【深度学习】AlexNet网络实现猫狗分类
AlexNet简介
AlexNet是一种卷积神经网络(Convolutional Neural Network,CNN)模型,它在2012年的ImageNet图像分类挑战赛中取得了重大突破,引发了深度学习在计算机视觉领域的热潮。下面是对AlexNet模型和CNN模型的关系以及原理的解释:
- AlexNet模型是一种CNN模型:
-
AlexNet是一种典型的卷积神经网络模型,它由多个卷积层、池化层和全连接层组成,通过这些层的堆叠和组合来提取图像的特征并进行分类。
-
CNN模型的原理:
-
CNN是一种专门用于处理具有网格结构的数据(如图像)的深度学习模型。它通过卷积层和池化层来提取图像的局部特征,并通过全连接层进行分类。
-
卷积层通过卷积操作对输入图像进行特征提取,通过滑动一个卷积核(filter)在图像上进行局部特征的提取,生成特征图(feature map)。
-
池化层通过降采样操作减小特征图的尺寸,并保留主要的特征信息。
-
全连接层将池化层输出的特征图转换为一维向量,并通过全连接神经网络进行分类。
3.AlexNet模型的原理:
- AlexNet模型是由Alex Krizhevsky等人提出的,它在CNN模型的基础上进行了一些创新和改进。
- AlexNet模型的网络结构包括多个卷积层、池化层和全连接层,其中使用了ReLU激活函数来增强非线性特性。
4.AlexNet模型的特点包括:
-
使用多个卷积层和池化层进行特征提取,通过堆叠多个卷积层来逐渐提取更高级别的特征。
-
使用了局部响应归一化(Local Response Normalization)层来增强模型的泛化能力。
-
使用了Dropout层来减少过拟合。
-
使用了大规模的训练数据和数据增强技术来提高模型的性能。
-
AlexNet模型在ImageNet图像分类挑战赛中取得了显著的成绩,为后续的深度学习模型的发展奠定了基础。
总结来说,AlexNet模型是一种经典的CNN模型,它通过卷积层、池化层和全连接层来提取图像的特征并进行分类。AlexNet模型在深度学习的发展中起到了重要的作用,对后续的CNN模型设计和图像分类任务产生了深远的影响。
代码:
1.导入所需的库:
torch:PyTorch库,用于构建和训练神经网络模型。
torch.nn:PyTorch的神经网络模块,包含了构建神经网络所需的类和函数。
torch.optim:PyTorch的优化器模块,包含了各种优化算法。
torchvision.transforms:PyTorch的图像转换模块,用于对图像进行预处理。
warnings:Python的警告模块,用于忽略警告信息。
torch.utils.data:PyTorch的数据加载模块,用于加载和处理数据。
torchvision.datasets:PyTorch的数据集模块,包含了常用的图像数据集。
torchvision.models:PyTorch的预训练模型模块,包含了一些经典的神经网络模型。
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
import torchvision.transforms as transforms
import warnings
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
from torchvision.datasets import ImageFolder
from torchvision.models import alexnet
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei'] # 用来正常显示中文标签
2.数据预处理并加载数据:
# 检查是否有可用的GPU
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
print(device)
#cuda显卡
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
# 数据预处理
transform = transforms.Compose([
transforms.Resize((224, 224)),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize((0.5, 0.5, 0.5), (0.5, 0.5, 0.5))
])
# 加载训练数据和测试数据
train_dataset = ImageFolder("dataset/train", transform=transform)
train_loader = DataLoader(train_dataset, batch_size=32, shuffle=True)
test_dataset = ImageFolder("dataset/test", transform=transform)
test_loader = DataLoader(test_dataset, batch_size=32, shuffle=False)
通过torch.cuda.is_available()函数判断是否有可用的GPU,并将设备设置为’cuda’或’cpu’。
使用torchvision.transforms.Compose函数定义了一系列的图像转换操作,包括调整大小、转换为张量、归一化等。
使用torchvision.datasets.ImageFolder类加载训练数据集和测试数据集,并应用之前定义的数据预处理操作。
使用torch.utils.data.DataLoader类将数据集包装成可迭代的数据加载器,设置批量大小和是否打乱数据。
3.定义AlexNet模型:
# 定义AlexNet模型
class AlexNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_classes=2):
super(AlexNet, self).__init__()
