目录
前言
正文
1.集合框架结构
2. ConcurrentHashMap
(1)验证 HashMap 不是线程安全的
(2)验证 Hashtable 是线程安全的
(3)验证 Hashtable 不支持并发 remove 操作
(4)验证 ConcurrentHashMap 线程安全特性
3.ConcurrentSkipListMap
4.ConcurrentSkipListSet
5.ConcurrentLinkedQueue
6.ConcurrentLinkedDeque
7.CopyOnWriteArrayList
8.CopyOnWriteArrarySet
9.SynchronousQueue
总结
前言
并发集合框架是为了在多线程环境下提供高效和线程安全的数据结构而设计的。Java 的并发集合框架提供了一组线程安全的集合类,可以在多线程应用程序中使用,以解决并发访问集合时可能出现的竞态条件和线程安全问题。
正文
对于高度并发的应用程序,使用并发集合可以显著提高性能。与传统的同步集合相比,它们提供了更高的并行度和更好的扩展性。并发集合框架中的数据结构经过优化,允许多个线程同时对其进行读写,以提高并发访问的性能。
Java 并发集合框架包括
ConcurrentHashMap、ConcurrentLinkedQueue、ConcurrentSkipListMap等。这些集合类可以在高并发读写场景中大大简化编程和提高性能。
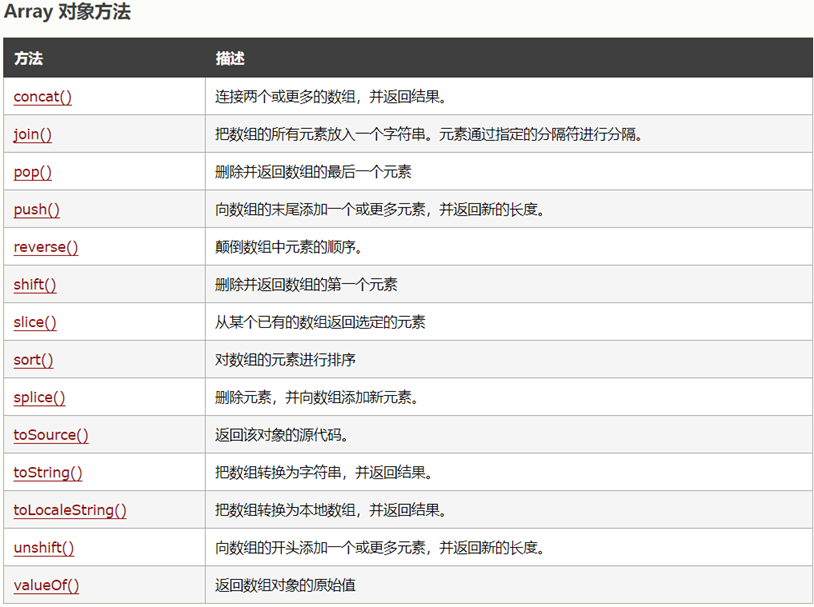
1.集合框架结构
JAVA 语言中的集合框架父接口是 Iterable,从这个接口向下一一继承就可以得到完整的 Java 集合框架结构。集合框架的继承与实现关系相当复杂,简化的集合框架接口结构如图所示:

可以发现出现 3 个继承分支(List、Set、Queue)的结构是接口 Collection,它是集合框架的主要功能抽象,另一个接口是 Map ,与集合 Collection 区分开来。虽然这些集合框架的知识点很重要,但我们主要对这些接口继续向下衍生的并发集合框架进行了解。
2. ConcurrentHashMap
类 ConcurrentHashMap 是支持并发操作的对象。
(1)验证 HashMap 不是线程安全的
创建测试用例
package org.example.Collection;
import java.util.HashMap;
public class Concurrent_HashMap {
static class MyService{
public HashMap map = new HashMap();
public void testMethod(){
for (int i = 0; i < 50000; i++) {
try {
if (!Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()) {
map.put(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" "+(i+1),Thread.currentThread().getName()+" "+(i+1));
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" "+(i+1));
}
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("Error: "+e.getMessage());
Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup().interrupt();
System.exit(0);
}
}
}
}
static class MyThread extends Thread{
private MyService service;
public MyThread(MyService service) {
this.service = service;
}
@Override
public void run() {
service.testMethod();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyService myService = new MyService();
MyThread a = new MyThread(myService);
MyThread b = new MyThread(myService);
a.start();
b.start();
}
}
运行程序结果如图:

程序运行后有很小的概率出现异常,说明 HashMap不能被多个线程操作,也就证明了 HashMap不是线程安全的。
(2)验证 Hashtable 是线程安全的
由于 HashMap 不适合在多线程的情况下使用。如果想在多线程环境中使用 key-value 的数据结构,可以使用 Hashtable 类,其内部的 put 和 get 方法都是同步的。
package org.example.Collection;
import java.util.Hashtable;
public class Concurrent_Hashtable {
static class MyService{
public Hashtable table = new Hashtable();
public void testMethod(){
for (int i = 0; i < 50000; i++) {
try {
if (!Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()) {
table.put(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" "+(i+1),Thread.currentThread().getName()+" "+(i+1));
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" "+(i+1));
}
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("Error: "+e.getMessage());
Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup().interrupt();
System.exit(0);
}
}
}
}
static class MyThread extends Thread{
private MyService service;
public MyThread(MyService service) {
this.service = service;
}
@Override
public void run() {
service.testMethod();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyService myService = new MyService();
MyThread a = new MyThread(myService);
MyThread b = new MyThread(myService);
a.start();
b.start();
}
}
运行结果如图

程序运行正确,每个线程添加 5000 个元素,说明 Hashtable 类在多线程环境中执行 put 操作不会报错,是线程安全的类。
但是,多个线程分别调用分别调用该类的 iterator() 方法返回 Iterator 对象,并调用 next() 方法取得元素,在执行 remove() 方法时会出现 ConcurrentModificationException 异常,也就是说 Hashtable 并不支持 Iterator 并发删除。
(3)验证 Hashtable 不支持并发 remove 操作
新建测试用例
package org.example.Collection;
import java.util.Hashtable;
import java.util.Iterator;
public class Concurrent_Hashtable {
static class MyService {
public Hashtable table = new Hashtable();
public MyService() {
for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {
table.put(Thread.currentThread().getName() + i + 1, "abc");
}
}
public void testMethod() {
Iterator iterator = table.keySet().iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()){
try {
Object object = iterator.next();
iterator.remove();
System.out.println(table.size()+" "+Thread.currentThread().getName());
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.exit(0);
}
}
}
}
static class MyThread extends Thread {
private MyService service;
public MyThread(MyService service) {
this.service = service;
}
@Override
public void run() {
service.testMethod();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyService myService = new MyService();
MyThread a = new MyThread(myService);
MyThread b = new MyThread(myService);
a.start();
b.start();
}
}运行结果如图

程序运行后出现异常,说明 Hashtable 在获得 Iterator 对象后,不允许多个线程同时执行 remove 删除操作,否则出现 java.util.ConcurrentModificationException 异常。
根据上面的测试可以分析出,Hashtable 类支持多线程环境下的 put 添加操作,却不支持 remove 删除操作,但 ConcurrentHashMap 支持这两个操作。
(4)验证 ConcurrentHashMap 线程安全特性
ConcurrentHashMap 是 JDK 并发包中提供的支持并发操作的 Map 对象。其继承与实现信息如图。

新建测试用例
package org.example.Collection;
import java.util.Hashtable;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
public class Concurrent_HashMap {
static class MyService{
public ConcurrentHashMap map = new ConcurrentHashMap();
public void testMethod(){
for (int i = 0; i < 50000; i++) {
try {
if (!Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()) {
map.put(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" "+(i+1),Thread.currentThread().getName()+" "+(i+1));
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" "+(i+1));
}
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("Error: "+e.getMessage());
Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup().interrupt();
System.exit(0);
}
}
}
}
static class MyThread extends Thread{
private MyService service;
public MyThread(MyService service) {
this.service = service;
}
@Override
public void run() {
service.testMethod();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyService myService = new MyService();
MyThread a = new MyThread(myService);
MyThread b = new MyThread(myService);
a.start();
b.start();
}
}
运行结果如图:

此运行结果说明类 ConcurrentHashMap 支持在多线程环境中执行 put 操作。
并且支持并发 remove 操作;
package org.example.Collection;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
public class Concurrent_Hashtable {
static class MyService {
public ConcurrentHashMap map = new ConcurrentHashMap();
public MyService() {
for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {
map.put(Thread.currentThread().getName() + i + 1, "abc");
}
}
public void testMethod() {
Iterator iterator = map.keySet().iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()){
try {
Object object = iterator.next();
iterator.remove();
System.out.println(map.size()+" "+Thread.currentThread().getName());
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.exit(0);
}
}
}
}
static class MyThread extends Thread {
private MyService service;
public MyThread(MyService service) {
this.service = service;
}
@Override
public void run() {
service.testMethod();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyService myService = new MyService();
MyThread a = new MyThread(myService);
MyThread b = new MyThread(myService);
a.start();
b.start();
}
}
运行结果如图:

运行结果是成功的,说明类 ConcurrentHashMap 在功能上比 Hashtable 更完善,支持并发情况下的 put 和 remove 操作。
ConcurrentHashMap 不支持排序,LinkedHashMap 支持 key 排序,但不支持并发。那么,如果出现这种及要求并发安全,又要求排序的情况,我们就可以使用类 ConcurrentSkipListMap。
3.ConcurrentSkipListMap
ConcurrentSkipListMap 支持排序。
package org.example.Collection;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentSkipListMap;
public class Concurrent_SkipListMap {
static class Userinfo implements Comparable<Userinfo>{
private int id;
private String username;
public Userinfo(int id, String username) {
this.id = id;
this.username = username;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Userinfo o) {
if (this.getId() > o.getId()){
return 1;
}else {
return -1;
}
}
}
static class MyService{
private ConcurrentSkipListMap<Userinfo,String> map = new ConcurrentSkipListMap<>();
public MyService() {
Userinfo userinfo1 = new Userinfo(1,"userinfo1");
Userinfo userinfo3 = new Userinfo(3,"userinfo3");
Userinfo userinfo5 = new Userinfo(5,"userinfo5");
Userinfo userinfo2 = new Userinfo(2,"userinfo2");
Userinfo userinfo4 = new Userinfo(4,"Userinfo4");
map.put(userinfo1,"u1");
map.put(userinfo3,"u3");
map.put(userinfo5,"u5");
map.put(userinfo2,"u2");
map.put(userinfo4,"u4");
}
public void testMethod(){
Map.Entry<Userinfo,String> entry = map.pollFirstEntry();
System.out.println("map.size()="+map.size());
Userinfo userinfo = entry.getKey();
System.out.println(
userinfo.getId()+" "+userinfo.getUsername()+" "
+map.get(userinfo)+" "+entry.getValue()
);
}
}
static class MyThread extends Thread{
private MyService myService;
public MyThread(MyService myService) {
this.myService = myService;
}
@Override
public void run() {
myService.testMethod();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
MyService service = new MyService();
MyThread a1 = new MyThread(service);
MyThread a2 = new MyThread(service);
MyThread a3 = new MyThread(service);
MyThread a4 = new MyThread(service);
MyThread a5 = new MyThread(service);
a1.start();
Thread.sleep(1000);
a2.start();
Thread.sleep(1000);
a3.start();
Thread.sleep(1000);
a4.start();
Thread.sleep(1000);
a5.start();
}
}
运行结果如图:

控制台打印出 null 值是使用 polldFirstEntry 方法将当前的 Entry 对象从类 ConcurrentSkipListMap 中删除造成的。
4.ConcurrentSkipListSet
类 ConcurrentSkipListSet 支持排序且不允许元素重复。
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentSkipListMap;
public class Concurrent_SkipListSet {
static class Userinfo implements Comparable<Userinfo>{
private int id;
private String username;
public Userinfo() {
}
public Userinfo(int id, String username) {
this.id = id;
this.username = username;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Userinfo o) {
if (this.getId() > o.getId()){
return 1;
}else {
return -1;
}
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
final int prime = 31;
int result = 1;
result = prime* result+id;
result = prime * result +((username == null)?0:username.hashCode());
return result;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (this == obj){
return true;
}
if (obj == null){
return false;
}
if (getClass() != obj.getClass()){
return false;
}
Userinfo orther = (Userinfo) obj;
if (id != orther.id){
return false;
}
if (username == null){
if (orther.username != null){
if (orther.username != null){
return false;
}
}
}else if (!username.equals(orther.username)){
return false;
}
return true;
}
}
static class MyService{
private ConcurrentSkipListMap<Concurrent_SkipListMap.Userinfo,String> map = new ConcurrentSkipListMap<>();
public MyService() {
Concurrent_SkipListMap.Userinfo userinfo1 = new Concurrent_SkipListMap.Userinfo(1,"userinfo1");
Concurrent_SkipListMap.Userinfo userinfo3 = new Concurrent_SkipListMap.Userinfo(3,"userinfo3");
Concurrent_SkipListMap.Userinfo userinfo5 = new Concurrent_SkipListMap.Userinfo(5,"userinfo5");
Concurrent_SkipListMap.Userinfo userinfo2 = new Concurrent_SkipListMap.Userinfo(2,"userinfo2");
Concurrent_SkipListMap.Userinfo userinfo4 = new Concurrent_SkipListMap.Userinfo(4,"Userinfo4");
map.put(userinfo1,"u1");
map.put(userinfo3,"u3");
map.put(userinfo5,"u5");
map.put(userinfo2,"u2");
map.put(userinfo4,"u4");
}
public void testMethod(){
Map.Entry<Concurrent_SkipListMap.Userinfo,String> entry = map.pollFirstEntry();
System.out.println("map.size()="+map.size());
Concurrent_SkipListMap.Userinfo userinfo = entry.getKey();
System.out.println(
userinfo.getId()+" "+userinfo.getUsername()+" "
+map.get(userinfo)+" "+entry.getValue()
);
}
}
static class MyThread extends Thread{
private MyService myService;
public MyThread(MyService myService) {
this.myService = myService;
}
@Override
public void run() {
myService.testMethod();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
MyService service = new MyService();
MyThread a1 = new MyThread(service);
MyThread a2 = new MyThread(service);
MyThread a3 = new MyThread(service);
MyThread a4 = new MyThread(service);
MyThread a5 = new MyThread(service);
a1.start();
Thread.sleep(1000);
a2.start();
Thread.sleep(1000);
a3.start();
Thread.sleep(1000);
a4.start();
Thread.sleep(1000);
a5.start();
}
}运行结果如图:

从结果来看,排序成功,并且不支持重复元素。
5.ConcurrentLinkedQueue
ConcurrentLinkedQueue 提供了并发环境下的队列操作。
package org.example.Collection;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentLinkedQueue;
public class Concurrent_LinkedQueue {
static class MyService{
public ConcurrentLinkedQueue queue = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue();
}
static class MyThread extends Thread{
private MyService myService;
public MyThread(MyService myService) {
this.myService = myService;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 50; i++) {
myService.queue.add(Thread.currentThread().getName()+(i+1));
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
MyService service = new MyService();
MyThread a = new MyThread(service);
MyThread b = new MyThread(service);
a.setName("a");
b.setName("b");
a.start();
b.start();
a.join();
b.join();
System.out.println(service.queue.size());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
方法运行结果如图:

- 方法 poll() 没有获得数据时返回 null,获得数据时则移除表头,并将表头进行返回。
- 方法 element() 没有获得数据时出现 NoSuch'ElementException 异常,获得数据时则不移除表头,并将表头进行返回。
- 方法 peek() 没有获得数据时返回 null,获得数据时则不移除表头,并将表头进行返回。
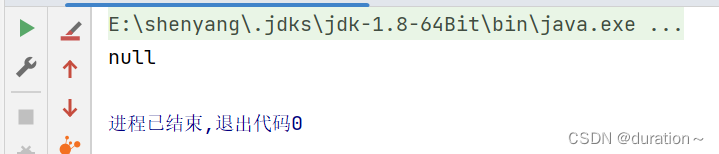
测试 main 方法 poll():
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyService service = new MyService();
System.out.println(service.queue.poll());
}运行结果如图:
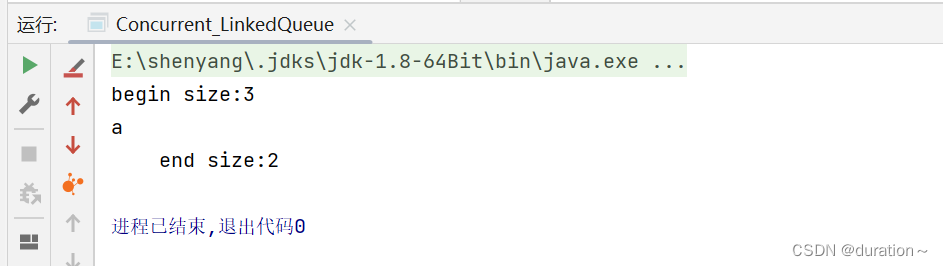
修改 main 方法 poll():
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyService service = new MyService();
service.queue.add("a");
service.queue.add("b");
service.queue.add("c");
System.out.println("begin size:" + service.queue.size());
System.out.println(service.queue.poll());
System.out.println(" end size:" + service.queue.size());
}
运行结果:
修改 main 方法 elemen():
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyService service = new MyService();
/*service.queue.add("a");
service.queue.add("b");
service.queue.add("c");*/
System.out.println("begin size:" + service.queue.size());
System.out.println(service.queue.element());
System.out.println(" end size:" + service.queue.size());
}运行结果如图:
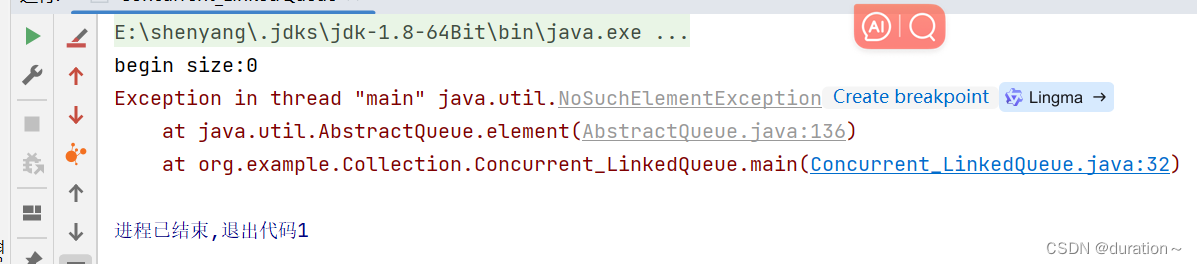
出现没有元素的异常。
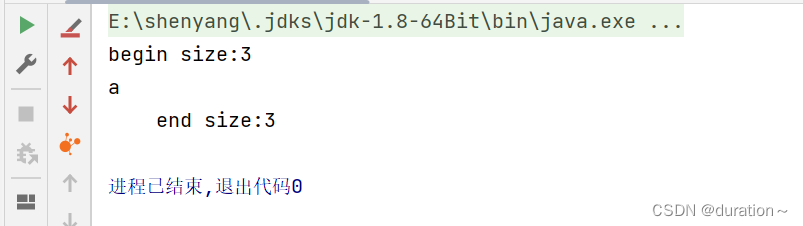
修改 main 的代码如下 elemen():
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyService service = new MyService();
service.queue.add("a");
service.queue.add("b");
service.queue.add("c");
System.out.println("begin size:" + service.queue.size());
System.out.println(service.queue.element());
System.out.println(" end size:" + service.queue.size());
}运行结果如图:

可见,打印出队列中元素的个数为 3 。
修改 main 方法如下 peek():
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyService service = new MyService();
/*service.queue.add("a");
service.queue.add("b");
service.queue.add("c");*/
System.out.println("begin size:" + service.queue.size());
System.out.println(service.queue.peek());
System.out.println(" end size:" + service.queue.size());
}运行结果如图:

修改 main 方法如下 peek():
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyService service = new MyService();
service.queue.add("a");
service.queue.add("b");
service.queue.add("c");
System.out.println("begin size:" + service.queue.size());
System.out.println(service.queue.peek());
System.out.println(" end size:" + service.queue.size());
}运行结果如图:
6.ConcurrentLinkedDeque
ConcurrentLinkedQueue 仅支持对队列头进行操作,类 ConcurrentLinkedDeque 支持对队列头和列尾双向进行操作。
创建测试用例:
package org.example.Collection;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentLinkedDeque;
public class Concurrent_LinedQueue {
static class MyService {
public ConcurrentLinkedDeque deque = new ConcurrentLinkedDeque();
public MyService() {
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
deque.add("string" + (i + 1));
}
}
}
static class MyThreadF extends Thread {
private MyService service;
public MyThreadF(MyService service) {
this.service = service;
}
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("value=" + service.deque.pollFirst()
+ " queue.size()=" + service.deque.size());
}
}static class MyThreadL extends Thread {
private MyService service;
public MyThreadL(MyService service) {
this.service = service;
}
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("value=" + service.deque.pollLast()
+ " queue.size()=" + service.deque.size());
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
MyService service = new MyService();
MyThreadF aF = new MyThreadF(service);
MyThreadF bF = new MyThreadF(service);
MyThreadL aL = new MyThreadL(service);
MyThreadL bL = new MyThreadL(service);
aF.start();
Thread.sleep(1000);
aL.start();
Thread.sleep(1000);
bF.start();
Thread.sleep(1000);
bL.start();
}
}
运行结果如图:

可见,数据成功从列头和列尾弹出,最后队列中的元素个数为 0。
7.CopyOnWriteArrayList
由于 ArraryList 为非线程安全的。如果想在并发环境下实现线程安全,我们可以使用类 CopyOnWriteArraryList。
import java.util.concurrent.CopyOnWriteArrayList;
public class CopyOn_WriteArraryList {
static class MyService {
public static CopyOnWriteArrayList list = new CopyOnWriteArrayList();
}
static class MyThread extends Thread {
private MyService service;
public MyThread(MyService service) {
this.service = service;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
service.list.add("anyString");
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
MyService service = new MyService();
MyThread[] aArray = new MyThread[100];
for (int i = 0; i < aArray.length; i++) {
aArray[i] = new MyThread(service);
}
for (int i = 0; i < aArray.length; i++) {
aArray[i].start();
}
Thread.sleep(3000);
System.out.println(service.list.size());
System.out.println("可以随机取得的值:" + service.list.get(5));
}
}程序运行结果如下:
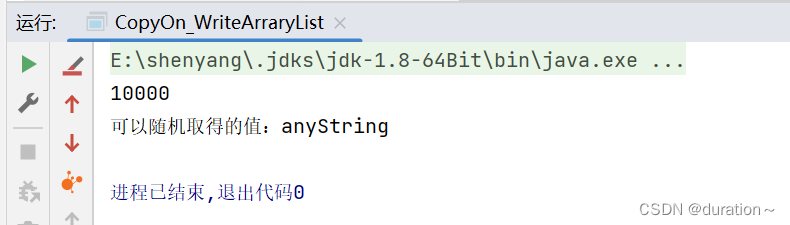
8.CopyOnWriteArrarySet
与类 CopyOnWriteArraryList 配套的还有一个类——CopyOnWriteArrarySet,它也可以解决多环境下 HashSet 不安全的问题。
package org.example.Collection;
import java.util.concurrent.CopyOnWriteArraySet;
public class CopyOn_WriteArrarySet {
static class MyService {
public static CopyOnWriteArraySet set = new CopyOnWriteArraySet();
}
static class MyThread extends Thread {
private MyService service;
public MyThread(MyService service) {
this.service = service;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
service.set.add(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"anything"+(i+1));
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
MyService service = new MyService();
MyThread[] aArray = new MyThread[100];
for (int i = 0; i < aArray.length; i++) {
aArray[i] = new MyThread(service);
}
for (int i = 0; i < aArray.length; i++) {
aArray[i].start();
}
Thread.sleep(3000);
System.out.println(service.set.size());
}
}
运行结果如下:
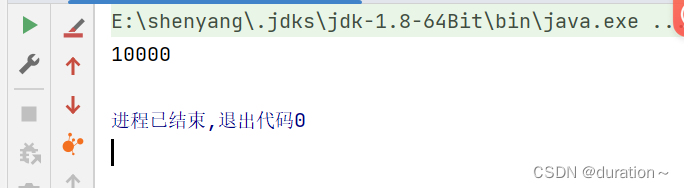
运行结果说明 100 个线程中,每个线程向队列添加100个元素,最终元素个数是正确的,呈线程安全的效果。
ConcurrentSkipListSet 是线程安全的有序集合, CopyOnWriteArrarySet 是线程安全的无序集合。我们可以将 CopyOnWriteArrarySet 理解成线程安全的 HashSet 。
9.SynchronousQueue
A blocking queue其中每个插入操作必须等待另一个线程相应的删除操作,反之亦然。 同步队列没有任何内部容量,甚至没有一个容量。 你不能peek在同步队列,因为一个元素,当您尝试删除它才存在; 您无法插入元素(使用任何方法),除非另有线程正在尝试删除它; 你不能迭代,因为没有什么可以迭代。 队列的头部是第一个排队的插入线程尝试添加到队列中的元素; 如果没有这样排队的线程,那么没有元素可用于删除,并且poll()将返回null 。 为了其他Collection方法(例如contains )的目的, SynchronousQueue充当空集合。 此队列不允许null元素。
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
SynchronousQueue queue = new SynchronousQueue();
System.out.println("step1");
queue.put("anyString");
System.out.println("step2");
System.out.println(queue.take());
System.out.println("step3");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}由于数据并没有被其他线程移走,所以此程序不能继续向下运行,运行结果如图:

新建测试用例
package org.example.Collection;
import java.util.concurrent.SynchronousQueue;
public class Sychronous_Queue {
static class MyService {
public static SynchronousQueue queue = new SynchronousQueue();
public void putMethod() {
try {
String putString = "anyString" + Math.random();
queue.put(putString);
System.out.println(" put=" + putString);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void takeMethod() {
try {
System.out.println(" take=" + queue.take());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
MyService service = new MyService();
Thread threadPut = new Thread() {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
service.putMethod();
}
}
};
Thread threadTake = new Thread() {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
service.takeMethod();
}
}
};
threadTake.start();
Thread.sleep(2000);
threadPut.start();
}
}
运行结果如图:
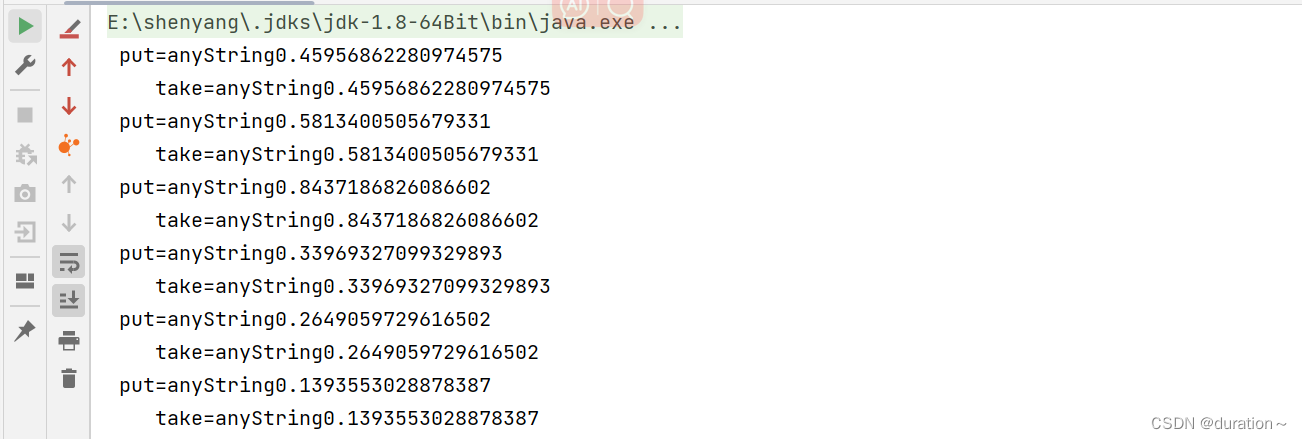
交替放入与取出。
总结
Java 的并发集合框架在多线程应用程序中具有重要的意义,它们提供了线程安全的数据结构,可以简化多线程编程并提高性能。通过选择合适的并发集合类,可以有效地处理并发访问和保证数据一致性。这样,开发人员就可以更好地利用多核处理器和并行计算能力,实现高效且安全的并发编程。