1、reference wrapper
例如声明如下的模板:
template <typename T>
void foo(T val);如果调用使用:
int x;
foo(std::ref(x));T变成int&,而使用调用
int x;
foo(std::cref(x));T变成const int&。
这个特性被C++标准库用在各个地方,例如:
make_pair()用此特性于是能够创建一个pair<>of reference
make_tuple()用此特性可以创建一个tuple<>of reference
std::vector<MyClass&> coll; //error
std::vector<std::reference_wrapper<MyClass>> coll; //ok2、function type wrapper
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <functional>
using namespace std;
void func(int x, int y) {
std::cout << "func" << std::endl;
}
class C {
public:
void memfunc(int x, int y) const{
std::cout << "C::memfunc" << std::endl;
}
};
int main()
{
std::vector<std::function<void(int,int)>> tasks;
tasks.push_back(func);
tasks.push_back([](int x, int y) {
std::cout << "lambda" << std::endl;
});
for (std::function<void(int,int)> f : tasks) {
f(3, 33);
}
std::function<void(const C&, int, int)> mf;
mf = &C::memfunc;
mf(C(), 2, 3);
return 0;
}
输入:
func
lambda
C::memfunc3、挑选最小值和最大值
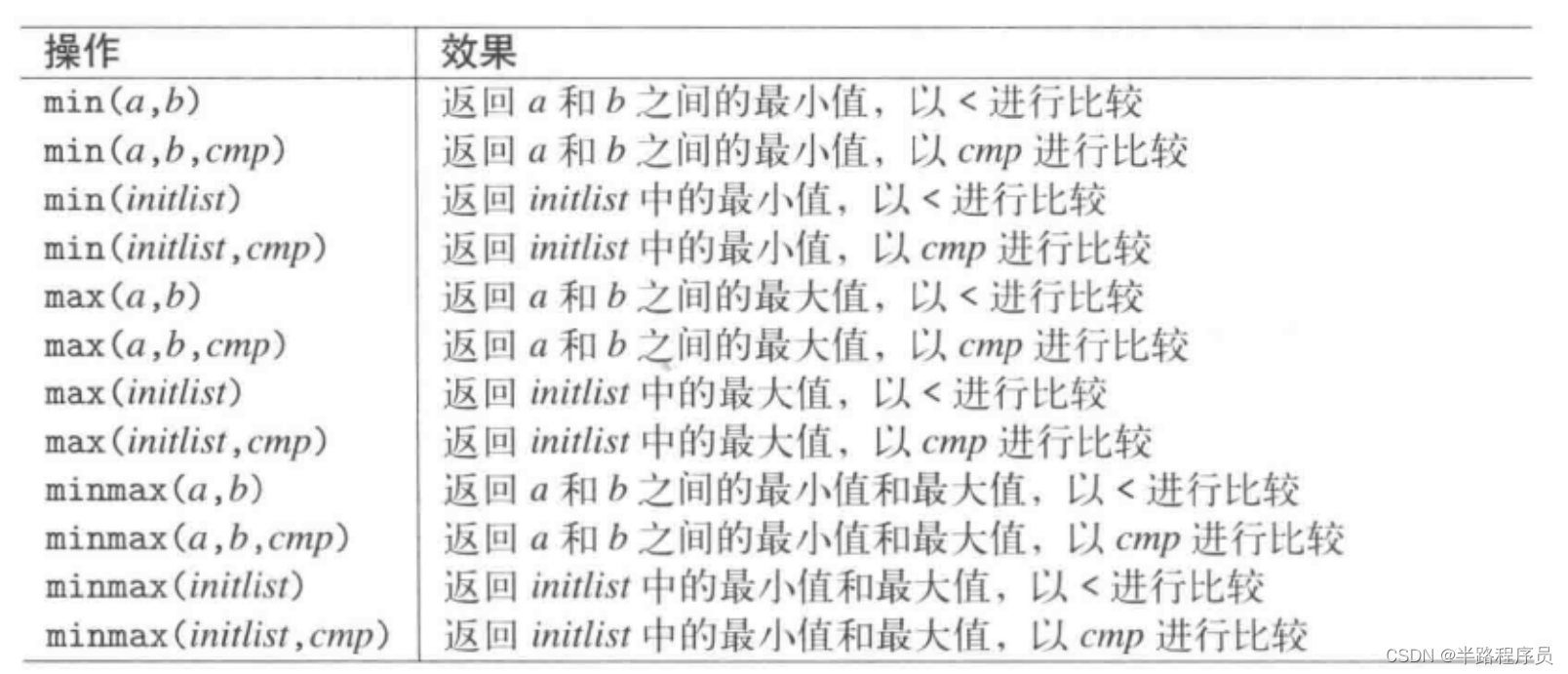
auto extremes = std::minmax({px, py, pz}, [](int*a, int*b) {
return *a < *b;
});两值互换:
namespace std {
template <typename T>
inline void swap(T& a, T& b) {
T tmp(std::move(a));
a = std::move(b);
b = std::move(tmp);
}
}4、class ratio<>
#include <ratio>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
typedef ratio<5,3> FiveThirds;
cout << FiveThirds::num << "/" << FiveThirds::den << endl;
typedef ratio<25,15> AlsoFiveThirds;
cout << AlsoFiveThirds::num << "/" << AlsoFiveThirds::den << endl;
ratio<42,42> one;
cout << one.num << "/" << one.den << endl;
ratio<0> zero;
cout << zero.num << "/" << zero.den << endl;
typedef ratio<7,-3> Neg;
cout << Neg::num << "/" << Neg::den << endl;
}
输出:
5/3
5/3
1/1
0/1
-7/3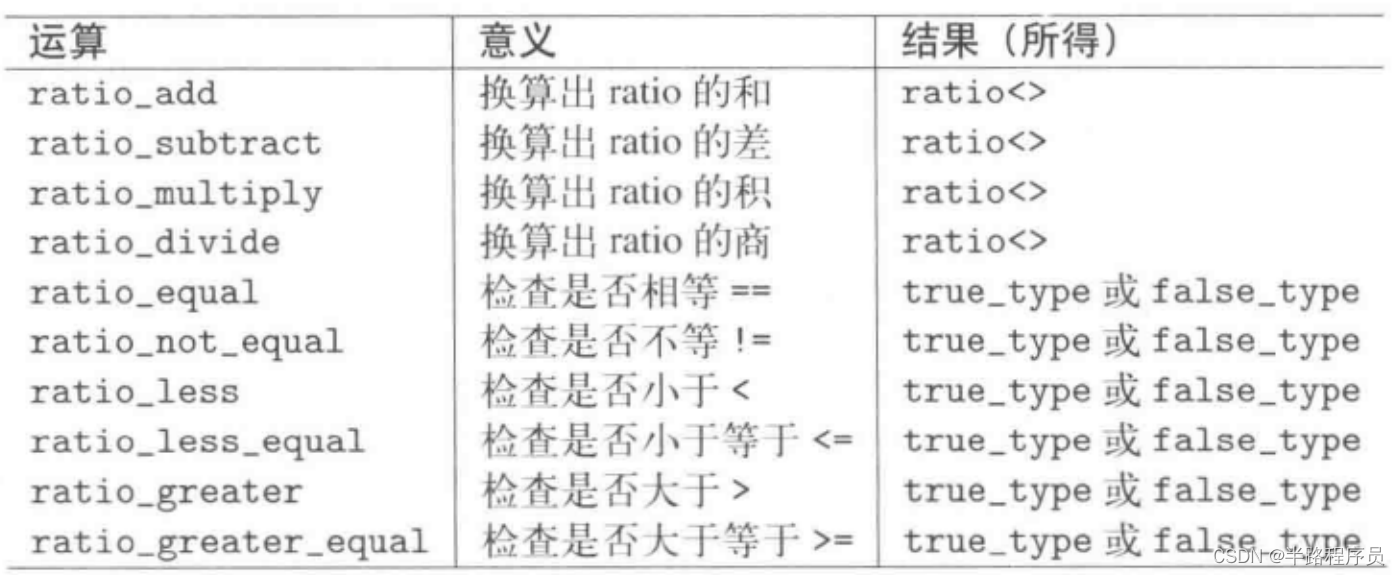
5、duration
#include <ratio>
#include <iostream>
#include <chrono>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
std::chrono::duration<int> twentySeconds(20); //以秒为单位
std::chrono::duration<double, std::ratio<60>> halfAMinute(0.5); //以60秒为单位
