shuffle.shape(300,)
train_size = 0.7train_index = shuffle[:int(len(x) * train_size)]test_index = shuffle[int(len(x) * train_size):]train_index.shape, test_index.shape((210,), (90,))
x[train_index].shape, y[train_index].shape((210, 2), (210,))
x[test_index].shape, y[test_index].shape((90, 2), (90,))
def my_train_test_split(x, y, train_size = 0.7, random_state = None):
if random_state:
np.random.seed(random_state)
shuffle = np.random.permutation(len(x))
train_index = shuffle[:int(len(x) * train_size)]
test_index = shuffle[int(len(x) * train_size):]
return x[train_index], x[test_index], y[train_index], y[test_index]x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = my_train_test_split(x, y, train_size = 0.7, random_state = 233)x_train.shape, x_test.shape, y_train.shape, y_test.shape((210, 2), (90, 2), (210,), (90,))
plt.scatter(x_train[:, 0], x_train[:, 1], c = y_train, s = 15)
plt.show()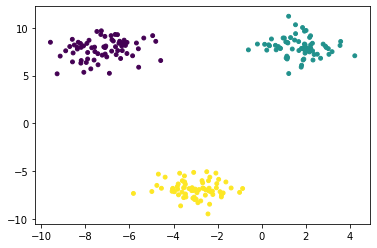
plt.scatter(x_test[:, 0], x_test[:, 1], c = y_test, s = 15)
plt.show()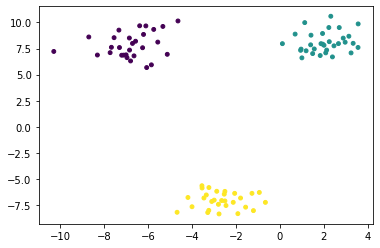
3.2、sklearn划分数据集
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_splitx_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(x, y, train_size = 0.7, random_state = 233)x_train.shape, x_test.shape, y_train.shape, y_test.shape((210, 2), (90, 2), (210,), (90,))
from collections import Counter
Counter(y_test)Counter({2: 34, 0: 25, 1: 31})
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(x, y, train_size = 0.7, random_state = 233, stratify = y)Counter(y_test)Counter({2: 30, 0: 30, 1: 30})
四、模型评价
import numpy as np
from sklearn import datasets
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
# 1、加载数据集
iris = datasets.load_iris()
X = iris.data
y = iris.target
# 2、拆分数据集,首先需乱序处理
# 2.1、自己拆分不调包 ~
shuffle_index = np.random.permutation(len(y))
train_ratio = 0.8
train_size = int(len(y)*train_ratio)
train_index = shuffle_index[:train_size]
test_index = shuffle_index[train_size:]
X_train = X[train_index]
y_train = y[train_index]
X_test = X[test_index]
y_test = y[test_index]
# 2.2、调包 ~
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X,y,train_size=0.8,random_state=666)
# 3、预测
knn_classifier = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=5)
knn_classifier.fit(X_train, y_train)
# 若不关注预测结果只关注预测精度
# accuracy_score(X_test,y_test)
y_predict = knn_classifier.predict(X_test)
print(y_predict)
# 4、评价
accutacy = np.sum(y_predict == y_test) / len(y_test)
# 或使用
accuracy_score(y_test,y_predict)五、超参数 Hyperpatameter
人为设置的参数 / 经验值 / 参数搜索
KNN的三个超参数:
k个最近的邻居
分类表决与加权分类表决
明氏距离中的p
首先加载数据
import numpy as np
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.datasets import load_irisiris = load_iris()x = iris.data
y = iris.targetx.shape, y.shape((150, 4), (150,))
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(x, y, train_size=0.7, random_state=233, stratify=y)x_train.shape, x_test.shape, y_train.shape, y_test.shape((105, 4), (45, 4), (105,), (45,))
