哈夫曼树
完整可编译运行代码见:Github::Data-Structures-Algorithms-and-Applications/_29huffmanTree
定长编码与可变长编码
定长编码
每个字符都用固定长度的编码来表示。
例如假设一个文本是由字符 a、u、x 和 z 组成的字符串,每个字符用2位二进制来编码(00=a,01=x,10=u,11=z)。利用此编码方法,字符串aaxuaxz的编码为00000110000111。解码时,从左到右,每次从编码中提取2位数字通过编码表翻译,便可获得原字符串。
可变长编码
字符存在不同长度的编码。 哈夫曼编码是一种可变长编码。
在字符串 aaxuaxz 中,a 出现 3 次。一个符号出现的次数称为频率(frequency)。符号 a、x、u、z在这个字符串中出现的频率分别是3、2、1、1。当不同字符出现的频率有很大差别时,我们可以通过可变长编码来缩短编码串的长度。
例如,如果使用编码(0=a,10=x,110=u,111=z),则aaxuaxz的编码为0010110010111,编码串长度是13位,比原来的14位要稍短一些。当不同字符的出现频率相差更大时,编码串的长度差别就会更明显。如果4个字符的频率分别为(996,2,1,1),则每个字符用2位编码所得到编码串长度为2000位,而用可变长编码所得到编码串长度仅为1006位。
为了保证正确解码,要求编码时没有任何一个代码是另一个代码的前缀。
可以使用二叉树来实现可变长编码,从根到外部节点的路径可用来编码,用0表示向左子树移动一步,用1表示向右子树移动一步。由于路径是从根节点到叶子节点,因此没有一个路径编码是另一个路径编码的前缀。
编码位串长度
可以对字符a,b,…,f编码。令S是由这些字符组成的字符串,F(x)是字符 x 的出现频率,其中 x 属于集合{a,s,c,d,e,f}。若利用这些代码对 S 进行编码,则编码位串的长度:
2
∗
F
(
a
)
+
3
∗
F
(
b
)
+
3
∗
F
(
c
)
+
3
∗
F
(
d
)
+
3
∗
F
(
e
)
+
2
∗
F
(
f
)
2*F(a)+3*F(b)+3*F(c)+3*F(d)+3*F(e)+2*F(f)
2∗F(a)+3∗F(b)+3∗F(c)+3∗F(d)+3∗F(e)+2∗F(f)
对于一颗有n个外部节点的二叉树,且外部节点标记为1,…, n,则对应的位串长度为:
W
E
P
=
∑
i
=
1
n
L
(
i
)
∗
F
(
i
)
WEP = \sum_{i=1}^nL(i) * F(i)
WEP=i=1∑nL(i)∗F(i)
其中L(i)从根到外部节点i的路径长度(即路径的边数);WEP是二叉树的加权外部路径长度(weighted external path length)。为了缩短编码串的长度,必须使用二叉树代码,二叉树的外部节点与要编码的字符串的字符对应,且WEP最小。一棵二叉树,如果对一组给定的频率,其 WEP 最小,那么这棵二叉树称为霍夫曼树(Huffman tree)。
哈夫曼编码
哈夫曼编码的流程:
1)确定字符串的符号和它们出现的频率。
2)建立霍夫曼树,其中外部节点用字符串中的符号表示,外部节点的权用相应符号的频率表示。
3)沿着从根到外部节点的路径遍历,取得每个符号的代码。
4)用代码替代字符串中的符号。
为了便于解码,需要保存从符号到代码的映射表或每个符号的频率表。
构造霍夫曼树的过程是,首先建立一组二叉树集合,每棵二叉树仅含一个外部节点,每个外部节点代表字符串的一个符号,其权等于该符号的频率。然后,不断从集合中选择两棵权最小的二叉树,把它们合并成一棵新的二叉树,合并方法是增加一个根节点,把这两棵二叉树分别作为左右子树。新二叉树的权是两棵子树的权之和。这个过程一直持续到仅剩下一棵树为止。
举例如图所示:
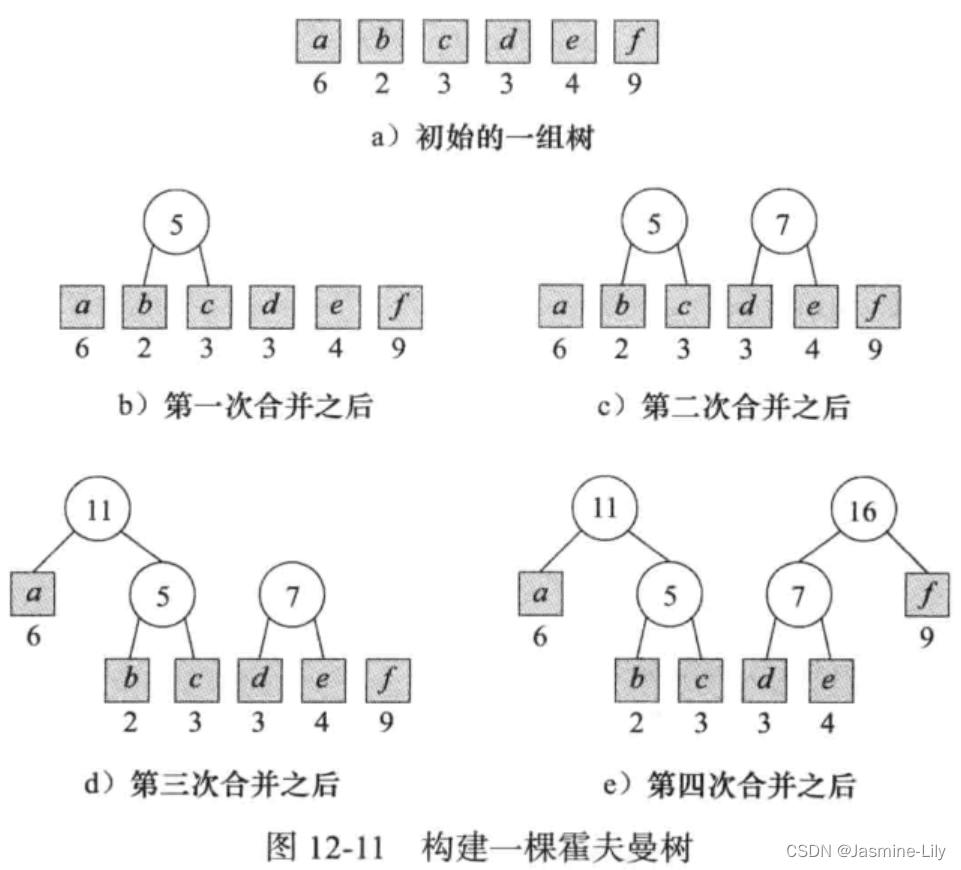
构建哈夫曼树
main.cpp
/*
Project name : allAlgorithmsTest
Last modified Date: 2023年12月15日21点59分
Last Version: V1.0
Descriptions: 哈夫曼树的构建函数与main函数
*/
#include "_28binaryTreeChains.h"
#include "huffmanNode.h"
template <class T>
binaryTreeChains<int>* huffmanTree(T weight[], int n)
{
// 建立一个二叉树集合,每个节点的weight为weight[i],tree为element为i,左右子树为空的树
vector<huffmanNode<T>> hNode(n);
binaryTreeChains<int> emptyTree;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
hNode[i-1].weight = weight[i-1];
hNode[i-1].tree = new binaryTreeChains<int>;
hNode[i-1].tree->makeTree(i, emptyTree, emptyTree);
}
// 将节点存储为一个小根堆
std::priority_queue<huffmanNode<T>, std::vector<huffmanNode<T>>, std::greater<>> heap(hNode.begin(),
hNode.end());
// 从小根堆里面不断合并树
// 直到小根堆里只有一颗树
huffmanNode<T> w, x, y;
binaryTreeChains<int> *z;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
// 从小根堆取出两个元素
x = heap.top(); heap.pop();
y = heap.top(); heap.pop();
// 将两棵树合并为一颗树
z = new binaryTreeChains<int>;
z->makeTree(0, *x.tree, *y.tree);
w.weight = x.weight + y.weight;
w.tree = z;
heap.push(w);
delete x.tree;
delete y.tree;
}
// 返回小根堆里的最后一颗树
return heap.top().tree;
}
int main()
{
int a[5];
int n = 5;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
a[i-1] = 2 * i;
binaryTreeChains<int> *x = huffmanTree(a, n);
x->postOrderOutput();
x->preOrderOutput();
x->inOrderOutput();
return 0;
}
huffmanNode.h
/*
Project name : allAlgorithmsTest
Last modified Date: 2023年12月15日21点59分
Last Version: V1.0
Descriptions: 哈夫曼树的结点结构体
*/
#ifndef _29HUFFMANTREE_HUFFMANNODE_H
#define _29HUFFMANTREE_HUFFMANNODE_H
#include "_28binaryTreeChains.h"
template<class T>
struct huffmanNode
{
binaryTreeChains<int> *tree{};// 对于外部节点,element域的值是它所表示的符号,对于内部节点,element域的值是0。
T weight;// 表示符号出现的频率
huffmanNode(){weight = 0;}
explicit huffmanNode(T pweight){weight = pweight;}
operator T () const {return weight;}