self.features = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(3, 64, kernel_size=11, stride=4, padding=2),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2),
nn.Conv2d(64, 192, kernel_size=5, padding=2),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2),
nn.Conv2d(192, 384, kernel_size=3, padding=1),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(384, 256, kernel_size=3, padding=1),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=3, padding=1),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2),
)
self.avgpool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((6, 6))
self.classifier = nn.Sequential(
nn.Dropout(),
nn.Linear(256 * 6 * 6, 4096),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Dropout(),
nn.Linear(4096, 4096),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Linear(4096, num_classes),
)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.features(x)
x = self.avgpool(x)
x = torch.flatten(x, 1)
x = self.classifier(x)
return x
model = AlexNet()
# 将模型移动到GPU上
model = model.to(device)
创建一个继承自torch.nn.Module的子类AlexNet,其中包含了AlexNet模型的网络结构和前向传播方法。
网络结构包括卷积层、ReLU激活函数、最大池化层和全连接层。
通过self.features定义了卷积层和池化层的结构,通过self.classifier定义了全连接层的结构。
前向传播方法将输入数据经过卷积层、池化层、全连接层等操作,得到输出结果。
创建一个AlexNet模型的实例对象model。
使用model.to(device)将模型移动到之前检查的可用设备上。
4.定义损失函数和优化器:
# 定义损失函数和优化器
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.001, momentum=0.9)
定义交叉熵损失函数nn.CrossEntropyLoss()。
定义随机梯度下降优化器optim.SGD,设置学习率和动量。
5.定义学习率调度器:
# 定义学习率调度器
scheduler = optim.lr_scheduler.StepLR(optimizer, step_size=5, gamma=0.1)
使用optim.lr_scheduler.StepLR定义学习率调度器,设置学习率衰减的步长和衰减因子。
6.训练模型:
# 训练模型
epochs = 10 # 修改为您想要的训练轮数
train_loss_list = []
train_acc_list = []
test_acc_list = []
for epoch in range(epochs):
running_loss = 0.0
correct = 0
total = 0
for images, labels in train_loader:
images = images.to(device)
labels = labels.to(device)
optimizer.zero_grad()
outputs = model(images)
loss = criterion(outputs, labels)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
running_loss += loss.item()
_, predicted = torch.max(outputs.data, 1)
total += labels.size(0)
correct += (predicted == labels).sum().item()
train_accuracy = correct / total
train_loss = running_loss / len(train_loader)
train_loss_list.append(train_loss)
train_acc_list.append(train_accuracy)
# 测试模型
correct = 0
total = 0
with torch.no_grad():
for images, labels in test_loader:
images = images.to(device)
labels = labels.to(device)
outputs = model(images)
_, predicted = torch.max(outputs.data, 1)
total += labels.size(0)
correct += (predicted == labels).sum().item()
test_accuracy = correct / total
test_acc_list.append(test_accuracy)
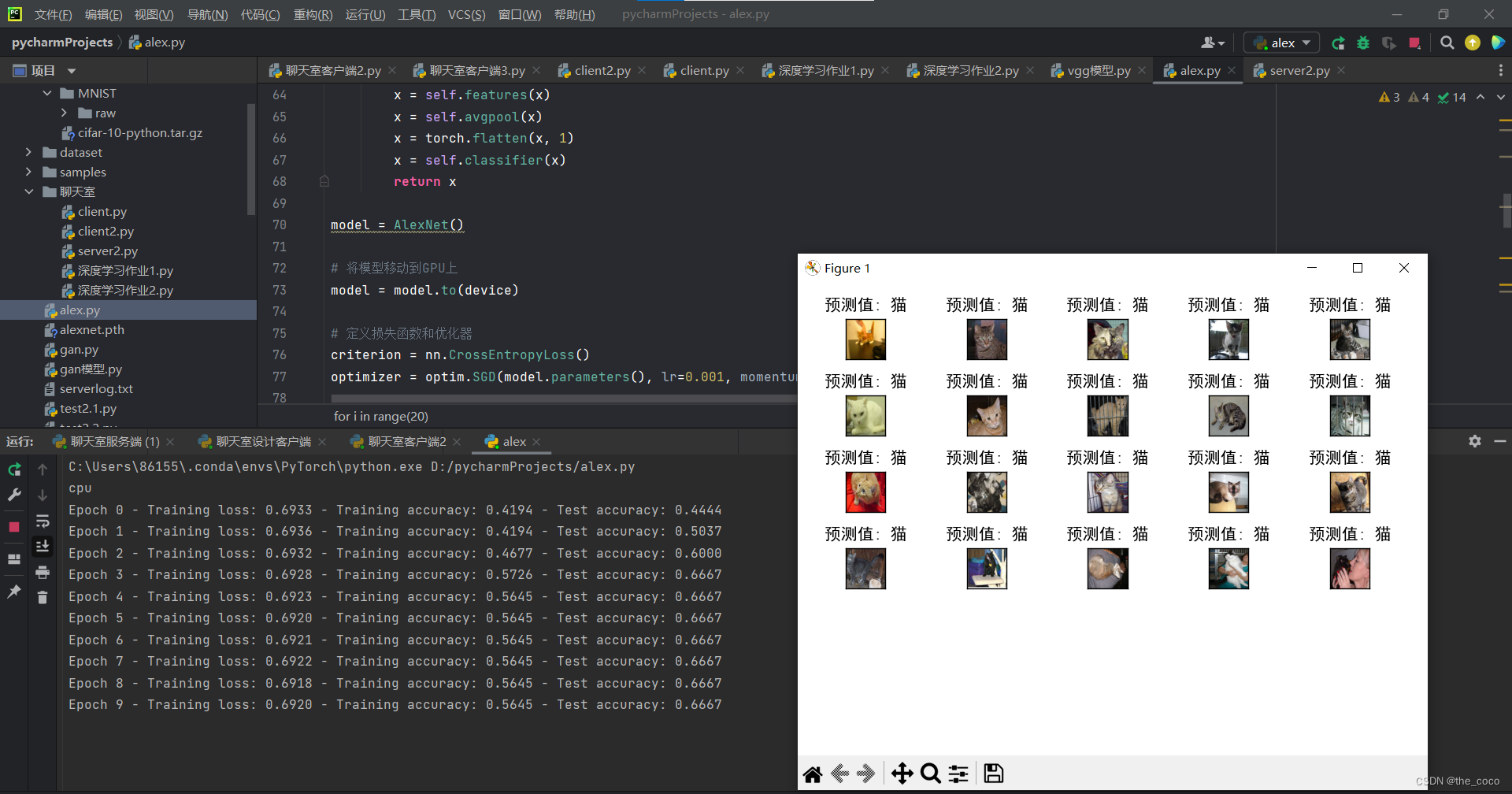