5.1、超参数
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifierneigh = KNeighborsClassifier(
n_neighbors=3,
weights='distance',#'uniform',
p = 2
)neigh.fit(x_train, y_train)KNeighborsClassifier
KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=3, weights='distance')
neigh.score(x_test, y_test)0.9777777777777777
best_score = -1
best_n = -1
best_weight = ''
best_p = -1
for n in range(1, 20):
for weight in ['uniform', 'distance']:
for p in range(1, 7):
neigh = KNeighborsClassifier(
n_neighbors=n,
weights=weight,
p = p
)
neigh.fit(x_train, y_train)
score = neigh.score(x_test, y_test)
if score > best_score:
best_score = score
best_n = n
best_weight = weight
best_p = p
print("n_neighbors:", best_n)
print("weights:", best_weight)
print("p:", best_p)
print("score:", best_score)n_neighbors: 5 weights: uniform p: 2 score: 1.0
5.2、sklearn 超参数搜索
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCVparams = {
'n_neighbors': [n for n in range(1, 20)],
'weights': ['uniform', 'distance'],
'p': [p for p in range(1, 7)]
}grid = GridSearchCV(
estimator=KNeighborsClassifier(),
param_grid=params,
n_jobs=-1
)grid.fit(x_train, y_train)GridSearchCV
GridSearchCV(estimator=KNeighborsClassifier(), n_jobs=-1,
param_grid={'n_neighbors': [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12,
13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19],
'p': [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6],
'weights': ['uniform', 'distance']})
estimator: KNeighborsClassifier
KNeighborsClassifier()
KNeighborsClassifier
KNeighborsClassifier()
grid.best_params_{'n_neighbors': 9, 'p': 2, 'weights': 'uniform'}
grid.best_score_0.961904761904762
grid.best_estimator_KNeighborsClassifier
KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=9)
grid.best_estimator_.predict(x_test)array([2, 2, 0, 1, 1, 1, 2, 0, 2, 0, 0, 1, 0, 2, 1, 1, 0, 2, 2, 1, 0, 1,
1, 2, 2, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 2, 2, 0, 1, 1, 2, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 2, 0, 1,
1])
grid.best_estimator_.score(x_test, y_test)0.9555555555555556
六、特征归一化
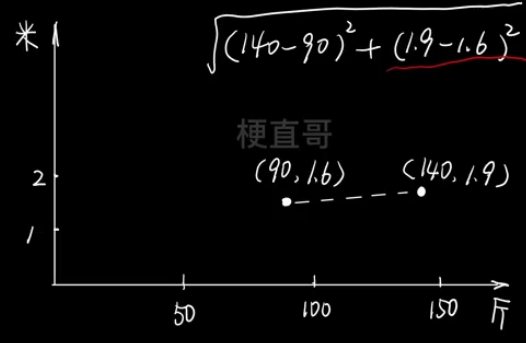
特征量纲不同。 为了消除数据特征量纲之间的影响,使得不同指标具有一定程度的可比性,能够同时反应每个指标的重要程度。
6.1、最值归一化方法
适用于数据分布在有限范围的情况。但受特殊数值影响很大。

X[:,0] = (X[:,0] - np.min(X[:,0])) / (np.max(X[:,0]) - np.min(X[:,0]))X[:5,0]array([0.22222222, 0.16666667, 0.11111111, 0.08333333, 0.19444444])
6.2、零均值归一化

X[:,0] = (X[:,0] - np.mean(X[:,0]))/np.std(X[:,0])X[:5,0]array([-0.90068117, -1.14301691, -1.38535265, -1.50652052, -1.02184904])
scikit-learn 中的StandardScaler
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScalerstandard_scaler = StandardScaler()standard_scaler.fit(X)standard_scaler.mean_array([5.84333333, 3.05733333, 3.758 , 1.19933333])
standard_scaler.scale_array([0.82530129, 0.43441097, 1.75940407, 0.75969263])
注意要重新赋值给X!
X = standard_scaler.transform(X)** 测试集如何归一化?
不是用测试集的均值和标准差,而是用训练集的!