std::chrono::duration<long, std::ratio<1, 1000>> oneMillisecond(1); //以1/1000秒为单位
std::chrono::seconds twentySeconds(20);
std::chrono::hours aDay(24);
std::chrono::milliseconds oneMillisecond(1);
}// 将毫秒单位的duration切割为小时,分钟,秒,毫秒
#include <ratio>
#include <iostream>
#include <chrono>
#include <iomanip>
using namespace std;
using namespace std::chrono;
milliseconds ms(7255042);
template <typename V, typename R>
ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, const chrono::duration<V,R>& d) {
os << "[" << d.count() << " of " << R::num << "/" << R::den << "]";
return os;
}
// 将毫秒单位的duration切割为小时,分钟,秒,毫秒
int main()
{
hours hh = duration_cast<hours>(ms);
minutes mm = duration_cast<minutes>(ms%chrono::hours(1));
seconds ss = duration_cast<seconds>(ms%chrono::minutes(1));
milliseconds msec = duration_cast<milliseconds>(ms%chrono::seconds(1));
cout << "raw: " << hh << "::" << mm << "::"
<< ss << "::" << msec << endl;
cout << " " << setfill('0') << setw(2) << hh.count() << "::"
<< setw(2) << mm.count() << "::"
<< setw(2) << ss.count() << "::"
<< setw(2) << msec.count() << endl;
}#include <ratio>
#include <iostream>
#include <chrono>
#include <iomanip>
using namespace std;
using namespace std::chrono;
template <typename C>
void printClockData ()
{
using namespace std;
cout << "- precision: ";
// if time unit is less than or equal to one millisecond
typedef typename C::period P; // type of time unit
if (ratio_less_equal<P,milli>::value) {
// convert to and print as milliseconds
typedef typename ratio_multiply<P,kilo>::type TT;
cout << fixed << double(TT::num)/TT::den
<< " milliseconds" << endl;
}
else {
// print as seconds
cout << fixed << double(P::num)/P::den << " seconds" << endl;
}
cout << "- is_steady: " << boolalpha << C::is_steady << endl;
}
int main()
{
std::cout << "system_clock: " << std::endl;
printClockData<std::chrono::system_clock>();
std::cout << "\nhigh_resolution_clock: " << std::endl;
printClockData<std::chrono::high_resolution_clock>();
