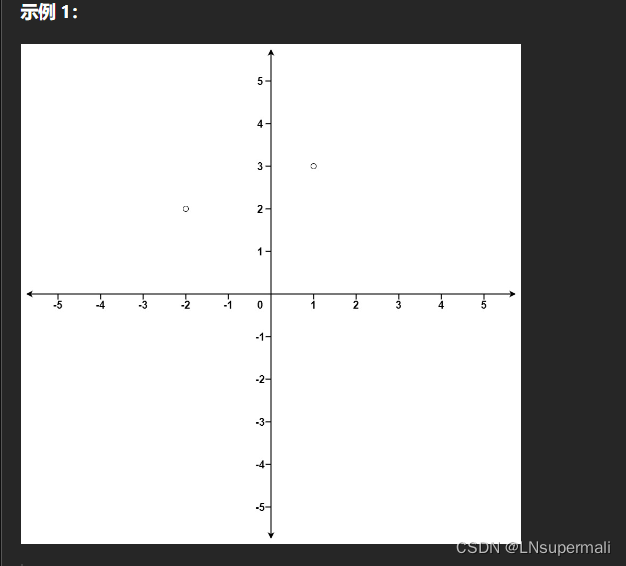
Problem: 973. 最接近原点的 K 个点
文章目录
- 题目描述
- 思路
- 解题方法
- 复杂度
- Code
题目描述
给定一个数组 points ,其中 points[i] = [xi, yi] 表示 X-Y 平面上的一个点,并且是一个整数 k ,返回离原点 (0,0) 最近的 k 个点。
这里,平面上两点之间的距离是 欧几里德距离( √(x1 - x2)2 + (y1 - y2)2 )。
你可以按 任何顺序 返回答案。除了点坐标的顺序之外,答案 确保 是 唯一 的。
思路
由于本题的数据是静态的即为了获取前TOP K我们既可以利用排序法(一般较多使用快速排序,多用于处理静态数据),也可以使用堆(多用于处理动态的数据)的解法来解决!
排序法:
我们将每个顶点距离原点的欧几里得距离排序,取出前K小的即可(实际操作中只需要对顶点坐标的坐标差的平方和排序即刻)
大顶堆解法:
1.我们创建一个大顶堆,先将前K个顶点坐标差的平方和添加进大顶堆
2.再依次计算第K + 1到N个顶点坐标差的平方和,并依次与当前大顶堆顶的元素比较,若小于当前大顶堆的堆顶元素,则更新堆顶元素为当前的顶点的坐标差的平方和
解题方法
排序法:
1.利用java内置的排序方法,并重新定义一个Comparator接口比较计算了两个点到原点的欧几里得距离的平方
2.返回前k的顶点坐标(二维数组)
大顶堆解法:
1.我们创建一个大顶堆,堆中存取一个int类型的数组,数组的下标0位置存储该顶点到原点欧几里得距离的平方,下标为1位置存储该顶点在二维数组中的一维索引
2.再依次计算第K + 1到N个顶点坐标差的平方和,并依次与当前大顶堆顶的元素比较,若小于当前大顶堆的堆顶元素,则更新堆顶元素为当前的顶点的坐标差的平方和,与该顶点在二维数组中的一维索引
3.定义二维结果数组,存储当前大顶堆的前k大个元素,并返回(具体操作看代码)
复杂度
排序法:
时间复杂度:
O ( n l o g n ) O(nlogn) O(nlogn)
空间复杂度:
O ( l o g n ) O(logn) O(logn)
大顶堆解法:
时间复杂度:
O ( n l o g k ) O(nlogk) O(nlogk)
空间复杂度:
O ( k ) O(k) O(k)
Code
排序法
class Solution {
/**
* Get the first k points closest to the origin using sort
*
* @param points Vertex coordinate array
* @param k Given number
* @return int[][]
*/
public int[][] kClosest(int[][] points, int k) {
Arrays.sort(points, new Comparator<int[]>() {
public int compare(int[] point1, int[] point2) {
return (point1[0] * point1[0] + point1[1] * point1[1]) - (point2[0] * point2[0] + point2[1] * point2[1]);
}
});
return Arrays.copyOfRange(points, 0, k);
}
}
class Solution {
/**
* Gets the first k vertices closest to the origin
*
* @param points Vertex coordinate array
* @param k Given number
* @return int[][]
*/
public int[][] kClosest(int[][] points, int k) {
//Create an maxQueue
PriorityQueue<int[]> maxQueue = new PriorityQueue<>(new Comparator<int[]>() {
@Override
public int compare(int[] o1, int[] o2) {
return o2[0] - o1[0];
}
});
//Adds the square of the Euclidean distance for the first k coordinates to the maxQueue
for (int i = 0; i < k; ++i) {
maxQueue.offer(new int[]{points[i][0] * points[i][0] + points[i][1] * points[i][1], i});
}
int n = points.length;
/*
1.Add the square of the Euclidean distance from k+1 to n vertices to the maxQueue
2.If the value is less than the value for the top of the maxQueue, its value is updated
*/
for (int i = k; i < n; ++i) {
int distance = points[i][0] * points[i][0] + points[i][1] * points[i][1];
if (distance < maxQueue.peek()[0]) {
maxQueue.poll();
maxQueue.offer(new int[]{distance, i});
}
}
int[][] result = new int[k][2];
for (int i = 0; i < k; ++i) {
result[i] = points[maxQueue.poll()[1]];
}
return result;
}
}