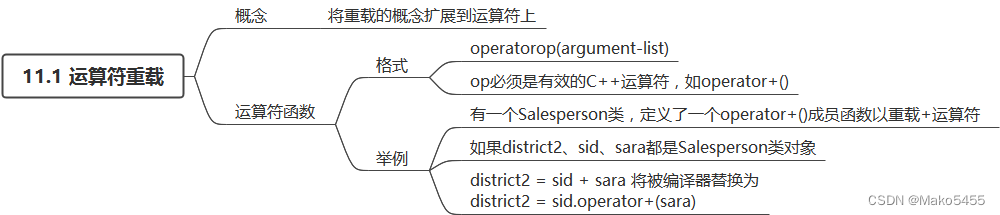
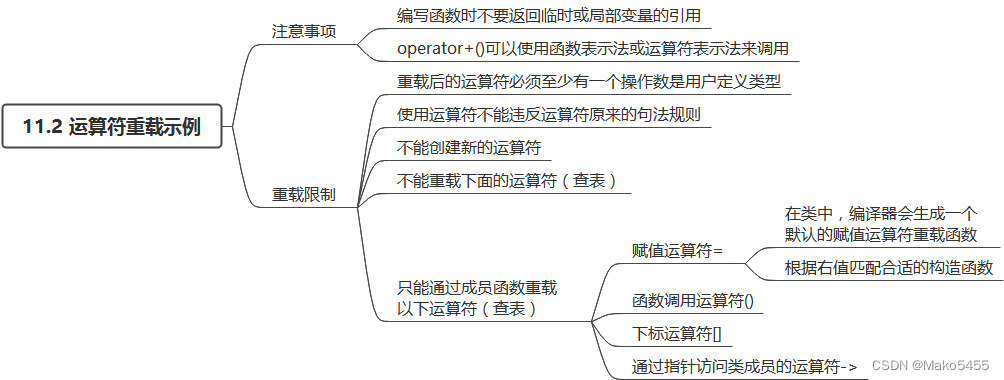
11.1 运算符重载
11.2 计算时间:一个运算符重载示例
运算符重载示例(计算时间)
头文件mytime0.h
#ifndef __MYTIME0__H__
#define __MYTIME0__H__
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Time {
private:
int hours;
int minutes;
public:
Time();
Time(int h, int m = 0);
void AddMin(int m); // 分钟相加
void AddHr(int h); // 小时相加
void Reset(int h = 0, int m = 0); // 复位时间
Time operator+(const Time &t) const; // 求和(运算符重载)
Time operator-(const Time &t) const; // 减法
Time operator*(double mult) const; // 乘法
friend Time operator*(double mult, const Time &t); // 乘法(友元函数)
friend ostream &operator<<(ostream &os, const Time &t); // cout输出(友元函数)
};
#endif源代码mytime0.cpp
#include "mytime0.h"
Time::Time() {
hours = minutes = 0;
}
Time::Time(int h, int m) {
hours = h;
minutes = m;
}
void Time::AddMin(int m) {
minutes += m;
hours += minutes / 60;
minutes %= 60;
}
void Time::AddHr(int h) {
hours += h;
}
void Time::Reset(int h, int m) {
hours = h;
minutes = m;
}
Time Time::operator+(const Time &t) const{
Time sum;
sum.minutes = minutes + t.minutes;
sum.hours = hours + t.hours + sum.minutes / 60;
sum.minutes %= 60;
return sum;
}
Time Time::operator-(const Time &t) const {
Time diff;
int tot1, tot2;
tot1 = hours * 60 + minutes;
tot2 = t.hours * 60 + t.minutes;
diff.hours = (tot1 - tot2) / 60;
diff.minutes = (tot1 - tot2) % 60;
return diff;
}
Time Time::operator*(double mult) const {
Time result;
long totalminutes = hours * 60 * mult + minutes * mult;
result.hours = totalminutes / 60;
result.minutes = totalminutes % 60;
return result;
}
Time operator*(double mult, const Time &t) {
Time result;
long totalminutes = t.hours * 60 * mult + t.minutes * mult;
result.hours = totalminutes / 60;
result.minutes = totalminutes % 60;
return result;
}
ostream &operator<<(ostream &os, const Time &t) {
os << t.hours << " hours, " << t.minutes << " minutes." << endl;
return os;
}源代码usetime0.cpp
#include "mytime0.h"
int main() {
Time coding(4, 35);
Time fixing(2, 47);
cout << "coding time = ";
cout << coding;
cout << "fixing time = ";
cout << fixing;
Time total = coding + fixing; // 运算符+重载(运算符表示法)
cout << total;
Time Planning = coding.operator+(fixing); // 运算符+重载(函数表示法)
cout << Planning;
Time diff = coding - fixing; // 运算符-重载
cout << diff;
Time adjusted = coding * 1.5; // 运算符*重载
cout << adjusted;
Time adjusted1 = 1.5 * coding; // 运算符*重载(友元函数)
cout << adjusted1;
cout << "************************" << endl;
cout << coding << fixing << endl; // cout连续输出
return 0;
}11.3 友元

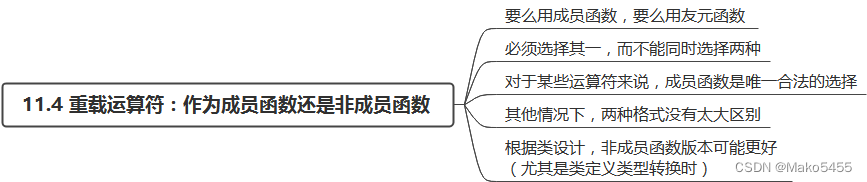
11.4 重载运算符:作为成员函数还是非成员函数
11.5 再谈重载:一个矢量类

醉汉漫步问题(走几步可以离原点大于指定的距离)
头文件vector.h
#ifndef __VECTOR__H__
#define __VECTOR__H__
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
