一、为什么要使用ThreadLocal?
1.1、概述
并发场景下,会存在多个线程同时修改一个共享变量的场景,这就有可能会出现线程安全的问题。为了解决线程安全问题,可以用加锁的方式,比如对核心代码使用synchronized或者Lock进行加锁,从而起到线程隔离的效果。但是加锁的方式,在高并发下会导致系统变慢,加锁示意图如下:
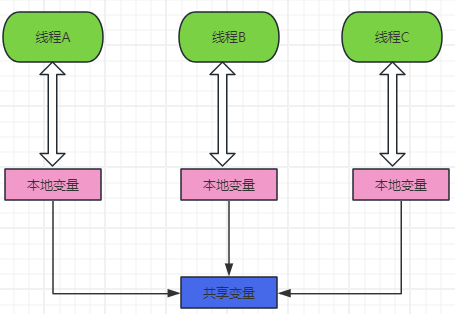
还有另外一种方案,就是使用空间换时间的方式,即:使用ThreadLocal,使用ThreadLocal访问共享变量时,会在每个线程本地保存一份共享变量的副本。多线程对共享变量修改时,实际上每个线程操作的是自己的变量副本,从而保证线程安全。示意图如下:
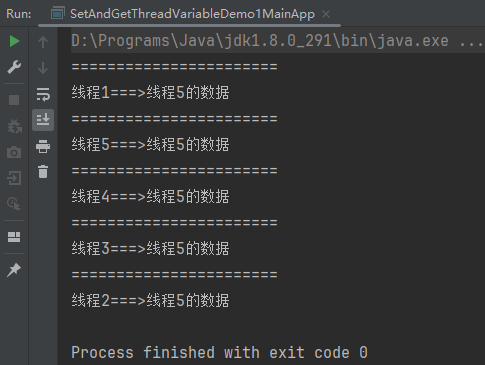
1.2、线程不安全案例
/**
* @Author : 一叶浮萍归大海
* @Date: 2023/11/21 11:50
* @Description: 需求:线程隔离(线程不安全案例代码)
*/
public class SetAndGetThreadVariableDemo1MainApp {
/**
* 共享变量
*/
private String content;
public String getContent() {
return content;
}
public void setContent(String content) {
this.content = content;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SetAndGetThreadVariableDemo1MainApp app = new SetAndGetThreadVariableDemo1MainApp();
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
new Thread(() -> {
try {
app.setContent(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "的数据");
System.out.println("=======================");
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "===>" + app.getContent());
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}, "线程" + i).start();
}
}
}
1.3、线程不安全案例(ThreadLocal解决)
/**
* @Author : 一叶浮萍归大海
* @Date: 2023/11/21 11:50
* @Description: 需求:线程隔离(ThreadLocal实现)
* 在多线程并发的场景下,每个线程中的变量都是互相独立的
* 线程A: 设置(变量1) 获取(变量1)
* 线程B: 设置(变量2) 获取(变量2)
*
* ThreadLocal:
* 1、set():将变量绑定到当前线程中
* 2、get():获取当前线程绑定的变量
*/
public class SetAndGetThreadVariableDemo2MainApp {
private String content;
ThreadLocal<String> threadLocal = new ThreadLocal<>();
public String getContent() {
return threadLocal.get();
}
public void setContent(String content) {
threadLocal.set(content);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SetAndGetThreadVariableDemo2MainApp app = new SetAndGetThreadVariableDemo2MainApp();
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
new Thread(() -> {
try {
app.setContent(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "的数据");
System.out.println("=======================");
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "===>" + app.getContent());
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}, "线程" + i).start();
}
}
}
1.4、线程不安全案例(synchronized解决)
/**
* @Author : 一叶浮萍归大海
* @Date: 2023/11/21 11:50
* @Description: 需求:线程隔离(synchronized实现)
*
*/
public class SetAndGetThreadVariableDemo3MainApp {
private String content;
public String getContent() {
return content;
}
public void setContent(String content) {
this.content = content;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SetAndGetThreadVariableDemo3MainApp app = new SetAndGetThreadVariableDemo3MainApp();
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
new Thread(() -> {
try {
synchronized (SetAndGetThreadVariableDemo3MainApp.class) {
app.setContent(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "的数据");
System.out.println("=======================");
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "===>" + app.getContent());
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}, "线程" + i).start();
}
}
}