import numpy as np
from sklearn import datasets
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier
iris = datasets.load_iris()
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test = train_test_split(iris.data,iris.target,train_size=0.8,random_state=666)
standard_scaler = StandardScaler()
standard_scaler.fit(X_train)
X_train_standard = standard_scaler.transform(X_train)
X_test_standard = standard_scaler.transform(X_test)
knn_classifier = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=5)
knn_classifier.fit(X_train_standard,y_train)
knn_classifier.score(X_test_standard, y_test)七、KNN 回归任务实现
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt# 样本特征
data_X = [
[1.3, 6],
[3.5, 5],
[4.2, 2],
[5, 3.3],
[2, 9],
[5, 7.5],
[7.2, 4 ],
[8.1, 8],
[9, 2.5]
]
data_y = [0.1,0.3,0.5,0.7,0.9,1.1,1.3,1.5,1.7]X_train = np.array(data_X)
y_train = np.array(data_y)
data_new = np.array([4,5])plt.scatter(X_train[:,0],X_train[:,1],color='black')
plt.scatter(data_new[0], data_new[1],color='b', marker='^')
for i in range(len(y_train)):
plt.annotate(y_train[i], xy=X_train[i], xytext=(-15,-15), textcoords='offset points')
plt.show()
distances = [np.sqrt(np.sum((data - data_new)**2)) for data in X_train]
sort_index = np.argsort(distances)k = 5
first_k = [y_train[i] for i in sort_index[:k]]from collections import Counter
Counter(first_k).most_common(1)
predict_y = Counter(first_k).most_common(1)[0][0]
predict_y0.3
k = 5
first_k = [y_train[i] for i in sort_index[:k]]
np.mean(first_k)0.54
7.2、KNN回归 Scikit learn 实现
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsRegressorknn_reg = KNeighborsRegressor(n_neighbors=5)knn_reg.fit(X_train, y_train)KNeighborsRegressor
KNeighborsRegressor()
predict_y = knn_reg.predict(data_new.reshape(1,-1))predict_yarray([0.54])
7.3、Boston 数据集
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import sklearn
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.datasets import load_boston
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")boston = load_boston()
x = boston.data
y = boston.target
x.shape, y.shape((506, 13), (506,))
print(boston.DESCR).. _boston_dataset:
Boston house prices dataset
---------------------------
**Data Set Characteristics:**
:Number of Instances: 506
:Number of Attributes: 13 numeric/categorical predictive. Median Value (attribute 14) is usually the target.
:Attribute Information (in order):
- CRIM per capita crime rate by town
- ZN proportion of residential land zoned for lots over 25,000 sq.ft.
- INDUS proportion of non-retail business acres per town
- CHAS Charles River dummy variable (= 1 if tract bounds river; 0 otherwise)
- NOX nitric oxides concentration (parts per 10 million)
- RM average number of rooms per dwelling
- AGE proportion of owner-occupied units built prior to 1940
- DIS weighted distances to five Boston employment centres
- RAD index of accessibility to radial highways
- TAX full-value property-tax rate per $10,000
- PTRATIO pupil-teacher ratio by town
- B 1000(Bk - 0.63)^2 where Bk is the proportion of black people by town
- LSTAT % lower status of the population
- MEDV Median value of owner-occupied homes in $1000's
:Missing Attribute Values: None
:Creator: Harrison, D. and Rubinfeld, D.L.
This is a copy of UCI ML housing dataset.
https://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/machine-learning-databases/housing/
This dataset was taken from the StatLib library which is maintained at Carnegie Mellon University.
The Boston house-price data of Harrison, D. and Rubinfeld, D.L. 'Hedonic
prices and the demand for clean air', J. Environ. Economics & Management,
vol.5, 81-102, 1978. Used in Belsley, Kuh & Welsch, 'Regression diagnostics
...', Wiley, 1980. N.B. Various transformations are used in the table on
pages 244-261 of the latter.
The Boston house-price data has been used in many machine learning papers that address regression
problems.
.. topic:: References
- Belsley, Kuh & Welsch, 'Regression diagnostics: Identifying Influential Data and Sources of Collinearity', Wiley, 1980. 244-261.
- Quinlan,R. (1993). Combining Instance-Based and Model-Based Learning. In Proceedings on the Tenth International Conference of Machine Learning, 236-243, University of Massachusetts, Amherst. Morgan Kaufmann.
x_train ,x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(x, y ,train_size = 0.7, random_state=233)from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsRegressorknn_reg = KNeighborsRegressor(n_neighbors=5, weights='distance', p=2)knn_reg.fit(x_train, y_train)KNeighborsRegressor
KNeighborsRegressor(weights='distance')
knn_reg.score(x_test, y_test)0.49308828546554706
归一化
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScalerstandardScaler = StandardScaler()standardScaler.fit(x_train)StandardScaler
StandardScaler()
x_train = standardScaler.transform(x_train)x_test = standardScaler.transform(x_test)knn_reg.fit(x_train, y_train)KNeighborsRegressor
KNeighborsRegressor(weights='distance')
knn_reg.score(x_test, y_test)0.8315777292735131
代码参考于
Chapter-04/4-7 特征归一化.ipynb · 梗直哥/Machine-Learning - Gitee.com