bool operator>(const huffmanNode &a) const { return weight > a.weight; }
};
#endif //_29HUFFMANTREE_HUFFMANNODE_H
_28binaryTreeChains.h
/*
Project name : allAlgorithmsTest
Last modified Date: 2022年8月27日09点44分
Last Version: V1.0
Descriptions: 用链表表示的二叉树.h
笔记:
1.静态函数指针初始化格式:void (*binaryTreeChains<E>::visit)(binaryTreeNode<E>*) = 0;
2.不能单独专门化成员模板函数,只能针对整个类专门化。
3.在模板函数中可以使用typeid()区别对待特定数据类型。
本程序注意事项:
1.所有关于前缀、后缀、中缀表达式的全部使用了char类型代表元素,char类型数组存储整个表达式
*/
#pragma once
#ifndef _BINARYTREECHAINS_H_
#define _BINARYTREECHAINS_H_
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <cstring>
#include <stack>
#include <queue>
#include "_1myExceptions.h"
#include "_28binaryTreeNode.h"
#include "_28binaryTree.h"
using namespace std;
template<class E>
class binaryTreeChains : public binaryTree<binaryTreeNode<E>>
{
public:
/*二叉树的基础成员函数*/
/*构造函数函数*/
binaryTreeChains() {
root = nullptr; treeSize = 0;
}
/*练习44:编写类linkedBinaryTree的一个复制构造函数。测试代码。*/
/* 计算时间复杂性。复制构造函数*/
binaryTreeChains(binaryTreeChains<E>& m) {
root = treeCreateTree(m.root);
}
/*练习题33和练习题35*/
/*构造函数---先序和中序遍历或后序和中序创建二叉树*/
/*flag == false时,是先序和中序遍历构建二叉树;flag == true时,是后序和中序构建二叉树*/
binaryTreeChains(E preOrPostOrder[], E inOrder[],int length,bool flag)
{
if(flag == false)
root = preInCreateTree(preOrPostOrder, inOrder, length);
else
root = postInCreateTree(preOrPostOrder, inOrder, length);
}
/*构造函数---前缀或后缀或中缀表达式创建二叉树*/
/*
练习37:当flag = 1时,前缀表达式创建二叉树
当flag = 2时,中缀表达式创建二叉树
练习36:当flag = 3时,后缀表达式创建二叉树
*/
binaryTreeChains(E expression[], int length,int flag)
{
switch (flag)
{
case 1:
root = preExprCreateTree(expression, length);
break;
case 2:
root = inExprCreateTree(expression, length);
break;
case 3:
root = postExprCreateTree(expression, length);
break;
}
}
/*析构函数*/
~binaryTreeChains() { erase(); }
/*当树为空时,返回true;否则,返回false*/
bool empty() const { return treeSize == 0; }
/*返回元素个数*/
int size() const { return treeSize; }
/*前序遍历二叉树,使用函数指针的目的是是的本函数可以实现多种目的*/
void preOrder(void(*theVisit)(binaryTreeNode<E>*))
{
visit = theVisit;
/*是因为递归,所以才要这样的*/
preOrder(root);/*这里调用的是成员函数,preOrder()*/
}
/*前序遍历---输出endl*/
void preOrderOutput() { preOrder(output); cout << endl; }
/*前序遍历---不使用递归而使用迭代函数*/
vector<E> iterativePreOrder();
/*中序遍历二叉树,使用函数指针的目的是是的本函数可以实现多种目的*/
void inOrder(void(*theVisit)(binaryTreeNode<E>*))
{
visit = theVisit;
/*是因为递归,所以才要这样的*/
inOrder(root);/*这里调用的是静态成员函数inOrder()*/
}
/*中序遍历---输出endl*/
void inOrderOutput() { inOrder(output); cout << endl; }
/*中序遍历---不使用递归而使用迭代函数*/
vector<E> iterativeInOrder();
/*后续遍历二叉树,使用函数指针的目的是是的本函数可以实现多种目的*/
void postOrder(void(*theVisit)(binaryTreeNode<E>*))
{
visit = theVisit;
/*是因为递归,所以才要这样的*/
postOrder(root);/*这里调用的是静态成员函数inOrder()*/
}
/*后序遍历---输出endl*/
void postOrderOutput() { postOrder(output); cout << endl; }
/*后序遍历---不使用递归而使用迭代函数*/
vector<E> iterativePostOrder();
/*层次遍历二叉树*/
void levelOrder(void (*theVisit)(binaryTreeNode<E>*));
/*层次遍历---输出endl*/
void levelOrderOutput() { levelOrder(output); cout << endl; }
/*清空二叉树 这里必须使用后序遍历 不然会出错*/
void erase()
{
postOrder(dispose);
root = nullptr;
treeSize = 0;
}
/*输入时为了将root根节点传递给createBiTree()函数*/
void input(void)
{
createBiTree(root);
}
/*是一个手动创建二叉树的函数,使用本函数得手动设置各节点之间的关系,见信号放大器应用的使用*/
/*将左数和右数合并为一个树(也就是this树)*/
void makeTree(const E& element, binaryTreeChains<E>&, binaryTreeChains<E>&);
/*练习45:比较二叉树*this和二叉树m*/
bool compare(binaryTreeChains<E>& m)
{
return compareTree(root, m.root);
}
/*练习46:交换每一个结点的左右子树*/
void swapTrees()
{
swapTrees(root);
}
/*练习27:计算二叉树高度*/
int height() const { return height(root); }
/*练习47:计算二叉树的最大高度差*/
int maxHeightDifference()
{
return maxHeightDifference(root);
}
/*练习29:计算二叉树在那一层具有最多的结点---返回值为结点最多的层*/