namespace VECTOR {
class Vector {
public:
enum Mode{RECT, POL}; // 直角坐标RECT代表0,极坐标POL代表1
private:
double x;
double y;
double mag; // 极坐标的长度
double ang; // 极坐标的角度
Mode mode; // 当前模式
void set_mag();
void set_ang();
void set_x();
void set_y();
public:
Vector(); // 默认构造函数
Vector(double n1, double n2, Mode form = RECT); // 构造函数
void reset(double n1, double n2, Mode form = RECT); // 恢复默认值
double xval() const { return x; }
double yval() const { return y; }
double magval() const { return mag; }
double angval() const { return ang; }
void polar_mode(); // 设置成极坐标
void rect_mode(); // 设置成直角坐标
Vector operator+(const Vector &b) const; // +运算符重载
Vector operator-(const Vector &b) const; // -运算符重载
Vector operator-() const; // -运算符重载(坐标取负值)
Vector operator*(double n) const; // *运算符重载
friend Vector operator*(double n, const Vector &a); // *运算符重载(友元函数)
friend ostream &operator<<(ostream &os, const Vector &v); // <<运算符重载
};
}
#endif源代码main.cpp
#include "vector.h"
#include <cstdlib>
#include <ctime>
using namespace std;
using namespace VECTOR;
int main() {
double target; // 目标走多远
double dstep; // 一步走多远
Vector result(0.0,0.0); // 使用构造函数创建对象
double direction; // 方向
srand(time(NULL)); // 使用系统时间来初始化种子(种子不变则随机数不变)
Vector step; // 使用默认构造函数
unsigned long steps = 0; // 记录走了几步
cout << "Enter target distance(q to quit): ";
while (cin >> target) {
cout << "Enter the step length: ";
if (!(cin >> dstep)) break;
while (result.magval() < target) {
direction = rand() % 360; // 0~359度的随机方向
step.reset(dstep, direction, Vector::POL); // 极坐标
result = result + step;
steps++;
}
cout << "After " << steps << " step, achieve the target distance." << endl;
cout << result; // 打印坐标
result.polar_mode(); // 转换为极坐标
cout << result;
cout << endl;
steps = 0;
result.reset(0.0, 0.0); // 复位结果
cout << "Enter target distance(q to quit): ";
}
cout << "Bye!" << endl;
return 0;
}源代码vector.cpp
#include "vector.h"
#include <cmath>
namespace VECTOR {
const double Rad_to_deg = 45.0 / atan(1.0);
void Vector::set_mag() {
mag = sqrt(x * x + y * y);
}
void Vector::set_ang() {
if (x == 0.0 && y == 0.0) ang = 0.0;
else ang = atan2(y, x); // 弧度值
}
void Vector::set_x() {
x = mag * cos(ang);
}
void Vector::set_y() {
y = mag * sin(ang);
}
Vector::Vector() {
x = y = mag = ang = 0.0;
mode = RECT;
}
Vector::Vector(double n1, double n2, Mode form) {
mode = form;
if (form == RECT) {
x = n1;
y = n2;
set_mag();
set_ang();
}
else if (form == POL) {
mag = n1;
ang = n2 / Rad_to_deg; // 传进来的是角度,需要转换为弧度
set_x();
set_y();
}
else {
cout << "Error" << endl;
x = y = mag = ang = 0.0;
mode = RECT;
}
}
void Vector::reset(double n1, double n2, Mode form) {
mode = form;
if (form == RECT) {
x = n1;
y = n2;
set_mag();
set_ang();
}
else if (form == POL) {
mag = n1;