std::cout << "\nsteady_clock: " << std::endl;
printClockData<std::chrono::steady_clock>();
}
输出:
system_clock:
- precision: 0.000001 milliseconds
- is_steady: false
high_resolution_clock:
- precision: 0.000001 milliseconds
- is_steady: false
steady_clock:
- precision: 0.000001 milliseconds
- is_steady: true下面的程序将timepoint赋值给tp,并转换为日历表示法,window运行会报错,LInux下运行正常:
#include <chrono>
#include <ctime>
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
std::string asString (const std::chrono::system_clock::time_point& tp)
{
// convert to system time:
std::time_t t = std::chrono::system_clock::to_time_t(tp);
std::string ts = std::ctime(&t); // convert to calendar time
ts.resize(ts.size()-1); // skip trailing newline
return ts;
}
int main()
{
// print the epoch of this system clock:
std::chrono::system_clock::time_point tp;
std::cout << "epoch: " << asString(tp) << std::endl;
// print current time:
tp = std::chrono::system_clock::now();
std::cout << "now: " << asString(tp) << std::endl;
// print minimum time of this system clock:
tp = std::chrono::system_clock::time_point::min();
std::cout << "min: " << asString(tp) << std::endl;
// print maximum time of this system clock:
tp = std::chrono::system_clock::time_point::max();
std::cout << "max: " << asString(tp) << std::endl;
}
输出:
epoch: Thu Jan 1 08:00:00 1970
now: Thu Nov 30 21:29:29 2023
min: Tue Sep 21 08:18:27 1677
max: Sat Apr 12 07:47:16 2262
#include <chrono>
#include <ctime>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
string asString (const chrono::system_clock::time_point& tp)
{
time_t t = chrono::system_clock::to_time_t(tp); // convert to system time
string ts = ctime(&t); // convert to calendar time
ts.resize(ts.size()-1); // skip trailing newline
return ts;
}
int main()
{
// define type for durations that represent day(s):
typedef chrono::duration<int,ratio<3600*24>> Days;
// process the epoch of this system clock
chrono::time_point<chrono::system_clock> tp;