int layerMaxNumOfNode();
/*计算二叉树在在哪一层具有最多的结点--返回值为结点最多的层的结点数量*/
int maxNumOfNodeInLayer();
/*二叉树表达式的成员函数*/
/*计算树的表达式的值*/
int compulateTree()
{
return compulateTree(root);
}
private:
/*二叉树基础私有成员*/
binaryTreeNode<E>* root;//指向根的指针
int treeSize;//树的结点个数
static void (*visit)(binaryTreeNode<E>*);//是一个函数指针,返回值为void 函数参数为binaryTreeNode<E>*
static void preOrder(binaryTreeNode<E>* t);
static void inOrder(binaryTreeNode<E>* t);
static void postOrder(binaryTreeNode<E>* t);
static void dispose(binaryTreeNode<E>* t) { delete t; }
static void output(binaryTreeNode<E>* t) { cout << t->element << " "; }
/*创建二叉树---递归---作为私有成员只能被成员函数调用*/
void createBiTree(binaryTreeNode<E>*& tree);
/*复制构造函数调用的函数*/
binaryTreeNode<E>* treeCreateTree(binaryTreeNode<E>*& node);
/*私有成员函数---用于比较二叉树compare()*/
bool compareTree(binaryTreeNode<E>* thisNode, binaryTreeNode<E>* xNode);
/*私有成员函数---交换树的每个结点的左右子树---递归*/
void swapTrees(binaryTreeNode<E>*& node);
/*私有成员函数---计算二叉树高度---返回根为node的树的高度*/
int height(binaryTreeNode<E>* node) const;
/*私有成员函数---计算结点node的左右子树高度的差值*/
int heightDifference(binaryTreeNode<E>* node) const;
/*私有成员函数---计算二叉树的最大高度差---返回值为二叉树的最大高度差*/
int maxHeightDifference(binaryTreeNode<E>* node) const;
binaryTreeNode<E>* preInCreateTree(E preOrder[], E inOrder[], int size);
binaryTreeNode<E>* postInCreateTree(E postOrder[], E inOrder[], int size);
/*二叉树表达式的私有成员*/
/*计算树的表达式的值*/
/*本程序所有关于前缀、中缀、后缀表达式的处理全部是char类型,并且只能进行个位数的计算*/
int compulateTree(binaryTreeNode<E>* node) const;
binaryTreeNode<E>* preExprCreateTree(E expression[], int length);
binaryTreeNode<E>* inExprCreateTree(E expression[], int length);
binaryTreeNode<E>* postExprCreateTree(E expression[], int length);
};
/*私有静态成员初始化*/
/*这里是静态函数指针成员的初始化,不初始化会引发LINK错误*/
template<class E>
void (*binaryTreeChains<E>::visit)(binaryTreeNode<E>*) = 0; // visit function
/*二叉树的普通成员函数*/
/*前序遍历 递归*/
template<class E>
void binaryTreeChains<E>::preOrder(binaryTreeNode<E>* t)
{
if (t != nullptr)
{
visit(t);/*访问树根*/
preOrder(t->leftChild);/*前序遍历左子树*/
preOrder(t->rightChild);/*前序遍历右子树*/
}
}
/*前序遍历---不使用递归而使用迭代函数*/
template<class E>
vector<E> binaryTreeChains<E>::iterativePreOrder()
{
binaryTreeNode<E>* currentNode = root;
stack<binaryTreeNode<E>*> st;
vector<E> result;
/*写法1---前序中序后序遍历非递归统一版*/
/*首先将父节点入栈*/
if (currentNode != nullptr)
st.push(currentNode);
while (!st.empty())
{
currentNode = st.top();
st.pop();
/*如果遇到nullptr,则输出当前栈顶元素*/
if (currentNode == nullptr)
{
result.push_back(st.top()->element);
st.pop();
}
/*如果没有遇到nullptr,则按照右左中的顺序入栈结点,最后入栈nullptr*/
else
{
if (currentNode->rightChild != nullptr)
st.push(currentNode->rightChild);
if (currentNode->leftChild != nullptr)
st.push(currentNode->leftChild);
st.push(currentNode);
/*每次都在已遍历的根节点后入栈nullptr*/
st.push(nullptr);
}
}
///*写法2*/
///*当结点为nullptr并且栈为空时结束循环*/
//while (currentNode != nullptr || !st.empty())
//{
// /*先将左边的左边的元素入栈*/
// while (currentNode != nullptr)
// {
// st.push(currentNode);
// result.push_back(currentNode->element);
// currentNode = currentNode->leftChild;
// }
// /*然后一个一个遍历左边的元素,并将该元素存储到vector中*/
// currentNode = st.top();
// st.pop();
// currentNode = currentNode->rightChild;
//}
return result;
}
/*中序遍历 递归*/
template<class E>
void binaryTreeChains<E>::inOrder(binaryTreeNode<E>* t)
{
if (t != nullptr)
{
inOrder(t->leftChild);/*中序遍历左子树*/
visit(t);/*访问树根*/
inOrder(t->rightChild);/*中序遍历右子树*/
}
}
/*中序遍历---不使用递归而使用迭代函数*/
template<class E>
vector<E> binaryTreeChains<E>::iterativeInOrder()
{
binaryTreeNode<E>* currentNode = root;
stack<binaryTreeNode<E>*> st;
vector<E> result;
/*写法1---前序中序后序遍历非递归统一版*/