print("Epoch {} - Training loss: {:.4f} - Training accuracy: {:.4f} - Test accuracy: {:.4f}".format(epoch, train_loss, train_accuracy, test_accuracy))
# 更新学习率
scheduler.step()
使用range(epochs)循环进行指定轮数的训练。
在每个epoch中,遍历训练数据集,将数据移动到设备上,通过前向传播计算输出,计算损失并进行反向传播和优化。
计算训练集的准确率和损失,并将其记录在列表中。
在每个epoch结束后,使用测试数据集评估模型的准确率,并将其记录在列表中。
打印每个epoch的训练损失、训练准确率和测试准确率。
使用学习率调度器更新学习率。
7.保存模型:
# 保存模型
torch.save(model.state_dict(), "alexnet.pth")
8.加载预训练的模型参数:
model.load_state_dict(torch.load('alexnet.pth'))
9.将模型移动到CPU上进行预测:
model = model.to('cpu')
10.可视化预测结果:
examples = enumerate(test_loader)
_, (imgs, _) = next(examples)
fig = plt.figure()
# for i in range(len(imgs)):
for i in range(20):
img = imgs[i].numpy()
img = img.transpose(1, 2, 0)
img = (img + 1) / 2
with torch.no_grad():
output = model(torch.unsqueeze(imgs[i], 0))
_, predicted = torch.max(output.data, 1)
if predicted.item() == 0:
pre_value = "狗"
else:
pre_value = "猫"
plt.subplot(6, 5, i + 1)
###########################
plt.tight_layout()
plt.imshow(img)
plt.title("预测值: {}".format(pre_value))
plt.xticks([])
plt.yticks([])
plt.show()
从测试数据集中获取一批图像数据。
对每个图像进行预测,并将预测结果和图像可视化展示出来。
运行结果:
 注:数据集可以更换为自己的数据集
注:数据集可以更换为自己的数据集
完整代码:
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
import torchvision.transforms as transforms
import warnings
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
from torchvision.datasets import ImageFolder
from torchvision.models import alexnet
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei'] # 用来正常显示中文标签
# 检查是否有可用的GPU
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
print(device)
#cuda显卡
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
# 数据预处理
transform = transforms.Compose([
transforms.Resize((224, 224)),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize((0.5, 0.5, 0.5), (0.5, 0.5, 0.5))
])
# 加载训练数据和测试数据
train_dataset = ImageFolder("dataset/train", transform=transform)
train_loader = DataLoader(train_dataset, batch_size=32, shuffle=True)
test_dataset = ImageFolder("dataset/test", transform=transform)
test_loader = DataLoader(test_dataset, batch_size=32, shuffle=False)
# 定义AlexNet模型
class AlexNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_classes=2):
super(AlexNet, self).__init__()
self.features = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(3, 64, kernel_size=11, stride=4, padding=2),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2),
nn.Conv2d(64, 192, kernel_size=5, padding=2),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2),
nn.Conv2d(192, 384, kernel_size=3, padding=1),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(384, 256, kernel_size=3, padding=1),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=3, padding=1),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2),