cout << "epoch: " << asString(tp) << endl;
// add one day, 23 hours, and 55 minutes
tp += Days(1) + chrono::hours(23) + chrono::minutes(55);
cout << "later: " << asString(tp) << endl;
// process difference from epoch in minutes and days:
auto diff = tp - chrono::system_clock::time_point();
cout << "diff: "
<< chrono::duration_cast<chrono::minutes>(diff).count()
<< " minute(s)" << endl;
Days days = chrono::duration_cast<Days>(diff);
cout << "diff: " << days.count() << " day(s)" << endl;
// subtract one year (hoping it is valid and not a leap year)
tp -= chrono::hours(24*365);
cout << "-1 year: " << asString(tp) << endl;
// subtract 50 years (hoping it is valid and ignoring leap years)
tp -= chrono::duration<int,ratio<3600*24*365>>(50);
cout << "-50 years: " << asString(tp) << endl;
// subtract 50 years (hoping it is valid and ignoring leap years)
tp -= chrono::duration<int,ratio<3600*24*365>>(50);
cout << "-50 years: " << asString(tp) << endl;
}
输出:
epoch: Thu Jan 1 08:00:00 1970
later: Sat Jan 3 07:55:00 1970
diff: 2875 minute(s)
diff: 1 day(s)
-1 year: Fri Jan 3 07:55:00 1969
-50 years: Thu Jan 16 07:55:00 1919
-50 years: Wed Jan 27 08:00:43 1869
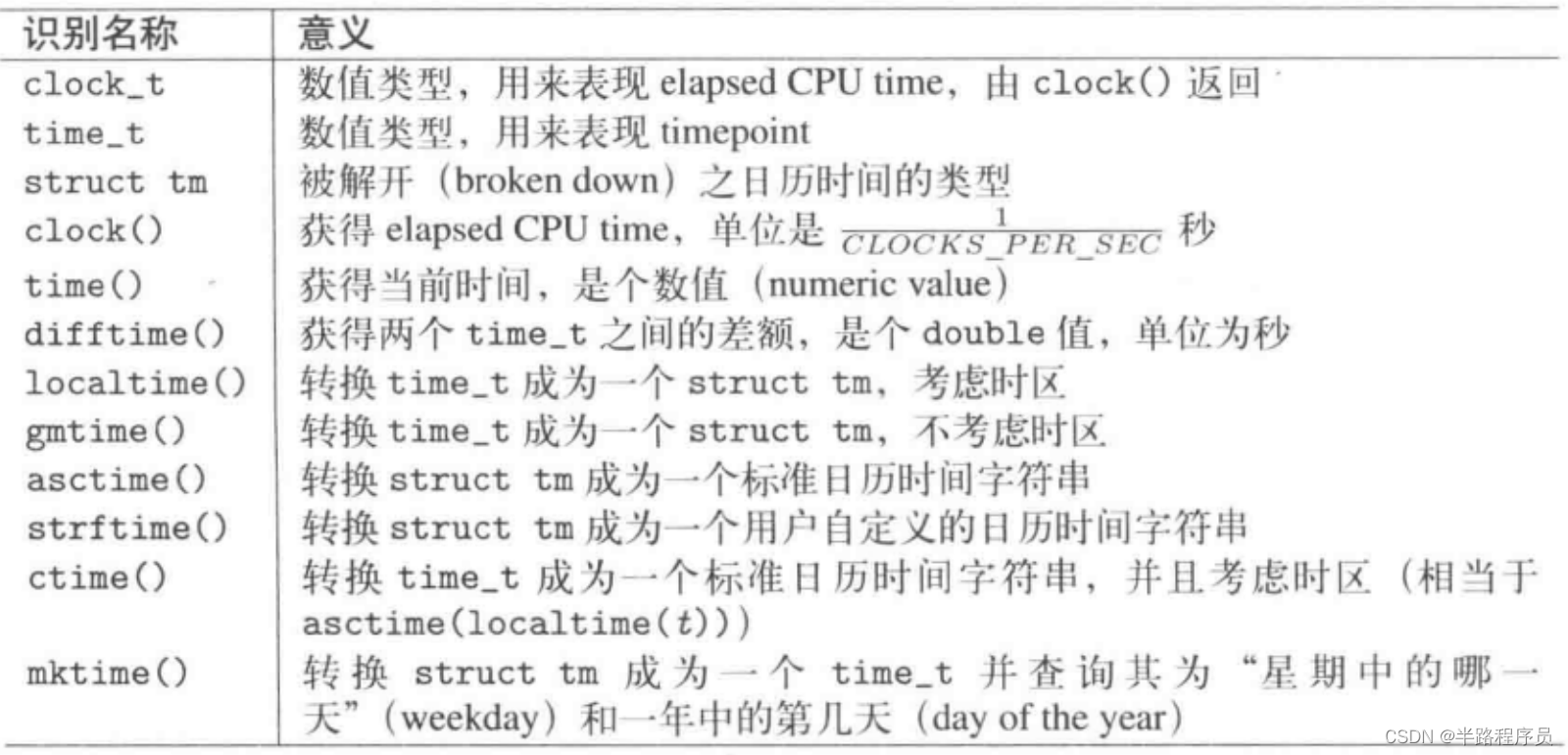
6、timepoint与日历时间的转换
#include <chrono>
#include <ctime>
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
// convert timepoint of system clock to calendar time string
inline std::string asString(const std::chrono::system_clock::time_point& tp) {
std::time_t t = std::chrono::system_clock::to_time_t(tp);
std::string ts = ctime(&t); // convert to calendar time
ts.resize(ts.size()-1); //skip trailing newline
return ts;
}
// convert calender time to timepoint of system clock
inline std::chrono::system_clock::time_point
makeTimePoint(int year, int mon, int day, int hour, int min, int sec=0) {
struct std::tm t;
t.tm_sec = sec;
t.tm_min = min;
t.tm_hour = hour;
t.tm_mday = day;
t.tm_mon = mon - 1;
t.tm_year = year-1900;
t.tm_isdst = -1;
std::time_t tt = std::mktime(&t);
if (tt == -1) {