/*首先将父节点入栈*/
if (currentNode != nullptr)
st.push(currentNode);
while (!st.empty())
{
currentNode = st.top();
st.pop();
/*如果遇到nullptr,则输出当前栈顶元素*/
if (currentNode == nullptr)
{
result.push_back(st.top()->element);
st.pop();
}
/*如果没有遇到nullptr,则按照右左中的顺序入栈结点,最后入栈nullptr*/
else
{
if (currentNode->rightChild != nullptr)
st.push(currentNode->rightChild);
st.push(currentNode);
/*每次都在已遍历的根节点后入栈nullptr*/
st.push(nullptr);
if (currentNode->leftChild != nullptr)
st.push(currentNode->leftChild);
}
}
/*写法2*/
///*当结点为nullptr并且栈为空时结束循环*/
//while (currentNode != nullptr || !st.empty())
//{
// /*先将左边的左边的元素入栈*/
// while (currentNode != nullptr)
// {
// st.push(currentNode);
// currentNode = currentNode->leftChild;
// }
// /*然后一个一个遍历左边的元素,并将该元素存储到vector中*/
// currentNode = st.top();
// st.pop();
// result.push_back(currentNode->element);
// currentNode = currentNode->rightChild;
//}
return result;
}
/*后序遍历 递归*/
template<class E>
void binaryTreeChains<E>::postOrder(binaryTreeNode<E>* t)
{
if (t != nullptr)
{
postOrder(t->leftChild);/*后序遍历左子树*/
postOrder(t->rightChild);/*后序遍历右子树*/
visit(t);/*访问树根*/
}
}
/*后序遍历---不使用递归而使用迭代函数*/
template<class E>
vector<E> binaryTreeChains<E>::iterativePostOrder()
{
binaryTreeNode<E>* currentNode = root;
stack<binaryTreeNode<E>*> st;
vector<E> result;
/*前序中序后序遍历非递归统一版*/
/*首先将父节点入栈*/
if (currentNode != nullptr)
st.push(currentNode);
while (!st.empty())
{
currentNode = st.top();
st.pop();
/*如果遇到nullptr,则输出当前栈顶元素*/
if (currentNode == nullptr)
{
result.push_back(st.top()->element);
st.pop();
}
/*如果没有遇到nullptr,则按照右左中的顺序入栈结点,最后入栈nullptr*/
else
{
st.push(currentNode);
/*每次都在已遍历的根节点后入栈nullptr*/
st.push(nullptr);
if (currentNode->rightChild != nullptr)
st.push(currentNode->rightChild);
if (currentNode->leftChild != nullptr)
st.push(currentNode->leftChild);
}
}
return result;
}
/*层次遍历二叉树 非递归*/
template<class E>
void binaryTreeChains<E>::levelOrder(void (*theVisit)(binaryTreeNode<E>*))
{
visit = theVisit;
binaryTreeNode<E>* temp;
queue<binaryTreeNode<E>*> que;
que.push(root);
while (!que.empty())
{
temp = que.front();
que.pop();
visit(temp);
if (temp->leftChild != nullptr)
que.push(temp->leftChild);
if (temp->rightChild != nullptr)
que.push(temp->rightChild);
}
}
/*创建二叉树---递归---模板的实现*/
template<class E>
void binaryTreeChains<E>::createBiTree(binaryTreeNode<E>*& tree)
{
E data;
cout << "Please enter the tree element:";
while (!(cin >> data))
{
cin.clear();//清空标志位
while (cin.get() != '\n')//删除无效的输入
continue;
cout << "Please enter the tree element:";
}
cin.get();
/*针对char类型的特例*/
if (typeid(data) == typeid(char)) {
if (data == '#')
tree = nullptr;
else {
treeSize++;
tree = new binaryTreeNode<E>(data);
createBiTree(tree->leftChild);
createBiTree(tree->rightChild);
}
/*关于二叉树对于设置信号放大器的应用我新定义了成员函数maketree()生成二叉树
这里会报错:C2228“.degradeFromParent”的左边必须有类/结构/联合
我实在是不知道怎么改
*/
//else if (typeid(data) == typeid(booster))
// if (data.degradeFromParent == 999)
// tree = nullptr;
// else
// {
// treeSize++;
// tree = new binaryTreeNode<E>(data);
// createBiTree(tree->leftChild);
// createBiTree(tree->rightChild);
// }
}
else/*针对其他类型*/{
if (data == 999)
tree = nullptr;//当遇到999时,令树的根节点为nullptr,从而结束该分支的递归
else
{
treeSize++;
tree = new binaryTreeNode<E>(data);
createBiTree(tree->leftChild);
createBiTree(tree->rightChild);
}
}
}
/*是一个手动创建二叉树的函数,使用本函数得手动设置各节点之间的关系,见信号放大器应用的使用*/
/*将左树和右树合并为一个树*/
template<class E>
void binaryTreeChains<E>::makeTree(const E& element, binaryTreeChains<E>& left, binaryTreeChains<E>& right)
{// Combine left, right, and element to make new tree.
// left, right, and this must be different trees.