ang = n2 / Rad_to_deg; // 传进来的是角度,需要转换为弧度
set_x();
set_y();
}
else {
cout << "Error" << endl;
x = y = mag = ang = 0.0;
mode = RECT;
}
}
void Vector::polar_mode() {
mode = POL;
}
void Vector::rect_mode() {
mode = RECT;
}
Vector Vector::operator+(const Vector &b) const {
return Vector(x + b.x, y + b.y); // 使用构造函数
}
Vector Vector::operator-(const Vector &b) const {
return Vector(x - b.x, y - b.y);
}
Vector Vector::operator-() const {
return Vector(-x, -y);
}
Vector Vector::operator*(double n) const {
return Vector(n * x, n * y);
}
Vector operator*(double n, const Vector &a) {
return a * n;
}
ostream &operator<<(ostream &os, const Vector &v) {
if (v.mode == Vector::RECT) {
os << "x, y = " << v.x << ", " << v.y << endl;
}
else if (v.mode == Vector::POL) {
os << "mag, ang = " << v.mag << ", " << v.ang << endl;
}
else {
os << "Invalid mode." << endl;
}
return os;
}
}11.6 类的自动转换和强制类型转换
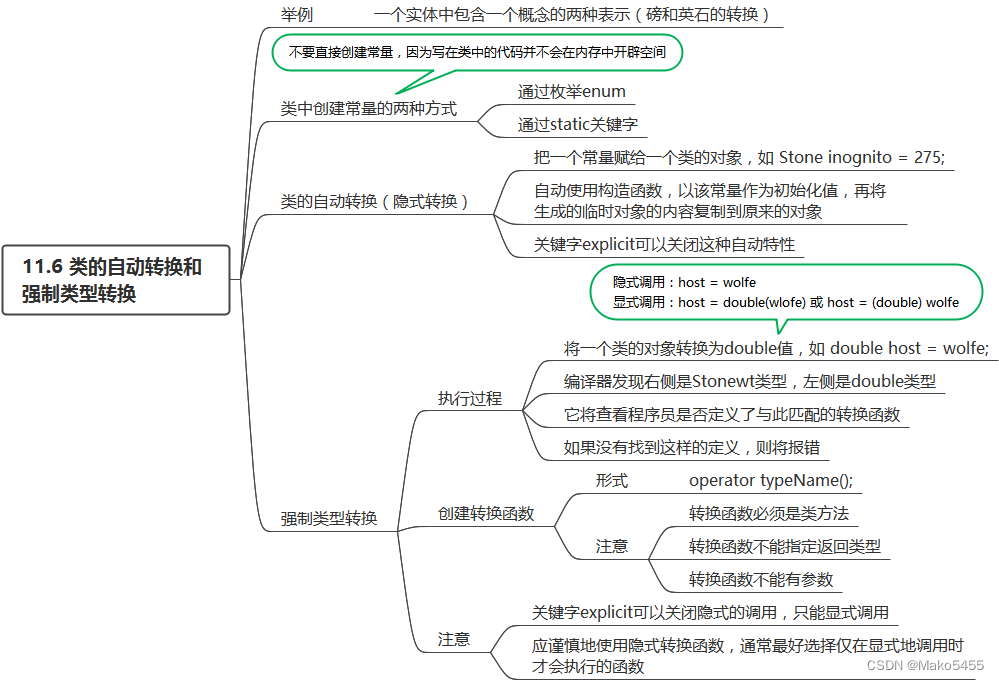
类的类型转换示例(磅和英石的转换)
头文件stonewt.h
#ifndef __STONEWT__H__
#define __STONEWT__H__
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Stonewt {
private:
enum{Lbs_per_stn = 14}; // 用枚举方式创建常量
int stone;
double pds_left;
double pounds;
public:
Stonewt(double lbs); // 构造函数1
Stonewt(double stn, double lbs); // 构造函数2
Stonewt(); // 默认构造函数
void Show_lbs() const;
void Show_stns() const;
operator double() const; // 转换函数1
operator int() const; // 转换函数2
};
#endif源代码main.cpp
#include "stonewt.h"
using namespace std;
int main() {
Stonewt incognito = 275; // == Stonewt incognito(275)
Stonewt wolfe(285.7); // 构造函数1
Stonewt taft(21, 8); // 构造函数2
incognito.Show_stns();
wolfe.Show_stns();
taft.Show_stns();
cout << "*************************" << endl;
incognito = 276.8; // 类的自动的类型转换(隐式转换)
incognito.Show_stns();
Stonewt poppins(9, 2.8);
double p_wt = poppins; // 使用转换函数把Stonewt类转换成double值(隐式调用)
cout << "poppins = " << p_wt << endl;
int weight = poppins;
cout << "poppins = " << weight << endl;
cout << "poppins = " << int(poppins) << endl; // 显式调用
return 0;
}源代码stonewt.cpp
#include "stonewt.h"
Stonewt::Stonewt(double lbs) {
stone = (int)lbs / Lbs_per_stn;
pds_left = (int)lbs % Lbs_per_stn + lbs - (int)lbs;
pounds = lbs;
}
Stonewt::Stonewt(double stn, double lbs) {
stone = stn;
pds_left = lbs;
pounds = stn * Lbs_per_stn + lbs;
}
Stonewt::Stonewt() {
stone = pds_left = pounds = 0;
}
void Stonewt::Show_stns() const {
cout << stone << " stones, " << pds_left << " pounds." << endl;
}
void Stonewt::Show_lbs() const {
cout << pounds << " pounds." << endl;
}
Stonewt::operator int() const {
return int (pounds + 0.5); // 四舍五入
}
Stonewt::operator double() const {
return pounds;
}











![[数据结构]深入浅出讲解二叉树-平衡二叉树-左右旋转](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/3dca1e34f7324920b24897dff94f5e70.png)