throw "no valid system time";
}
return std::chrono::system_clock::from_time_t(tt);
}
int main() {
auto tp1 = makeTimePoint(2023, 11, 30, 00, 00);
std::cout << asString(tp1) << std::endl;
auto tp2 = makeTimePoint(2023, 03, 23, 12, 33);
std::cout << asString(tp2) << std::endl;
return 0;
}
输出:
Thu Nov 30 00:00:00 2023
Thu Mar 23 12:33:00 20237、<cstring>中的定义式
//在ptr所指的前len个byte中找出字符c
memchr(const void* ptr, int c, size_t len)
//比较ptr1和ptr2所指的前len个byte
memcmp(const void* ptr1, const void* ptr2, size_t len)
//将fromPtr所指的前len个byte复制到toPtr
memcpy(void* toPtr, const void* fromPtr, size_t len)
//将fromPtr所指的前len个byte复制到toPtr(区域可重叠)
memmove(void* toPtr, const void* fromPtr, size_t len)
//将ptr所指的前len个byte赋值为字符c
memset(void* ptr, int c, size_t len)8、algorithm
(1)find
#include <algorithm>
#include <list>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
list<int> coll;
// insert elements from 20 to 40
for (int i=20; i<=40; ++i) {
coll.push_back(i);
}
// find position of element with value 3
// - there is none, so pos3 gets coll.end()
auto pos3 = find (coll.begin(), coll.end(), // range
3); // value
// reverse the order of elements between found element and the end
// - because pos3 is coll.end() it reverses an empty range
reverse (pos3, coll.end());
// find positions of values 25 and 35
list<int>::iterator pos25, pos35;
pos25 = find (coll.begin(), coll.end(), // range
25); // value
pos35 = find (coll.begin(), coll.end(), // range
35); // value
// print the maximum of the corresponding range
// - note: including pos25 but excluding pos35
cout << "max: " << *max_element (pos25, pos35) << endl;
// process the elements including the last position
cout << "max: " << *max_element (pos25, ++pos35) << endl;
}(2)find_if
查找最先出现的25或者35
#include <algorithm>
#include <list>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
list<int> coll;
// insert elements from 20 to 40
for (int i=20; i<=40; ++i) {
coll.push_back(i);
}
auto pos = find_if(coll.begin(), coll.end(),
[](int i) {