// create combined tree
root = new binaryTreeNode<E>(element, left.root, right.root);
treeSize = left.treeSize + right.treeSize + 1;
// deny access from trees left and right
left.root = right.root = NULL;
left.treeSize = right.treeSize = 0;
}
/*练习24:根据二叉树创建二叉树---用于复制构造函数*/
template<class E>
binaryTreeNode<E>* binaryTreeChains<E>::treeCreateTree(binaryTreeNode<E>*& node)
{
binaryTreeNode<E>* head = nullptr;
if (node != nullptr)
{
treeSize++;
// cout << "node->element = " << node->element << endl;
head = new binaryTreeNode<E>(node->element);
head->leftChild = treeCreateTree(node->leftChild);
head->rightChild = treeCreateTree(node->rightChild);
}
return head;
}
/*练习45:私有成员函数---用于比较二叉树compare()*/
template<class E>
bool binaryTreeChains<E>::compareTree(binaryTreeNode<E>* thisNode, binaryTreeNode<E>* xNode)
{
/*两个结点都为空时,二叉树相等*/
if (thisNode == nullptr && xNode == nullptr)
return true;
/*一个结点为空,一个结点非空,则二叉树不相等*/
if ((thisNode == nullptr && xNode != nullptr) || (thisNode != nullptr && xNode == nullptr))
return false;
/*两个结点的元素不等,则二叉树不相等*/
if (thisNode->element != xNode->element)
return false;
else/*两个结点相等,则比较彼此的左子树和右子树*/
return compareTree(thisNode->leftChild, xNode->leftChild) && compareTree(thisNode->rightChild, xNode->rightChild);
}
/*练习46:私有成员函数---交换树的每个结点的左右子树---递归*/
template<class E>
void binaryTreeChains<E>::swapTrees(binaryTreeNode<E>*& node)
{
if (node != nullptr)
{
swapTrees(node->leftChild);
swapTrees(node->rightChild);
binaryTreeNode<E>* temp = node->leftChild;
node->leftChild = node->rightChild;
node->rightChild = temp;
}
}
/*练习27:私有成员函数---计算二叉树高度---返回根为node的树的高度*/
template<class E>
int binaryTreeChains<E>::height(binaryTreeNode<E>* node) const
{
if (node == nullptr)
return 0;
int hl = height(node->leftChild);
int hr = height(node ->rightChild);
if (hl > hr)
return ++hl;
else
return ++hr;
}
/*私有成员函数---计算结点node的左右子树高度的差值*/
template<class E>
int binaryTreeChains<E>::heightDifference(binaryTreeNode<E>* node) const
{
if (node == nullptr)
return 0;
int lh = height(node->leftChild);
int rh = height(node->rightChild);
// cout << node->element << ":" << lh << endl;
// cout << node->element << ":" << rh << endl;
if (lh > rh)
return lh - rh;
else
return rh - lh;
}
/*练习47:私有成员函数---计算二叉树的最大高度差---返回值为二叉树的最大高度差*/
template<class E>
int binaryTreeChains<E>::maxHeightDifference(binaryTreeNode<E>* node) const
{
if (node == nullptr)
return 0;
int height = heightDifference(node);//当前结点的左右子树的高度差
int hl = maxHeightDifference(node->leftChild);//当前结点的左子树的左右子树的高度差
int hr = maxHeightDifference(node->rightChild);//当前结点的右子树的左右子树的高度差
if (height >= hl && height >= hr)
return height;
else if (hl >= height && hl >= hr)
return hl;
else if (hr >= height && hr >= hl)
return hr;
}
/*练习29:计算二叉树在那一层具有最多的结点---返回值为结点最多的层*/
/*当二叉树为空时,返回0*/
template<class E>
int binaryTreeChains<E>::layerMaxNumOfNode()
{
if (root == nullptr)
return 0;
int num = 0;//累加每层的结点数
int layer = 0;//记录当前的层数
int maxNum = 0;//存储结点最多的层的结点个数
int maxLayer = 0;//存储结点最多的层的层数
binaryTreeNode<E>* lastNode = root;//存储上一层最后一个结点的元素位置
binaryTreeNode<E>* nextNode = nullptr;//存储当前层最后一个结点的元素位置
binaryTreeNode<E>* currentNode;
queue<binaryTreeNode<E>*> que;
que.push(root);
while (!que.empty())
{
currentNode = que.front();
que.pop();
num++;
if (currentNode->leftChild != nullptr)
{
que.push(currentNode->leftChild);
nextNode = currentNode->leftChild;
}
if (currentNode->rightChild != nullptr)
{
que.push(currentNode->rightChild);
nextNode = currentNode->rightChild;
}
if (currentNode == lastNode)
{
layer++;//刚刚处理完第几层