)
self.avgpool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((6, 6))
self.classifier = nn.Sequential(
nn.Dropout(),
nn.Linear(256 * 6 * 6, 4096),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Dropout(),
nn.Linear(4096, 4096),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Linear(4096, num_classes),
)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.features(x)
x = self.avgpool(x)
x = torch.flatten(x, 1)
x = self.classifier(x)
return x
model = AlexNet()
# 将模型移动到GPU上
model = model.to(device)
# 定义损失函数和优化器
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.001, momentum=0.9)
# 定义学习率调度器
scheduler = optim.lr_scheduler.StepLR(optimizer, step_size=5, gamma=0.1)
# 训练模型
epochs = 10 # 修改为您想要的训练轮数
train_loss_list = []
train_acc_list = []
test_acc_list = []
for epoch in range(epochs):
running_loss = 0.0
correct = 0
total = 0
for images, labels in train_loader:
images = images.to(device)
labels = labels.to(device)
optimizer.zero_grad()
outputs = model(images)
loss = criterion(outputs, labels)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
running_loss += loss.item()
_, predicted = torch.max(outputs.data, 1)
total += labels.size(0)
correct += (predicted == labels).sum().item()
train_accuracy = correct / total
train_loss = running_loss / len(train_loader)
train_loss_list.append(train_loss)
train_acc_list.append(train_accuracy)
# 测试模型
correct = 0
total = 0
with torch.no_grad():
for images, labels in test_loader:
images = images.to(device)
labels = labels.to(device)
outputs = model(images)
_, predicted = torch.max(outputs.data, 1)
total += labels.size(0)
correct += (predicted == labels).sum().item()
test_accuracy = correct / total
test_acc_list.append(test_accuracy)
print("Epoch {} - Training loss: {:.4f} - Training accuracy: {:.4f} - Test accuracy: {:.4f}".format(epoch, train_loss, train_accuracy, test_accuracy))
# 更新学习率
scheduler.step()
# 保存模型
torch.save(model.state_dict(), "alexnet.pth")
# 加载预训练的模型参数
model.load_state_dict(torch.load('alexnet.pth'))
# 将模型移动到CPU上进行预测
model = model.to('cpu')
examples = enumerate(test_loader)
_, (imgs, _) = next(examples)
fig = plt.figure()
# for i in range(len(imgs)):
for i in range(20):
img = imgs[i].numpy()
img = img.transpose(1, 2, 0)
img = (img + 1) / 2
with torch.no_grad():
output = model(torch.unsqueeze(imgs[i], 0))
_, predicted = torch.max(output.data, 1)
if predicted.item() == 0:
pre_value = "狗"
else:
pre_value = "猫"
plt.subplot(6, 5, i + 1)
###########################
plt.tight_layout()
plt.imshow(img)
plt.title("预测值: {}".format(pre_value))
plt.xticks([])
plt.yticks([])
plt.show()