return i == 25 || i == 35;
});
if (pos == coll.end()) {
std::cout << "not found" << std::endl;
exit(1);
}
list<int>::const_iterator pos25, pos35;
if (*pos == 25) {
// 先找到25
pos25 = pos;
pos35 = find(++pos, coll.end(), 35);
std::cout << *pos35 << std::endl;
} else {
pos35 = pos;
pos25 = find(++pos, coll.end(), 25);
std::cout << *pos25 << std::endl;
}
}9、insert iterator
#include <algorithm>
#include <list>
#include <vector>
#include <set>
#include <iterator>
#include <deque>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
list<int> coll1 = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8};
vector<int> coll2;
copy(coll1.begin(), coll1.end(), back_inserter(coll2));
deque<int> coll3;
copy(coll1.begin(), coll1.end(), front_inserter(coll3));
set<int> coll4;
copy(coll1.begin(), coll1.end(), inserter(coll4, coll4.begin()));
for (auto &ele : coll2) {
std::cout << ele << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
for (auto &ele : coll3) {
std::cout << ele << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
for(auto & ele : coll4) {
std::cout << ele << " ";
}
}
输出:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8inserter的作用是在“初始化时接受的第二个实参”所指的位置的前面插入元素,内部调用成员函数insert(),并以新值和新位置作为实参传入,所有的STL容器都提供insert()成员函数,这是唯一可以用于关联式容器身上的一种预定义inserter。

10、stream iterator
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <iterator>
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector<string> coll;
// 使用ctrl+z 回车进行终止
copy(istream_iterator<string>(cin),
istream_iterator<string>(),
back_inserter(coll));
sort(coll.begin(), coll.end());
unique_copy(coll.cbegin(), coll.cend(),
ostream_iterator<string>(cout, "\n"));
}11、reverse iterator
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <iterator>
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector<int> coll;
for (int i = 1; i <= 9; i++) {
coll.push_back(i);
}
copy(coll.crbegin(), coll.crend(),
ostream_iterator<int>(cout, " "));
}
输出:
9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1