lastNode = nextNode;
nextNode = nullptr;
if (num > maxNum)
{
maxNum = num;
maxLayer = layer;
}
num = 0;
}
}
return maxLayer;
}
/*计算二叉树在在哪一层具有最多的结点--返回值为结点最多的层的结点数量*/
/*当二叉树为空时,返回0*/
template<class E>
int binaryTreeChains<E>::maxNumOfNodeInLayer()
{
if (root == nullptr)
return 0;
int num = 0;//累加每层的结点数
int layer = 0;//记录当前的层数
int maxNum = 0;//存储结点最多的层的结点个数
int maxLayer = 0;//存储结点最多的层的层数
binaryTreeNode<E>* lastNode = root;//存储上一层最后一个结点的元素位置
binaryTreeNode<E>* nextNode = nullptr;//存储当前层最后一个结点的元素位置
binaryTreeNode<E>* currentNode = nullptr;
queue<binaryTreeNode<E>*> que;
que.push(root);
while (!que.empty())
{
currentNode = que.front();
que.pop();
num++;
if (currentNode->leftChild != nullptr)
{
que.push(currentNode->leftChild);
nextNode = currentNode->leftChild;
}
if (currentNode->rightChild != nullptr)
{
que.push(currentNode->rightChild);
nextNode = currentNode->rightChild;
}
if (currentNode == lastNode)
{
layer++;//刚刚处理完第几层
lastNode = nextNode;
nextNode = nullptr;
if (num > maxNum)
{
maxNum = num;
maxLayer = layer;
}
num = 0;
}
}
return maxNum;
}
/*使用前序和中序遍历构建二叉树*/
/*关键点在于找到根节点在中序中的位置,该位置之前为该根的左子树,该位置之后为该根的右子树*/
template<class E>
binaryTreeNode<E>* binaryTreeChains<E>::preInCreateTree(E preOrder[], E inOrder[], int size)
{
/*如果没有左右子树,则返回nullptr*/
if (size == 0)
return nullptr;
binaryTreeNode<E>* rootData = new binaryTreeNode<E>(preOrder[0]);
/*找到根节点的位置,中序中该位置左侧就是该根节点的左子树,该位置右侧就是该根节点的右子树*/
int rootLoc = findRootLoc<E>(inOrder, preOrder[0] ,size);
/*创建左子树和右子树*/
rootData->leftChild = preInCreateTree(preOrder + 1, inOrder, rootLoc);
rootData->rightChild = preInCreateTree(preOrder + 1 + rootLoc, inOrder + rootLoc + 1, size - 1 - rootLoc);
return rootData;
}
/*使用后序和中序遍历构建二叉树*/
/*关键点在于找到根节点在中序中的位置,该位置之前为该根的左子树,该位置之后为该根的右子树*/
template<class E>
binaryTreeNode<E>* binaryTreeChains<E>::postInCreateTree(E postOrder[], E inOrder[], int size)
{
/*如果没有左右子树,则返回nullptr*/
if (size == 0)
return nullptr;
binaryTreeNode<E>* rootData = new binaryTreeNode<E>(postOrder[size-1]);
/*找到根节点的位置,中序中该位置左侧就是该根节点的左子树,该位置右侧就是该根节点的右子树*/
int rootLoc = findRootLoc<E>(inOrder, postOrder[size-1], size);
/*创建左子树和右子树*/
rootData->leftChild = postInCreateTree(postOrder, inOrder, rootLoc);
rootData->rightChild = postInCreateTree(postOrder + rootLoc, inOrder + rootLoc + 1, size - 1 - rootLoc);
return rootData;
}
/*二叉树表达式的成员函数*/
/*计算树的表达式的值*/
/*用字符串记录表达式*/
/*这个函数需要使用char类型的树,其他类型的二叉树不满足要求*/
template<class E>
int binaryTreeChains<E>::compulateTree(binaryTreeNode<E>* node) const
{
if (node == nullptr)
return 0;
if (node->leftChild == nullptr && node->rightChild == nullptr) //左右子树都是nullptr时,说明它是叶子节点,而叶子结点就是数而非符号
return node->element - '0';//就返回叶子结点
int a = compulateTree(node->leftChild);//先计算左子树
int b = compulateTree(node->rightChild);//再计算右子树
switch (node->element)//当前结点不是叶子节点时,说明他是符号结点
{
case '+':
return a + b;
case '-':
return a - b;
case '*':
return a * b;
case '/':
if (b != 0)
return a / b;
else
throw illegalParameterValue("除数不能为0!");
}
}
/*使用全部是二元操作符的前缀表达式创建二叉树*/
/*从尾元素开始遍历表达式的元素*/
/*如果是数据,则生成binaryTreeNode并入栈*/
/*如果不是数据,则生成binaryTreeNode,从栈中弹出两个数据形成其子树,第一个弹出的是其左子树,第二个弹出的是其右子树;然后再将当前结点入栈*/
template<class E>
binaryTreeNode<E>* binaryTreeChains<E>::preExprCreateTree(E expression[],int length)
{
stack<binaryTreeNode<E>*> st;//用于存储已经处理的数据生成的binaryTreeNode
binaryTreeNode<E>* temp = nullptr;
for (int i = length-1; i >= 0; i--)
{
/*如果是数据,则生成二叉树结点入栈*/
if (expression[i] >= '0' && expression[i] <= '9')
{
temp = new binaryTreeNode<E>(expression[i]);
st.push(temp);
}
else
{
temp = new binaryTreeNode<E>(expression[i]);
temp->leftChild = st.top();
st.pop();
temp->rightChild = st.top();
st.pop();
st.push(temp);
}
}
return temp;
}
/*使用全部是二元操作符的中缀表达式(包含括号以表明优先级)创建二叉树*/
/*如果是数据,则生成binaryTreeNode并入数据栈*/
/*
操作符处理规则:
如果当前操作符优先级大于操作符栈的顶部元素,直接入操作符栈
如果当前操作符优先级小于或等于操作符栈的顶部元素,先将顶部元素出操作符栈再将当前操作符入操作符栈
当前操作符为左括号时直接入栈
当前操作符为右括号时,让栈顶到左括号为止的操作符出操作符栈,括号不出现在后缀表达式中
出操作符栈时:生成当前符号的binaryTreeNode,其右子树为数据栈的栈顶元素,数据栈顶元素出栈,其左子树为数据栈当前的栈顶元素,数据栈顶元素出栈;
当前符号binaryTreeNode入数据栈。
*/
/*获取操作符优先级的getPriority()函数是一个非成员函数*/
template<class E>
binaryTreeNode<E>* binaryTreeChains<E>::inExprCreateTree(E expression[], int length)
{
stack<binaryTreeNode<E>*> st;//用于存储已经处理的数据生成的binaryTreeNode
stack<E> opStack;
binaryTreeNode<E>* temp = nullptr;
E data;
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++)
{
data = expression[i];
/*如果是数据,则生成二叉树结点入栈*/
if (data >= '0' && data <= '9')
{
temp = new binaryTreeNode<E>(data);
st.push(temp);
}
else
{
if (opStack.empty())
opStack.push(data);
else
switch (data)
{
case '(':opStack.push(data); break;//当遇到左括号时,直接将其入栈
case ')'://当遇到右括号时,让栈顶到左括号的操作符出栈
while (opStack.top() != '(')
{
temp = new binaryTreeNode<E>(opStack.top());
opStack.pop();
temp->rightChild = st.top();
st.pop();
temp->leftChild = st.top();
st.pop();
st.push(temp);
}
opStack.pop();//让(出栈
break;
/*当遇到+ - * /时,当其优先级大于栈顶元素时,入栈;否则,先将栈顶元素出栈,再将当前元素入栈*/
case '+':
case '-':
case '*':
case '/':
if (getPriority(data) > getPriority(opStack.top()))
opStack.push(data);
else
{
temp = new binaryTreeNode<E>(opStack.top());
opStack.pop();
temp->rightChild = st.top();
st.pop();
temp->leftChild = st.top();
st.pop();
st.push(temp);
}
break;
default:break;
}
/*当检查到中缀表达式的最后一个元素且栈非空时,将栈中的元素全部输出到后缀表达式*/
if (!opStack.empty() && i == length - 1)
while (!opStack.empty())
{
temp = new binaryTreeNode<E>(opStack.top());
opStack.pop();
temp->rightChild = st.top();
st.pop();
temp->leftChild = st.top();
st.pop();
st.push(temp);
}
}
}
return temp;
}
/*使用全部是二元操作符的后缀表达式创建二叉树*/
/*从首元素开始遍历表达式的元素*/
/*如果是数据,则生成binaryTreeNode并入栈*/
/*如果不是数据,则生成binaryTreeNode,从栈中弹出两个数据形成其子树,第一个弹出的是其右子树,第二个弹出的是其左子树;然后再将当前结点入栈*/
template<class E>
binaryTreeNode<E>* binaryTreeChains<E>::postExprCreateTree(E expression[], int length)
{
stack<binaryTreeNode<E>*> st;//用于存储已经处理的数据生成的binaryTreeNode
binaryTreeNode<E>* temp = nullptr;
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++)
{
/*如果是数据,则生成二叉树结点入栈*/
if (expression[i] >= '0' && expression[i] <= '9')
{
temp = new binaryTreeNode<E>(expression[i]);
st.push(temp);
}
else
{
temp = new binaryTreeNode<E>(expression[i]);
temp->rightChild = st.top();
st.pop();
temp->leftChild = st.top();
st.pop();
st.push(temp);
}
}
return temp;
}
#endif
_28binaryTree.h
/*
Project name : allAlgorithmsTest
Last modified Date: 2022年8月27日09点43分
Last Version: V1.0
Descriptions: 二叉树的抽象类
*/
#pragma once
#ifndef _BINARYTREE_H_
#define _BINARYTREE_H_
template<class T>
class binaryTree
{
public:
virtual ~binaryTree() {}
virtual bool empty() const = 0;
virtual int size() const = 0;
virtual void preOrder(void (*)(T*)) = 0;
virtual void inOrder(void (*)(T*)) = 0;
virtual void postOrder(void (*)(T*)) = 0;
virtual void levelOrder(void (*)(T*)) = 0;
};
#endif
_28binaryTreeNode.h
/*
Project name : allAlgorithmsTest
Last modified Date: 2022年8月27日09点44分
Last Version: V1.0
Descriptions: 二叉树的结点结构体
*/
#pragma once
#ifndef _BINARYTREENODE_H_
#define _BINARYTREENODE_H_
template<class T>
struct binaryTreeNode
{
T element;
binaryTreeNode<T>* leftChild,//左子树
*rightChild;//右子树
/*默认构造函数*/
binaryTreeNode() { leftChild = rightChild = nullptr; }
/*只初始化element*/
binaryTreeNode(T melement)
{
element = melement;
leftChild = rightChild = nullptr;
}
/*三个元素都初始化*/
binaryTreeNode(T melement, binaryTreeNode<T>* mleftChild, binaryTreeNode<T>* mrightChild)
{
element = melement;
leftChild = mleftChild;
rightChild = mrightChild;
}
};
#endif
_1myExceptions.h
/*
Project name : allAlgorithmsTest
Last modified Date: 2022年8月13日17点38分
Last Version: V1.0
Descriptions: 综合各种异常
*/
#pragma once
#ifndef _MYEXCEPTIONS_H_
#define _MYEXCEPTIONS_H_
#include <string>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
// illegal parameter value
class illegalParameterValue
{
public:
illegalParameterValue(string theMessage = "Illegal parameter value")
{message = theMessage;}
void outputMessage() {cout << message << endl;}
private:
string message;
};
// illegal input data
class illegalInputData
{
public:
illegalInputData(string theMessage = "Illegal data input")
{message = theMessage;}
void outputMessage() {cout << message << endl;}
private:
string message;
};
// illegal index
class illegalIndex
{
public:
illegalIndex(string theMessage = "Illegal index")
{message = theMessage;}
void outputMessage() {cout << message << endl;}
private:
string message;
};
// matrix index out of bounds
class matrixIndexOutOfBounds
{
public:
matrixIndexOutOfBounds
(string theMessage = "Matrix index out of bounds")
{message = theMessage;}
void outputMessage() {cout << message << endl;}
private:
string message;
};
// matrix size mismatch
class matrixSizeMismatch
{
public:
matrixSizeMismatch(string theMessage =
"The size of the two matrics doesn't match")
{message = theMessage;}
void outputMessage() {cout << message << endl;}
private:
string message;
};
// stack is empty
class stackEmpty
{
public:
stackEmpty(string theMessage =
"Invalid operation on empty stack")
{message = theMessage;}
void outputMessage() {cout << message << endl;}
private:
string message;
};
// queue is empty
class queueEmpty
{
public:
queueEmpty(string theMessage =
"Invalid operation on empty queue")
{message = theMessage;}
void outputMessage() {cout << message << endl;}
private:
string message;
};
// hash table is full
class hashTableFull
{
public:
hashTableFull(string theMessage =
"The hash table is full")
{message = theMessage;}
void outputMessage() {cout << message << endl;}
private:
string message;
};
// edge weight undefined
class undefinedEdgeWeight
{
public:
undefinedEdgeWeight(string theMessage =
"No edge weights defined")
{message = theMessage;}
void outputMessage() {cout << message << endl;}
private:
string message;
};
// method undefined
class undefinedMethod
{
public:
undefinedMethod(string theMessage =
"This method is undefined")
{message = theMessage;}
void outputMessage() {cout << message << endl;}
private:
string message;
};
#endif
运行结果
"C:\Users\15495\Documents\Jasmine\prj\_Algorithm\Data Structures, Algorithms and Applications in C++\_29huffmanTree\cmake-build-debug\_29huffmanTree.exe"
3 1 2 0 0 4 5 0 0
0 0 3 0 1 2 0 4 5
3 0 1 0 2 0 4 0 5
Process finished with exit code 0
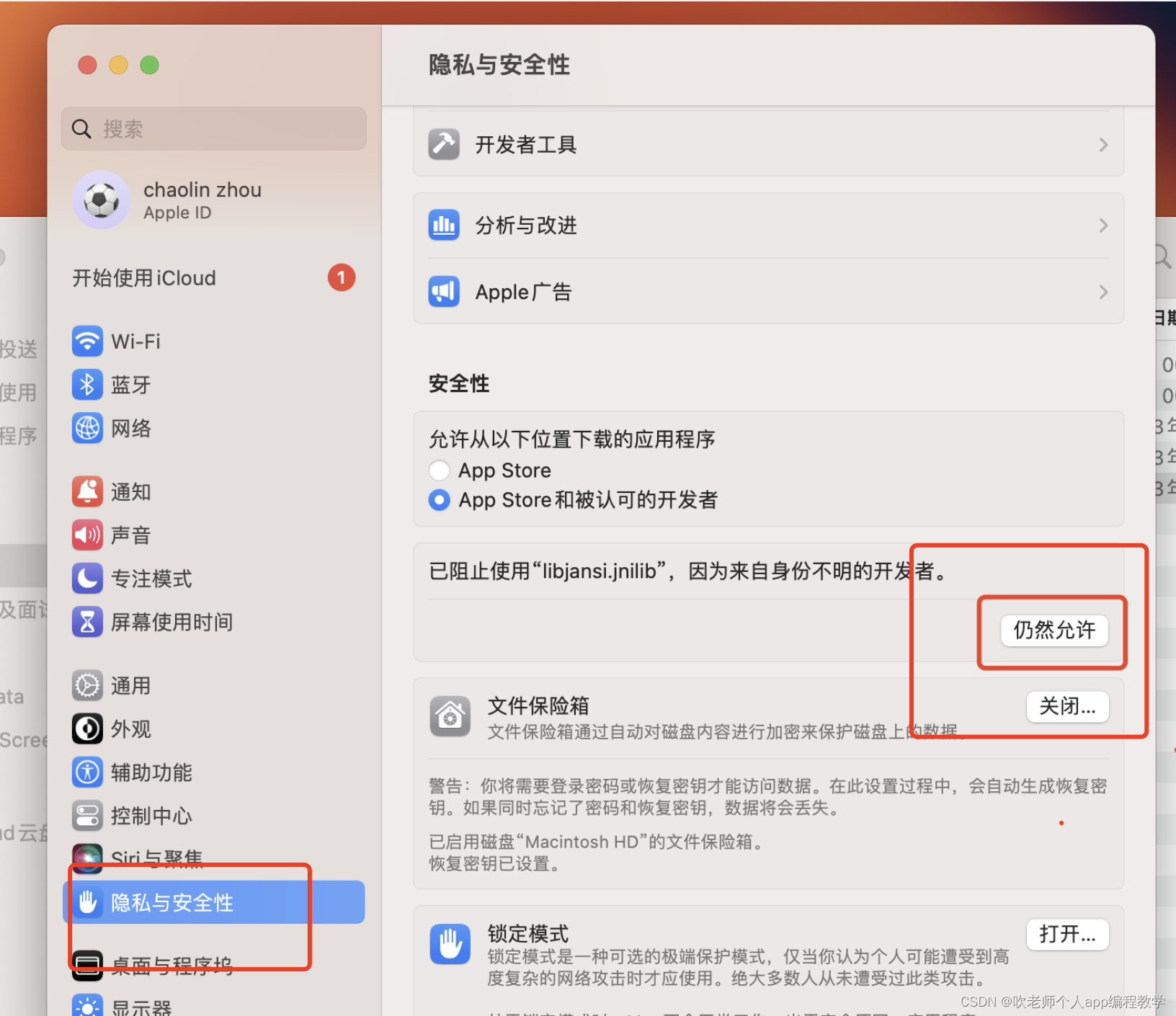
![Docker单点部署 Elasticsearch + Kibana [8.11.3]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/cf9f7b935fb145f09c0ebd8e5bd67b5a.png)

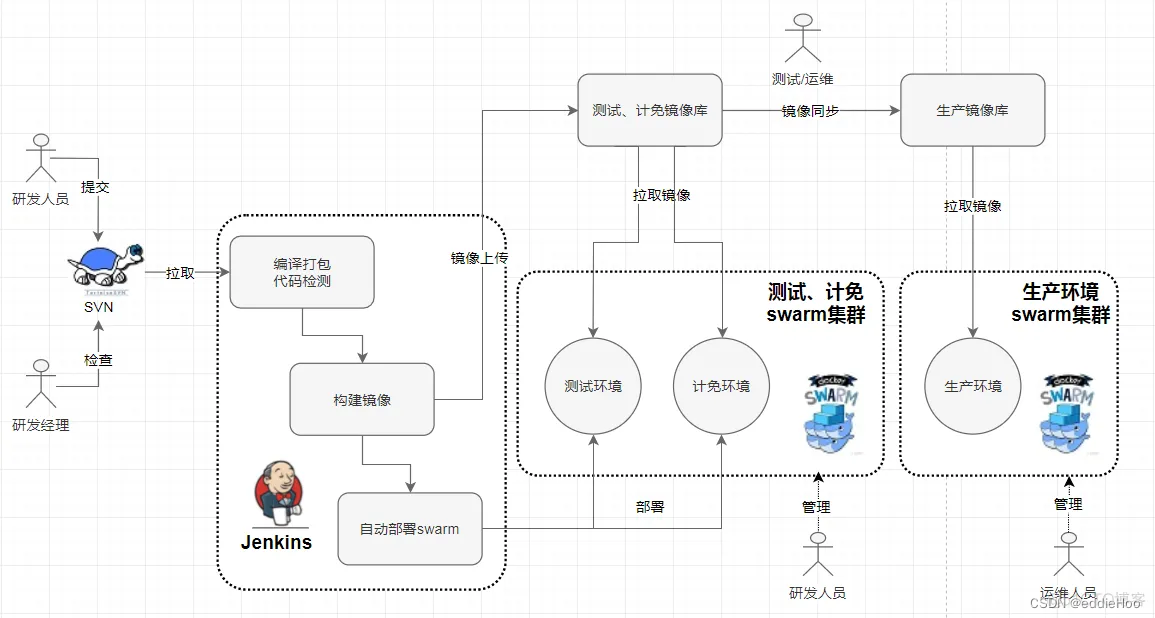
![[C++]——学习模板](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/2ef4dbd63a494421b92781cea6d97744.png)


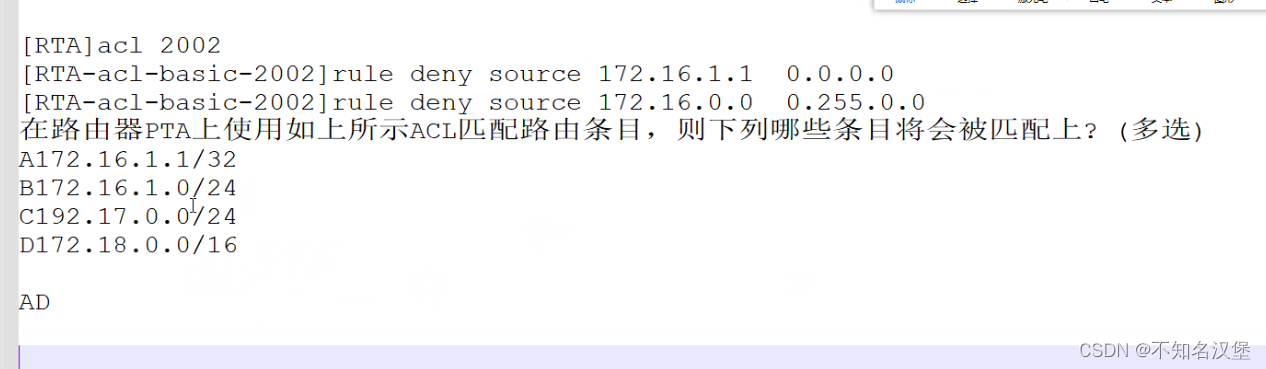
![[Linux] Tomcat部署和优化](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/9c26e3cd316c4dd9be598b71c237d84d.png)